A guide covering Advanced Matrix Extensions (AMX) including the applications, libraries and tools that will make you a better and more efficient Advanced Matrix Extensions (AMX) development.
Note: You can easily convert this markdown file to a PDF in VSCode using this handy extension Markdown PDF.
Intel® Architecture Instruction Set Extensions and Future Features Programming Reference (PDF)
Advanced Matrix Extensions (AMX) is an x86 extension that introduces a new programming framework for working with matrices (rank-2 tensors). The extensions introduce two new components: a 2-dimensional register file with registers called 'tiles' and a set of accelerators that are able to operate on those tiles. The tiles represent a sub-array portion from a large 2-dimensional memory image.
Data Streaming Accelerator (DSA) is a high-performance data copy and transformation accelerator that will be integrated in future Intel® processors, targeted for optimizing streaming data movement and transformation operations common with applications for high-performance storage, networking, persistent memory, and various data processing applications.
Tile matrix MULtiply unit (TMUL) is an accelerator that is part of AMX comprising a grid of fused multiply-add units capable of operating on tiles. Its existence is defined by the AMX-INT8 and AMX-BF16 sub-extensions.
Tile control register (TILECFG) is a process that allows a programmer to configure the size of those tiles (in terms of rows and bytes_per_row). Depending on the algorithm being implemented, the size of the tile can be changed to more naturally represent that algorithm.
Data-driven accelerators are types of accelerators that operate on a set of data independent of the CPU.
-
Vector accelerator is an accelerator used for vector performing large vector operations.
-
AI accelerator is an accelerator that operates on predictive models such as artificial neural networks.
Algorithm-driven accelerators are types of accelerators that perform a specific algorithm on dedicated hardware.
-
Compression accelerator is an accelerator that performs compression using various algorithms.
-
Cryptographic accelerator is an accelerator that performs various cryptography operations.
Cryptocurrency accelerator is a special cryptographic accelerator designed to accelerate cryptocurrency transactions.
Graphics accelerator is an accelerator used for the manipulation and creation of images.
DSP accelerator is an accelerator that performs algorithms used for the processing of digial signals.
Programmable accelerator is an accelerator that come in the form of an FPGA and can implement any function necessary.
FPGA(Field Programmable Gate Arrays) are semiconductor devices that are based around a matrix of configurable logic blocks (CLBs) connected via programmable interconnects. FPGAs can be reprogrammed to desired application or functionality requirements after manufacturing.
TinyFPGA is a new series of boards that are low-cost, open source FPGA boards in a tiny form factor.
FPGA & SoC Design Tools from Microsemi
QuickLogic Embedded FPGA (eFPGA) Intellectual Property (IP) and Software
FPGA for Beginners with Development Boards from Digilent®
Hundreds of FPGA Projects on Instructables
FPGA Fundamentals from NI(National Instruments)
Getting Started With LabVIEW FPGA from NI(National Instruments)
Programming and FPGA Basics - INTEL® FPGAS
FPGA Online Training Courses on LinkedIn Learning
UMass Lowell's Graduate Certificate in Field Programmable Gate Arrays(FPGA)
FPGA Design Fundamentals Course (UC San Diego Extension)
FPGA II Course (UC San Diego Extension)
FPGAs & SoCs Training from Microsemi
DSP fundamentals for FPGAs course from MATLAB and Simulink Training
LabVIEW FPGA is a software add-on for LabVIEW that you can use to more efficiently and effectively design FPGA-based systems through a highly integrated development environment, IP libraries, a high-fidelity simulator, and debugging features.
Apio is a multiplatform toolbox, with static pre-built packages, project configuration tools and easy command interface to verify, synthesize, simulate and upload your verilog designs.
IceStorm is a project that aims at documenting the bitstream format of Lattice iCE40 FPGAs and providing simple tools for analyzing and creating bitstream files.
Icestudio is a visual editor for open FPGA boards. Built on top of the Icestorm project using Apio.
FuseSoC is an award-winning package manager and a set of build tools for HDL (Hardware Description Language) code and FPGA/ASIC development.
OpenWiFi is an open-source IEEE802.11/Wi-Fi baseband chip/FPGA design.
PipeCNN is an OpenCL-based FPGA Accelerator for Large-Scale Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). Currently, there is a growing trend among developers in the FPGA community to utilize High Level Synthesis (HLS) tools to design and implement customized circuits on FPGAs.
Verilator is an open-source SystemVerilog simulator and lint system.
Verilog to Routing(VTR) is a collaborative project to provide a open-source framework for conducting FPGA architecture and CAD Research & Development. The VTR design flow takes as input a Verilog description of a digital circuit, and a description of the target FPGA architecture.
PlatformIO is a professional collaborative platform for embedded development with no vendor lock-in. It provides support for multiplatforms and frameworks such as IoT, Arduino, CMSIS, ESP-IDF, FreeRTOS, libOpenCM3, mbed OS, Pulp OS, SPL, STM32Cube, Zephyr RTOS, ARM, AVR, Espressif (ESP8266/ESP32), FPGA, MCS-51 (8051), MSP430, Nordic (nRF51/nRF52), NXP i.MX RT, PIC32, RISC-V.
PlatformIO for VSCode is a plugin that provides support for the PlatformIO IDE on VSCode.
Tock is an embedded operating system designed for running multiple concurrent, mutually distrustful applications on Cortex-M and RISC-V based embedded platforms. Tock's design centers around protection, both from potentially malicious applications and from device drivers.
OpenTimer is a High-Performance Timing Analysis Tool for VLSI Systems.
LLVM is a library that has collection of modular/reusable compiler and toolchain components (assemblers, compilers, debuggers, etc.). With these components LLVM can be used as a compiler framework, providing a front-end(parser and lexer) and a back-end (code that converts LLVM's representation to actual machine code).
TinyGo is a Go compiler(based on LLVM) intended for use in small places such as microcontrollers, WebAssembly (Wasm), and command-line tools.
Chipyard is an open source framework for agile development of Chisel-based systems-on-chip. It will allow you to leverage the Chisel HDL, Rocket Chip SoC generator, and other Berkeley projects to produce a RISC-V SoC with everything from MMIO-mapped peripherals to custom accelerators.
The Eclipse Embedded CDT is a collection of plug-ins for Arm & RISC-V C/C++ developers. Unicorn is a lightweight, multi-platform, multi-architecture CPU emulator framework(ARM, AArch64, M68K, Mips, Sparc, X86) based on QEMU.
Keystone is a lightweight multi-platform, multi-architecture(Arm, Arm64, Hexagon, Mips, PowerPC, Sparc, SystemZ & X86) assembler framework.
Reko is a decompiler for machine code binaries.
Renode is Antmicro's virtual development framework for multinode embedded networks (both wired and wireless) and is intended to enable a scalable workflow for creating effective, tested and secure IoT systems.
Diosix is a lightweight, secure, multiprocessor bare-metal hypervisor written in Rust for RISC-V.
LLVM is a library that has collection of modular/reusable compiler and toolchain components (assemblers, compilers, and debuggers). With these components LLVM can be used as a compiler framework, providing a front-end(parser and lexer) and a back-end (code that converts LLVM's representation to actual machine code).
Clang is a language front-end and tooling infrastructure for languages in the C language family (C, C++, Objective C/C++, OpenCL, CUDA, and RenderScript) for the LLVM project.
How To Setup Clang Tooling For LLVM
Using Clang-Tidy in Visual Studio
Configure VS Code for Clang/LLVM on macOS
Visual Studio Code is a code editor redefined and optimized for building and debugging modern web and cloud applications.
Code Server is a tool that allows you to run VS Code on any machine anywhere and access it in the browser.
Clang-Format is a tool to format C/C++/Java/JavaScript/Objective-C/Objective-C++/Protobuf code.
Clang-Tidy is a clang-based C++ "linter" tool. Its purpose is to provide an extensible framework for diagnosing and fixing typical programming errors, like style violations, interface misuse, or bugs that can be deduced via static analysis. clang-tidy is modular and provides a convenient interface for writing new checks.
Clangd is a Visual Studio Code extension that provides C/C++ language IDE features for VS Code using clangd.
LLD is a linker from the LLVM project that is a drop-in replacement for system linkers and runs much faster than them. It also provides features that are useful for toolchain developers. The linker supports ELF (Unix), PE/COFF (Windows), Mach-O (macOS) and WebAssembly in descending order.
TinyGo is a Go compiler(based on LLVM) intended for use in small places such as microcontrollers, WebAssembly (Wasm), and command-line tools.
FileCheck is a flexible pattern matching file verifier.
tblgen is a description to C++ Code.
clang-tblgen is a description to C++ Code for Clang.
lldb-tblgen is a description to C++ Code for LLDB.
llvm-tblgen is a target description to C++ Code for LLVM.
mlir-tblgen is a description to C++ Code for MLIR.
lit is a LLVM Integrated Tester.
llvm-exegesis is a LLVM Machine Instruction Benchmark.
llvm-locstats is a calculate statistics on DWARF debug location.
llvm-pdbutil is a PDB File forensics and diagnostics.
llvm-profgen is a LLVM SPGO profile generation tool
bugpoint is a automatic test case reduction tool.
llvm-extract is a extract a function from an LLVM module.
llvm-bcanalyzer is a LLVM bitcode analyzer.
llvm-addr2line is a drop-in replacement for addr2line.
llvm-ar is a LLVM archiver.
llvm-cxxfilt is a LLVM symbol name demangler.
llvm-install-name-tool is a LLVM tool for manipulating install-names and rpaths.
llvm-nm is a list LLVM bitcode and object file’s symbol table.
llvm-objcopy is a object copying and editing tool.
llvm-objdump is a LLVM’s object file dumper.
llvm-ranlib is a generates an archive index.
llvm-readelf is a GNU-style LLVM Object Reader.
llvm-size is a print size information.
llvm-strings is a print strings.
llvm-strip is a object stripping tool.
C++ is a cross-platform language that can be used to build high-performance applications developed by Bjarne Stroustrup, as an extension to the C language.
C is a general-purpose, high-level language that was originally developed by Dennis M. Ritchie to develop the UNIX operating system at Bell Labs. It supports structured programming, lexical variable scope, and recursion, with a static type system. C also provides constructs that map efficiently to typical machine instructions, which makes it one was of the most widely used programming languages today.
Embedded C is a set of language extensions for the C programming language by the C Standards Committee to address issues that exist between C extensions for different embedded systems. The extensions hep enhance microprocessor features such as fixed-point arithmetic, multiple distinct memory banks, and basic I/O operations. This makes Embedded C the most popular embedded software language in the world.
C & C++ Developer Tools from JetBrains
Open source C++ libraries on cppreference.com
C++ Tools and Libraries Articles
Introduction C++ Education course on Google Developers
C and C++ Coding Style Guide by OpenTitan
Learn C : An Interactive C Tutorial
C++ Online Training Courses on LinkedIn Learning
Learn C Programming Online Courses on edX
Learn C++ with Online Courses on edX
Coding for Everyone: C and C++ course on Coursera
C++ For C Programmers on Coursera
Basics of Embedded C Programming for Beginners on Udemy
C++ For Programmers Course on Udacity
C++ Fundamentals Course on Pluralsight
Introduction to C++ on MIT Free Online Course Materials
Introduction to C++ for Programmers | Harvard
Online C Courses | Harvard University
C++ Client Libraries for Google Cloud Services
Visual Studio is an integrated development environment (IDE) from Microsoft; which is a feature-rich application that can be used for many aspects of software development. Visual Studio makes it easy to edit, debug, build, and publish your app. By using Microsoft software development platforms such as Windows API, Windows Forms, Windows Presentation Foundation, and Windows Store.
