Zhongwei Wan1, Xin Wang1, Che Liu2, Samiul Alam1, Yu Zheng3, Zhongnan Qu4, Shen Yan5, Yi Zhu6, Quanlu Zhang7, Mosharaf Chowdhury8, Mi Zhang1
1The Ohio State University, 2Imperial College London, 3Michigan State University, 4Amazon AWS AI, 5Google Research, 6Boson AI, 7Microsoft Research Asia, 8University of Michigan
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in important tasks such as natural language understanding, language generation, and complex reasoning and have the potential to make a substantial impact on our society. Such capabilities, however, come with the considerable resources they demand, highlighting the strong need to develop effective techniques for addressing the efficiency challenges posed by LLMs. In this survey, we provide a systematic and comprehensive review of efficient LLMs research. We organize the literature in a taxonomy consisting of three main categories, covering distinct yet interconnected efficient LLMs topics from model-centric, data-centric, and framework-centric perspective, respectively. We hope our survey can serve as a valuable resource to help researchers and practitioners gain a systematic understanding of the research developments in efficient LLMs and inspire them to contribute to this important and exciting field. We will actively maintain this repository and incorporate new research as it emerges.
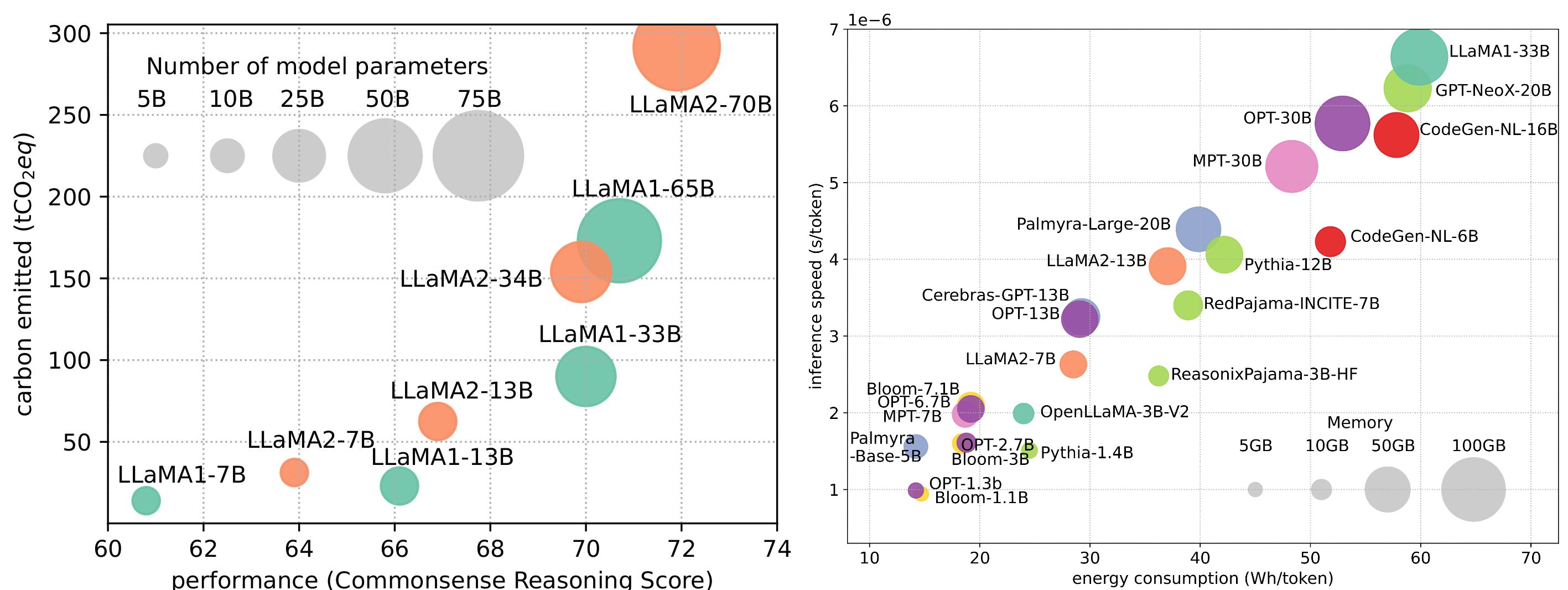
Although LLMs are leading the next wave of AI revolution, the remarkable capabilities of LLMs come at the cost of their substantial resource demands. Figure 1 (left) illustrates the relationship between model performance and the carbon emissions during training for LLaMA series. As shown, the amount of carbon emitted grows exponentially as the number of model parameter scales up. In addition to training, inference also contributes quite significantly to the operational cost of LLMs. As depicted in Figure 2 (right), more advanced LLMs exhibit higher memory usage and energy consumption during inference, presenting challenges for these models in expanding their reach to a broader customer base and diverse applications in a cost-effective way. With the rapid expansion of applications and the customer base for LLMs, the operational cost during inference in terms of energy consumption and memory usage would increase and exceed the training cost and become the dominant factor for the overall environmental impact.
- Model-Centric Methods
- Data-Centric Methods
- LLM Frameworks
- LLM.int8(): 8-bit Matrix Multiplication for Transformers at Scale, NeurlPS, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- GPTQ: Accurate Quantization for Generative Pre-trained Transformers, ICLR, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Optimal Brain Compression: A Framework for Accurate Post-Training Quantization and Pruning, NeurIPS, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- QuIP: 2-Bit Quantization of Large Language Models With Guarantees, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- AWQ: Activation-aware Weight Quantization for LLM Compression and Acceleration, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- OWQ: Lessons learned from activation outliers for weight quantization in large language models, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- SpQR: A Sparse-Quantized Representation for Near-Lossless LLM Weight Compression, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- FineQuant: Unlocking Efficiency with Fine-Grained Weight-Only Quantization for LLMs, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- ZeroQuant-FP: A Leap Forward in LLMs Post-Training W4A8 Quantization Using Floating-Point Formats, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- SmoothQuant: Accurate and Efficient Post-Training Quantization for Large Language Models, NeurlPS-ENLSP, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- OliVe: Accelerating Large Language Models via Hardware-friendly Outlier-Victim Pair Quantization, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- RPTQ: Reorder-based Post-training Quantization for Large Language Models, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Outlier Suppression+: Accurate quantization of large language models by equivalent and optimal shifting and scaling, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- QLLM: Accurate and Efficient Low-Bitwidth Quantization for Large Language Models, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Compression of Generative Pre-trained Language Models via Quantization, ACL, 2022 [Paper]
