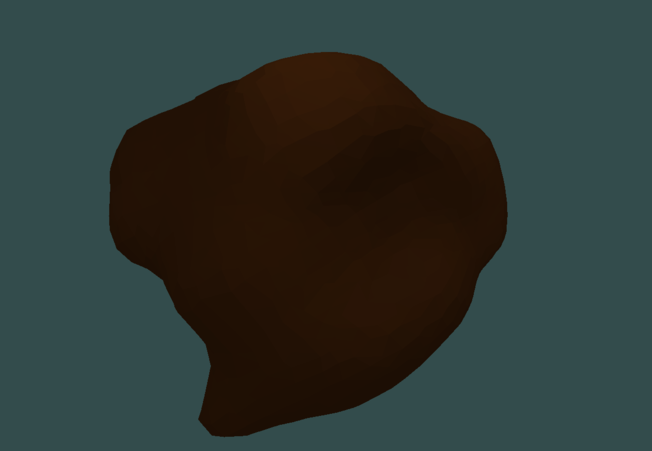
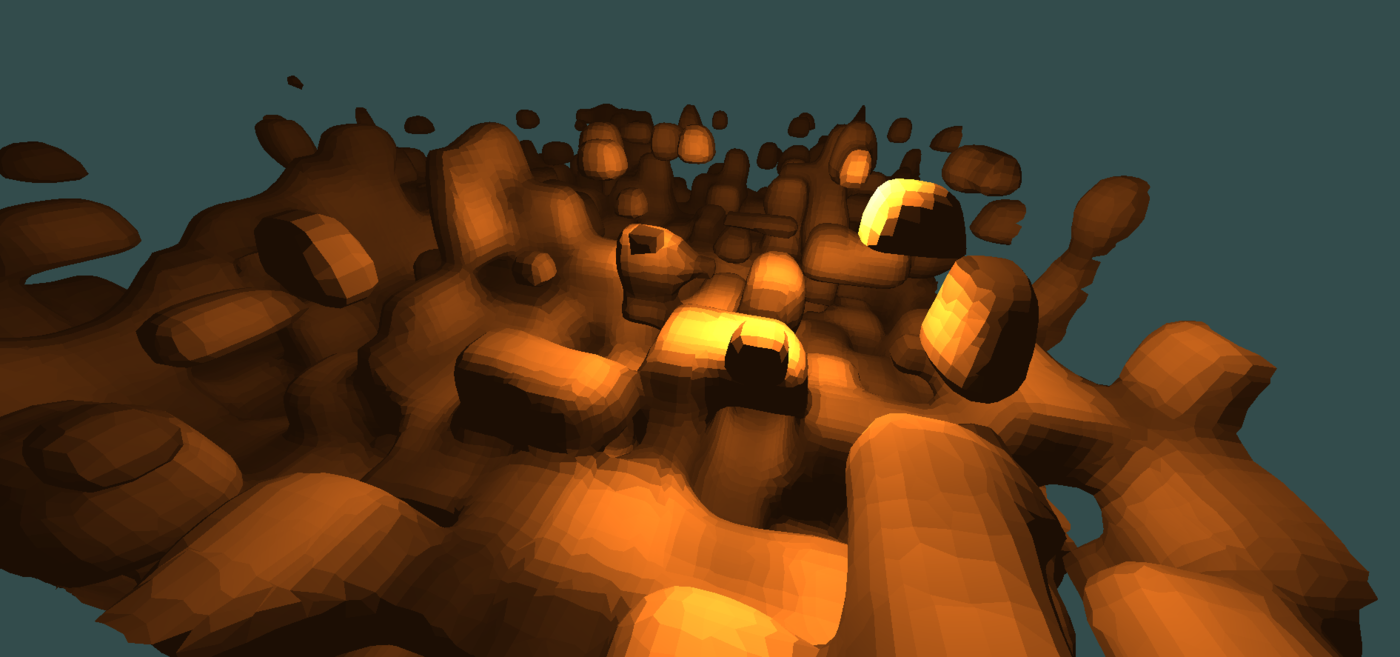
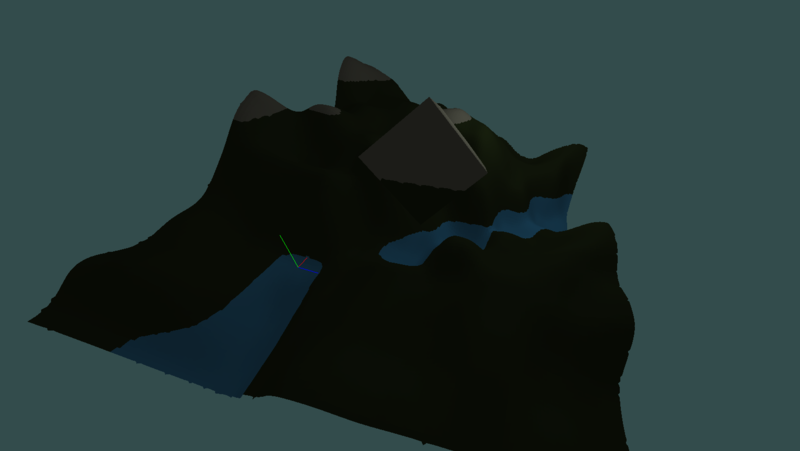
experimental 3D voxel engine
REQUIRES NVIDIA VIDEO CARD(will be optional)
1)minimum OpenGL version 3.3 is required + libGL.so should be available in your PATH
2)install GLFW3