Visual Studio Code is a code editor redefined and optimized for building and debugging modern web and cloud applications.
Vcpkg is a C++ Library Manager for Windows, Linux, and MacOS.
ReSharper C++ is a Visual Studio Extension for C++ developers developed by JetBrains.
AppCode is constantly monitoring the quality of your code. It warns you of errors and smells and suggests quick-fixes to resolve them automatically. AppCode provides lots of code inspections for Objective-C, Swift, C/C++, and a number of code inspections for other supported languages. All code inspections are run on the fly.
CLion is a cross-platform IDE for C and C++ developers developed by JetBrains.
Code::Blocks is a free C/C++ and Fortran IDE built to meet the most demanding needs of its users. It is designed to be very extensible and fully configurable. Built around a plugin framework, Code::Blocks can be extended with plugins.
CppSharp is a tool and set of libraries which facilitates the usage of native C/C++ code with the .NET ecosystem. It consumes C/C++ header and library files and generates the necessary glue code to surface the native API as a managed API. Such an API can be used to consume an existing native library in your managed code or add managed scripting support to a native codebase.
Conan is an Open Source Package Manager for C++ development and dependency management into the 21st century and on par with the other development ecosystems.
High Performance Computing (HPC) SDK is a comprehensive toolbox for GPU accelerating HPC modeling and simulation applications. It includes the C, C++, and Fortran compilers, libraries, and analysis tools necessary for developing HPC applications on the NVIDIA platform.
Thrust is a C++ parallel programming library which resembles the C++ Standard Library. Thrust's high-level interface greatly enhances programmer productivity while enabling performance portability between GPUs and multicore CPUs. Interoperability with established technologies such as CUDA, TBB, and OpenMP integrates with existing software.
Boost is an educational opportunity focused on cutting-edge C++. Boost has been a participant in the annual Google Summer of Code since 2007, in which students develop their skills by working on Boost Library development.
Automake is a tool for automatically generating Makefile.in files compliant with the GNU Coding Standards. Automake requires the use of GNU Autoconf.
Cmake is an open-source, cross-platform family of tools designed to build, test and package software. CMake is used to control the software compilation process using simple platform and compiler independent configuration files, and generate native makefiles and workspaces that can be used in the compiler environment of your choice.
GDB is a debugger, that allows you to see what is going on `inside' another program while it executes or what another program was doing at the moment it crashed.
GCC is a compiler Collection that includes front ends for C, C++, Objective-C, Fortran, Ada, Go, and D, as well as libraries for these languages.
GSL is a numerical library for C and C++ programmers. It is free software under the GNU General Public License. The library provides a wide range of mathematical routines such as random number generators, special functions and least-squares fitting. There are over 1000 functions in total with an extensive test suite.
OpenGL Extension Wrangler Library (GLEW) is a cross-platform open-source C/C++ extension loading library. GLEW provides efficient run-time mechanisms for determining which OpenGL extensions are supported on the target platform.
Libtool is a generic library support script that hides the complexity of using shared libraries behind a consistent, portable interface. To use Libtool, add the new generic library building commands to your Makefile, Makefile.in, or Makefile.am.
Maven is a software project management and comprehension tool. Based on the concept of a project object model (POM), Maven can manage a project's build, reporting and documentation from a central piece of information.
TAU (Tuning And Analysis Utilities) is capable of gathering performance information through instrumentation of functions, methods, basic blocks, and statements as well as event-based sampling. All C++ language features are supported including templates and namespaces.
Clang is a production quality C, Objective-C, C++ and Objective-C++ compiler when targeting X86-32, X86-64, and ARM (other targets may have caveats, but are usually easy to fix). Clang is used in production to build performance-critical software like Google Chrome or Firefox.
OpenCV is a highly optimized library with focus on real-time applications. Cross-Platform C++, Python and Java interfaces support Linux, MacOS, Windows, iOS, and Android.
Libcu++ is the NVIDIA C++ Standard Library for your entire system. It provides a heterogeneous implementation of the C++ Standard Library that can be used in and between CPU and GPU code.
ANTLR (ANother Tool for Language Recognition) is a powerful parser generator for reading, processing, executing, or translating structured text or binary files. It's widely used to build languages, tools, and frameworks. From a grammar, ANTLR generates a parser that can build parse trees and also generates a listener interface that makes it easy to respond to the recognition of phrases of interest.
Oat++ is a light and powerful C++ web framework for highly scalable and resource-efficient web application. It's zero-dependency and easy-portable.
JavaCPP is a program that provides efficient access to native C++ inside Java, not unlike the way some C/C++ compilers interact with assembly language.
Cython is a language that makes writing C extensions for Python as easy as Python itself. Cython is based on Pyrex, but supports more cutting edge functionality and optimizations such as calling C functions and declaring C types on variables and class attributes.
Spdlog is a very fast, header-only/compiled, C++ logging library.
Infer is a static analysis tool for Java, C++, Objective-C, and C. Infer is written in OCaml.
Linear algebra is the math of vectors and matrices. The only prerequisite for this guide is a basic understanding of high school math concepts like numbers, variables, equations, and the fundamental arithmetic operations on real numbers: addition (denoted +), subtraction (denoted −), multiplication (denoted implicitly), and division (fractions). Also, you should also be familiar with functions that take real numbers as inputs and give real numbers as outputs, f : R → R.
Linear Algebra - Online Courses | Harvard University
Linear Algebra | MIT Open Learning Library
Top Linear Algebra Courses on Coursera
Mathematics for Machine Learning: Linear Algebra on Coursera
Top Linear Algebra Courses on Udemy
Learn Linear Algebra with Online Courses and Classes on edX
The Math of Data Science: Linear Algebra Course on edX
Linear Algebra in Twenty Five Lectures | UC Davis
Linear Algebra | UC San Diego Extension
Linear Algebra for Machine Learning | UC San Diego Extension
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Interactive Online Video | Wolfram
Linear Algebra Resources | Dartmouth
We now define the math operations for vectors. The operations we can perform on vectors ~u = (u1, u2, u3) and ~v = (v1, v2, v3) are: addition, subtraction, scaling, norm (length), dot product, and cross product:
The dot product and the cross product of two vectors can also be described in terms of the angle θ between the two vectors.
Vector Operations. Source: slideserve
Vector Operations. Source: pinterest
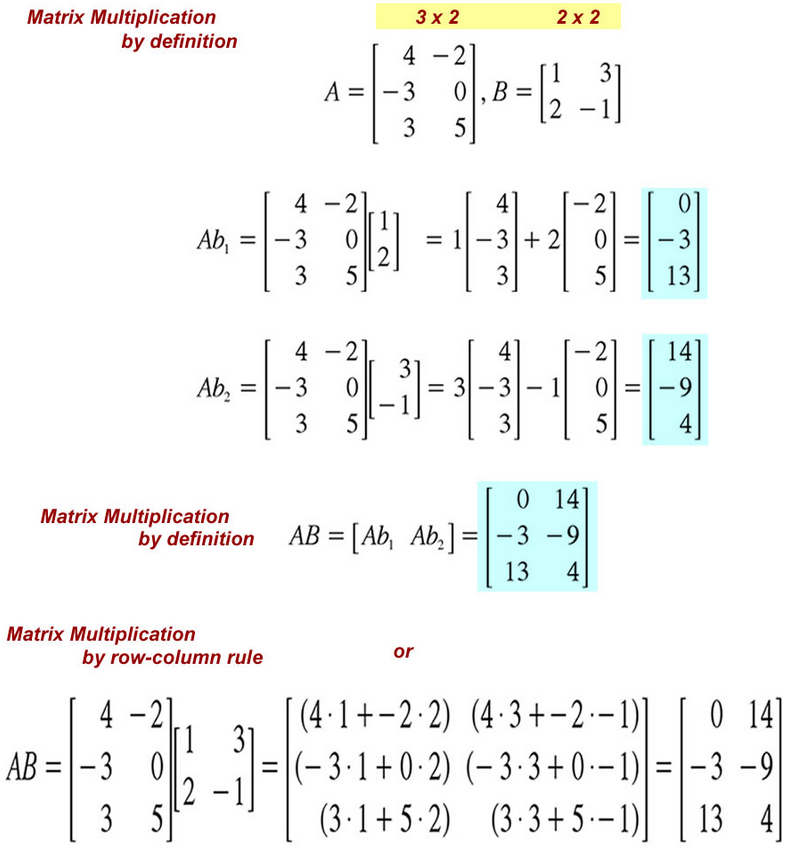
We denote by A the matrix as a whole and refer to its entries as aij .The mathematical operations defined for matrices are the following:
• determinant (denoted det(A) or |A|) Note that the matrix product is not a commutative operation.
Matrix Operations. Source: SDSU Physics
Check for modules that allow Matrix Operations. Source: DPS Concepts
The matrix-vector product is an important special case of the matrix product.
There are two fundamentally different yet equivalent ways to interpret the matrix-vector product. In the column picture, (C), the multiplication of the
matrix A by the vector ~x produces a linear combination of the columns of the matrix: y = Ax = x1A[:,1] + x2A[:,2], where A[:,1] and A[:,2] are the first and second columns of the matrix A. In the row picture, (R), multiplication of the matrix A by the vector ~x produces a column vector with coefficients equal to the dot products of rows of the matrix with the vector ~x.
Matrix-vector product. Source: wikimedia
Matrix-vector Product. Source: mathisfun
The matrix-vector product is used to define the notion of a linear transformation, which is one of the key notions in the study of linear algebra. Multiplication by a matrix A ∈ R m×n can be thought of as computing a linear transformation TA that takes n-vectors as inputs and produces m-vectors as outputs:
Linear Transformations. Source: slideserve
Elementary matrices for linear transformations in R^2. Source:Quora
Fundamental theorem of linear algebra for Vector Spaces. Source: wikimedia
Fundamental theorem of linear algebra. Source: wolfram
System of Linear Equations by Graphing. Source: slideshare
Systems of equations as matrix equations. Source: mathisfun
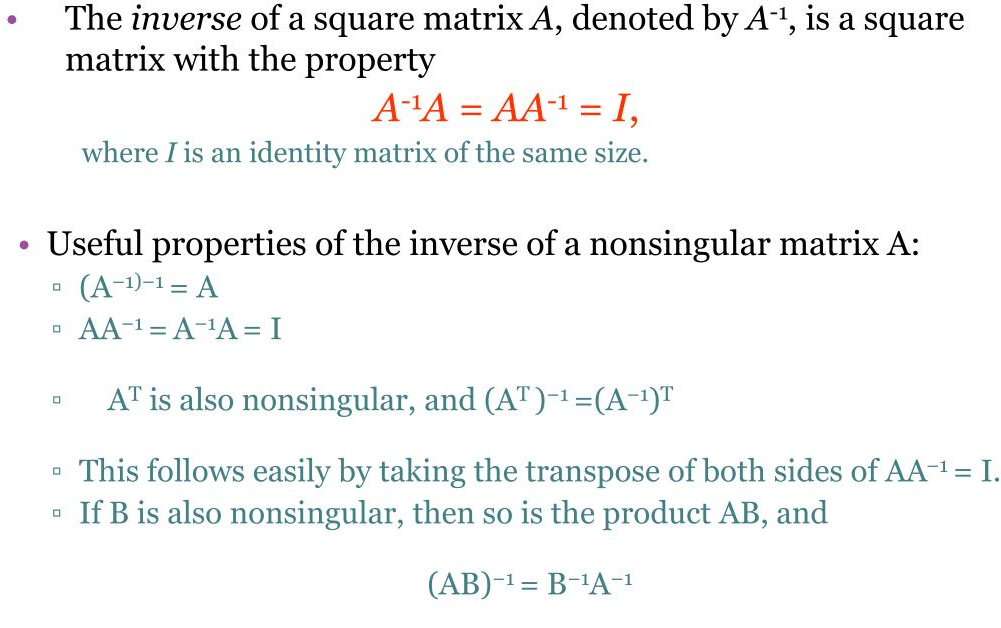
In this section we’ll look at several different approaches for computing the inverse of a matrix. The matrix inverse is unique so no matter which method we use to find the inverse, we’ll always obtain the same answer.
