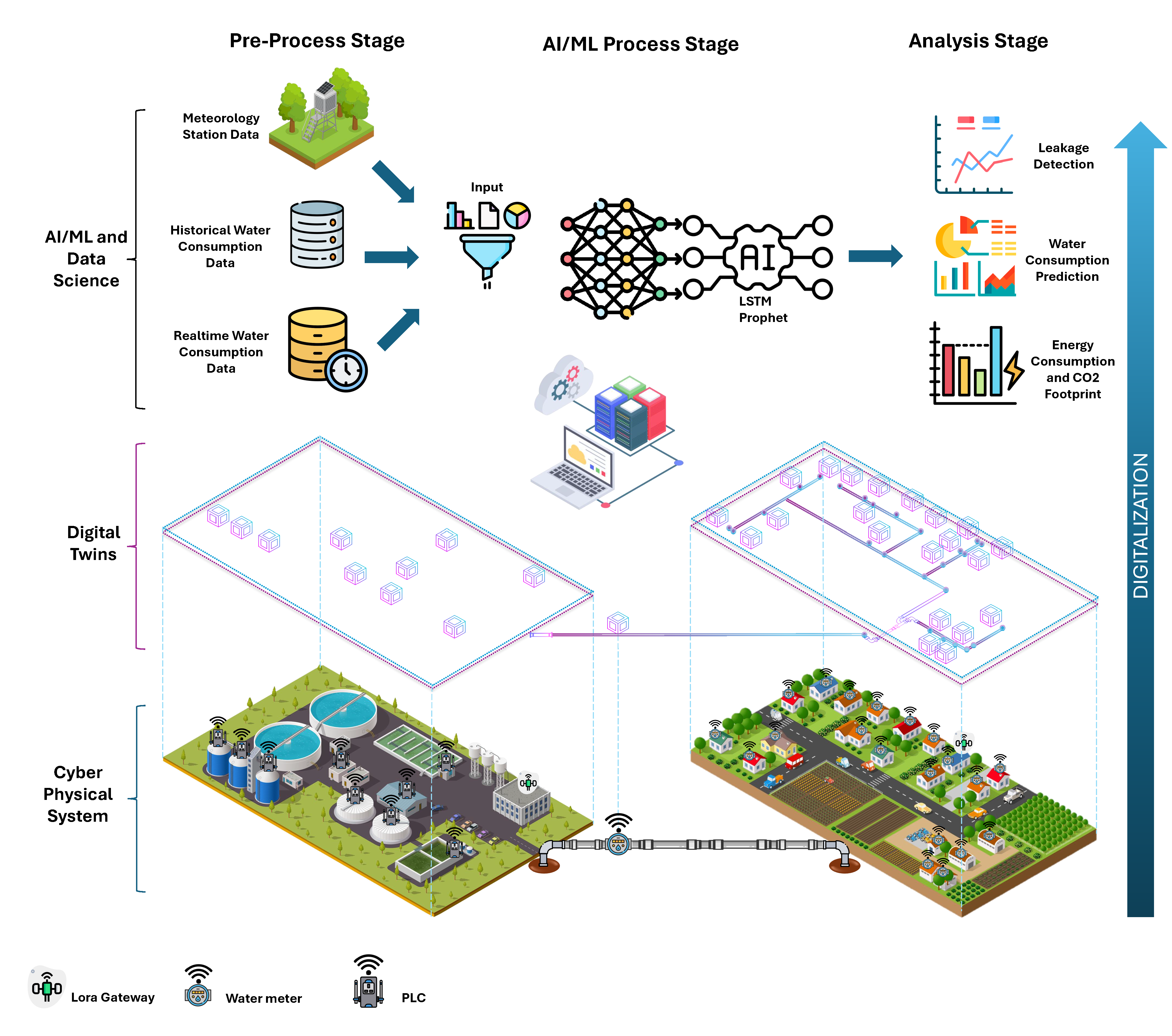
This project focuses on leveraging machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) models for water consumption forecasting, using data collected through Digital Twins implemented across various villages in Spain. By providing real-time and historical data, these Digital Twins enable more accurate predictions and optimized resource management.
