Common repo for our ongoing research on motion forecasting in self-driving vehicles.
Clone this repo, afterwards init external submodules with:
git submodule update --init --recursiveCreate a conda environment named "future-motion" with:
conda env create -f conda_env.ymlPrepare Waymo Open Motion and Argoverse 2 Forecasting datasets by following the instructions in src/external_submodules/hptr/README.md.
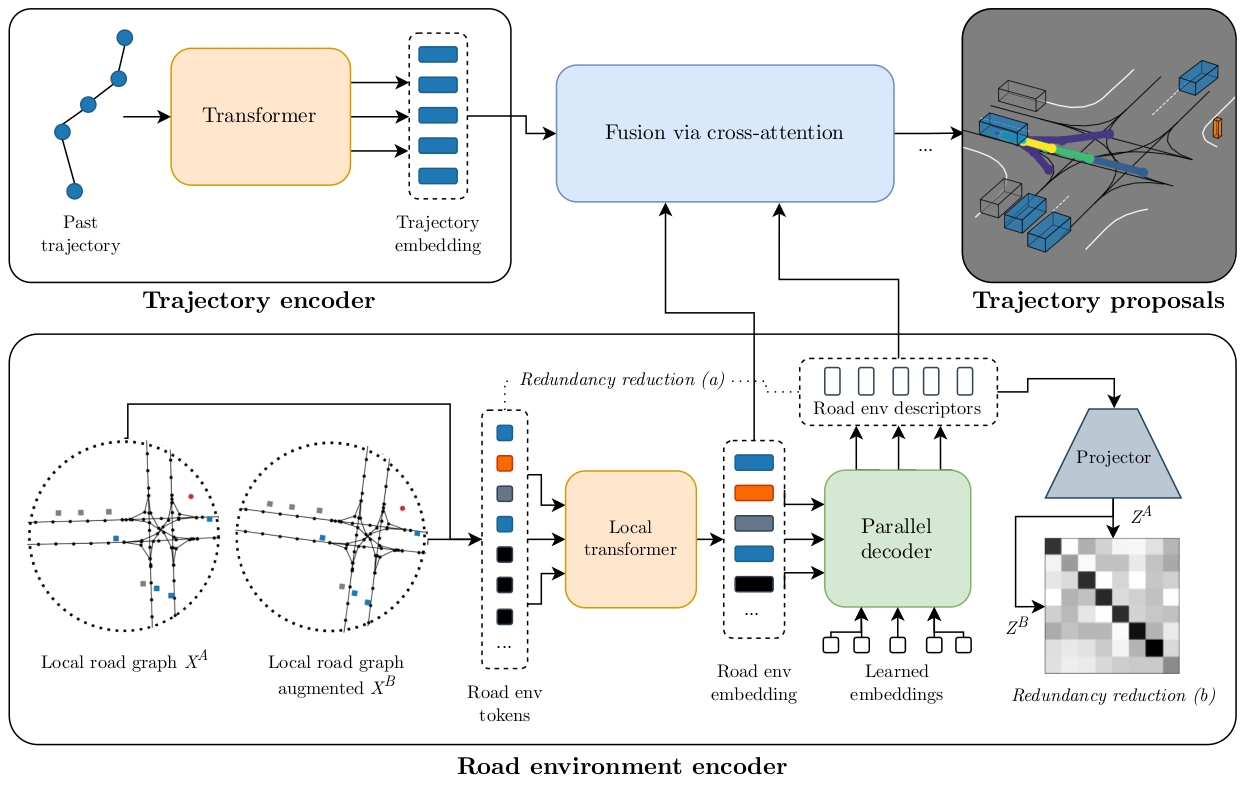
Our RedMotion model consists of two encoders. The trajectory encoder generates an embedding for the past trajectory of the current agent. The road environment encoder generates sets of local and global road environment embeddings as context. We use two redundancy reduction mechanisms, (a) architecture-induced and (b) self-supervised, to learn rich representations of road environments. All embeddings are fused via cross-attention to yield trajectory proposals per agent.