Inverse of 2x2 Matrix. Source: pinterest
One approach for computing the inverse is to use the Gauss–Jordan elimination procedure.
Elementray row operations. Source: YouTube
Every row operation we perform on a matrix is equivalent to a leftmultiplication by an elementary matrix.
Elementary Matrices. Source: SDSU Physics
Finding the inverse of a matrix is to use the Transpose method.
Transpose of a Matrix. Source: slideserve
In this section discuss a number of other important topics of linear algebra.
Intuitively, a basis is any set of vectors that can be used as a coordinate system for a vector space. You are certainly familiar with the standard basis for the xy-plane that is made up of two orthogonal axes: the x-axis and the y-axis.
Basis. Source: wikimedia
Change of Basis. Source: wikimedia
Matrix representations of linear transformations. Source: slideserve
The dimension of a vector space is defined as the number of vectors in a basis for that vector space. Consider the following vector space S = span{(1, 0, 0),(0, 1, 0),(1, 1, 0)}. Seeing that the space is described by three vectors, we might think that S is 3-dimensional. This is not the case, however, since the three vectors are not linearly independent so they don’t form a basis for S. Two vectors are sufficient to describe any vector in S; we can write S = span{(1, 0, 0),(0, 1, 0)}, and we see these two vectors are linearly independent so they form a basis and dim(S) = 2. There is a general procedure for finding a basis for a vector space. Suppose you are given a description of a vector space in terms of m vectors V = span{~v1, ~v2, . . . , ~vm} and you are asked to find a basis for V and the dimension of V. To find a basis for V, you must find a set of linearly independent vectors that span V. We can use the Gauss–Jordan elimination procedure to accomplish this task. Write the vectors ~vi as the rows of a matrix M. The vector space V corresponds to the row space of the matrix M. Next, use row operations to find the reduced row echelon form (RREF) of the matrix M. Since row operations do not change the row space of the matrix, the row space of reduced row echelon form of the matrix M is the same as the row space of the original set of vectors. The nonzero rows in the RREF of the matrix form a basis for vector space V and the numbers of nonzero rows is the dimension of V.
Basis and Dimension. Source: sliderserve
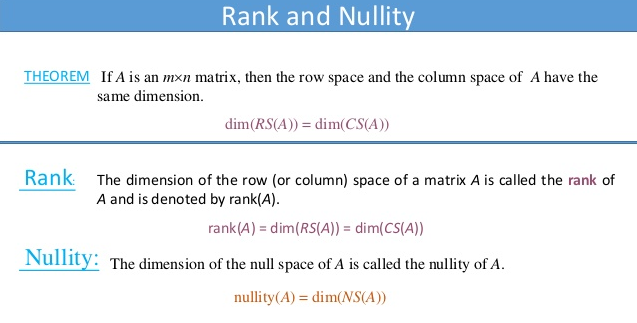
Recall the fundamental vector spaces for matrices that we defined in Section II-E: the column space C(A), the null space N (A), and the row space R(A). A standard linear algebra exam question is to give you a certain matrix A and ask you to find the dimension and a basis for each of its fundamental spaces. In the previous section we described a procedure based on Gauss–Jordan elimination which can be used “distill” a set of linearly independent vectors which form a basis for the row space R(A). We will now illustrate this procedure with an example, and also show how to use the RREF of the matrix A to find bases for C(A) and N (A).
Row space and Column space. Source: slideshare
Row space and Column space. Source: slideshare
Rank and Nullity. Source: slideshare
There is an important distinction between matrices that are invertible and those that are not as formalized by the following theorem. Theorem. For an n×n matrix A, the following statements are equivalent:
Invertible Matrix theorem. Source: SDSU Physics
The determinant of a matrix, denoted det(A) or |A|, is a special way to combine the entries of a matrix that serves to check if a matrix is invertible or not.
Determinant of a Square Matrix. Source: stackexchange
Determinant of matrix. Source: onlinemathlearning
The set of eigenvectors of a matrix is a special set of input vectors for which the action of the matrix is described as a simple scaling. When a matrix is multiplied by one of its eigenvectors the output is the same eigenvector multiplied by a constant Aeλ = λeλ. The constant λ is called an eigenvalue of A.
Generalized EigenVectors. Source: YouTube
Linear regression is an approach to model the relationship between two variables by fitting a linear equation to observed data. One variable is considered to be an explanatory variable, and the other is considered to be a dependent variable.
Multiple Linear Regression. Source: Medium
HVM (Hardware Virtual Machine) is a virtualization type that provides the ability to run an operating system directly on top of a virtual machine without any modification, as if it were run on the bare-metal hardware.
PV(ParaVirtualization) is an efficient and lightweight virtualization technique introduced by the Xen Project team, later adopted by other virtualization solutions. PV does not require virtualization extensions from the host CPU and thus enables virtualization on hardware architectures that do not support Hardware-assisted virtualization.
Network functions virtualization (NFV) is the replacement of network appliance hardware with virtual machines. The virtual machines use a hypervisor to run networking software and processes such as routing and load balancing. NFV allows for the separation of communication services from dedicated hardware, such as routers and firewalls. This separation means network operations can provide new services dynamically and without installing new hardware. Deploying network components with network functions virtualization only takes hours compared to months like with traditional networking solutions.
Software Defined Networking (SDN) is an approach to networking that uses software-based controllers or application programming interfaces (APIs) to communicate with underlying hardware infrastructure and direct traffic on a network. This model differs from that of traditional networks, which use dedicated hardware devices (routers and switches) to control network traffic.
Virtualized Infrastructure Manager (VIM) is a service delivery and reduce costs with high performance lifecycle management Manage the full lifecycle of the software and hardware comprising your NFV infrastructure (NFVI), and maintaining a live inventory and allocation plan of both physical and virtual resources.
Management and Orchestration(MANO) is an ETSI-hosted initiative to develop an Open Source NFV Management and Orchestration (MANO) software stack aligned with ETSI NFV. Two of the key components of the ETSI NFV architectural framework are the NFV Orchestrator and VNF Manager, known as NFV MANO.
Magma is an open source software platform that gives network operators an open, flexible and extendable mobile core network solution. Their mission is to connect the world to a faster network by enabling service providers to build cost-effective and extensible carrier-grade networks. Magma is 3GPP generation (2G, 3G, 4G or upcoming 5G networks) and access network agnostic (cellular or WiFi). It can flexibly support a radio access network with minimal development and deployment effort.
OpenRAN is an intelligent Radio Access Network(RAN) integrated on general purpose platforms with open interface between software defined functions. Open RANecosystem enables enormous flexibility and interoperability with a complete openess to multi-vendor deployments.
Open vSwitch(OVS)is an open source production quality, multilayer virtual switch licensed under the open source Apache 2.0 license. It is designed to enable massive network automation through programmatic extension, while still supporting standard management interfaces and protocols (NetFlow, sFlow, IPFIX, RSPAN, CLI, LACP, 802.1ag).
Edge is a distributed computing framework that brings enterprise applications closer to data sources such as IoT devices or local edge servers. This proximity to data at its source can deliver strong business benefits, including faster insights, improved response times and better bandwidth availability.
Multi-access edge computing (MEC) is an Industry Specification Group (ISG) within ETSI to create a standardized, open environment which will allow the efficient and seamless integration of applications from vendors, service providers, and third-parties across multi-vendor Multi-access Edge Computing platforms.
Virtualized network functions(VNFs) is a software application used in a Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) implementation that has well defined interfaces, and provides one or more component networking functions in a defined way. For example, a security VNF provides Network Address Translation (NAT) and firewall component functions.
Cloud-Native Network Functions(CNF) is a network function designed and implemented to run inside containers. CNFs inherit all the cloud native architectural and operational principles including Kubernetes(K8s) lifecycle management, agility, resilience, and observability.
Physical Network Function(PNF) is a physical network node which has not undergone virtualization. Both PNFs and VNFs (Virtualized Network Functions) can be used to form an overall Network Service.
Network functions virtualization infrastructure(NFVI) is the foundation of the overall NFV architecture. It provides the physical compute, storage, and networking hardware that hosts the VNFs. Each NFVI block can be thought of as an NFVI node and many nodes can be deployed and controlled geographically.
Virtualization-based Security (VBS) is a hardware virtualization feature to create and isolate a secure region of memory from the normal operating system.
Hypervisor-Enforced Code Integrity (HVCI) is a mechanism whereby a hypervisor, such as Hyper-V, uses hardware virtualization to protect kernel-mode processes against the injection and execution of malicious or unverified code. Code integrity validation is performed in a secure environment that is resistant to attack from malicious software, and page permissions for kernel mode are set and maintained by the hypervisor.
KVM (for Kernel-based Virtual Machine) is a full virtualization solution for Linux on x86 hardware containing virtualization extensions (Intel VT or AMD-V). It consists of a loadable kernel module, kvm.ko, that provides the core virtualization infrastructure and a processor specific module, kvm-intel.ko or kvm-amd.ko.
QEMU is a fast processor emulator using a portable dynamic translator. QEMU emulates a full system, including a processor and various peripherals. It can be used to launch a different Operating System without rebooting the PC or to debug system code.
Hyper-V enables running virtualized computer systems on top of a physical host. These virtualized systems can be used and managed just as if they were physical computer systems, however they exist in virtualized and isolated environment. Special software called a hypervisor manages access between the virtual systems and the physical hardware resources. Virtualization enables quick deployment of computer systems, a way to quickly restore systems to a previously known good state, and the ability to migrate systems between physical hosts.
VirtManager is a graphical tool for managing virtual machines via libvirt. Most usage is with QEMU/KVM virtual machines, but Xen and libvirt LXC containers are well supported. Common operations for any libvirt driver should work.
oVirt is an open-source distributed virtualization solution, designed to manage your entire enterprise infrastructure. oVirt uses the trusted KVM hypervisor and is built upon several other community projects, including libvirt, Gluster, PatternFly, and Ansible.Founded by Red Hat as a community project on which Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization is based allowing for centralized management of virtual machines, compute, storage and networking resources, from an easy-to-use web-based front-end with platform independent access.
HyperKit is a toolkit for embedding hypervisor capabilities in your application. It includes a complete hypervisor, based on xhyve/bhyve, which is optimized for lightweight virtual machines and container deployment. It is designed to be interfaced with higher-level components such as the VPNKit and DataKit. HyperKit currently only supports macOS using the Hypervisor.framework making it a core component of Docker Desktop for Mac.
Intel® Graphics Virtualization Technology (Intel® GVT) is a full GPU virtualization solution with mediated pass-through, starting from 4th generation Intel Core (TM) processors with Intel processor graphics(Broadwell and newer). It can be used to virtualize the GPU for multiple guest virtual machines, effectively providing near-native graphics performance in the virtual machine and still letting your host use the virtualized GPU normally.