Our digital twin system aggregates data from water meters, meteorological stations, and programmable logic controllers (PLCs). It analyzes this data using AI/ML models to forecast water consumption and detect possible leaks, thereby improving overall efficiency in water resource management.
Accurate water consumption forecasting is vital for effective resource management, infrastructure planning, and sustainability. This report compares various time series forecasting models for predicting water consumption over 6-month and 18-month horizons. The models include traditional statistical methods, like the Prophet model with custom seasonalities and regressors, and more advanced machine learning approaches like XGBoost, LightGBM, and LSTM neural networks.
We applied advanced feature engineering to improve predictive performance, incorporating lag features, rolling statistics, and domain-specific variables such as maximum temperature and day of the week. Both Prophet and LSTM models were optimized through hyperparameter tuning, including techniques like dropout layers, learning rate adjustments, and stacking ensemble methods.
The five top-performing models for the 6-month and 18-month forecasts were evaluated using key performance metrics, including Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE), and Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE). The following sections present the detailed results.
| No | Model | 6 M MAE | 6 M RMSE | 6 M MAPE | 18 M MAE | 18 M RMSE | 18 M MAPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 😊 | LightGBM | 5.90 | 8.25 | 19.64% | 11.77 | 18.31 | 24.98% |
| 2 😊 | LSTM Hyper. Tuning Plus | 5.96 | 9.38 | 18.64% | 12.63 | 20.66 | 25.61% |
| 3 😊 | Prophet Adv. Engineering | 6.21 | 8.75 | 20.61% | 10.12 | 17.02 | 21.43% |
| 4 😊 | Advanced Prophet | 6.24 | 8.78 | 20.77% | 11.14 | 18.02 | 22.34% |
| 5 😊 | LSTM Rolling Mean Features | 7.94 | 10.82 | 27.59% | 12.33 | 20.57 | 24.67% |
These results underscore the effectiveness of combining feature engineering, hyperparameter tuning, and advanced machine learning techniques to improve water consumption forecasting accuracy. The models also demonstrated robust performance in the 18-month forecasts, showcasing their versatility across different forecasting horizons.
| No | Model | 6 M MAE | 6 M RMSE | 6 M MAPE | 18 M MAE | 18 M RMSE | 18 M MAPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Prophet Basic | 10.37 | 13.66 | 22.45% | 19.70 | 28.68 | 22.45% |
| 2 | Prophet + Seasonality | 12.39 | 14.91 | 22.45% | 24.25 | 35.02 | 22.45% |
| 3 | Advanced Prophet | 6.24 | 8.78 | 20.77% | 11.14 | 18.02 | 22.34% |
| 4 | Prophet Adv. Engineering | 6.21 | 8.75 | 20.61% | 10.12 | 17.02 | 21.43% |
| 5 | XGBoost | 7.02 | 8.74 | 24.93% | 12.34 | 18.50 | 27.49% |
| 6 | LightGBM | 5.90 | 8.25 | 19.64% | 11.77 | 18.31 | 24.98% |
| 7 | Stacking XGBoost + LightGBM | 6.57 | 8.70 | 22.45% | 12.48 | 18.94 | 27.62% |
| 8 | LSTM Network | 7.31 | 10.74 | 22.43% | 16.03 | 22.16 | 39.95% |
| 9 | LSTM Hyperparameter Tuning | 6.51 | 9.61 | 21.34% | 12.72 | 20.61 | 26.47% |
| 10 | LSTM Hyper. Tuning Plus | 5.96 | 9.38 | 18.64% | 12.63 | 20.66 | 25.61% |
| 11 | LSTM Hyper. Tuning Changed Params | 6.52 | 9.63 | 21.38% | 13.33 | 20.60 | 29.21% |
| 12 | LSTM + GRU Hybrid | 8.18 | 10.10 | 30.10% | 14.64 | 22.32 | 34.06% |
| 13 | LSTM Rolling Mean Features | 7.94 | 10.82 | 27.59% | 12.33 | 20.57 | 24.67% |
Below is a preview of the Digital Twin system diagram:
-
Data Sources:
-
Historical Water Consumption Data: Collected from sensors and databases over time.

