In this project, you'll classify images from the CIFAR-10 dataset. The dataset consists of airplanes, dogs, cats, and other objects. You'll preprocess the images, then train a convolutional neural network on all the samples. The images need to be normalized and the labels need to be one-hot encoded. You'll get to apply what you learned and build a convolutional, max pooling, dropout, and fully connected layers. At the end, you'll get to see your neural network's predictions on the sample images.
Run the following cell to download the CIFAR-10 dataset for python.
"""
DON'T MODIFY ANYTHING IN THIS CELL THAT IS BELOW THIS LINE
"""
from urllib.request import urlretrieve
from os.path import isfile, isdir
from tqdm import tqdm
import problem_unittests as tests
import tarfile
cifar10_dataset_folder_path = 'cifar-10-batches-py'
# Use Floyd's cifar-10 dataset if present
floyd_cifar10_location = '/input/cifar-10/python.tar.gz'
if isfile(floyd_cifar10_location):
tar_gz_path = floyd_cifar10_location
else:
tar_gz_path = 'cifar-10-python.tar.gz'
class DLProgress(tqdm):
last_block = 0
def hook(self, block_num=1, block_size=1, total_size=None):
self.total = total_size
self.update((block_num - self.last_block) * block_size)
self.last_block = block_num
if not isfile(tar_gz_path):
with DLProgress(unit='B', unit_scale=True, miniters=1, desc='CIFAR-10 Dataset') as pbar:
urlretrieve(
'https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar-10-python.tar.gz',
tar_gz_path,
pbar.hook)
if not isdir(cifar10_dataset_folder_path):
with tarfile.open(tar_gz_path) as tar:
tar.extractall()
tar.close()
tests.test_folder_path(cifar10_dataset_folder_path)All files found!
The dataset is broken into batches to prevent your machine from running out of memory. The CIFAR-10 dataset consists of 5 batches, named data_batch_1, data_batch_2, etc.. Each batch contains the labels and images that are one of the following:
- airplane
- automobile
- bird
- cat
- deer
- dog
- frog
- horse
- ship
- truck
Understanding a dataset is part of making predictions on the data. Play around with the code cell below by changing the batch_id and sample_id. The batch_id is the id for a batch (1-5). The sample_id is the id for a image and label pair in the batch.
Ask yourself "What are all possible labels?", "What is the range of values for the image data?", "Are the labels in order or random?". Answers to questions like these will help you preprocess the data and end up with better predictions.
%matplotlib inline
%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'retina'
import helper
import numpy as np
# Explore the dataset
batch_id = 5
sample_id = 15
helper.display_stats(cifar10_dataset_folder_path, batch_id, sample_id)Stats of batch 5:
Samples: 10000
Label Counts: {0: 1014, 1: 1014, 2: 952, 3: 1016, 4: 997, 5: 1025, 6: 980, 7: 977, 8: 1003, 9: 1022}
First 20 Labels: [1, 8, 5, 1, 5, 7, 4, 3, 8, 2, 7, 2, 0, 1, 5, 9, 6, 2, 0, 8]
Example of Image 15:
Image - Min Value: 8 Max Value: 236
Image - Shape: (32, 32, 3)
Label - Label Id: 9 Name: truck
In the cell below, implement the normalize function to take in image data, x, and return it as a normalized Numpy array. The values should be in the range of 0 to 1, inclusive. The return object should be the same shape as x.
def normalize(x):
"""
Normalize a list of sample image data in the range of 0 to 1
: x: List of image data. The image shape is (32, 32, 3)
: return: Numpy array of normalize data
"""
# TODO: Implement Function
res = (x - 0)/255
return res
"""
DON'T MODIFY ANYTHING IN THIS CELL THAT IS BELOW THIS LINE
"""
tests.test_normalize(normalize)Tests Passed
Just like the previous code cell, you'll be implementing a function for preprocessing. This time, you'll implement the one_hot_encode function. The input, x, are a list of labels. Implement the function to return the list of labels as One-Hot encoded Numpy array. The possible values for labels are 0 to 9. The one-hot encoding function should return the same encoding for each value between each call to one_hot_encode. Make sure to save the map of encodings outside the function.
Hint: Don't reinvent the wheel.
def one_hot_encode(x):
"""
One hot encode a list of sample labels. Return a one-hot encoded vector for each label.