Apple Hypervisor is a frameowrk that builds virtualization solutions on top of a lightweight hypervisor, without third-party kernel extensions. Hypervisor provides C APIs so you can interact with virtualization technologies in user space, without writing kernel extensions (KEXTs). As a result, the apps you create using this framework are suitable for distribution on the Mac App Store.
Apple Virtualization Framework is a framework that provides high-level APIs for creating and managing virtual machines on Apple silicon and Intel-based Mac computers. This framework is used to boot and run a Linux-based operating system in a custom environment that you define. It also supports the Virtio specification, which defines standard interfaces for many device types, including network, socket, serial port, storage, entropy, and memory-balloon devices.
Apple Paravirtualized Graphics Framework is a framework that implements hardware-accelerated graphics for macOS running in a virtual machine, hereafter known as the guest. The operating system provides a graphics driver that runs inside the guest, communicating with the framework in the host operating system to take advantage of Metal-accelerated graphics.
Cloud Hypervisor is an open source Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM) that runs on top of KVM. The project focuses on exclusively running modern, cloud workloads, on top of a limited set of hardware architectures and platforms. Cloud workloads refers to those that are usually run by customers inside a cloud provider. Cloud Hypervisor is implemented in Rust and is based on the rust-vmm crates.
VMware vSphere Hypervisor is a bare-metal hypervisor that virtualizes servers; allowing you to consolidate your applications while saving time and money managing your IT infrastructure.
Xen is focused on advancing virtualization in a number of different commercial and open source applications, including server virtualization, Infrastructure as a Services (IaaS), desktop virtualization, security applications, embedded and hardware appliances, and automotive/aviation.
Ganeti is a virtual machine cluster management tool built on top of existing virtualization technologies such as Xen or KVM and other open source software. Once installed, the tool assumes management of the virtual instances (Xen DomU).
Packer is an open source tool for creating identical machine images for multiple platforms from a single source configuration. Packer is lightweight, runs on every major operating system, and is highly performant, creating machine images for multiple platforms in parallel. Packer does not replace configuration management like Chef or Puppet. In fact, when building images, Packer is able to use tools like Chef or Puppet to install software onto the image.
Vagrant is a tool for building and managing virtual machine environments in a single workflow. With an easy-to-use workflow and focus on automation, Vagrant lowers development environment setup time, increases production parity, and makes the "works on my machine" excuse a relic of the past. It provides easy to configure, reproducible, and portable work environments built on top of industry-standard technology and controlled by a single consistent workflow to help maximize the productivity and flexibility of you and your team.
Parallels Desktop is a Desktop Hypervisor that delivers the fastest, easiest and most powerful application for running Windows/Linux on Mac (including the new Apple M1 chip) and ChromeOS.
VMware Fusion is a Desktop Hypervisor that deliver desktop and ‘server’ virtual machines, containers and Kubernetes clusters to developers, and IT professionals on the Mac.
VMware Workstation is a hosted hypervisor that runs on x64 versions of Windows and Linux operating systems; it enables users to set up virtual machines on a single physical machine, and use them simultaneously along with the actual machine.
Parallel Computing is a computing environment in which two or more processors (cores, computers) work simultaneously to solve a single problem. Large problems can often be divided into smaller ones, which can then be solved at the same time. There are several different forms of parallel computing: [bit-level]https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bit-level_parallelism), instruction-level, data, and task parallelism.
Accelerated Computing - Training | NVIDIA Developer
Fundamentals of Accelerated Computing with CUDA Python Course | NVIDIA
Top Parallel Computing Courses Online | Coursera
Top Parallel Computing Courses Online | Udemy
Scientific Computing Masterclass: Parallel and Distributed
Learn Parallel Computing in Python | Udemy
GPU computing in Vulkan | Udemy
High Performance Computing Courses | Udacity
Parallel Computing Courses | Stanford Online
Parallel Computing | MIT OpenCourseWare
Multithreaded Parallelism: Languages and Compilers | MIT OpenCourseWare
Parallel Computing with CUDA | Pluralsight
HPC Architecture and System Design | Intel
MATLAB Parallel Server™ is a tool that lets you scale MATLAB® programs and Simulink® simulations to clusters and clouds. You can prototype your programs and simulations on the desktop and then run them on clusters and clouds without recoding. MATLAB Parallel Server supports batch jobs, interactive parallel computations, and distributed computations with large matrices.
Parallel Computing Toolbox™ is a tool that lets you solve computationally and data-intensive problems using multicore processors, GPUs, and computer clusters. High-level constructs such as parallel for-loops, special array types, and parallelized numerical algorithms enable you to parallelize MATLAB® applications without CUDA or MPI programming. The toolbox lets you use parallel-enabled functions in MATLAB and other toolboxes. You can use the toolbox with Simulink® to run multiple simulations of a model in parallel. Programs and models can run in both interactive and batch modes.
Statistics and Machine Learning Toolbox™ is a tool that provides functions and apps to describe, analyze, and model data. You can use descriptive statistics, visualizations, and clustering for exploratory data analysis; fit probability distributions to data; generate random numbers for Monte Carlo simulations, and perform hypothesis tests. Regression and classification algorithms let you draw inferences from data and build predictive models either interactively, using the Classification and Regression Learner apps, or programmatically, using AutoML.
OpenMP is an API that supports multi-platform shared-memory parallel programming in C/C++ and Fortran. The OpenMP API defines a portable, scalable model with a simple and flexible interface for developing parallel applications on platforms from the desktop to the supercomputer.
CUDA® is a parallel computing platform and programming model developed by NVIDIA for general computing on graphical processing units (GPUs). With CUDA, developers are able to dramatically speed up computing applications by harnessing the power of GPUs.
Message Passing Interface (MPI) is a standardized and portable message-passing standard designed to function on parallel computing architectures.
Microsoft MPI (MS-MPI) is a Microsoft implementation of the Message Passing Interface standard for developing and running parallel applications on the Windows platform.
Slurm is a free open-source workload manager designed specifically to satisfy the demanding needs of high performance computing.
Portable Batch System (PBS) Pro is a fast, powerful workload manager designed to improve productivity, optimize utilization and efficiency, and simplify administration for clusters, clouds, and supercomputers.
AWS ParallelCluster is an AWS-supported open source cluster management tool that makes it easy for you to deploy and manage High Performance Computing (HPC) clusters on AWS. ParallelCluster uses a simple text file to model and provision all the resources needed for your HPC applications in an automated and secure manner.
Numba is an open source, NumPy-aware optimizing compiler for Python sponsored by Anaconda, Inc. It uses the LLVM compiler project to generate machine code from Python syntax. Numba can compile a large subset of numerically-focused Python, including many NumPy functions. Additionally, Numba has support for automatic parallelization of loops, generation of GPU-accelerated code, and creation of ufuncs and C callbacks.
Chainer is a Python-based deep learning framework aiming at flexibility. It provides automatic differentiation APIs based on the define-by-run approach (dynamic computational graphs) as well as object-oriented high-level APIs to build and train neural networks. It also supports CUDA/cuDNN using CuPy for high performance training and inference.
XGBoost is an optimized distributed gradient boosting library designed to be highly efficient, flexible and portable. It implements machine learning algorithms under the Gradient Boosting framework. XGBoost provides a parallel tree boosting (also known as GBDT, GBM) that solve many data science problems in a fast and accurate way. It supports distributed training on multiple machines, including AWS, GCE, Azure, and Yarn clusters. Also, it can be integrated with Flink, Spark and other cloud dataflow systems.
cuML is a suite of libraries that implement machine learning algorithms and mathematical primitives functions that share compatible APIs with other RAPIDS projects. cuML enables data scientists, researchers, and software engineers to run traditional tabular ML tasks on GPUs without going into the details of CUDA programming. In most cases, cuML's Python API matches the API from scikit-learn.
Apache Cassandra™ is an open source NoSQL distributed database trusted by thousands of companies for scalability and high availability without compromising performance. Cassandra provides linear scalability and proven fault-tolerance on commodity hardware or cloud infrastructure make it the perfect platform for mission-critical data.
Apache Flume is a distributed, reliable, and available service for efficiently collecting, aggregating, and moving large amounts of streaming event data.
Apache Mesos is a cluster manager that provides efficient resource isolation and sharing across distributed applications, or frameworks. It can run Hadoop, Jenkins, Spark, Aurora, and other frameworks on a dynamically shared pool of nodes.
Apache HBase™ is an open-source, NoSQL, distributed big data store. It enables random, strictly consistent, real-time access to petabytes of data. HBase is very effective for handling large, sparse datasets. HBase serves as a direct input and output to the Apache MapReduce framework for Hadoop, and works with Apache Phoenix to enable SQL-like queries over HBase tables.
Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) is a distributed file system that handles large data sets running on commodity hardware. It is used to scale a single Apache Hadoop cluster to hundreds (and even thousands) of nodes. HDFS is one of the major components of Apache Hadoop, the others being MapReduce and YARN.
Apache Arrow is a language-independent columnar memory format for flat and hierarchical data, organized for efficient analytic operations on modern hardware like CPUs and GPUs.
Apache Spark™ is a unified analytics engine for large-scale data processing. It provides high-level APIs in Scala, Java, Python, and R, and an optimized engine that supports general computation graphs for data analysis. It also supports a rich set of higher-level tools including Spark SQL for SQL and DataFrames, MLlib for machine learning, GraphX for graph processing, and Structured Streaming for stream processing.
Apache PredictionIO is an open source machine learning framework for developers, data scientists, and end users. It supports event collection, deployment of algorithms, evaluation, querying predictive results via REST APIs. It is based on scalable open source services like Hadoop, HBase (and other DBs), Elasticsearch, Spark and implements what is called a Lambda Architecture.
Microsoft Project Bonsai is a low-code AI platform that speeds AI-powered automation development and part of the Autonomous Systems suite from Microsoft. Bonsai is used to build AI components that can provide operator guidance or make independent decisions to optimize process variables, improve production efficiency, and reduce downtime.
Cluster Manager for Apache Kafka(CMAK) is a tool for managing Apache Kafka clusters.
BigDL is a distributed deep learning library for Apache Spark. With BigDL, users can write their deep learning applications as standard Spark programs, which can directly run on top of existing Spark or Hadoop clusters.
Apache Cassandra™ is an open source NoSQL distributed database trusted by thousands of companies for scalability and high availability without compromising performance. Cassandra provides linear scalability and proven fault-tolerance on commodity hardware or cloud infrastructure make it the perfect platform for mission-critical data.
Apache Flume is a distributed, reliable, and available service for efficiently collecting, aggregating, and moving large amounts of streaming event data.
Apache Mesos is a cluster manager that provides efficient resource isolation and sharing across distributed applications, or frameworks. It can run Hadoop, Jenkins, Spark, Aurora, and other frameworks on a dynamically shared pool of nodes.
Apache Beam is an open source, unified model and set of language-specific SDKs for defining and executing data processing workflows, and also data ingestion and integration flows, supporting Enterprise Integration Patterns (EIPs) and Domain Specific Languages (DSLs).
Jupyter Notebook is an open-source web application that allows you to create and share documents that contain live code, equations, visualizations and narrative text. Jupyter is used widely in industries that do data cleaning and transformation, numerical simulation, statistical modeling, data visualization, data science, and machine learning.
Neo4j is the only enterprise-strength graph database that combines native graph storage, advanced security, scalable speed-optimized architecture, and ACID compliance to ensure predictability and integrity of relationship-based queries.