-
Real-time Water Consumption Data: Continuously monitored and collected daily. This data is captured every 8 hours from water meters in the village.

-
Meteorological Data: Collected from meteorological stations to improve prediction accuracy. We evaluated the relationship between different parameters and water consumption using the Pearson correlation method. Our analysis revealed that maximum temperature positively correlates with water consumption. The results of this correlation analysis are presented in the following figure.


-
-
Main Features:
- Water Consumption Prediction: AI and ML models, including LSTM and Prophet, are used for forecasting daily water usage.
- Leakage Detection: Early detection of water leakages by analyzing consumption patterns.
- Energy Consumption and CO2 Footprint: Monitoring the energy impact of water distribution and associated CO2 emissions (These parameters result from maintaining the water distribution network). For example, each operator has several tasks with a variety of time, location, priority, and other metrics, and the scheduling with preemption (Urgent tasks) is an NP-hard problem.

-
Pre-Processing and AI/ML Pipeline: The project follows a well-defined data pipeline that includes:
- Pre-processing Stage: Data cleaning, normalization, and preparation for analysis.
- Analysis Stage: Applying models like LSTM and Prophet for time series forecasting.
- Post-Processing Stage: Interpret the model outputs to provide actionable insights regarding water consumption and leakage detection.
- Data Input: Collecting historical and real-time water consumption and meteorological data.
- Pre-Processing: Cleaning and preparing the data for machine learning models.
- AI/ML Processing: Applying LSTM and Prophet models to predict future water consumption and detect anomalies such as leakages.
- Output: Predictions and analytics related to water usage, energy consumption, and environmental impact.
| No | Main Method | Algorithm Name | Differences/Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Prophet | Prophet Basic | Basic model, no additional seasonality or regressors |
| Prophet + Seasonality | Includes seasonality components (e.g., yearly or weekly) | ||
| Advanced Prophet | Includes advanced features like holidays added regressors | ||
| Prophet Adv. Engineering | Custom feature engineering (lag, rolling means, etc.) | ||
| 2 | LSTM | LSTM Basic | Vanilla LSTM, no additional tuning or feature engineering |
| LSTM Hyperparameter Tuning | LSTM with tuned hyperparameters (e.g., learning rate, units) | ||
| LSTM + GRU Hybrid | Combination of LSTM and GRU layers for better generalization | ||
| LSTM Rolling Mean Features | LSTM with rolling mean features for smoother predictions | ||
| 3 | XGBoost | XGBoost Basic | Basic XGBoost model without additional feature engineering |
| XGBoost with Feature Engineering | XGBoost with advanced feature engineering (lag, etc.) | ||
| 4 | LightGBM | LightGBM Basic | Basic LightGBM model, no feature engineering |
| LightGBM with Feature Engineering | LightGBM with engineered features (e.g., lags, moving averages) | ||
| 5 | Stacking | Stacking XGBoost + LightGBM | Ensemble of XGBoost and LightGBM, stacking the models |
- Digital Twins: Simulating the water consumption of villages in Spain, providing a virtual representation for better decision-making and forecasting.
- AI/ML Techniques: Leveraging advanced machine learning algorithms to generate accurate forecasts and detect anomalies in water usage.
-
Set up the Environment:
- Install necessary dependencies by running:
pip install -r requirements.txt
- Install necessary dependencies by running:
-
Run the Jupyter Notebook:
- The project's core is in the Jupyter notebook
Water_Consumption_Forecasting.ipynb. Open it to explore the data and model workflow:jupyter notebook Water_Consumption_Forecasting.ipynb
- The project's core is in the Jupyter notebook
- Expand the data sources to include additional villages.
- Improve the models' accuracy by incorporating more environmental and socioeconomic data.
- Integrate real-time alerts for water leakage and unusual consumption patterns.
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.