- LLM-QAT: Data-Free Quantization Aware Training for Large Language Models, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- BitNet: Scaling 1-bit Transformers for Large Language Models, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- QLoRA: Efficient Finetuning of Quantized LLMs, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Memory-Efficient Fine-Tuning of Compressed Large Language Models via sub-4-bit Integer Quantization, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- QA-LoRA: Quantization-Aware Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- LoftQ: LoRA-Fine-Tuning-Aware Quantization for Large Language Models, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- LLM-Pruner: On the Structural Pruning of Large Language Models, Github, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Sheared LLaMA: Accelerating Language Model Pre-training via Structured Pruning, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Accelerated Sparse Neural Training: A Provable and Efficient Method to Find N:M Transposable Masks, NeurIPS, 2021 [Paper] [Code]
- Pruning Meets Low-Rank Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- SparseGPT: Massive Language Models Can Be Accurately Pruned in One-Shot, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- A Simple and Effective Pruning Approach for Large Language Models, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- One-Shot Sensitivity-Aware Mixed Sparsity Pruning for Large Language Models, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- TensorGPT: Efficient Compression of the Embedding Layer in LLMs based on the Tensor-Train Decomposition, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- ZeroQuant-V2: Exploring Post-training Quantization in LLMs from Comprehensive Study to Low Rank Compensation, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- LoSparse: Structured Compression of Large Language Models based on Low-Rank and Sparse Approximation, ICML, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Baby Llama: knowledge distillation from an ensemble of teachers trained on a small dataset with no performance penalty, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Knowledge Distillation of Large Language Models Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- GKD: Generalized Knowledge Distillation for Auto-regressive Sequence Models, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Propagating Knowledge Updates to LMs Through Distillation, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Less is More: Task-aware Layer-wise Distillation for Language Model Compression, ICML, 2023 [Paper]
- Compression of Generative Pre-trained Language Models via Quantization, ACL, 2022 [Paper]
- Token-Scaled Logit Distillation for Ternary Weight Generative Language Models, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Instruction Tuning with GPT-4 Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Meta-learning via Language Model In-context Tuning, Arxiv, 2021, [Paper] [Code]
- MetaICL: Learning to Learn In Context, Arxiv, 2021, [Paper] [Code]
- In-context Learning Distillation: Transferring Few-shot Learning Ability of Pre-trained Language Models, Arxiv, 2022 [Paper]
- Explanations from Large Language Models Make Small Reasoners Better, Arxiv, 2022 [Paper]
- Lion: Adversarial Distillation of Closed-Source Large Language Model, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- DISCO: Distilling Counterfactuals with Large Language Models, Arxiv, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- Specializing Smaller Language Models towards Multi-Step Reasoning, ICML, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Distilling Step-by-Step! Outperforming Larger Language Models with Less Training Data and Smaller Model Sizes, ACL, 2023 [Paper]