ElasticSearch is a search engine based on the Lucene library. It provides a distributed, multitenant-capable full-text search engine with an HTTP web interface and schema-free JSON documents. Elasticsearch is developed in Java.
Logstash is a tool for managing events and logs. When used generically, the term encompasses a larger system of log collection, processing, storage and searching activities.
Kibana is an open source data visualization plugin for Elasticsearch. It provides visualization capabilities on top of the content indexed on an Elasticsearch cluster. Users can create bar, line and scatter plots, or pie charts and maps on top of large volumes of data.
Trino is a Distributed SQL query engine for big data. It is able to tremendously speed up ETL processes, allow them all to use standard SQL statement, and work with numerous data sources and targets all in the same system.
Extract, transform, and load (ETL) is a data pipeline used to collect data from various sources, transform the data according to business rules, and load it into a destination data store.
Redis(REmote DIctionary Server) is an open source (BSD licensed), in-memory data structure store, used as a database, cache, and message broker. It provides data structures such as strings, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets with range queries, bitmaps, hyperloglogs, geospatial indexes, and streams.
Apache OpenNLP is an open-source library for a machine learning based toolkit used in the processing of natural language text. It features an API for use cases like Named Entity Recognition, Sentence Detection, POS(Part-Of-Speech) tagging, Tokenization Feature extraction, Chunking, Parsing, and Coreference resolution.
Apache Airflow is an open-source workflow management platform created by the community to programmatically author, schedule and monitor workflows. Install. Principles. Scalable. Airflow has a modular architecture and uses a message queue to orchestrate an arbitrary number of workers. Airflow is ready to scale to infinity.
Open Neural Network Exchange(ONNX) is an open ecosystem that empowers AI developers to choose the right tools as their project evolves. ONNX provides an open source format for AI models, both deep learning and traditional ML. It defines an extensible computation graph model, as well as definitions of built-in operators and standard data types.
Apache MXNet is a deep learning framework designed for both efficiency and flexibility. It allows you to mix symbolic and imperative programming to maximize efficiency and productivity. At its core, MXNet contains a dynamic dependency scheduler that automatically parallelizes both symbolic and imperative operations on the fly. A graph optimization layer on top of that makes symbolic execution fast and memory efficient. MXNet is portable and lightweight, scaling effectively to multiple GPUs and multiple machines. Support for Python, R, Julia, Scala, Go, Javascript and more.
AutoGluon is toolkit for Deep learning that automates machine learning tasks enabling you to easily achieve strong predictive performance in your applications. With just a few lines of code, you can train and deploy high-accuracy deep learning models on tabular, image, and text data.
Open Computing Language (OpenCL) is an open standard for parallel programming of heterogeneous platforms consisting of CPUs, GPUs, and other hardware accelerators found in supercomputers, cloud servers, personal computers, mobile devices and embedded platforms.
Khronos Technology Courses and Training
Introduction to Intel® OpenCL Tools
Introduction to OpenCL on FPGAs Course | Coursera
Compiling OpenCL Kernel to FPGAs Course | Coursera
RenderDoc is a stand-alone graphics debugger that allows quick and easy single-frame capture and detailed introspection of any application using Vulkan, D3D11, OpenGL & OpenGL ES or D3D12 across Windows, Linux, Android, Stadia, or Nintendo Switch™.
GPUVerify is a tool for formal analysis of GPU kernels written in OpenCL and CUDA. The tool can prove that kernels are free from certain types of defect, including data races.
OpenCL ICD Loader is an Installable Client Driver (ICD) mechanism to allow developers to build applications against an Installable Client Driver loader (ICD loader) rather than linking their applications against a specific OpenCL implementation.
clBLAS is a software library containing BLAS functions written in OpenCL.
clFFT is a software library containing FFT functions written in OpenCL.
clSPARSE is a software library containing Sparse functions written in OpenCL.
clRNG is an OpenCL based software library containing random number generation functions.
CLsmith is a tool that makes use of two existing testing techniques, Random Differential Testing and Equivalence Modulo Inputs (EMI), applying them in a many-core environment, OpenCL. Its primary feature is the generation of random OpenCL kernels, exercising many features of the language. It also brings a novel idea of applying EMI, via dead-code injection.
Oclgrind is a virtual OpenCL device simulator, including an OpenCL runtime with ICD support. The goal is to provide a platform for creating tools to aid OpenCL development. In particular, this project currently implements utilities for debugging memory access errors, detecting data-races and barrier divergence, collecting instruction histograms, and for interactive OpenCL kernel debugging. The simulator is built on an interpreter for LLVM IR.
NVIDIA® Nsight™ Visual Studio Edition is an application development environment for heterogeneous platforms which brings GPU computing into Microsoft Visual Studio. NVIDIA Nsight™ VSE allows you to build and debug integrated GPU kernels and native CPU code as well as inspect the state of the GPU and memory.
Radeon™ GPU Profiler is a performance tool that can be used by developers to optimize DirectX®12, Vulkan® and OpenCL™ applications for AMD RDNA™ and GCN hardware.
Radeon™ GPU Analyzer is a compiler and code analysis tool for Vulkan®, DirectX®, OpenGL® and OpenCL™.
AMD Radeon ProRender is a powerful physically-based rendering engine that enables creative professionals to produce stunningly photorealistic images on virtually any GPU, any CPU, and any OS in over a dozen leading digital content creation and CAD applications.
NVIDIA Omniverse is a powerful, multi-GPU, real-time simulation and collaboration platform for 3D production pipelines based on Pixar's Universal Scene Description and NVIDIA RTX.
Intel® SDK For OpenCL™ Applications is an offload compute-intensive workloads. Customize heterogeneous compute applications and accelerate performance with kernel-based programming.
NVIDIA NGC is a hub for GPU-optimized software for deep learning, machine learning, and high-performance computing (HPC) workloads.
NVIDIA NGC Containers is a registry that provides researchers, data scientists, and developers with simple access to a comprehensive catalog of GPU-accelerated software for AI, machine learning and HPC. These containers take full advantage of NVIDIA GPUs on-premises and in the cloud.
NVIDIA cuDNN is a GPU-accelerated library of primitives for deep neural networks. cuDNN provides highly tuned implementations for standard routines such as forward and backward convolution, pooling, normalization, and activation layers. cuDNN accelerates widely used deep learning frameworks, including Caffe2, Chainer, Keras, MATLAB, MxNet, PyTorch, and TensorFlow.
NVIDIA Container Toolkit is a collection of tools & libraries that allows users to build and run GPU accelerated Docker containers. The toolkit includes a container runtime library and utilities to automatically configure containers to leverage NVIDIA GPUs.
CUDA Toolkit. Source: NVIDIA Developer CUDA
CUDA is a parallel computing platform and programming model developed by NVIDIA for general computing on graphical processing units (GPUs). With CUDA, developers are able to dramatically speed up computing applications by harnessing the power of GPUs. In GPU-accelerated applications, the sequential part of the workload runs on the CPU, which is optimized for single-threaded. The compute intensive portion of the application runs on thousands of GPU cores in parallel. When using CUDA, developers can program in popular languages such as C, C++, Fortran, Python and MATLAB.
CUDA GPU support for TensorFlow
NVIDIA Deep Learning cuDNN Documentation
NVIDIA GPU Cloud Documentation
NVIDIA NGC is a hub for GPU-optimized software for deep learning, machine learning, and high-performance computing (HPC) workloads.
NVIDIA NGC Containers is a registry that provides researchers, data scientists, and developers with simple access to a comprehensive catalog of GPU-accelerated software for AI, machine learning and HPC. These containers take full advantage of NVIDIA GPUs on-premises and in the cloud.
CUDA Toolkit is a collection of tools & libraries that provide a development environment for creating high performance GPU-accelerated applications. The CUDA Toolkit allows you can develop, optimize, and deploy your applications on GPU-accelerated embedded systems, desktop workstations, enterprise data centers, cloud-based platforms and HPC supercomputers. The toolkit includes GPU-accelerated libraries, debugging and optimization tools, a C/C++ compiler, and a runtime library to build and deploy your application on major architectures including x86, Arm and POWER.
NVIDIA cuDNN is a GPU-accelerated library of primitives for deep neural networks. cuDNN provides highly tuned implementations for standard routines such as forward and backward convolution, pooling, normalization, and activation layers. cuDNN accelerates widely used deep learning frameworks, including Caffe2, Chainer, Keras, MATLAB, MxNet, PyTorch, and TensorFlow.
CUDA-X HPC is a collection of libraries, tools, compilers and APIs that help developers solve the world's most challenging problems. CUDA-X HPC includes highly tuned kernels essential for high-performance computing (HPC).
NVIDIA Container Toolkit is a collection of tools & libraries that allows users to build and run GPU accelerated Docker containers. The toolkit includes a container runtime library and utilities to automatically configure containers to leverage NVIDIA GPUs.
Minkowski Engine is an auto-differentiation library for sparse tensors. It supports all standard neural network layers such as convolution, pooling, unpooling, and broadcasting operations for sparse tensors.
CUTLASS is a collection of CUDA C++ template abstractions for implementing high-performance matrix-multiplication (GEMM) at all levels and scales within CUDA. It incorporates strategies for hierarchical decomposition and data movement similar to those used to implement cuBLAS.
CUB is a cooperative primitives for CUDA C++ kernel authors.
Tensorman is a utility for easy management of Tensorflow containers by developed by System76.Tensorman allows Tensorflow to operate in an isolated environment that is contained from the rest of the system. This virtual environment can operate independent of the base system, allowing you to use any version of Tensorflow on any version of a Linux distribution that supports the Docker runtime.
Numba is an open source, NumPy-aware optimizing compiler for Python sponsored by Anaconda, Inc. It uses the LLVM compiler project to generate machine code from Python syntax. Numba can compile a large subset of numerically-focused Python, including many NumPy functions. Additionally, Numba has support for automatic parallelization of loops, generation of GPU-accelerated code, and creation of ufuncs and C callbacks.
Chainer is a Python-based deep learning framework aiming at flexibility. It provides automatic differentiation APIs based on the define-by-run approach (dynamic computational graphs) as well as object-oriented high-level APIs to build and train neural networks. It also supports CUDA/cuDNN using CuPy for high performance training and inference.
CuPy is an implementation of NumPy-compatible multi-dimensional array on CUDA. CuPy consists of the core multi-dimensional array class, cupy.ndarray, and many functions on it. It supports a subset of numpy.ndarray interface.
CatBoost is a fast, scalable, high performance Gradient Boosting on Decision Trees library, used for ranking, classification, regression and other machine learning tasks for Python, R, Java, C++. Supports computation on CPU and GPU.
cuDF is a GPU DataFrame library for loading, joining, aggregating, filtering, and otherwise manipulating data. cuDF provides a pandas-like API that will be familiar to data engineers & data scientists, so they can use it to easily accelerate their workflows without going into the details of CUDA programming.
cuML is a suite of libraries that implement machine learning algorithms and mathematical primitives functions that share compatible APIs with other RAPIDS projects. cuML enables data scientists, researchers, and software engineers to run traditional tabular ML tasks on GPUs without going into the details of CUDA programming. In most cases, cuML's Python API matches the API from scikit-learn.
ArrayFire is a general-purpose library that simplifies the process of developing software that targets parallel and massively-parallel architectures including CPUs, GPUs, and other hardware acceleration devices.
Thrust is a C++ parallel programming library which resembles the C++ Standard Library. Thrust's high-level interface greatly enhances programmer productivity while enabling performance portability between GPUs and multicore CPUs.