on ubuntu/debian it should be as simple as:
sudo apt-get install libglfw3-dev
or compile glfw3 from sources
3)CUDA is required (probably will be optional later), PATH also must be properly set
4)lapacke:
on ubuntu/debian:
sudo apt-get install liblapacke-dev
or compile from sources
5)install cmake(probably with GUI for simplicity)
on ubuntu/debian:
sudo apt-get install cmake-gui
6)compile cmake project in bindings directory of this project. After that copy outputted libvoxelizedBindings.a to the root of the project
7)install LDC https://dlang.org/download.html, DUB tool should be in your path after installation
8)run export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=. && dub run --build=release
Not yet tested(won't compile out of the box, needs some changes)
Will add Windows as target platform later
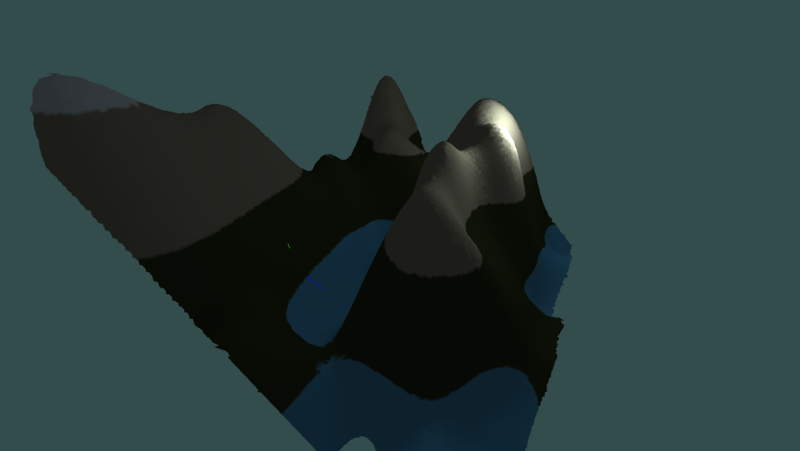
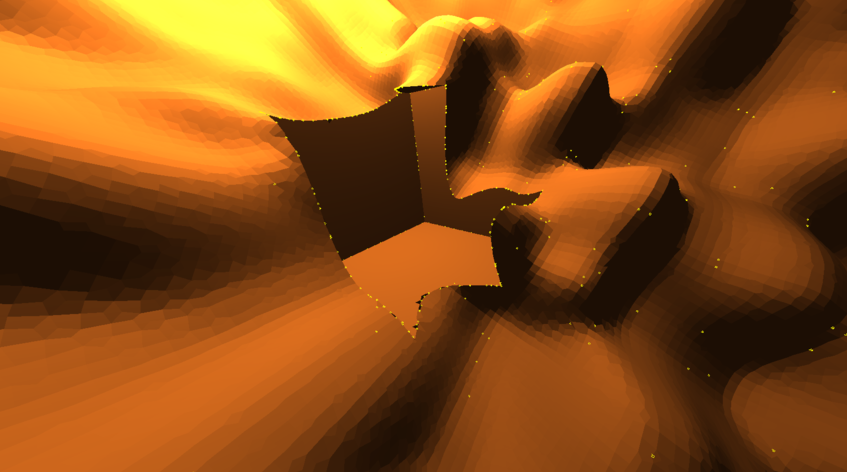
adaptive dual contouring (non manifold yet, produces self-intersecting triangles yet)