- Large Language Models Are Reasoning Teachers, ACL, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- SCOTT: Self-Consistent Chain-of-Thought Distillation, ACL’23, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Symbolic Chain-of-Thought Distillation: Small Models Can Also "Think" Step-by-Step, ACL, 2023 [Paper]
- Distilling Reasoning Capabilities into Smaller Language Models, ACL’23, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Mixed precision training, Arxiv, 2017 [Paper]
- Bfloat16 Processing for Neural Networks, ARITH, 2019 [Paper]
- A study of BFLOAT16 for deep learning training, Arxiv, 2019 [Paper]
- GACT: Activation compressed training for generic network architectures, ICML, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- Mesa: A memory-saving training framework for transformers, Arxiv, 2021 [Paper] [Code]
- Efficient Training of BERT by Progressively Stacking ICML, 2019 [Paper] [Code]
- Progressively Stacking 2.0: A Multi-stage Layerwise Training Method for BERT Training Speedup, Arxiv, 2020 [Paper]
- Reusing Pretrained Models by Multi-linear Operators for Efficient Training, NeurIPS, 2023 [Paper]
- On the Transformer Growth for Progressive BERT Training, Arxiv, 2020 [Paper] [Code]
- Knowledge Inheritance for Pre-trained Language Models, NAACL, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- Staged Training for Transformer Language Models, ICML, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- bert2BERT: Towards Reusable Pretrained Language Models, Arxiv, 2021 [Paper]
- Learning to Grow Pretrained Models for Efficient Transformer Training, ICLR, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- 2x Faster Language Model Pre-training via Masked Structural Growth, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- FLM-101B: An Open LLM and How to Train It with $100 K Budget, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- On weight initialization in deep neural networks, Arxiv, 2017 [Paper] [Code]
- Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing humanlevel performance on imagenet classification, ICCV, 2015 [Paper]
- Fixup initialization: Residual learning without normalization, ICLR, 2019 [Paper]
- ZerO initialization: Initializing neural networks with only zeros and ones, TMLR, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- Batch normalization biases residual blocks towards the identity function in deep networks, NeurIPS 2020 [Paper]
- Rezero is all you need: Fast convergence at large depth, UAI, 2021 [Paper] [Code]
- Improving Transformer Optimization Through Better Initialization, ICML, 2020 [Paper] [Code]
- Deepnet: Scaling transformers to 1,000 layers, Arxiv, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- Adam: A method for stochastic optimization, ICLR, 2015 [Paper]
- Decoupled weight decay regularization, ICLR, 2019 [Paper] [Code]
- Symbolic Discovery of Optimization Algorithms, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Sophia: A Scalable Stochastic Second-order Optimizer for Language Model Pre-training, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- PyTorch Distributed: Experiences on Accelerating Data Parallel Training
- Measuring the Effects of Data Parallelism on Neural Network Training
- PipeDream: Fast and Efficient Pipeline Parallel DNN Training
- GPipe: Efficient Training of Giant Neural Networks using Pipeline Parallelism, NeurIPS, 2018
- Maximizing Parallelism in Distributed Training for Huge Neural Networks
- Efficient Large-Scale Language Model Training on GPU Clusters Using Megatron-LM, SC'21, 2021
- Tesseract: Parallelize the Tensor Parallelism Efficiently, ICPP, 2022, [Paper]
- An Efficient 2D Method for Training Super-Large Deep Learning Models, IPDPS, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- ZeRO: Memory Optimizations Toward Training Trillion Parameter Models, SC'20, 2020 [Paper]
- PyTorch FSDP: Experiences on Scaling Fully Sharded Data Parallel, Proc. VLDB Endow, 2023 [Paper]
- ZeRO-Offload: Democratizing Billion-Scale Model Training