AresDB is a GPU-powered real-time analytics storage and query engine. It features low query latency, high data freshness and highly efficient in-memory and on disk storage management.
Arraymancer is a tensor (N-dimensional array) project in Nim. The main focus is providing a fast and ergonomic CPU, Cuda and OpenCL ndarray library on which to build a scientific computing ecosystem.
Kintinuous is a real-time dense visual SLAM system capable of producing high quality globally consistent point and mesh reconstructions over hundreds of metres in real-time with only a low-cost commodity RGB-D sensor.
GraphVite is a general graph embedding engine, dedicated to high-speed and large-scale embedding learning in various applications.
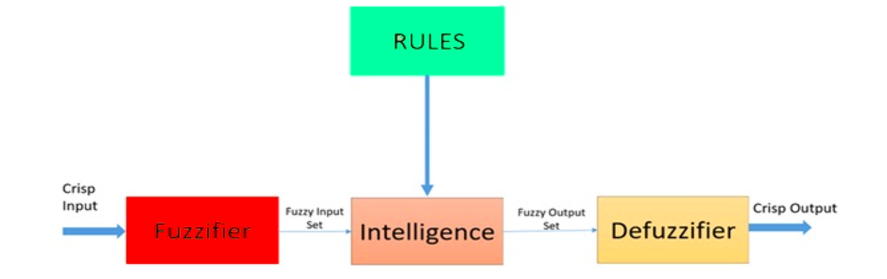
Fuzzy logic is a heuristic approach that allows for more advanced decision-tree processing and better integration with rules-based programming.
Architecture of a Fuzzy Logic System. Source: ResearchGate
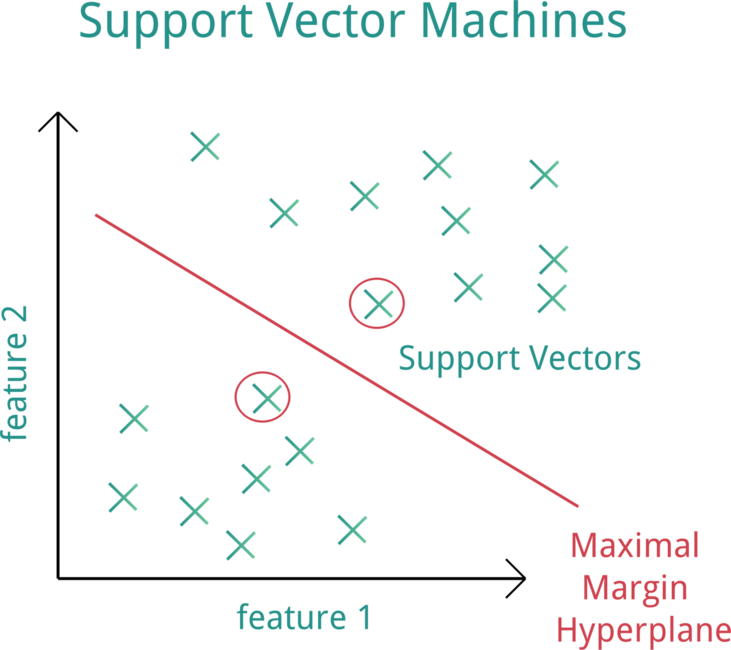
Support Vector Machine (SVM) is a supervised machine learning model that uses classification algorithms for two-group classification problems.
Support Vector Machine (SVM). Source:OpenClipArt
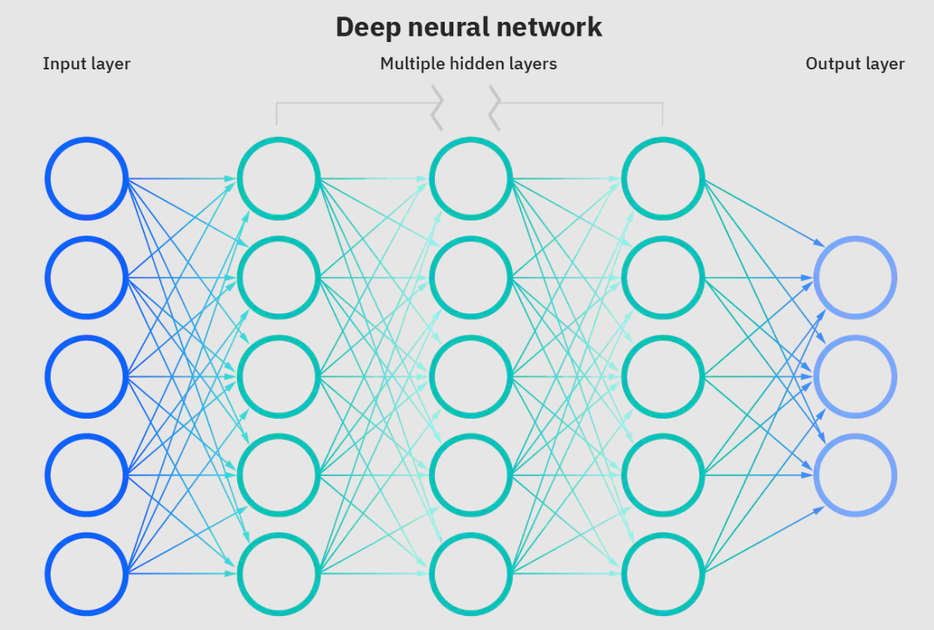
Neural networks are a subset of machine learning and are at the heart of deep learning algorithms. The name/structure is inspired by the human brain copying the process that biological neurons/nodes signal to one another.
Deep neural network. Source: IBM
Convolutional Neural Networks (R-CNN) is an object detection algorithm that first segments the image to find potential relevant bounding boxes and then run the detection algorithm to find most probable objects in those bounding boxes.
Convolutional Neural Networks. Source:CS231n
Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) is a type of artificial neural network which uses sequential data or time series data.
Recurrent Neural Networks. Source: Slideteam
Multilayer Perceptrons (MLPs) is multi-layer neural networks composed of multiple layers of perceptrons with a threshold activation.
Multilayer Perceptrons. Source: DeepAI
Random forest is a commonly-used machine learning algorithm, which combines the output of multiple decision trees to reach a single result. A decision tree in a forest cannot be pruned for sampling and therefore, prediction selection. Its ease of use and flexibility have fueled its adoption, as it handles both classification and regression problems.
Random forest. Source: wikimedia
Decision trees are tree-structured models for classification and regression.
**Decision Trees. Source: CMU
Naive Bayes is a machine learning algorithm that is used solved calssification problems. It's based on applying Bayes' theorem with strong independence assumptions between the features.
Bayes' theorem. Source:mathisfun
Machine Learning is a branch of artificial intelligence (AI) focused on building apps using algorithms that learn from data models and improve their accuracy over time without needing to be programmed.
Machine Learning by Stanford University from Coursera
AWS Training and Certification for Machine Learning (ML) Courses
Machine Learning Scholarship Program for Microsoft Azure from Udacity
Microsoft Certified: Azure Data Scientist Associate
Microsoft Certified: Azure AI Engineer Associate
Azure Machine Learning training and deployment
Learning Machine learning and artificial intelligence from Google Cloud Training
Machine Learning Crash Course for Google Cloud
Scheduling Jupyter notebooks on Amazon SageMaker ephemeral instances
How to run Jupyter Notebooks in your Azure Machine Learning workspace
Machine Learning Courses Online from Udemy
Machine Learning Courses Online from Coursera
Learn Machine Learning with Online Courses and Classes from edX
TensorFlow is an end-to-end open source platform for machine learning. It has a comprehensive, flexible ecosystem of tools, libraries and community resources that lets researchers push the state-of-the-art in ML and developers easily build and deploy ML powered applications.
Keras is a high-level neural networks API, written in Python and capable of running on top of TensorFlow, CNTK, or Theano.It was developed with a focus on enabling fast experimentation. It is capable of running on top of TensorFlow, Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit, R, Theano, or PlaidML.
PyTorch is a library for deep learning on irregular input data such as graphs, point clouds, and manifolds. Primarily developed by Facebook's AI Research lab.
Amazon SageMaker is a fully managed service that provides every developer and data scientist with the ability to build, train, and deploy machine learning (ML) models quickly. SageMaker removes the heavy lifting from each step of the machine learning process to make it easier to develop high quality models.
Azure Databricks is a fast and collaborative Apache Spark-based big data analytics service designed for data science and data engineering. Azure Databricks, sets up your Apache Spark environment in minutes, autoscale, and collaborate on shared projects in an interactive workspace. Azure Databricks supports Python, Scala, R, Java, and SQL, as well as data science frameworks and libraries including TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn.
Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit (CNTK) is an open-source toolkit for commercial-grade distributed deep learning. It describes neural networks as a series of computational steps via a directed graph. CNTK allows the user to easily realize and combine popular model types such as feed-forward DNNs, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs/LSTMs). CNTK implements stochastic gradient descent (SGD, error backpropagation) learning with automatic differentiation and parallelization across multiple GPUs and servers.
Apple CoreML is a framework that helps integrate machine learning models into your app. Core ML provides a unified representation for all models. Your app uses Core ML APIs and user data to make predictions, and to train or fine-tune models, all on the user's device. A model is the result of applying a machine learning algorithm to a set of training data. You use a model to make predictions based on new input data.
Tensorflow_macOS is a Mac-optimized version of TensorFlow and TensorFlow Addons for macOS 11.0+ accelerated using Apple's ML Compute framework.
Apache OpenNLP is an open-source library for a machine learning based toolkit used in the processing of natural language text. It features an API for use cases like Named Entity Recognition, Sentence Detection, POS(Part-Of-Speech) tagging, Tokenization Feature extraction, Chunking, Parsing, and Coreference resolution.
Apache Airflow is an open-source workflow management platform created by the community to programmatically author, schedule and monitor workflows. Install. Principles. Scalable. Airflow has a modular architecture and uses a message queue to orchestrate an arbitrary number of workers. Airflow is ready to scale to infinity.
Open Neural Network Exchange(ONNX) is an open ecosystem that empowers AI developers to choose the right tools as their project evolves. ONNX provides an open source format for AI models, both deep learning and traditional ML. It defines an extensible computation graph model, as well as definitions of built-in operators and standard data types.
Apache MXNet is a deep learning framework designed for both efficiency and flexibility. It allows you to mix symbolic and imperative programming to maximize efficiency and productivity. At its core, MXNet contains a dynamic dependency scheduler that automatically parallelizes both symbolic and imperative operations on the fly. A graph optimization layer on top of that makes symbolic execution fast and memory efficient. MXNet is portable and lightweight, scaling effectively to multiple GPUs and multiple machines. Support for Python, R, Julia, Scala, Go, Javascript and more.
AutoGluon is toolkit for Deep learning that automates machine learning tasks enabling you to easily achieve strong predictive performance in your applications. With just a few lines of code, you can train and deploy high-accuracy deep learning models on tabular, image, and text data.
Anaconda is a very popular Data Science platform for machine learning and deep learning that enables users to develop models, train them, and deploy them.
PlaidML is an advanced and portable tensor compiler for enabling deep learning on laptops, embedded devices, or other devices where the available computing hardware is not well supported or the available software stack contains unpalatable license restrictions.
OpenCV is a highly optimized library with focus on real-time computer vision applications. The C++, Python, and Java interfaces support Linux, MacOS, Windows, iOS, and Android.
Scikit-Learn is a Python module for machine learning built on top of SciPy, NumPy, and matplotlib, making it easier to apply robust and simple implementations of many popular machine learning algorithms.