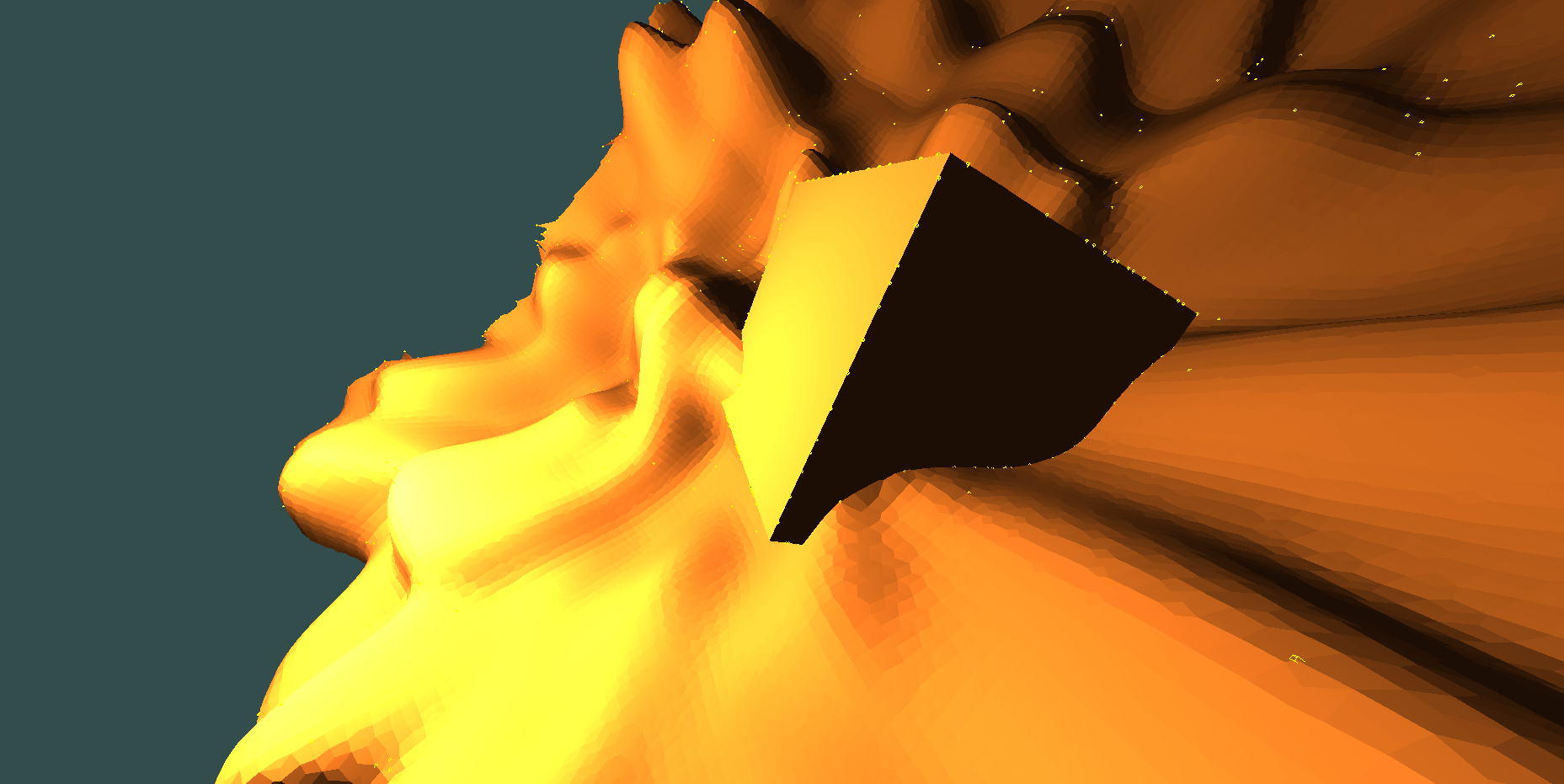
adaptive DC with octree simplification, cube in the middle is overly simplified (topology is a bit broken + non manifoldness uncovers itself in extra incorrect triangles below the cube):
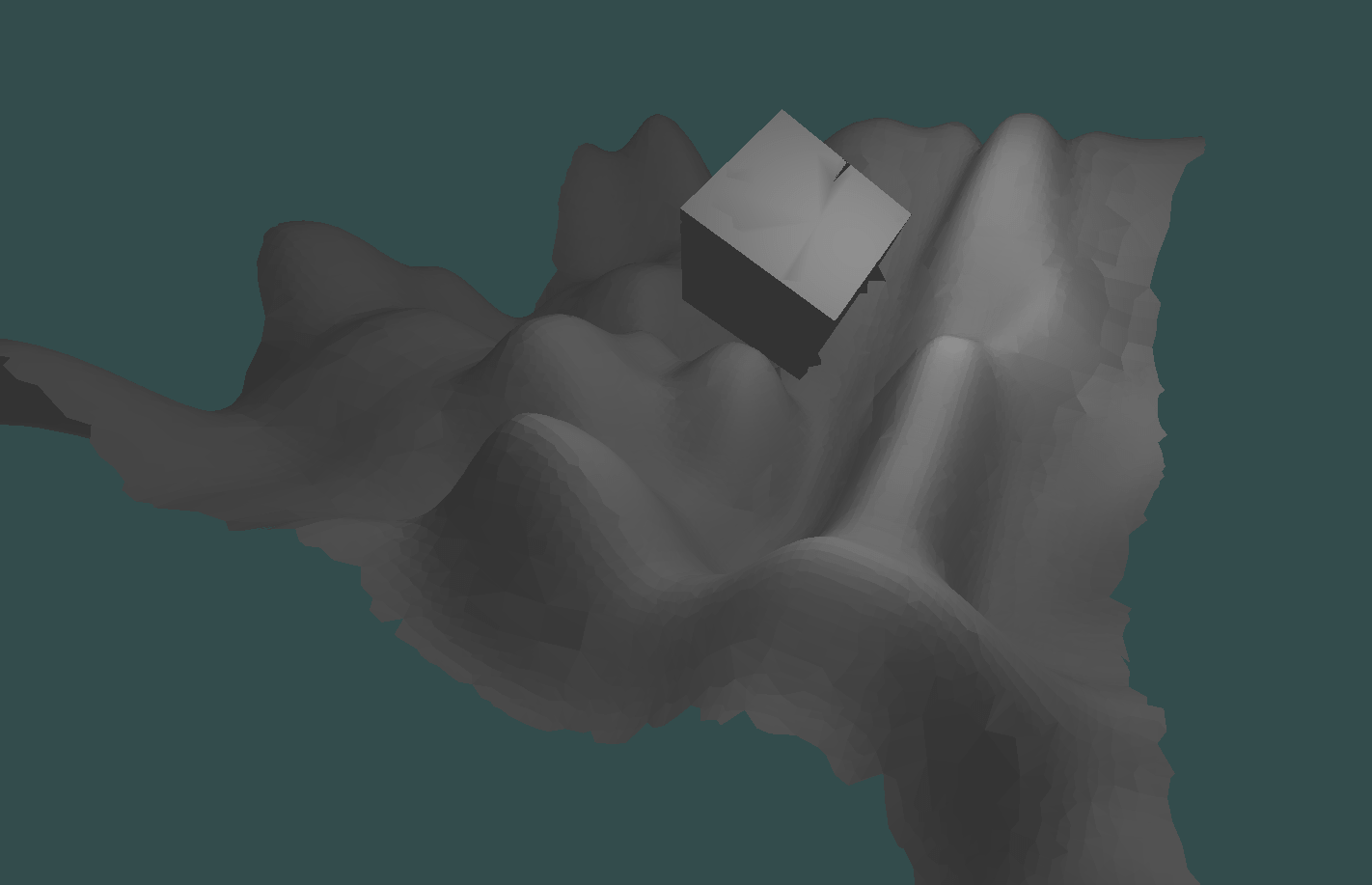