- FlashAttention: Fast and Memory-Efficient Exact Attention with IO-Awareness, NeurIPS, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- FlashAttention-2: Faster Attention with Better Parallelism and Work Partitioning, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- LLM-Adapters: An Adapter Family for Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning of Large Language Models, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Compacter: Efficient Low-Rank Hypercomplex Adapter Layers, NeurlPS, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Few-Shot Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning is Better and Cheaper than In-Context Learning, NeurlPS, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- Meta-Adapters: Parameter Efficient Few-shot Fine-tuning through Meta-Learning, AutoML, 2022 [Paper]
- AdaMix: Mixture-of-Adaptations for Parameter-efficient Model Tuning, ACL, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- OpenDelta: A Plug-and-play Library for Parameter-efficient Adaptation of Pre-trained Models, ACL Demo, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models, ICLR, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- LoRA-FA: Memory-efficient Low-rank Adaptation for Large Language Models Fine-tuning, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- LoraHub: Efficient Cross-Task Generalization via Dynamic LoRA Composition, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- LongLoRA: Efficient Fine-tuning of Long-Context Large Language Models, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Multi-Head Adapter Routing for Cross-Task Generalization, NeurIPS, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Parameter-efficient Fine-tuning Design Spaces, ICLR, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Adaptive Budget Allocation for Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning, ICLR, 2023 [Paper]
- DyLoRA: Parameter-Efficient Tuning of Pretrained Models using Dynamic Search-Free Low Rank Adaptation, EACL, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- CPET: Effective Parameter-Efficient Tuning for Compressed Large Language Models, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Tied-Lora: Enhacing parameter efficiency of LoRA with weight tying, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Prefix-Tuning: Optimizing Continuous Prompts for Generation ACL-IJCNLP, 2021 [Paper] [Code]
- P-Tuning v2: Prompt Tuning Can Be Comparable to Fine-tuning Universally Across Scales and Tasks ACL, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- LLaMA-Adapter: Efficient Fine-tuning of Language Models with Zero-init Attention, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- The Power of Scale for Parameter-Efficient Prompt Tuning, EMNLP, 2021 [Paper]
- GPT Understands, Too, AIOPEN, 2023 [Paper]
- Multitask Pre-training of Modular Prompt for Chinese Few-Shot Learning ACL, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- PPT: Pre-trained Prompt Tuning for Few-shot Learning, ACL, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- Multitask Prompt Tuning Enables Parameter-Efficient Transfer Learning, ICLR, 2023 [Paper]
- Memory-Efficient Selective Fine-Tuning, ICML Workshop, 2023 [Paper]
- CocktailSGD: Fine-tuning Foundation Models over 500Mbps Networks, ICML, 2023 [Paper]
- Full Parameter Fine-tuning for Large Language Models with Limited Resources, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Fine-Tuning Language Models with Just Forward Passes, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Fast Inference from Transformers via Speculative Decoding, ICML, 2023 [Paper]
- Accelerating LLM Inference with Staged Speculative Decoding, ES-FOMO at ICML, 2023 [Paper]
- Accelerating Large Language Model Decoding with Speculative Sampling, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Speculative Decoding with Big Little Decoder, NeurIPS, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- SpecInfer: Accelerating Generative LLM Serving with Speculative Inference and Token Tree Verification, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Inference with Reference: Lossless Acceleration of Large Language Models, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- SkipDecode: Autoregressive Skip Decoding with Batching and Caching for Efficient LLM Inference, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- H2O: Heavy-Hitter Oracle for Efficient Generative Inference of Large Language Models, ICML Workshop, 2023 [Paper]