Weka is an open source machine learning software that can be accessed through a graphical user interface, standard terminal applications, or a Java API. It is widely used for teaching, research, and industrial applications, contains a plethora of built-in tools for standard machine learning tasks, and additionally gives transparent access to well-known toolboxes such as scikit-learn, R, and Deeplearning4j.
Caffe is a deep learning framework made with expression, speed, and modularity in mind. It is developed by Berkeley AI Research (BAIR)/The Berkeley Vision and Learning Center (BVLC) and community contributors.
Theano is a Python library that allows you to define, optimize, and evaluate mathematical expressions involving multi-dimensional arrays efficiently including tight integration with NumPy.
nGraph is an open source C++ library, compiler and runtime for Deep Learning. The nGraph Compiler aims to accelerate developing AI workloads using any deep learning framework and deploying to a variety of hardware targets.It provides the freedom, performance, and ease-of-use to AI developers.
NVIDIA cuDNN is a GPU-accelerated library of primitives for deep neural networks. cuDNN provides highly tuned implementations for standard routines such as forward and backward convolution, pooling, normalization, and activation layers. cuDNN accelerates widely used deep learning frameworks, including Caffe2, Chainer, Keras, MATLAB, MxNet, PyTorch, and TensorFlow.
Jupyter Notebook is an open-source web application that allows you to create and share documents that contain live code, equations, visualizations and narrative text. Jupyter is used widely in industries that do data cleaning and transformation, numerical simulation, statistical modeling, data visualization, data science, and machine learning.
Apache Spark is a unified analytics engine for large-scale data processing. It provides high-level APIs in Scala, Java, Python, and R, and an optimized engine that supports general computation graphs for data analysis. It also supports a rich set of higher-level tools including Spark SQL for SQL and DataFrames, MLlib for machine learning, GraphX for graph processing, and Structured Streaming for stream processing.
Apache Spark Connector for SQL Server and Azure SQL is a high-performance connector that enables you to use transactional data in big data analytics and persists results for ad-hoc queries or reporting. The connector allows you to use any SQL database, on-premises or in the cloud, as an input data source or output data sink for Spark jobs.
Apache PredictionIO is an open source machine learning framework for developers, data scientists, and end users. It supports event collection, deployment of algorithms, evaluation, querying predictive results via REST APIs. It is based on scalable open source services like Hadoop, HBase (and other DBs), Elasticsearch, Spark and implements what is called a Lambda Architecture.
Cluster Manager for Apache Kafka(CMAK) is a tool for managing Apache Kafka clusters.
BigDL is a distributed deep learning library for Apache Spark. With BigDL, users can write their deep learning applications as standard Spark programs, which can directly run on top of existing Spark or Hadoop clusters.
Eclipse Deeplearning4J (DL4J) is a set of projects intended to support all the needs of a JVM-based(Scala, Kotlin, Clojure, and Groovy) deep learning application. This means starting with the raw data, loading and preprocessing it from wherever and whatever format it is in to building and tuning a wide variety of simple and complex deep learning networks.
Tensorman is a utility for easy management of Tensorflow containers by developed by System76.Tensorman allows Tensorflow to operate in an isolated environment that is contained from the rest of the system. This virtual environment can operate independent of the base system, allowing you to use any version of Tensorflow on any version of a Linux distribution that supports the Docker runtime.
Numba is an open source, NumPy-aware optimizing compiler for Python sponsored by Anaconda, Inc. It uses the LLVM compiler project to generate machine code from Python syntax. Numba can compile a large subset of numerically-focused Python, including many NumPy functions. Additionally, Numba has support for automatic parallelization of loops, generation of GPU-accelerated code, and creation of ufuncs and C callbacks.
Chainer is a Python-based deep learning framework aiming at flexibility. It provides automatic differentiation APIs based on the define-by-run approach (dynamic computational graphs) as well as object-oriented high-level APIs to build and train neural networks. It also supports CUDA/cuDNN using CuPy for high performance training and inference.
XGBoost is an optimized distributed gradient boosting library designed to be highly efficient, flexible and portable. It implements machine learning algorithms under the Gradient Boosting framework. XGBoost provides a parallel tree boosting (also known as GBDT, GBM) that solve many data science problems in a fast and accurate way. It supports distributed training on multiple machines, including AWS, GCE, Azure, and Yarn clusters. Also, it can be integrated with Flink, Spark and other cloud dataflow systems.
cuML is a suite of libraries that implement machine learning algorithms and mathematical primitives functions that share compatible APIs with other RAPIDS projects. cuML enables data scientists, researchers, and software engineers to run traditional tabular ML tasks on GPUs without going into the details of CUDA programming. In most cases, cuML's Python API matches the API from scikit-learn.
Deep Learning is a subset of machine learning, which is essentially a neural network with three or more layers. These neural networks attempt to simulate the behavior of the human brain,though, far from matching its ability. This allows the neural networks to "learn" from large amounts of data. The Learning can be supervised, semi-supervised or unsupervised.
Deep Learning Online Courses | NVIDIA
Top Deep Learning Courses Online | Coursera
Top Deep Learning Courses Online | Udemy
Learn Deep Learning with Online Courses and Lessons | edX
Deep Learning Online Course Nanodegree | Udacity
Machine Learning Course by Andrew Ng | Coursera
Machine Learning Engineering for Production (MLOps) course by Andrew Ng | Coursera
Data Science: Deep Learning and Neural Networks in Python | Udemy
Understanding Machine Learning with Python | Pluralsight
How to Think About Machine Learning Algorithms | Pluralsight
Deep Learning Courses | Stanford Online
Deep Learning - UW Professional & Continuing Education
Deep Learning Online Courses | Harvard University
Machine Learning for Everyone Courses | DataCamp
Artificial Intelligence Expert Course: Platinum Edition | Udemy
Top Artificial Intelligence Courses Online | Coursera
Learn Artificial Intelligence with Online Courses and Lessons | edX
Professional Certificate in Computer Science for Artificial Intelligence | edX
Artificial Intelligence Nanodegree program
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Online Courses | Udacity
Intro to Artificial Intelligence Course | Udacity
Edge AI for IoT Developers Course | Udacity
Reasoning: Goal Trees and Rule-Based Expert Systems | MIT OpenCourseWare
Expert Systems and Applied Artificial Intelligence
Autonomous Systems - Microsoft AI
Introduction to Microsoft Project Bonsai
Machine teaching with the Microsoft Autonomous Systems platform
Autonomous Maritime Systems Training | AMC Search
Top Autonomous Cars Courses Online | Udemy
Applied Control Systems 1: autonomous cars: Math + PID + MPC | Udemy
Learn Autonomous Robotics with Online Courses and Lessons | edX
Artificial Intelligence Nanodegree program
Autonomous Systems Online Courses & Programs | Udacity
Edge AI for IoT Developers Course | Udacity
Autonomous Systems MOOC and Free Online Courses | MOOC List
Robotics and Autonomous Systems Graduate Program | Standford Online
Mobile Autonomous Systems Laboratory | MIT OpenCourseWare
NVIDIA cuDNN is a GPU-accelerated library of primitives for deep neural networks. cuDNN provides highly tuned implementations for standard routines such as forward and backward convolution, pooling, normalization, and activation layers. cuDNN accelerates widely used deep learning frameworks, including Caffe2, Chainer, Keras, MATLAB, MxNet, PyTorch, and TensorFlow.
NVIDIA DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling) is a temporal image upscaling AI rendering technology that increases graphics performance using dedicated Tensor Core AI processors on GeForce RTX™ GPUs. DLSS uses the power of a deep learning neural network to boost frame rates and generate beautiful, sharp images for your games.
AMD FidelityFX Super Resolution (FSR) is an open source, high-quality solution for producing high resolution frames from lower resolution inputs. It uses a collection of cutting-edge Deep Learning algorithms with a particular emphasis on creating high-quality edges, giving large performance improvements compared to rendering at native resolution directly. FSR enables “practical performance” for costly render operations, such as hardware ray tracing for the AMD RDNA™ and AMD RDNA™ 2 architectures.
Intel Xe Super Sampling (XeSS) is a temporal image upscaling AI rendering technology that increases graphics performance similar to NVIDIA's DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling). Intel's Arc GPU architecture (early 2022) will have GPUs that feature dedicated Xe-cores to run XeSS. The GPUs will have Xe Matrix eXtenstions matrix (XMX) engines for hardware-accelerated AI processing. XeSS will be able to run on devices without XMX, including integrated graphics, though, the performance of XeSS will be lower on non-Intel graphics cards because it will be powered by DP4a instruction.
Jupyter Notebook is an open-source web application that allows you to create and share documents that contain live code, equations, visualizations and narrative text. Jupyter is used widely in industries that do data cleaning and transformation, numerical simulation, statistical modeling, data visualization, data science, and machine learning.
Apache Spark is a unified analytics engine for large-scale data processing. It provides high-level APIs in Scala, Java, Python, and R, and an optimized engine that supports general computation graphs for data analysis. It also supports a rich set of higher-level tools including Spark SQL for SQL and DataFrames, MLlib for machine learning, GraphX for graph processing, and Structured Streaming for stream processing.
Apache Spark Connector for SQL Server and Azure SQL is a high-performance connector that enables you to use transactional data in big data analytics and persists results for ad-hoc queries or reporting. The connector allows you to use any SQL database, on-premises or in the cloud, as an input data source or output data sink for Spark jobs.
Apache PredictionIO is an open source machine learning framework for developers, data scientists, and end users. It supports event collection, deployment of algorithms, evaluation, querying predictive results via REST APIs. It is based on scalable open source services like Hadoop, HBase (and other DBs), Elasticsearch, Spark and implements what is called a Lambda Architecture.
Cluster Manager for Apache Kafka(CMAK) is a tool for managing Apache Kafka clusters.
BigDL is a distributed deep learning library for Apache Spark. With BigDL, users can write their deep learning applications as standard Spark programs, which can directly run on top of existing Spark or Hadoop clusters.
Eclipse Deeplearning4J (DL4J) is a set of projects intended to support all the needs of a JVM-based(Scala, Kotlin, Clojure, and Groovy) deep learning application. This means starting with the raw data, loading and preprocessing it from wherever and whatever format it is in to building and tuning a wide variety of simple and complex deep learning networks.
Deep Learning Toolbox™ is a tool that provides a framework for designing and implementing deep neural networks with algorithms, pretrained models, and apps. You can use convolutional neural networks (ConvNets, CNNs) and long short-term memory (LSTM) networks to perform classification and regression on image, time-series, and text data. You can build network architectures such as generative adversarial networks (GANs) and Siamese networks using automatic differentiation, custom training loops, and shared weights. With the Deep Network Designer app, you can design, analyze, and train networks graphically. It can exchange models with TensorFlow™ and PyTorch through the ONNX format and import models from TensorFlow-Keras and Caffe. The toolbox supports transfer learning with DarkNet-53, ResNet-50, NASNet, SqueezeNet and many other pretrained models.
Reinforcement Learning Toolbox™ is a tool that provides an app, functions, and a Simulink® block for training policies using reinforcement learning algorithms, including DQN, PPO, SAC, and DDPG. You can use these policies to implement controllers and decision-making algorithms for complex applications such as resource allocation, robotics, and autonomous systems.
Deep Learning HDL Toolbox™ is a tool that provides functions and tools to prototype and implement deep learning networks on FPGAs and SoCs. It provides pre-built bitstreams for running a variety of deep learning networks on supported Xilinx® and Intel® FPGA and SoC devices. Profiling and estimation tools let you customize a deep learning network by exploring design, performance, and resource utilization tradeoffs.