problem with overly simplified cube can be easy solved by
storing extra information in voxels: can it(voxel) be simplified or not
or better: a distance at which simplification is prefered
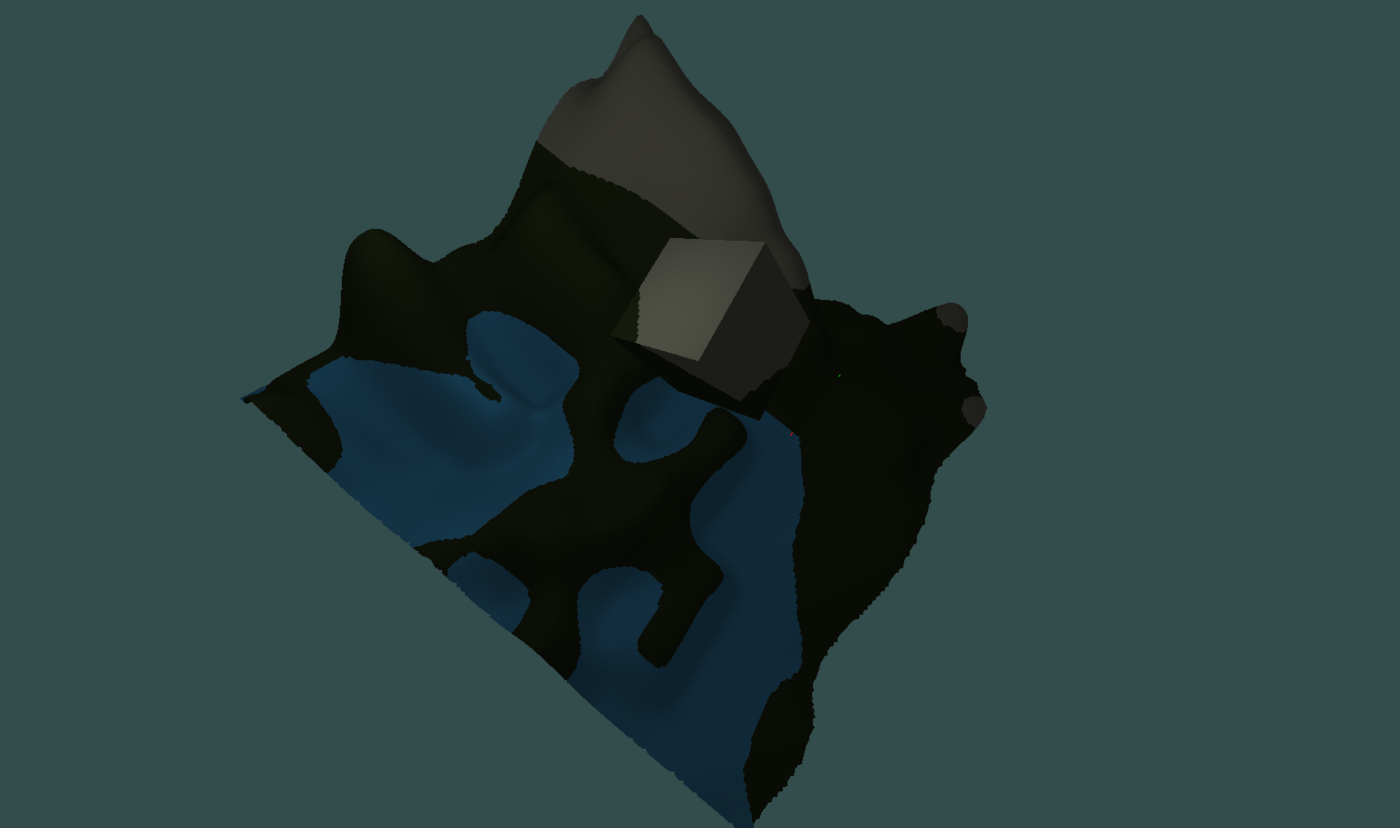
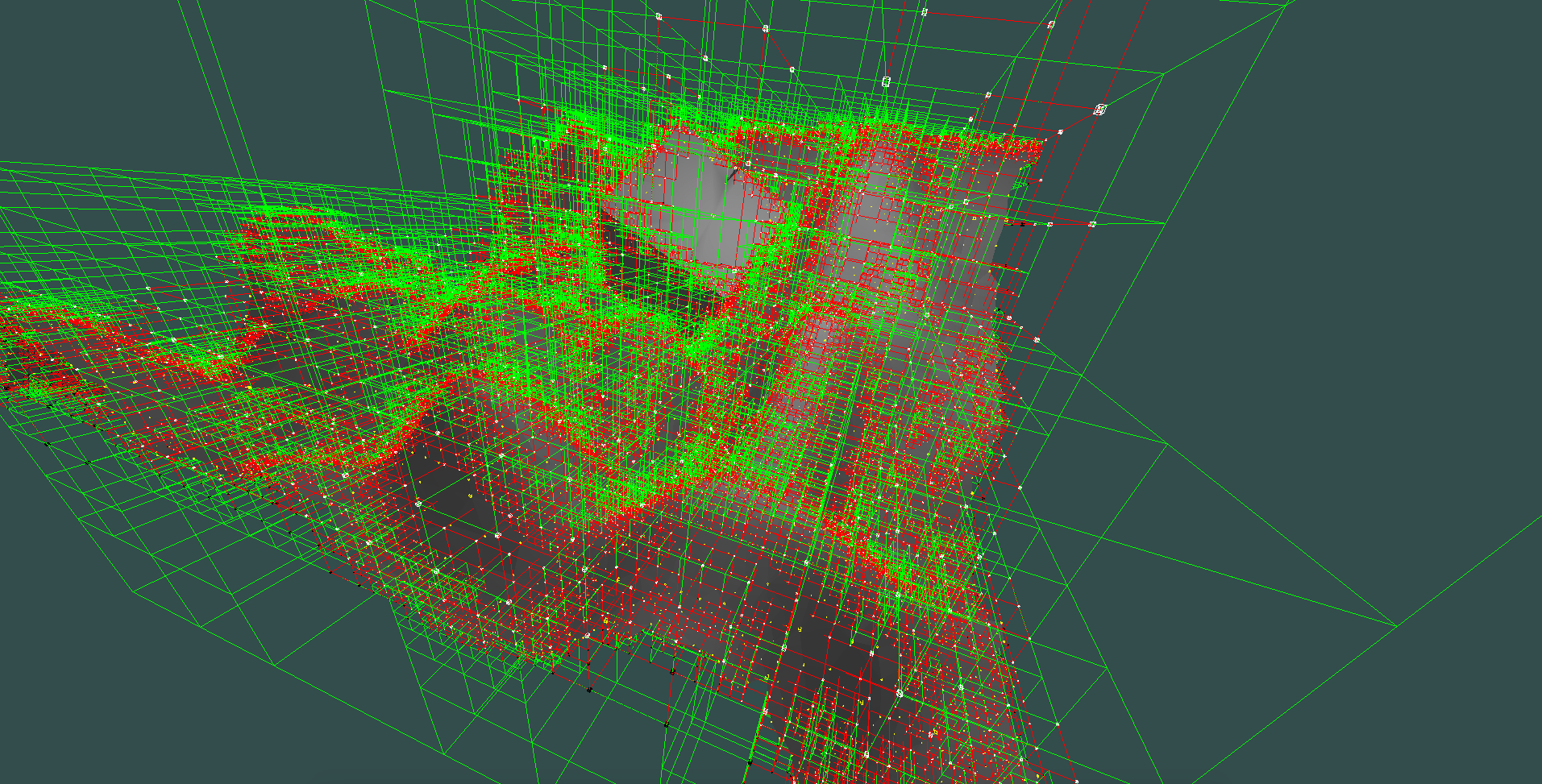
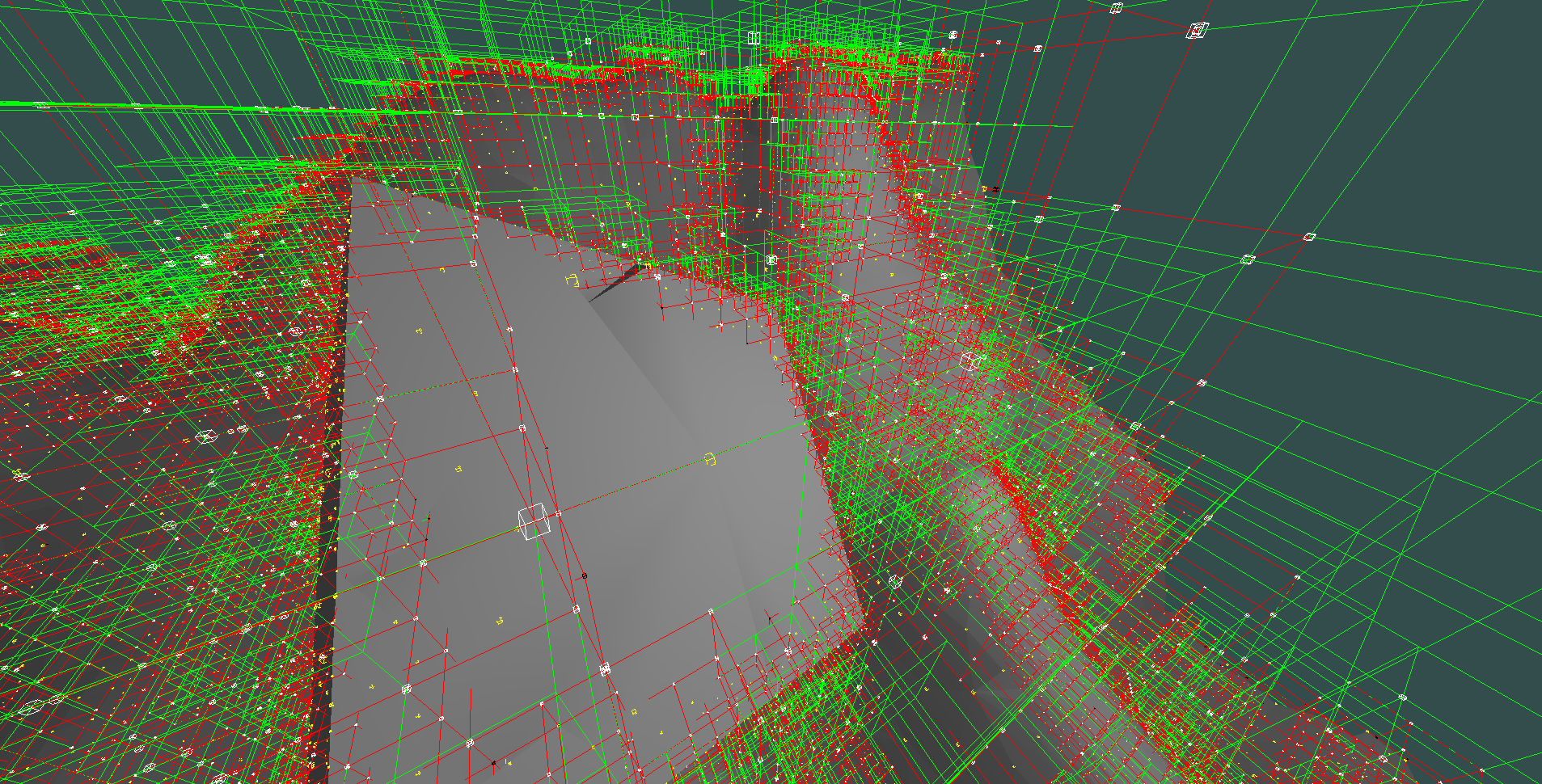