- Scissorhands: Exploiting the Persistence of Importance Hypothesis for LLM KV Cache Compression at Test Time, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Dynamic Context Pruning for Efficient and Interpretable Autoregressive Transformers, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Fast Transformer Decoding: One Write-Head is All You Need, Arxiv, 2019 [Paper]
- GQA: Training Generalized Multi-Query Transformer Models from Multi-Head Checkpoints, EMNLP, 2023 [Paper]
- FlexGen: High-Throughput Generative Inference of Large Language Models with a Single GPU, ICML, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Deja Vu: Contextual Sparsity for Efficient LLMs at Inference Time, ICML, 2023 [Paper]
- Efficiently Scaling Transformer Inference, MLSys, 2023 [Paper]
- EdgeMoE: Fast On-Device Inference of MoE-based Large Language Models, Arxiv, 2022 [Paper]
- S3: Increasing GPU Utilization during Generative Inference for Higher Throughput, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Efficient Memory Management for Large Language Model Serving with PagedAttention, SOSP, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- FlashAttention: Fast and Memory-Efficient Exact Attention with IO-Awareness, NeurIPS, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- FlashAttention-2: Faster Attention with Better Parallelism and Work Partitioning, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- DeepSpeed-inference: enabling efficient inference of transformer models at unprecedented scale, SC, 2022 [Paper]
- Orca: A Distributed Serving System for Transformer-Based Generative Models, OSDI, 2022 [Paper]
- Just-in-Time Dynamic-Batchin, NeurIPS Systems for ML Workshop, 2018 [Paper]
- SMDP-Based Dynamic Batching for Efficient Inference on GPU-Based Platforms, ICC, 2023 [Paper]
- Flash-Decoding for long-context inference, PyTorch, 2023 [Blog]
- FlashDecoding++: Faster Large Language Model Inference on GPUs, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Funnel-transformer: Filtering out sequential redundancy for efficient language processing, Arxiv, 2020 [Paper] [Code]
- Nyströmformer: A nyström-based algorithm for approximating self-attention, AAAI, 2021 [Paper] [Code]
- Set Transformer: A Framework for Attention-based Permutation-Invariant Neural Networks, ICML, 2019 [Paper]
- Sumformer: Universal Approximation for Efficient Transformers, ICML Workshop, 2023 [Paper]
- FLuRKA: Fast fused Low-Rank & Kernel Attention, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Scatterbrain: Unifying Sparse and Low-rank Attention, NeurlPS, 2021 [Paper] [Code]
- Linformer: Self-Attention with Linear Complexity, Arxiv, 2020 [Paper] [Code]
- Lightweight and Efficient End-to-End Speech Recognition Using Low-Rank Transformer, ICASSP, 2020 [Paper]
- Rethinking Attention with Performers, ICLR, 2021 [Paper] [Code]
- Random Feature Attention, ICLR, 2021 [Paper]
- Transformers are RNNs: Fast Autoregressive Transformers with Linear Attention, ICML, 2020 [Paper] [Code]
- Big bird: Transformers for longer sequences, NeurIPS, 2020 [Paper] [Code]
- Poolingformer: Long Document Modeling with Pooling Attention, ICML, 2021 [Paper]
- Longformer: The Long-Document Transformer, Arxiv, 2020 [Paper] [Code]
- Blockwise Self-Attention for Long Document Understanding, EMNLP, 2020 [Paper] [Code]
- Generating Long Sequences with Sparse Transformers, Arxiv, 2019 [Paper]
- Faster Causal Attention Over Large Sequences Through Sparse Flash Attention, ICML Workshop, 2023 [Paper]
- Reformer: The Efficient Transformer, ICLR, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- Sparse Sinkhorn Attention, ICML, 2020 [Paper]
- Fast Transformers with Clustered Attention, NeurIPS, 2020 [Paper] [Code]
- ClusterFormer: Neural Clustering Attention for Efficient and Effective Transformer, ACL, 2022 [Paper]