Parallel Computing Toolbox™ is a tool that lets you solve computationally and data-intensive problems using multicore processors, GPUs, and computer clusters. High-level constructs such as parallel for-loops, special array types, and parallelized numerical algorithms enable you to parallelize MATLAB® applications without CUDA or MPI programming. The toolbox lets you use parallel-enabled functions in MATLAB and other toolboxes. You can use the toolbox with Simulink® to run multiple simulations of a model in parallel. Programs and models can run in both interactive and batch modes.
XGBoost is an optimized distributed gradient boosting library designed to be highly efficient, flexible and portable. It implements machine learning algorithms under the Gradient Boosting framework. XGBoost provides a parallel tree boosting (also known as GBDT, GBM) that solve many data science problems in a fast and accurate way. It supports distributed training on multiple machines, including AWS, GCE, Azure, and Yarn clusters. Also, it can be integrated with Flink, Spark and other cloud dataflow systems.
LIBSVM is an integrated software for support vector classification, (C-SVC, nu-SVC), regression (epsilon-SVR, nu-SVR) and distribution estimation (one-class SVM). It supports multi-class classification.
Scikit-Learn is a simple and efficient tool for data mining and data analysis. It is built on NumPy,SciPy, and mathplotlib.
TensorFlow is an end-to-end open source platform for machine learning. It has a comprehensive, flexible ecosystem of tools, libraries and community resources that lets researchers push the state-of-the-art in ML and developers easily build and deploy ML powered applications.
Keras is a high-level neural networks API, written in Python and capable of running on top of TensorFlow, CNTK, or Theano.It was developed with a focus on enabling fast experimentation. It is capable of running on top of TensorFlow, Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit, R, Theano, or PlaidML.
PyTorch is a library for deep learning on irregular input data such as graphs, point clouds, and manifolds. Primarily developed by Facebook's AI Research lab.
Azure Databricks is a fast and collaborative Apache Spark-based big data analytics service designed for data science and data engineering. Azure Databricks, sets up your Apache Spark environment in minutes, autoscale, and collaborate on shared projects in an interactive workspace. Azure Databricks supports Python, Scala, R, Java, and SQL, as well as data science frameworks and libraries including TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn.
Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit (CNTK) is an open-source toolkit for commercial-grade distributed deep learning. It describes neural networks as a series of computational steps via a directed graph. CNTK allows the user to easily realize and combine popular model types such as feed-forward DNNs, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs/LSTMs). CNTK implements stochastic gradient descent (SGD, error backpropagation) learning with automatic differentiation and parallelization across multiple GPUs and servers.
Tensorflow_macOS is a Mac-optimized version of TensorFlow and TensorFlow Addons for macOS 11.0+ accelerated using Apple's ML Compute framework.
Apache Airflow is an open-source workflow management platform created by the community to programmatically author, schedule and monitor workflows. Install. Principles. Scalable. Airflow has a modular architecture and uses a message queue to orchestrate an arbitrary number of workers. Airflow is ready to scale to infinity.
Open Neural Network Exchange(ONNX) is an open ecosystem that empowers AI developers to choose the right tools as their project evolves. ONNX provides an open source format for AI models, both deep learning and traditional ML. It defines an extensible computation graph model, as well as definitions of built-in operators and standard data types.
Apache MXNet is a deep learning framework designed for both efficiency and flexibility. It allows you to mix symbolic and imperative programming to maximize efficiency and productivity. At its core, MXNet contains a dynamic dependency scheduler that automatically parallelizes both symbolic and imperative operations on the fly. A graph optimization layer on top of that makes symbolic execution fast and memory efficient. MXNet is portable and lightweight, scaling effectively to multiple GPUs and multiple machines. Support for Python, R, Julia, Scala, Go, Javascript and more.
AutoGluon is toolkit for Deep learning that automates machine learning tasks enabling you to easily achieve strong predictive performance in your applications. With just a few lines of code, you can train and deploy high-accuracy deep learning models on tabular, image, and text data.
Anaconda is a very popular Data Science platform for machine learning and deep learning that enables users to develop models, train them, and deploy them.
PlaidML is an advanced and portable tensor compiler for enabling deep learning on laptops, embedded devices, or other devices where the available computing hardware is not well supported or the available software stack contains unpalatable license restrictions.
OpenCV is a highly optimized library with focus on real-time computer vision applications. The C++, Python, and Java interfaces support Linux, MacOS, Windows, iOS, and Android.
Scikit-Learn is a Python module for machine learning built on top of SciPy, NumPy, and matplotlib, making it easier to apply robust and simple implementations of many popular machine learning algorithms.
Weka is an open source machine learning software that can be accessed through a graphical user interface, standard terminal applications, or a Java API. It is widely used for teaching, research, and industrial applications, contains a plethora of built-in tools for standard machine learning tasks, and additionally gives transparent access to well-known toolboxes such as scikit-learn, R, and Deeplearning4j.
Caffe is a deep learning framework made with expression, speed, and modularity in mind. It is developed by Berkeley AI Research (BAIR)/The Berkeley Vision and Learning Center (BVLC) and community contributors.
Theano is a Python library that allows you to define, optimize, and evaluate mathematical expressions involving multi-dimensional arrays efficiently including tight integration with NumPy.
Microsoft Project Bonsai is a low-code AI platform that speeds AI-powered automation development and part of the Autonomous Systems suite from Microsoft. Bonsai is used to build AI components that can provide operator guidance or make independent decisions to optimize process variables, improve production efficiency, and reduce downtime.
Microsoft AirSim is a simulator for drones, cars and more, built on Unreal Engine (with an experimental Unity release). AirSim is open-source, cross platform, and supports software-in-the-loop simulation with popular flight controllers such as PX4 & ArduPilot and hardware-in-loop with PX4 for physically and visually realistic simulations. It is developed as an Unreal plugin that can simply be dropped into any Unreal environment. AirSim is being developed as a platform for AI research to experiment with deep learning, computer vision and reinforcement learning algorithms for autonomous vehicles.
CARLA is an open-source simulator for autonomous driving research. CARLA has been developed from the ground up to support development, training, and validation of autonomous driving systems. In addition to open-source code and protocols, CARLA provides open digital assets (urban layouts, buildings, vehicles) that were created for this purpose and can be used freely.
ROS/ROS2 bridge for CARLA(package) is a bridge that enables two-way communication between ROS and CARLA. The information from the CARLA server is translated to ROS topics. In the same way, the messages sent between nodes in ROS get translated to commands to be applied in CARLA.
ROS Toolbox is a tool that provides an interface connecting MATLAB® and Simulink® with the Robot Operating System (ROS and ROS 2), enabling you to create a network of ROS nodes. The toolbox includes MATLAB functions and Simulink blocks to import, analyze, and play back ROS data recorded in rosbag files. You can also connect to a live ROS network to access ROS messages.
Robotics Toolbox™ provides a toolbox that brings robotics specific functionality(designing, simulating, and testing manipulators, mobile robots, and humanoid robots) to MATLAB, exploiting the native capabilities of MATLAB (linear algebra, portability, graphics). The toolbox also supports mobile robots with functions for robot motion models (bicycle), path planning algorithms (bug, distance transform, D*, PRM), kinodynamic planning (lattice, RRT), localization (EKF, particle filter), map building (EKF) and simultaneous localization and mapping (EKF), and a Simulink model a of non-holonomic vehicle. The Toolbox also including a detailed Simulink model for a quadrotor flying robot.
Image Processing Toolbox™ is a tool that provides a comprehensive set of reference-standard algorithms and workflow apps for image processing, analysis, visualization, and algorithm development. You can perform image segmentation, image enhancement, noise reduction, geometric transformations, image registration, and 3D image processing.
Computer Vision Toolbox™ is a tool that provides algorithms, functions, and apps for designing and testing computer vision, 3D vision, and video processing systems. You can perform object detection and tracking, as well as feature detection, extraction, and matching. You can automate calibration workflows for single, stereo, and fisheye cameras. For 3D vision, the toolbox supports visual and point cloud SLAM, stereo vision, structure from motion, and point cloud processing.
Robotics Toolbox™ is a tool that provides a toolbox that brings robotics specific functionality(designing, simulating, and testing manipulators, mobile robots, and humanoid robots) to MATLAB, exploiting the native capabilities of MATLAB (linear algebra, portability, graphics). The toolbox also supports mobile robots with functions for robot motion models (bicycle), path planning algorithms (bug, distance transform, D*, PRM), kinodynamic planning (lattice, RRT), localization (EKF, particle filter), map building (EKF) and simultaneous localization and mapping (EKF), and a Simulink model a of non-holonomic vehicle. The Toolbox also including a detailed Simulink model for a quadrotor flying robot.
Model Predictive Control Toolbox™ is a tool that provides functions, an app, and Simulink® blocks for designing and simulating controllers using linear and nonlinear model predictive control (MPC). The toolbox lets you specify plant and disturbance models, horizons, constraints, and weights. By running closed-loop simulations, you can evaluate controller performance.
Predictive Maintenance Toolbox™ is a tool that lets you manage sensor data, design condition indicators, and estimate the remaining useful life (RUL) of a machine. The toolbox provides functions and an interactive app for exploring, extracting, and ranking features using data-based and model-based techniques, including statistical, spectral, and time-series analysis.
Vision HDL Toolbox™ is a tool that provides pixel-streaming algorithms for the design and implementation of vision systems on FPGAs and ASICs. It provides a design framework that supports a diverse set of interface types, frame sizes, and frame rates. The image processing, video, and computer vision algorithms in the toolbox use an architecture appropriate for HDL implementations.
Automated Driving Toolbox™ is a MATLAB tool that provides algorithms and tools for designing, simulating, and testing ADAS and autonomous driving systems. You can design and test vision and lidar perception systems, as well as sensor fusion, path planning, and vehicle controllers. Visualization tools include a bird’s-eye-view plot and scope for sensor coverage, detections and tracks, and displays for video, lidar, and maps. The toolbox lets you import and work with HERE HD Live Map data and OpenDRIVE® road networks. It also provides reference application examples for common ADAS and automated driving features, including FCW, AEB, ACC, LKA, and parking valet. The toolbox supports C/C++ code generation for rapid prototyping and HIL testing, with support for sensor fusion, tracking, path planning, and vehicle controller algorithms.
UAV Toolbox is an application that provides tools and reference applications for designing, simulating, testing, and deploying unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) and drone applications. You can design autonomous flight algorithms, UAV missions, and flight controllers. The Flight Log Analyzer app lets you interactively analyze 3D flight paths, telemetry information, and sensor readings from common flight log formats.
Navigation Toolbox™ is a tool that provides algorithms and analysis tools for motion planning, simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM), and inertial navigation. The toolbox includes customizable search and sampling-based path planners, as well as metrics for validating and comparing paths. You can create 2D and 3D map representations, generate maps using SLAM algorithms, and interactively visualize and debug map generation with the SLAM map builder app.
Lidar Toolbox™ is a tool that provides algorithms, functions, and apps for designing, analyzing, and testing lidar processing systems. You can perform object detection and tracking, semantic segmentation, shape fitting, lidar registration, and obstacle detection. Lidar Toolbox supports lidar-camera cross calibration for workflows that combine computer vision and lidar processing.
Mapping Toolbox™ is a tool that provides algorithms and functions for transforming geographic data and creating map displays. You can visualize your data in a geographic context, build map displays from more than 60 map projections, and transform data from a variety of sources into a consistent geographic coordinate system.
- If would you like to contribute to this guide simply make a Pull Request.
Distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) Public License.