: x: List of sample Labels
: return: Numpy array of one-hot encoded labels
"""
# TODO: Implement Function
class_list = np.array([0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9])
return np.array([class_list==i for i in x])
"""
DON'T MODIFY ANYTHING IN THIS CELL THAT IS BELOW THIS LINE
"""
tests.test_one_hot_encode(one_hot_encode)Tests Passed
As you saw from exploring the data above, the order of the samples are randomized. It doesn't hurt to randomize it again, but you don't need to for this dataset.
Running the code cell below will preprocess all the CIFAR-10 data and save it to file. The code below also uses 10% of the training data for validation.
"""
DON'T MODIFY ANYTHING IN THIS CELL
"""
# Preprocess Training, Validation, and Testing Data
helper.preprocess_and_save_data(cifar10_dataset_folder_path, normalize, one_hot_encode)This is your first checkpoint. If you ever decide to come back to this notebook or have to restart the notebook, you can start from here. The preprocessed data has been saved to disk.
"""
DON'T MODIFY ANYTHING IN THIS CELL
"""
import pickle
import problem_unittests as tests
import helper
# Load the Preprocessed Validation data
valid_features, valid_labels = pickle.load(open('preprocess_validation.p', mode='rb'))For the neural network, you'll build each layer into a function. Most of the code you've seen has been outside of functions. To test your code more thoroughly, we require that you put each layer in a function. This allows us to give you better feedback and test for simple mistakes using our unittests before you submit your project.
Note: If you're finding it hard to dedicate enough time for this course each week, we've provided a small shortcut to this part of the project. In the next couple of problems, you'll have the option to use classes from the TensorFlow Layers or TensorFlow Layers (contrib) packages to build each layer, except the layers you build in the "Convolutional and Max Pooling Layer" section. TF Layers is similar to Keras's and TFLearn's abstraction to layers, so it's easy to pickup.
However, if you would like to get the most out of this course, try to solve all the problems without using anything from the TF Layers packages. You can still use classes from other packages that happen to have the same name as ones you find in TF Layers! For example, instead of using the TF Layers version of the
conv2dclass, tf.layers.conv2d, you would want to use the TF Neural Network version ofconv2d, tf.nn.conv2d.
Let's begin!
The neural network needs to read the image data, one-hot encoded labels, and dropout keep probability. Implement the following functions
- Implement
neural_net_image_input - Return a TF Placeholder
- Set the shape using
image_shapewith batch size set toNone. - Name the TensorFlow placeholder "x" using the TensorFlow
nameparameter in the TF Placeholder. - Implement
neural_net_label_input - Return a TF Placeholder
- Set the shape using
n_classeswith batch size set toNone. - Name the TensorFlow placeholder "y" using the TensorFlow
nameparameter in the TF Placeholder. - Implement
neural_net_keep_prob_input - Return a TF Placeholder for dropout keep probability.
- Name the TensorFlow placeholder "keep_prob" using the TensorFlow
nameparameter in the TF Placeholder.
These names will be used at the end of the project to load your saved model.
Note: None for shapes in TensorFlow allow for a dynamic size.
import tensorflow as tf
def neural_net_image_input(image_shape):
"""
Return a Tensor for a batch of image input
: image_shape: Shape of the images
: return: Tensor for image input.
"""
# TODO: Implement Function
return tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, image_shape[0], image_shape[1], image_shape[2]], name='x')
def neural_net_label_input(n_classes):
"""
Return a Tensor for a batch of label input
: n_classes: Number of classes
: return: Tensor for label input.
"""
# TODO: Implement Function
return tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_classes], name='y')
def neural_net_keep_prob_input():
"""
Return a Tensor for keep probability
: return: Tensor for keep probability.
"""
# TODO: Implement Function
return tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name='keep_prob')
"""
DON'T MODIFY ANYTHING IN THIS CELL THAT IS BELOW THIS LINE
"""
tf.reset_default_graph()
tests.test_nn_image_inputs(neural_net_image_input)
tests.test_nn_label_inputs(neural_net_label_input)
tests.test_nn_keep_prob_inputs(neural_net_keep_prob_input)Image Input Tests Passed.
Label Input Tests Passed.
Keep Prob Tests Passed.
Convolution layers have a lot of success with images. For this code cell, you should implement the function conv2d_maxpool to apply convolution then max pooling:
- Create the weight and bias using
conv_ksize,conv_num_outputsand the shape ofx_tensor. - Apply a convolution to
x_tensorusing weight andconv_strides. - We recommend you use same padding, but you're welcome to use any padding.
- Add bias
- Add a nonlinear activation to the convolution.