More details
This repo contains the refactored implementation of RedMotion, the original implementation is available here.
The Waymo Motion Prediction Challenge doesn't allow sharing the weights used in the challenge. However, we provide a Colab notebook for a model with a shorter prediction horizon (5s vs. 8s) as a demo.
Training
To train a RedMotion model (tra-dec config) from scratch, adapt the global variables in train.sh according to your setup (Weights & Biases, local paths, batch size and visible GPUs). The default batch size is set for A6000 GPUs with 48GB VRAM. Then start the training run with:
bash train.sh ac_red_motionFor reference, this wandb plot shows the validation mAP scores for the epochs 23 - 129 (default config, trained on 4 A6000 GPUs for ~100h).
Reference
@article{
wagner2024redmotion,
title={RedMotion: Motion Prediction via Redundancy Reduction},
author={Royden Wagner and Omer Sahin Tas and Marvin Klemp and Carlos Fernandez and Christoph Stiller},
journal={Transactions on Machine Learning Research},
issn={2835-8856},
year={2024},
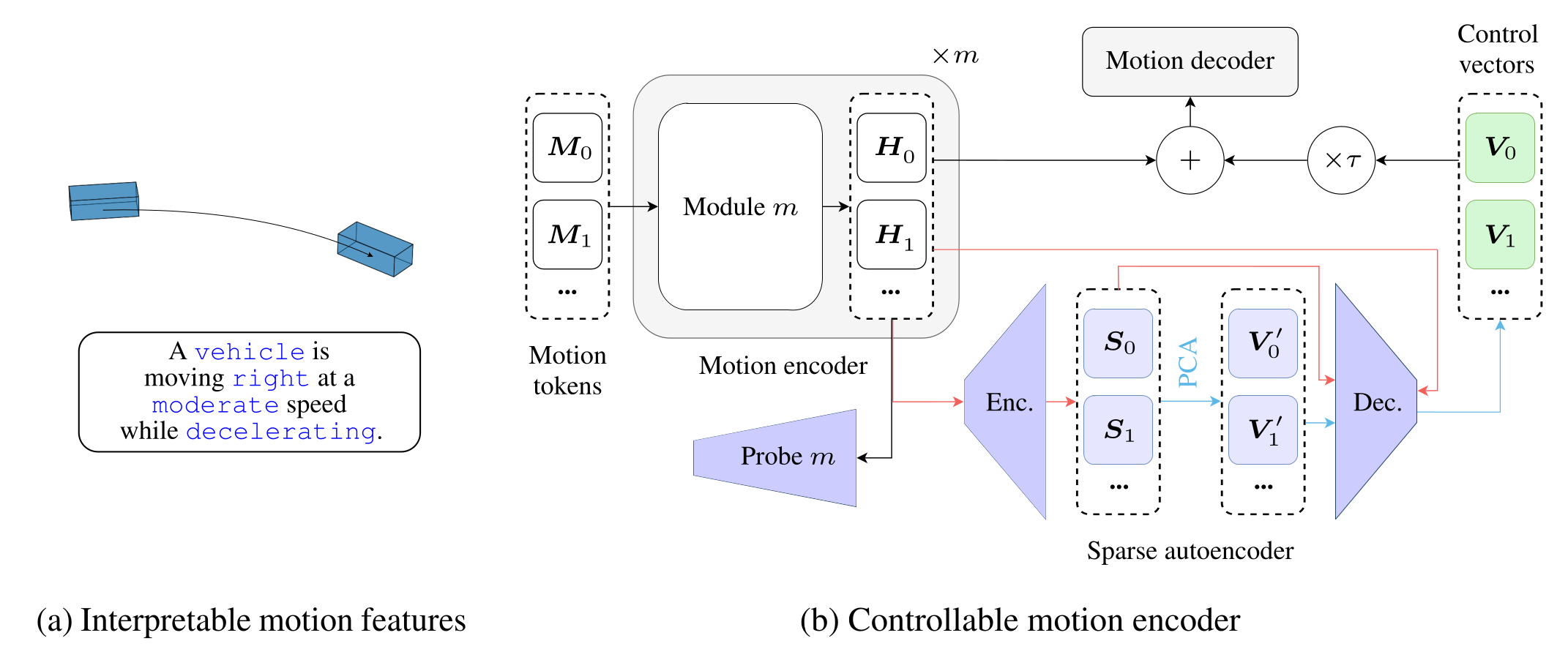
}We use natural language to quantize motion features in an inter-pretable way. (b) The corresponding direction, speed, and acceleration classes are highlighted in blue. (c) To reverse engineer motion forecasting models, we measure the degree to which these features are embedded in their hidden states H with linear probes. Furthermore, we use our discrete motion features to fit control vectors V that allow for controlling motion forecasts during inference.
