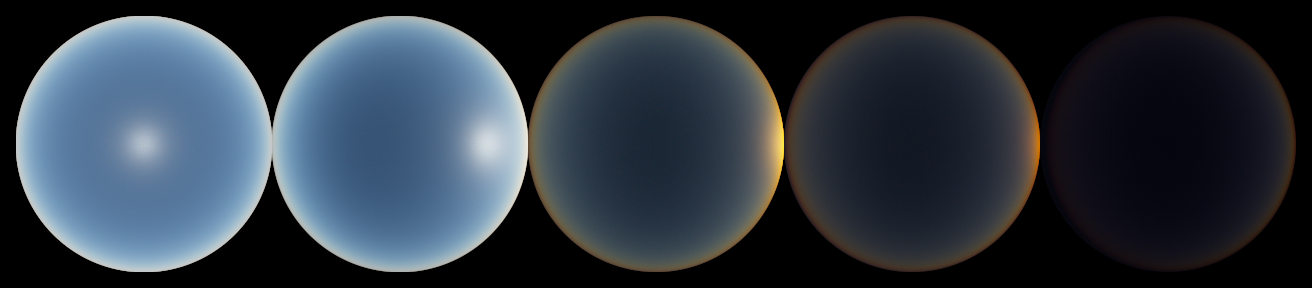
Skytracer is a Monte Carlo spectral volumetric path tracer that renders the Earth's atmosphere in different conditions. It was developed as part of my Master's Thesis to obtain ground truth references that could be used to optimize a real-time approximation for atmosphere rendering.
The atmosphere model is described by Guimera et al. in "A Physically-Based Spatio-Temporal Sky Model". In order to be as unbiased as possible, the volumetric path tracer uses delta tracking to find the next scattering/absorption event along the view ray, and ratio tracking to estimate the transmittance.
A real-time approximation of the results generated by Skytracer can be found in this Shadertoy.
This project is only known to work on Linux, but it probably builds on Windows and MacOS as long as you satisfy the required dependencies.
Skytracer depends on GLM (OpenGL Mathematics), which is provided as a Git submodule. To clone the repository, including submodules, use:
git clone --recursive https://github.com/fgarlin/skytracer
Alternatively, if you didn't use the --recursive option when cloning the repo, you can run:
git submodule init
git submodule update
The following dependencies are not bundled with Skytracer and must be installed before attempting to build the project:
- A compiler that supports C++17
- CMake >= 3.18
- zlib, required by TinyEXR to save EXR files
- TBB (Threading Building Blocks), for multi-threading
This project is compiled like most CMake projects. For example, in Linux you can run:
mkdir build && cd build
cmake ..
make -j8 # You can change 8 for the number of CPU cores in your systemOnce the project is compiled, the resulting binary can be used to generate EXR images of the Earth's atmosphere. The rendering configuration, atmospheric conditions and other settings can be changed through command-line arguments. Run ./skytracer --help to see a list of possible parameters.
An example usage is shown below:
./skytracer \
-w 512 -h 512 \ # We want a 512x512 image
-l 490 \ # Sample the 490 nm wavelength
-s 1024 \ # 1024 samples per pixel
-a 1000 \ # Set the camera altitude to 1 km above sea level
--aerosol-type urban \ # We want to simulate an urban environment
--elevation 30 \ # Sun elevation angle of 30 degrees over the horizon
example.exr # Output to example.exrNote that this renderer is monospectral, i.e. only a single wavelength is sampled during rendering, so the output image is grayscale. If you want to obtain an RGB image, several spectral samples have to be combined properly to obtain a correct result.
There are several ways to do spectral rendering. We provide a Python script on scripts/render_rgb.py that takes several uniformly distributed spectral samples and combines them using the CIE color matching functions. The output are two image files:
- An EXR image containing HDR linear sRGB color values
- A PNG image, which is a tonemapped and gamma corrected version of the HDR image
A suitable conda environment to run the script can be created and activated with:
conda env create -f environment.yaml
conda activate skytracerThe script has its own set of command-line arguments, which can be listed with python render_rgb.py --help. Any arguments not recognized by the Python script will be passed along to the Skytracer executable.
This code is released under the MIT license. See LICENSE for more details.