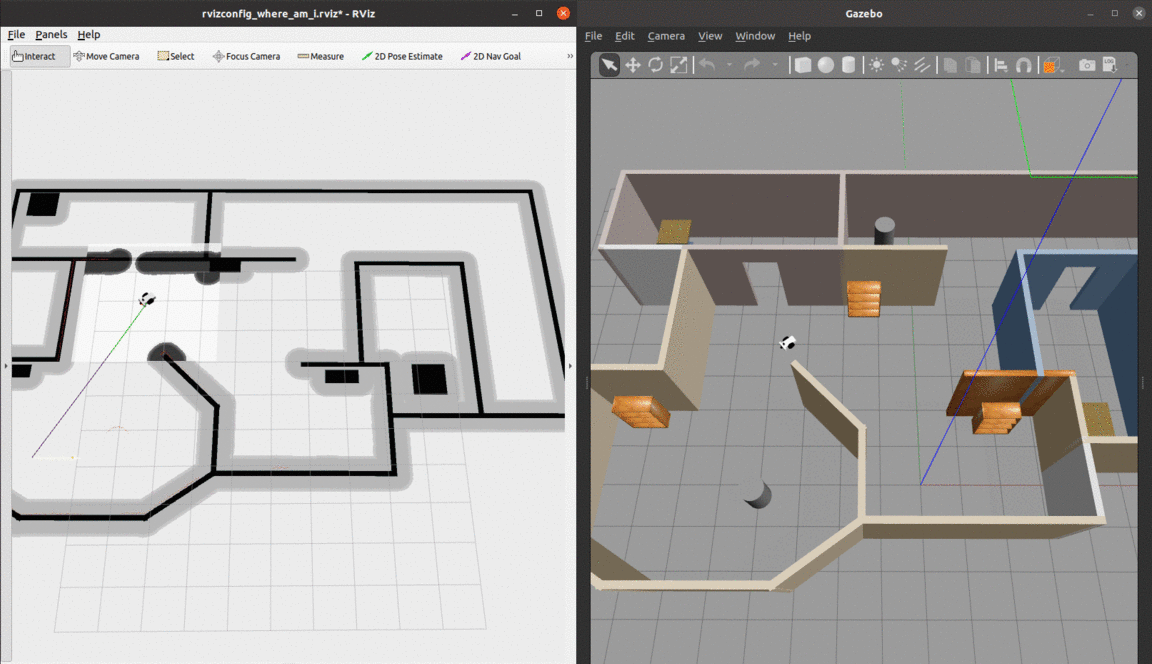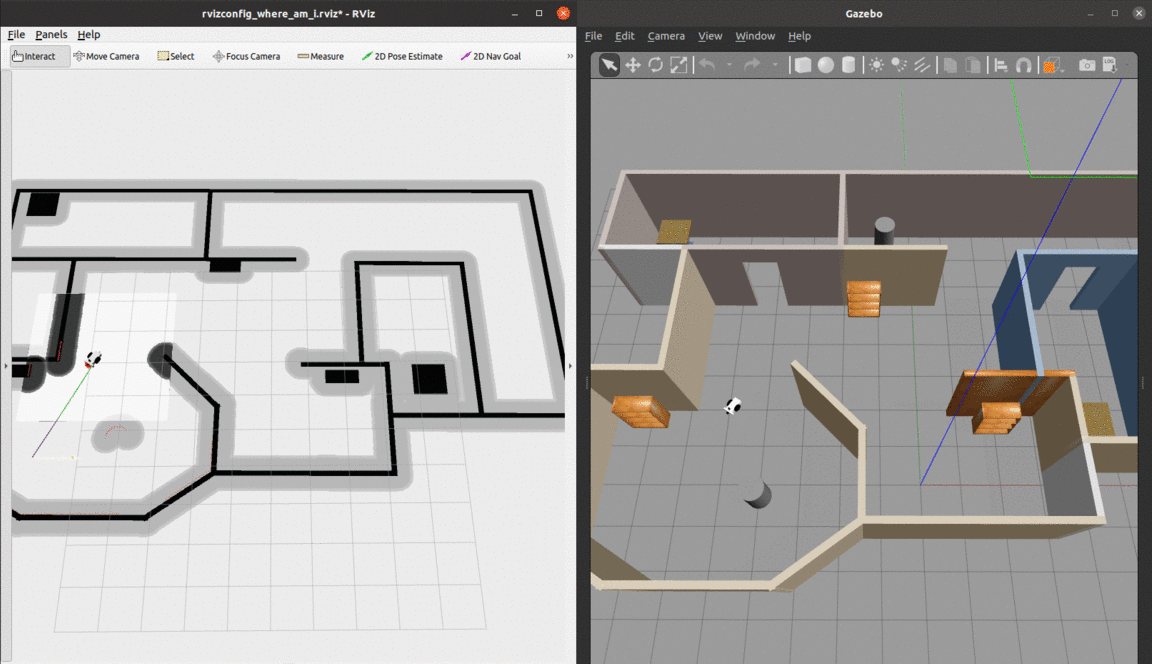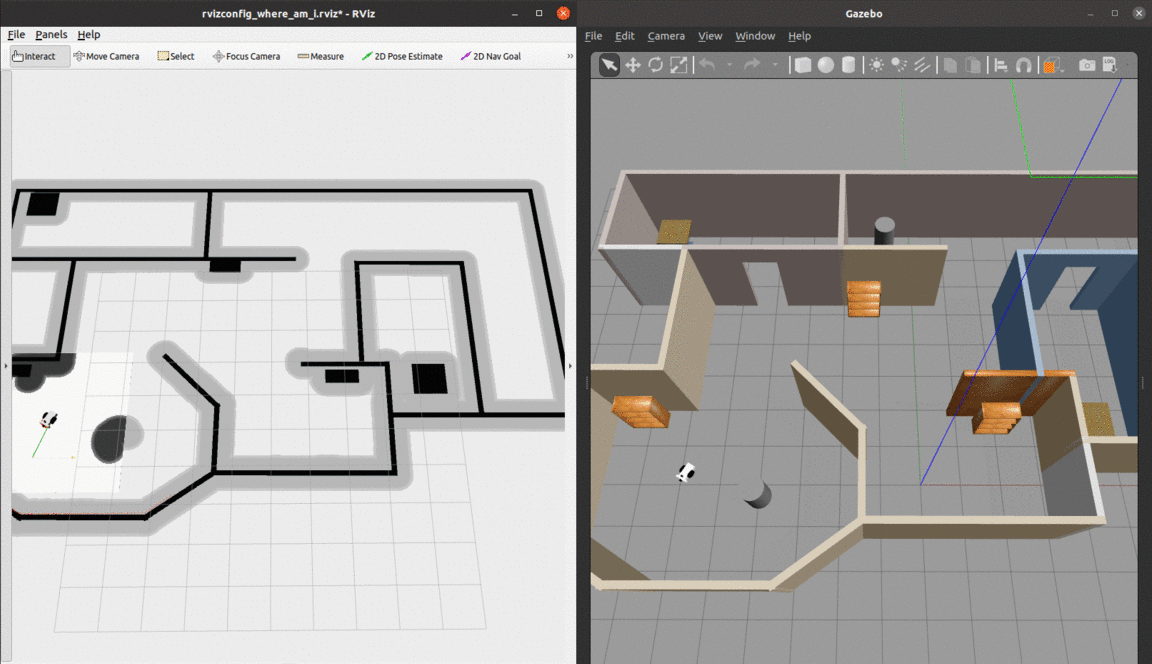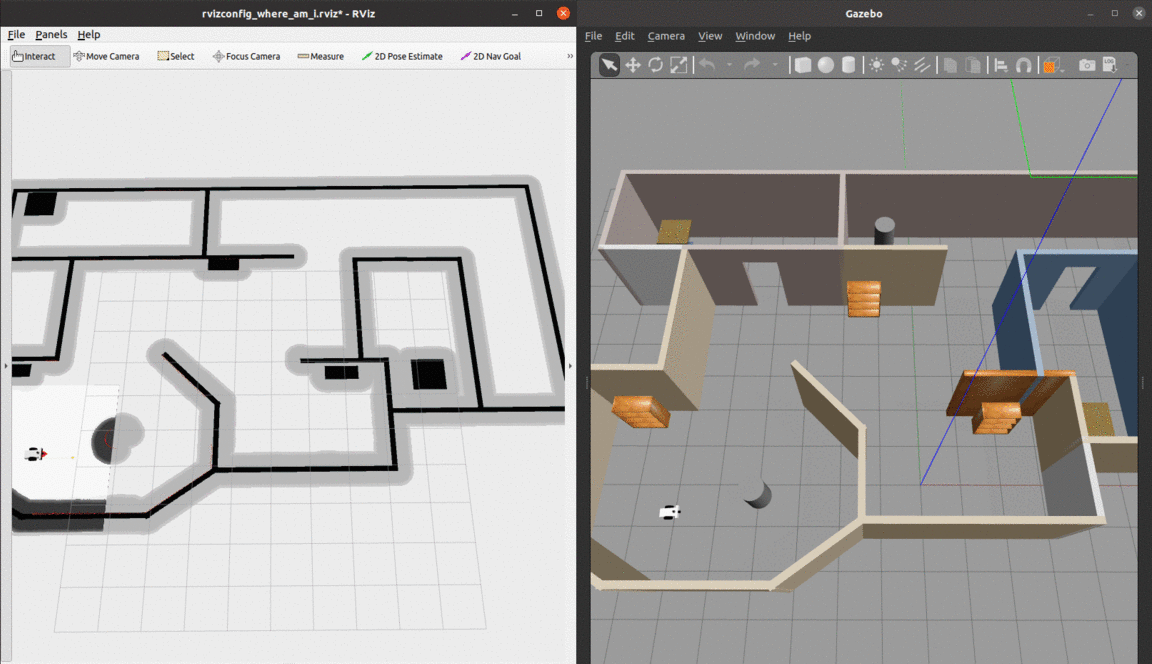
Localization of a differential drive mobile robot in ROS using Adaptive Monte Carlo Localization inside a custom Gazebo world.
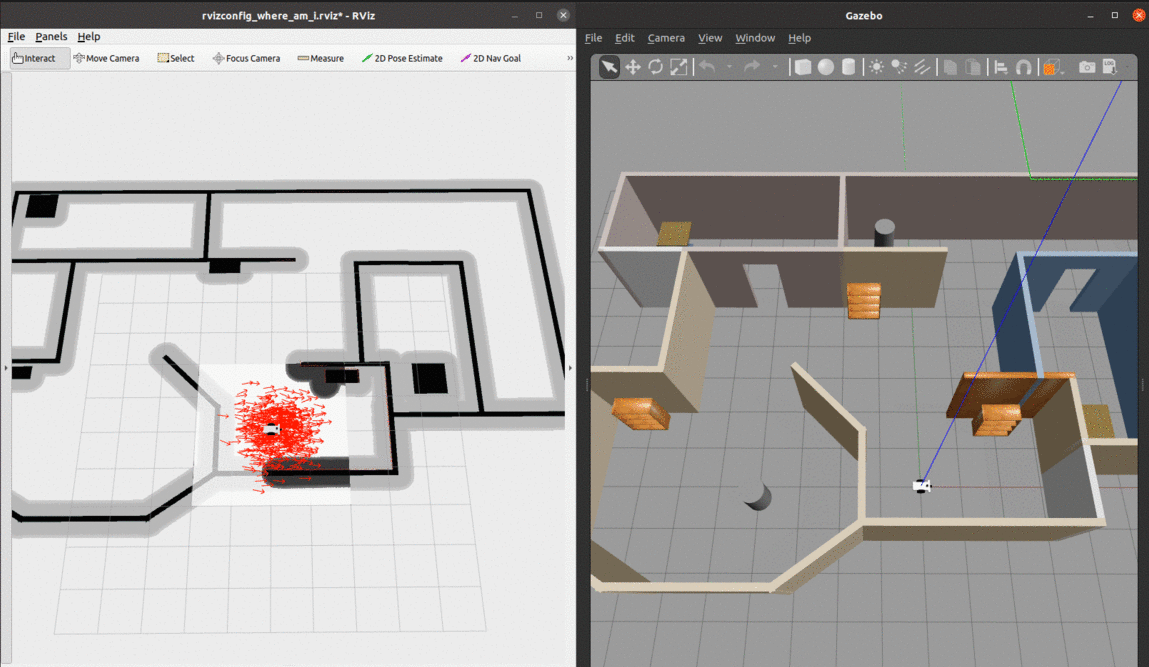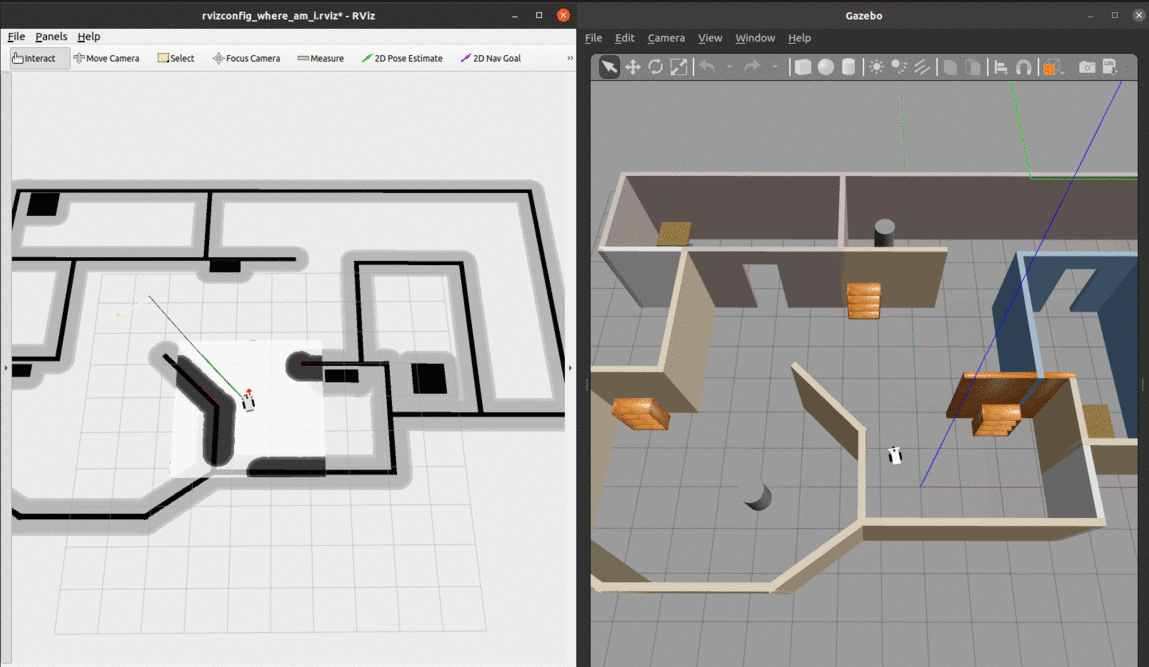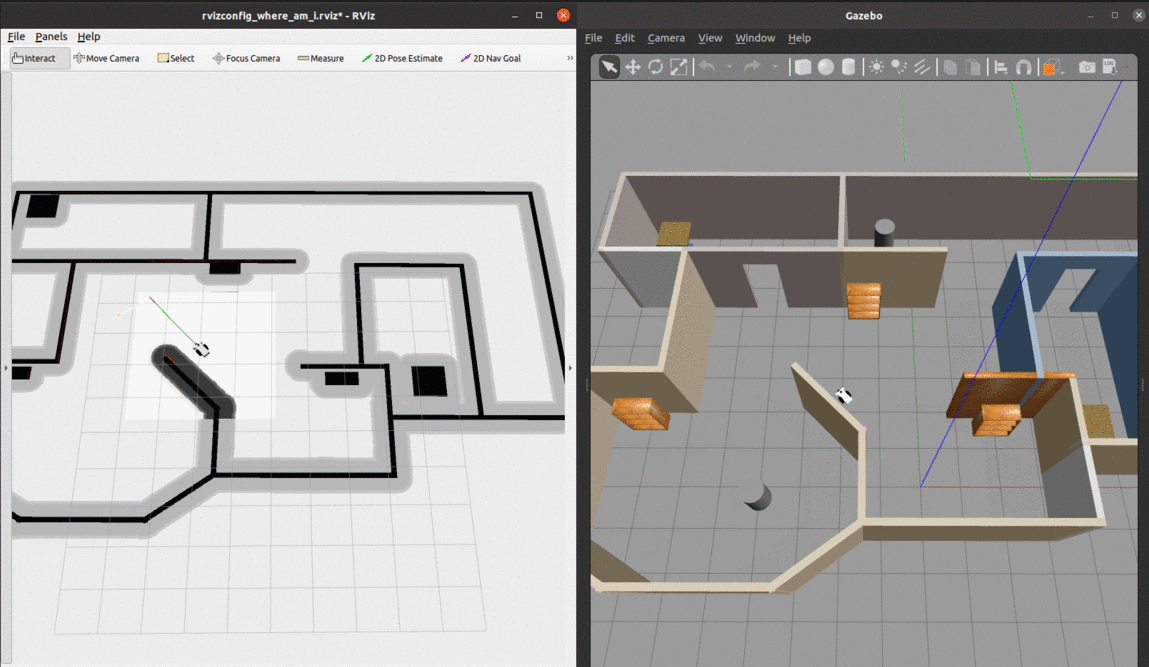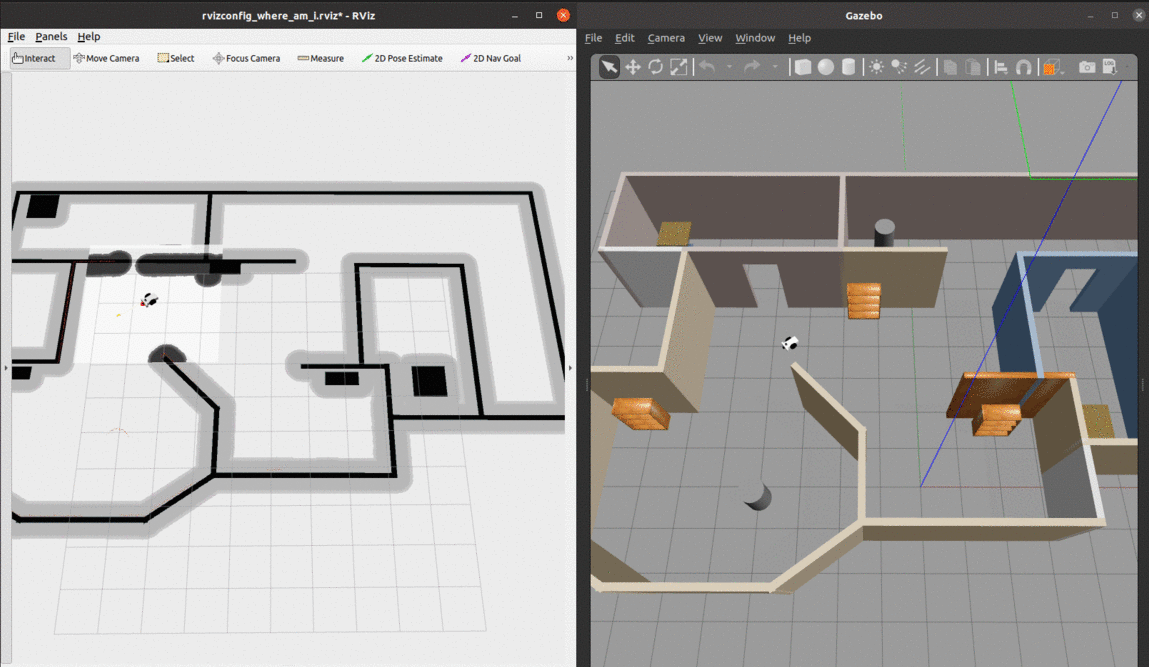
The robot uses odometry and laser scan data to localize itself through the amcl package, which is a probabilistic localization system for robots moving on a 2D plane. It implements the Adaptive Monte Carlo Localization approach, which uses a particle filter to track the pose of a robot against a known map and adjusts the number of particles over a time period for computational effieciency.
The project consists of the following parts:
- A ROS package that launches a custom robot model in a custom Gazebo world.
- The ROS
amclpackage and Navigation Stack to localize the robot. - Exploration and tuning of specific parameters corresponding to each package to achieve the best possible localization results.
The map of the environment was created with the pgm_map_creator ROS package using ROS Kinetic.
For a successful localization of the mobile robot, there are many parameters that need to be tuned for a specific robot and environment setup. Some of these parameters have been tuned and set in the config directory in order to make the robot accurately localize itself.
Navigation Stack
- We can see from the global cost map that the obstacles are inflated to provide a safety zone.
- The local cost map is represented by the white rectangle around the robot. The white space denotes free space and the black portions denote obstacles.
- The green and purple lines to the goal represent the local and global paths towards the given goal.
Sensors
- The red lines/dots on the walls and obstacles are formed by a LiDAR point cloud as measured by the sensor on top of the robot.
