This repository contains multiple examples to demonstrate the usage of LADAC. There are multicopter, airplane and eVTOL flight dynamic models as well as flight controllers for the specific vehicles. The flight dynamic models and the flight controllers are based on LADAC and written in MATLAB/Simulink. Moreover, there are interfaces to external programs like FlightGear (for visualization) and ArduPilot (for software in the loop tests and flight tests).
It is sometimes not clear how to get new aircraft configurations to fly with existing software such as ArduPilot or PX4. With such software, you usually have no insight into the dynamics of the open and closed loop of the aircraft and are limited to an empirical controller design through flight tests or simulations. This project provides the opportunity to design controllers specifically in MATLAB/Simulink. First, you can quickly parameterize existing aircraft models or easily create new aircraft models based on LADAC building blocks. Then you can analyze the dynamics of the aircraft and design controllers. Then it is possible to translate the created controller into C/C++ code (code generation) and implement it in software like ArduPilot. Finally, you can test your software in a software-in-the-loop simulation before running your code on a Pixhawk for flight testing.
-
MATLAB:
- You need MATLAB/Simulink 2018b or later (older versions may work but they are not supported).
- You may also need some MATLAB toolboxes like Curve Fitting Toolbox, Aerospace Blockset, Aerospace Toolbox, MATLAB Coder, MATLAB Compiler, Simulink Control Design, Simulink Coder depending on what you want to do.
-
Remote control:
You can use a remote control via USB if you have one. -
FlightGear:
You also should install FlightGear for visualization. Normally, any version should work. -
ArduPilot SITL:
You might install ArduPilot SITL if you want to do software in the loop simulations. -
Ground control station:
You might install a ground control station like QGroundControl or MissionPlanner for communication with ArduPilot SITL. -
LADAC-Examples:
Clone this project including the submodules LADAC and LADAC-Example-Data:git clone --recursive https://github.com/iff-gsc/ladac-examples.git
-
Start a simulation of quadcopter Bebop2 with loiter controller (both quadcopter dynamics and controller run in MATLAB/Simulink):
- Open MATLAB/Simulink.
- Run the Bebop2 initialization file
Copter/Bebop2/init_quadcopter_Bebop2_Loiter_INDI_simple.cd('Copter/Bebop2') init_quadcopter_Bebop2_Loiter_INDI_simple - Plug in a remote control via USB.
By default, the calibration settings of the Xbox-360 joystick are used as you can see in the init scriptinit_quadcopter_Bebop2_Loiter_INDI_simple.
This calibration settings may not be compatible with your joystick! Therefore, you should test and calibrate your joystick.
If you do not have connected a remote control, setjystck.enable = 0(else an error will occur). - Run the Simulink file
QuadcopterSimModel_INDI_Loiter_simple.slx(should open after step 2) to start the simulation. You can either control the system with the remote control (vertical velocity, yaw rate, pitch angle, roll angle) or dummy inputs will be performed.sim('QuadcopterSimModel_INDI_Loiter_simple') - You can view the system outputs in the block visualization clicking on the scopes. However, this is not visually intuitive.
-
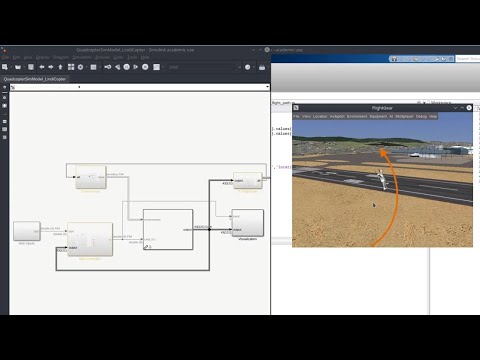
Visualize simulation with FlightGear:
- Run the start script of FlightGear by running
runfg_IRIS.bat(Windows) orrunfg_IRIS.sh(Linux):This will open FlightGear and load an IRIS quadcopter animation (for visualization only, the computation is carried out by MATLAB)../modules/ladac-examples-data/FlightGear/runfg_IRIS.sh
- Run the start script of FlightGear by running
-
Use the dynamics model of MATLAB/Simulink for software in the loop simulation of ArduPilot (controller runs in ArduPilot):
- Run a new MATLAB/Simulink simulation with Bebop2 quadcopter with the ArduPilot SITL interface:
cd('Copter/Bebop2') init_quadcopter_Bebop2_ArduPilot_SITL sim('QuadcopterSimModel_ArduCopter_SITL') - Run ArduPilot SITL in Gazebo mode from terminal (
sim_vehicle.pymust be on the path or you find it in the ArduPilot repository inTools/autotest/). Make sure that you have a proper ArduPilot configuration file for the ArduPilot SITL where you have set the joystick inputs etc. correctly. You should use the provided ArduPilot parameters file of the Bebop2 as a basis for the configuration, since the sensor filter and control parameters are already correctly set here for the Bebop2 Simulink model. Finaly you can start the ArduPilot SITL with the--add-param-fileoption (here, our parameter file is used as an example):The dynamics model in MATLAB/Simulink is tested with ArduCopter 4.2.0. If you run into any problems try checking out the older ArduCopter release in the ArduPilot repository with:sim_vehicle.py -v ArduCopter --model=gazebo --add-param-file=<path-to-repository>/modules/ladac-examples-data/ArduPilot_params/Parrot_Bebop2_MATLAB_SITL.paramgit checkout Copter-4.2.0 git submodule update --init --recursive - Control the quadcopter from ArduPilot. Therefore, you should use a ground control station (read QGroundControl or MissionPlanner documentation) or the MAVProxy command prompt.
- Run a new MATLAB/Simulink simulation with Bebop2 quadcopter with the ArduPilot SITL interface:
There are initialization m-files in multiple subfolders (e.g. Copter/Bebop2/init_...) to initialize the parameters of
the physical model as well as of the controller. There are simulation
slx-file (e.g. Copter/models/QuadcoterSimModel_...) for different kinds of vehicles
and different types of controllers.
Standard ArduPilot flight modes will only work if you load appropriate parameters for you vehicle.
The default parameters (e.g. -f gazebo-iris) only work for similar quadcopters (e.g. IRIS quadcopter).
For other vehicles you have to load different parameters using the --add-param-file option.
For some vehicles you find the parameters in modules/ladac-examples-data/ArduPilot_params. You can use these parameter files as a basis for your own configuration and add your joystick configuration, for example.
-
IRIS:
You can load the ArduPilot IRIS parameters with the-fparameter:sim_vehicle.py -v ArduCopter -f gazebo-iris --model=gazebo -
Muetze:
Muetze is very similar to IRIS. That is why ArduCopter works with-f gazebo-irisoption.
Please have a look at the LADAC readme.
Have a look at the LindiCopter autopilot.
You can implement your controllers in ArduPilot to quickly proceed to flight tests, see ArduPilot Custom Controller.
Before reporting a bug, please try the following:
- check
git status - restart MATLAB/Simulink
Create an issue and provide the following information:
- error message or discription of the problem
- steps of how to reproduce the error/problem
- utilized commit SHA-1 hash (e.g. 7d2e1a6c)