- Efficient Content-Based Sparse Attention with Routing Transformers, TACL, 2020 [Paper] [Code]
- A3: Accelerating Attention Mechanisms in Neural Networks with Approximation, HPCA, 2020 [Paper]
- Efficient Memory Management for Large Language Model Serving with PagedAttention, SOSP, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- FlashAttention: Fast and Memory-Efficient Exact Attention with IO-Awareness, NeurIPS, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- FlashAttention-2: Faster Attention with Better Parallelism and Work Partitioning, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Fast Transformer Decoding: One Write-Head is All You Need, Arxiv, 2019 [Paper]
- GQA: Training Generalized Multi-Query Transformer Models from Multi-Head Checkpoints, EMNLP, 2023 [Paper]
- Generating Long Sequences with Sparse Transformers, Arxiv, 2019 [Paper]
- FlashAttention: Fast and Memory-Efficient Exact Attention with IO-Awareness, NeurIPS, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- FlashAttention-2: Faster Attention with Better Parallelism and Work Partitioning, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Accelerated Inference for Large Transformer Models Using NVIDIA Triton Inference Server, Nvidia Blog, 2022 [Blog]
- GShard: Scaling Giant Models with Conditional Computation and Automatic Sharding, Arxiv, 2020 [Paper]
- Switch Transformers: Scaling to Trillion Parameter Models with Simple and Efficient Sparsity, JMLR, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- Efficient Large Scale Language Modeling with Mixtures of Experts, EMNLP, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- BASE Layers: Simplifying Training of Large, Sparse Models, ICML, 2021 [Paper] [Code]
- PanGu-Σ: Towards Trillion Parameter Language Model with Sparse Heterogeneous Computing, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Mixture-of-Experts with Expert Choice Routing, NeurIPS, 2022 [Paper]
- StableMoE: Stable Routing Strategy for Mixture of Experts, Arxiv, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- On the Representation Collapse of Sparse Mixture of Experts, NeurIPS, 2022 [Paper]
- TA-MoE: Topology-Aware Large Scale Mixture-of-Expert Training, NeurIPS, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- Lifelong Language Pretraining with Distribution-Specialized Experts, ICML, 2023 [Paper]
- Mixture-of-Experts Meets Instruction Tuning:A Winning Combination for Large Language Models, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- FastMoE: A Fast Mixture-of-Expert Training System, PPoPP, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- FasterMoE: modeling and optimizing training of large-scale dynamic pre-trained models, PPoPP, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- DeepSpeed-MoE: Advancing Mixture-of-Experts Inference and Training to Power Next-Generation AI Scale, ICML, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- Tutel: Adaptive mixture-of-experts at scale, MLSys, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- SmartMoE: Efficiently Training Sparsely-Activated Models through Combining Offline and Online Parallelization, USENIX ATC, 2023 [Paper]
- Train Short, Test Long: Attention with Linear Biases Enables Input Length Extrapolation, ICLR, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- A Length-Extrapolatable Transformer, ACL, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Extending Context Window of Large Language Models via Positional Interpolation, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- NTK interpolation, [Reddit post]
- YaRN: Efficient Context Window Extension of Large Language Models, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Functional Interpolation for Relative Positions Improves Long Context Transformers, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- The EOS Decision and Length Extrapolation, EMNLP, 2020 [Paper] [Code]
- Exploring Length Generalization in Large Language Models, NeurIPS, 2022 [Paper]
- ∞-former: Infinite Memory Transformer, ACL, 2022 [Paper]
- Transformer-XL: Attentive Language Models Beyond a Fixed-Length Context, ACL, 2019 [Paper] [Code]
- Memformer: A Memory-Augmented Transformer for Sequence Modeling, Arxiv, 2020 [Paper] [Code]