- Apply Max Pooling using
pool_ksizeandpool_strides. - We recommend you use same padding, but you're welcome to use any padding.
Note: You can't use TensorFlow Layers or TensorFlow Layers (contrib) for this layer, but you can still use TensorFlow's Neural Network package. You may still use the shortcut option for all the other layers.
def conv2d_maxpool(x_tensor, conv_num_outputs, conv_ksize, conv_strides, pool_ksize, pool_strides):
"""
Apply convolution then max pooling to x_tensor
:param x_tensor: TensorFlow Tensor
:param conv_num_outputs: Number of outputs for the convolutional layer
:param conv_ksize: kernal size 2-D Tuple for the convolutional layer
:param conv_strides: Stride 2-D Tuple for convolution
:param pool_ksize: kernal size 2-D Tuple for pool
:param pool_strides: Stride 2-D Tuple for pool
: return: A tensor that represents convolution and max pooling of x_tensor
"""
# TODO: Implement Function
#conv_ksize = [1, conv_ksize[0], conv_ksize[1], 1] #######BUG!!!! Misktook conv_ksize as con_strides
#conv net
conv_num_inputs = x_tensor.get_shape().as_list()[3] #tf.to_int32(x_tensor.shape[3], name='ToInt32')
conv_weight = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([conv_ksize[0],conv_ksize[1],conv_num_inputs,conv_num_outputs], stddev=0.1))
conv_bias = tf.Variable(tf.zeros(conv_num_outputs))
strides = [1,conv_strides[0],conv_strides[1],1]
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(x_tensor,conv_weight, strides=strides,padding='SAME') + conv_bias
conv = tf.nn.relu(conv)
#max pooling
pool_ksize = [1,pool_ksize[0],pool_ksize[1],1]
pool_strides = [1,pool_strides[0],pool_strides[1],1]
max_pooling_conv = tf.nn.max_pool(conv,ksize=pool_ksize,strides=pool_strides,padding='SAME')
return max_pooling_conv
"""
DON'T MODIFY ANYTHING IN THIS CELL THAT IS BELOW THIS LINE
"""
tests.test_con_pool(conv2d_maxpool)Tests Passed
Implement the flatten function to change the dimension of x_tensor from a 4-D tensor to a 2-D tensor. The output should be the shape (Batch Size, Flattened Image Size). Shortcut option: you can use classes from the TensorFlow Layers or TensorFlow Layers (contrib) packages for this layer. For more of a challenge, only use other TensorFlow packages.
def flatten(x_tensor):
"""
Flatten x_tensor to (Batch Size, Flattened Image Size)
: x_tensor: A tensor of size (Batch Size, ...), where ... are the image dimensions.
: return: A tensor of size (Batch Size, Flattened Image Size).
"""
# TODO: Implement Function
return tf.contrib.layers.flatten(x_tensor)
"""
DON'T MODIFY ANYTHING IN THIS CELL THAT IS BELOW THIS LINE
"""
tests.test_flatten(flatten)Tests Passed
Implement the fully_conn function to apply a fully connected layer to x_tensor with the shape (Batch Size, num_outputs). Shortcut option: you can use classes from the TensorFlow Layers or TensorFlow Layers (contrib) packages for this layer. For more of a challenge, only use other TensorFlow packages.
def fully_conn(x_tensor, num_outputs):
"""
Apply a fully connected layer to x_tensor using weight and bias
: x_tensor: A 2-D tensor where the first dimension is batch size.
: num_outputs: The number of output that the new tensor should be.
: return: A 2-D tensor where the second dimension is num_outputs.
"""
# TODO: Implement Function
return tf.contrib.layers.fully_connected(x_tensor, num_outputs)
"""
DON'T MODIFY ANYTHING IN THIS CELL THAT IS BELOW THIS LINE
"""
tests.test_fully_conn(fully_conn)Tests Passed
Implement the output function to apply a fully connected layer to x_tensor with the shape (Batch Size, num_outputs). Shortcut option: you can use classes from the TensorFlow Layers or TensorFlow Layers (contrib) packages for this layer. For more of a challenge, only use other TensorFlow packages.
Note: Activation, softmax, or cross entropy should not be applied to this.
def output(x_tensor, num_outputs):
"""
Apply a output layer to x_tensor using weight and bias
: x_tensor: A 2-D tensor where the first dimension is batch size.
: num_outputs: The number of output that the new tensor should be.