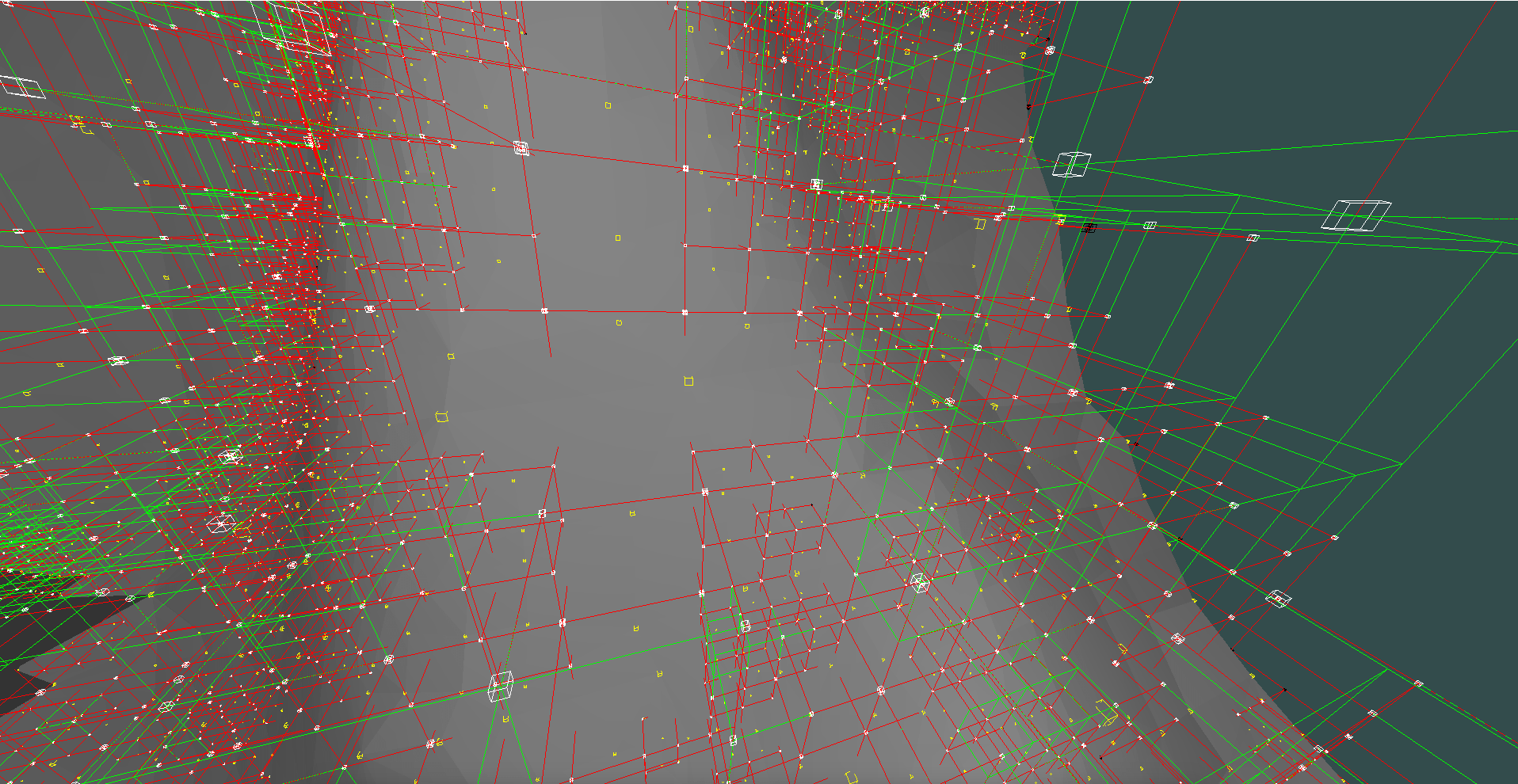
same scene but with debug info
green nodes of the octree are voxels that do not contain the surface
those are called homogeneous nodes
red nodes contain the surface and are called heterogeneous
both types of nodes mentioned are leaves of the tree
One more type is interior or internal node.