- Recurrent Memory Transformer, NeurIPS, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- Block-Recurrent Transformers, NeurIPS, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- Efficient Streaming Language Models with Attention Sinks, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Parallel Context Windows for Large Language Models, ACL, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Structured Prompting: Scaling In-Context Learning to 1,000 Examples, Arxiv, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- Naive Bayes-based Context Extension, Github repository, 2023 [Code]
- LongNet: Scaling Transformers to 1,000,000,000 Tokens, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Efficient Long-Text Understanding with Short-Text Models, TACL, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Memorizing Transformers, ICLR, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- Landmark Attention: Random-Access Infinite Context Length for Transformers, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Augmenting Language Models with Long-Term Memory, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Unlimiformer: Long-Range Transformers with Unlimited Length Input, NeurIPS, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Focused Transformer: Contrastive Training for Context Scaling, NeurIPS, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Retrieval meets Long Context Large Language Models, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Efficiently Modeling Long Sequences with Structured State Spaces, ICLR, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- Diagonal State Spaces are as Effective as Structured State Spaces, NeurIPS, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- Hungry Hungry Hippos: Towards Language Modeling with State Space Models, ICLR 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Long Range Language Modeling via Gated State Spaces, ICLR, 2023 [Paper]
- Block-State Transformers, NeurIPS, 2023 [Paper]
- RWKV: Reinventing RNNs for the Transformer Era, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Hyena Hierarchy: Towards Larger Convolutional Language Models, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- MEGABYTE: Predicting Million-byte Sequences with Multiscale Transformers, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Data Selection Strategies for Multi-Domain Sentiment Analysis, Arxiv, 2017 [Paper]
- Data Selection with Cluster-Based Language Difference Models and Cynical Selection, IWSLT, 2017 [Paper]
- Span Selection Pre-training for Question Answering, ACL, 2020 [Paper] [Code]
- NLP From Scratch Without Large-Scale Pretraining: A Simple and Efficient Framework, ICML, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- Data Selection for Language Models via Importance Resampling, NeurIPS, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Instruction Mining: When Data Mining Meets Large Language Model Finetuning, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Data-Efficient Finetuning Using Cross-Task Nearest Neighbors, ACL, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Data Selection for Fine-tuning Large Language Models Using Transferred Shapley Values, ACL SRW, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Maybe Only 0.5% Data is Needed: A Preliminary Exploration of Low Training Data Instruction Tuning, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- AlpaGasus: Training A Better Alpaca with Fewer Data, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- LIMA: Less Is More for Alignment, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Self-Adaptive In-Context Learning: An Information Compression Perspective for In-Context Example Selection and Ordering, ACL, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- What Makes Good In-Context Examples for GPT-3? DeeLIO, 2022 [Paper]
- Selective Annotation Makes Language Models Better Few-Shot Learners, ICLR, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Learning To Retrieve Prompts for In-Context Learning, NAACL-HLT, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- Unified Demonstration Retriever for In-Context Learning, ACL, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Fantastically Ordered Prompts and Where to Find Them: Overcoming Few-Shot Prompt Order Sensitivity, ACL, 2022 [Paper]