AMCL
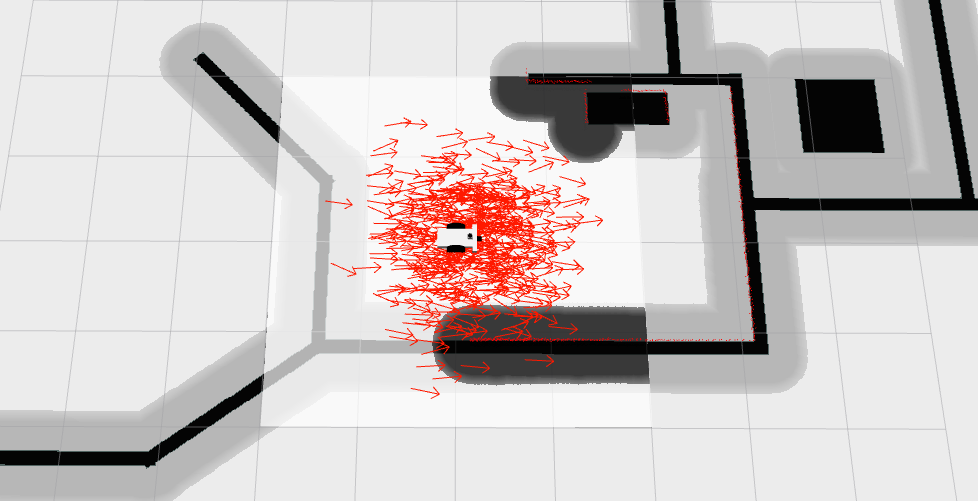
- The red arrows represent the particles of the Adaptive Monte-Carlo Localization node. They denote the possible robot poses in the environment.
At the begining, there are many particles spread around. As soon as the robot starts moving, it gets more confident about its location and the particles quickly converge to the true pose.
There are two packages in this project.
- my_robot: This package holds the robot and the Gazebo world.
- where-am-i: The localization of the robot with the Monte Carlo Localization
amclpackage, as well as the navigation functionality.
The directory structure is depicted below:
.RoboND-Where-Am-I # Where Am I Project
├── my_robot # my_robot package
│ ├── CMakeLists.txt # compiler instructions
│ ├── launch
│ │ ├── robot_description.launch
│ │ └── world.launch
│ ├── meshes
│ │ └── hokuyo.dae
│ ├── package.xml
│ ├── rviz
│ │ └── rvizconfig_where_am_i.rviz
│ ├── urdf
│ │ ├── my_robot.gazebo
│ │ └── my_robot.xacro
│ └── worlds
│ └── myworld_project3.world
├── where_am_i # where_am_i package
│ ├── CMakeLists.txt # compiler instructions
│ ├── config
│ │ ├── base_local_planner_params.yaml
│ │ ├── costmap_common_params.yaml
│ │ ├── global_costmap_params.yaml
│ │ └── local_costmap_params.yaml
│ ├── launch
│ │ └── amcl.launch
│ ├── maps
│ │ ├── mymap.pgm
│ │ └── mymap.yaml
│ └── package.xml
└── images # simulation images
├── localization.gif
├── navigation.gif
└── particles.png
The project was developed on Ubuntu 16.04 and 20.04 LTS with:
- ROS Kinetic/Noetic
- Gazebo 11.5.1
[Ubuntu 16.04 with ROS Kinetic was only used to create the map file of the environment. The rest of the project was developed on Ubuntu 20.04 with ROS Noetic.]
The following dependencies need to be installed:
$ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade -y
$ sudo apt-get install ros-${ROS_DISTRO}-navigation
$ sudo apt-get install ros-${ROS_DISTRO}-map-server
$ sudo apt-get install ros-${ROS_DISTRO}-move-base
$ sudo apt-get install ros-${ROS_DISTRO}-amclTo run this project, you must have ROS and Gazebo installed.
$ mkdir -p /catkin_ws/src/
$ cd catkin_ws/src/
$ catkin_init_workspace$ git clone https://github.com/elena-ecn/RoboticsND-Where-Am-I.git$ cd /catkin_ws/
$ catkin_make$ source devel/setup.bash$ roslaunch my_robot world.launchIn a new terminal (Ctrl+Shift+T), type:
$ source devel/setup.bash
$ roslaunch where_am_i amcl.launchSend a 2D Nav Goal from RViz: Click the 2D Nav Goal button in the toolbar, then click and drag on the map to send the goal to the robot. It will start moving and localize itself in the process.
The contents of this repository are covered under the MIT License.