: return: A 2-D tensor where the second dimension is num_outputs.
"""
# TODO: Implement Function
return tf.contrib.layers.fully_connected(x_tensor, num_outputs, activation_fn=None)
"""
DON'T MODIFY ANYTHING IN THIS CELL THAT IS BELOW THIS LINE
"""
tests.test_output(output)Tests Passed
Implement the function conv_net to create a convolutional neural network model. The function takes in a batch of images, x, and outputs logits. Use the layers you created above to create this model:
- Apply 1, 2, or 3 Convolution and Max Pool layers
- Apply a Flatten Layer
- Apply 1, 2, or 3 Fully Connected Layers
- Apply an Output Layer
- Return the output
- Apply TensorFlow's Dropout to one or more layers in the model using
keep_prob.
def conv_net(x, keep_prob):
"""
Create a convolutional neural network model
: x: Placeholder tensor that holds image data.
: keep_prob: Placeholder tensor that hold dropout keep probability.
: return: Tensor that represents logits
"""
# TODO: Apply 1, 2, or 3 Convolution and Max Pool layers
# Play around with different number of outputs, kernel size and stride
# Function Definition from Above:
# conv2d_maxpool(x_tensor, conv_num_outputs, conv_ksize, conv_strides, pool_ksize, pool_strides)
print(x)
conv = conv2d_maxpool(x,
conv_num_outputs=64,
conv_ksize=[5,5],
conv_strides=[1,1],
pool_ksize=[4,4],
pool_strides=[2,2])
print(conv)
conv = conv2d_maxpool(conv,
conv_num_outputs=64,
conv_ksize=[3,3],
conv_strides=[1,1],
pool_ksize=[2,2],
pool_strides=[2,2])
print(conv)
conv = conv2d_maxpool(conv,
conv_num_outputs=64,
conv_ksize=[2,2],
conv_strides=[1,1],
pool_ksize=[3,3],
pool_strides=[2,2])
print(conv)
#con kernel size 设为1比较好?
# Apply a Flatten Layer
flat_conv = flatten(conv)
print(flat_conv)
# 2 Fully-Connected Layers.
#fc = fully_conn(flattened_conv, 512)
fc = fully_conn(flat_conv, 128)
print(fc)
# Dropout layer.
fc = tf.nn.dropout(fc, keep_prob)
# Output Layer.
return output(fc, 10)
"""
DON'T MODIFY ANYTHING IN THIS CELL THAT IS BELOW THIS LINE
"""
##############################
## Build the Neural Network ##
##############################
# Remove previous weights, bias, inputs, etc..
tf.reset_default_graph()
# Inputs
x = neural_net_image_input((32, 32, 3))
y = neural_net_label_input(10)
keep_prob = neural_net_keep_prob_input()
# Model
logits = conv_net(x, keep_prob)
# Name logits Tensor, so that is can be loaded from disk after training
logits = tf.identity(logits, name='logits')
# Loss and Optimizer
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=y))
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer().minimize(cost)
# Accuracy
correct_pred = tf.equal(tf.argmax(logits, 1), tf.argmax(y, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred, tf.float32), name='accuracy')
tests.test_conv_net(conv_net)Tensor("x:0", shape=(?, 32, 32, 3), dtype=float32)
Tensor("MaxPool:0", shape=(?, 16, 16, 64), dtype=float32)
Tensor("MaxPool_1:0", shape=(?, 8, 8, 64), dtype=float32)
Tensor("MaxPool_2:0", shape=(?, 4, 4, 64), dtype=float32)
Tensor("Flatten/Reshape:0", shape=(?, 1024), dtype=float32)
Tensor("fully_connected/Relu:0", shape=(?, 128), dtype=float32)
Tensor("Placeholder:0", shape=(?, 32, 32, 3), dtype=float32)
Tensor("MaxPool_3:0", shape=(?, 16, 16, 64), dtype=float32)
Tensor("MaxPool_4:0", shape=(?, 8, 8, 64), dtype=float32)
Tensor("MaxPool_5:0", shape=(?, 4, 4, 64), dtype=float32)
Tensor("Flatten_1/Reshape:0", shape=(?, 1024), dtype=float32)
Tensor("fully_connected_2/Relu:0", shape=(?, 128), dtype=float32)
Neural Network Built!
Implement the function train_neural_network to do a single optimization. The optimization should use optimizer to optimize in session with a feed_dict of the following:
xfor image inputyfor labelskeep_probfor keep probability for dropout
This function will be called for each batch, so tf.global_variables_initializer() has already been called.