Those are not rendered, they can contain all 3 types of nodes as their child nodes (exactly 8)
little yellow boxes represent points in space that form the geometry, only those are present in the output triangulated surface
exactly one point is generated in non manifold DC per heterogeneous voxel
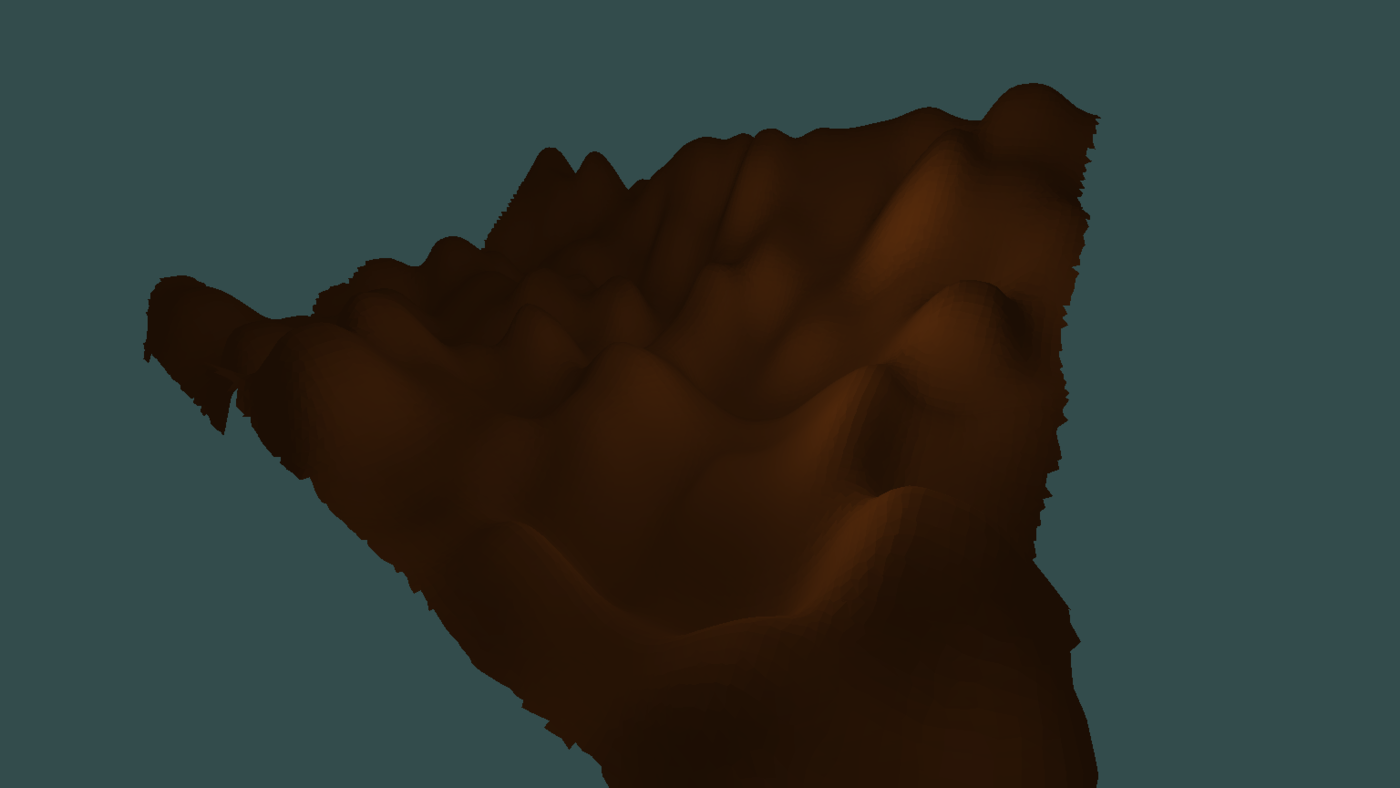
a bit more simplification showing
in uniform variant of DC all nodes would be of the same minimal size
that would require more processing power and memory but also the output would more topologically correct