- What Makes Good In-Context Examples for GPT-3? DeeLIO, 2022 [Paper]
- Instruction Induction: From Few Examples to Natural Language Task Descriptions, ACL, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Large Language Models Are Human-Level Prompt Engineers, ICLR, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Self-Instruct: Aligning Language Models with Self-Generated Instructions, Arxiv, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- Large Language Models as Optimizers, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Emergent Abilities of Large Language Models, TMLR, 2022 [Paper]
- Automatic Chain of Thought Prompting in Large Language Models, ICLR, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Measuring and Narrowing the Compositionality Gap in Language Models, EMNLP, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- ReAct: Synergizing Reasoning and Acting in Language Models, ICLR, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Least-to-Most Prompting Enables Complex Reasoning in Large Language Models, ICLR, 2023 [Paper]
- Graph of Thoughts: Solving Elaborate Problems with Large Language Models, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Tree of Thoughts: Deliberate Problem Solving with Large Language Models, NeurIPS, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Self-Consistency Improves Chain of Thought Reasoning in Language Models, ICLR, 2023 [Paper]
- Graph of Thoughts: Solving Elaborate Problems with Large Language Models, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Contrastive Chain-of-Thought Prompting, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Everything of Thoughts: Defying the Law of Penrose Triangle for Thought Generation, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Learning to Compress Prompts with Gist Tokens, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Adapting Language Models to Compress Contexts, EMNLP, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- In-context Autoencoder for Context Compression in a Large Language Model, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- LongLLMLingua: Accelerating and Enhancing LLMs in Long Context Scenarios via Prompt Compression, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Discrete Prompt Compression with Reinforcement Learning, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Nugget 2D: Dynamic Contextual Compression for Scaling Decoder-only Language Models, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- Self-Instruct: Aligning Language Model with Self Generated Instructions, ACL, 2023 [paper] [Code]
- Tuning Language Models as Training Data Generators for Augmentation-Enhanced Few-Shot Learning, ICML, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- Large Language Models Are Human-Level Prompt Engineers, ICLR, 2023 [Paper] [Code]
- TempLM: Distilling Language Models into Template-Based Generators, Arxiv, 2022 [Paper] [Code]
- PromptGen: Automatically Generate Prompts using Generative Models, Findings-NAACL, 2022 [Paper]
- AutoPrompt: Eliciting Knowledge from Language Models with Automatically Generated Prompts, EMNLP, 2020 [Paper] [Code]
- TeGit: Generating High-Quality Instruction-Tuning Data with Text-Grounded Task Design, Arxiv, 2023 [Paper]
- DeepSpeed [Code]
- Megatron [Code]
- Alpa [Code]
- ColossalAI [Code]
- FairScale [Code]
- Pax [Code]
- Composer [Code]
- vLLM [Code]
- Parallelformers [Code]
- OpenLLM [Code]
- Ray-LLM [Code]
- MLC-LLM [Code]
- Sax [Code]
- Mosec [Code]
- LLM-Foundry [Code]
If you find this useful for your work, please consider citing:
@misc{wan2023efficient,
title={Efficient Large Language Models: A Survey},
author={Zhongwei Wan and Xin Wang and Che Liu and Samiul Alam and Yu Zheng and Zhongnan Qu and Shen Yan and Yi Zhu and Quanlu Zhang and Mosharaf Chowdhury and Mi Zhang},
year={2023},
eprint={2312.03863},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL}
}