More details
Gradio demos
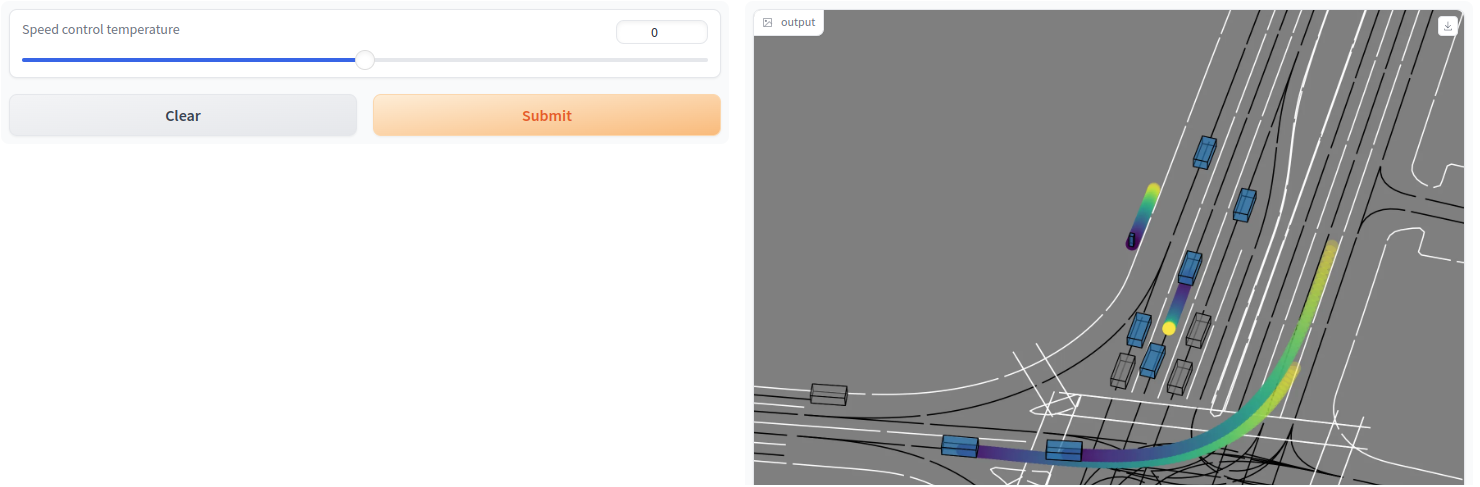
Use this Colab notebook to start Gradio demos for our speed control vectors.
In contrast to the qualitative results in our paper, we show the motion forecasts for the focal agent and 8 other agents in a scene. Press the submit button with the default temperature = 0 to visualize the default (non-controlled) forecasts, then change the temperature and resubmit to visualize the changes. The example is from the Waymo Open dataset and shows motion forecasts for vehicles and a pedestrian (top center).
For very low control temperatures (e.g, -100), almost all agents are becoming static. For very high control temperatures (e.g., 85), even the static (shown in grey) agents begin to move, and the pedestrian does not move faster anymore. We hypothesize that the model has learned a reasonable upper bound for the speed of a pedestrian.
Training
Soon to be released.