Note: Nothing needs to be returned. This function is only optimizing the neural network.
def train_neural_network(session, optimizer, keep_probability, feature_batch, label_batch):
"""
Optimize the session on a batch of images and labels
: session: Current TensorFlow session
: optimizer: TensorFlow optimizer function
: keep_probability: keep probability
: feature_batch: Batch of Numpy image data
: label_batch: Batch of Numpy label data
"""
# TODO: Implement Function
session.run(optimizer, feed_dict={x: feature_batch, #(None,32,32,3)
y: label_batch,
keep_prob: keep_probability
})
#print('accuracy:',accr)
"""
DON'T MODIFY ANYTHING IN THIS CELL THAT IS BELOW THIS LINE
"""
tests.test_train_nn(train_neural_network)Tests Passed
Implement the function print_stats to print loss and validation accuracy. Use the global variables valid_features and valid_labels to calculate validation accuracy. Use a keep probability of 1.0 to calculate the loss and validation accuracy.
def print_stats(session, feature_batch, label_batch, cost, accuracy):
"""
Print information about loss and validation accuracy
: session: Current TensorFlow session
: feature_batch: Batch of Numpy image data
: label_batch: Batch of Numpy label data
: cost: TensorFlow cost function
: accuracy: TensorFlow accuracy function
"""
# TODO: Implement Function
loss = session.run(cost, feed_dict={x: feature_batch,
y: label_batch,
keep_prob: 1.})
valid_acc = session.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: valid_features,
y: valid_labels,
keep_prob: 1.})
print(loss, valid_acc)Tune the following parameters:
- Set
epochsto the number of iterations until the network stops learning or start overfitting - Set
batch_sizeto the highest number that your machine has memory for. Most people set them to common sizes of memory: - 64
- 128
- 256
- ...
- Set
keep_probabilityto the probability of keeping a node using dropout
# TODO: Tune Parameters
epochs = 40
batch_size = 512
keep_probability = 0.75Instead of training the neural network on all the CIFAR-10 batches of data, let's use a single batch. This should save time while you iterate on the model to get a better accuracy. Once the final validation accuracy is 50% or greater, run the model on all the data in the next section.
"""
DON'T MODIFY ANYTHING IN THIS CELL
"""
print('Checking the Training on a Single Batch...')
with tf.Session() as sess:
# Initializing the variables
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
# Training cycle
for epoch in range(epochs):
batch_i = 1
for batch_features, batch_labels in helper.load_preprocess_training_batch(batch_i, batch_size):
train_neural_network(sess, optimizer, keep_probability, batch_features, batch_labels)
print('Epoch {:>2}, CIFAR-10 Batch {}: '.format(epoch + 1, batch_i), end='')
print_stats(sess, batch_features, batch_labels, cost, accuracy)Checking the Training on a Single Batch...
Epoch 1, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 2.16415 0.234
Epoch 2, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 1.99352 0.3154
Epoch 3, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 1.83268 0.3694
Epoch 4, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 1.74429 0.3884
Epoch 5, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 1.66053 0.4168
Epoch 6, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 1.59822 0.4344
Epoch 7, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 1.52216 0.4524
Epoch 8, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 1.48215 0.4608
Epoch 9, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 1.40063 0.485
Epoch 10, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 1.36138 0.5028
Epoch 11, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 1.30815 0.5158
Epoch 12, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 1.23955 0.5294
Epoch 13, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 1.19615 0.5474
Epoch 14, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 1.14775 0.5522
Epoch 15, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 1.17475 0.537
Epoch 16, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 1.11416 0.5444
Epoch 17, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 1.07549 0.5582
Epoch 18, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 1.01537 0.5678
Epoch 19, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 1.00924 0.5692
Epoch 20, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.961232 0.5688
Epoch 21, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.916566 0.5822
Epoch 22, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.938028 0.563
Epoch 23, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.848046 0.5882
Epoch 24, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.849767 0.587
Epoch 25, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.845707 0.579
Epoch 26, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.784807 0.592
Epoch 27, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.736665 0.6032
Epoch 28, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.743103 0.5946
Epoch 29, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.757316 0.587
Epoch 30, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.680976 0.5914
Epoch 31, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.691691 0.5814
Epoch 32, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.678632 0.5926
Epoch 33, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.647683 0.6052
Epoch 34, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.644398 0.585
Epoch 35, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.612985 0.5982
Epoch 36, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.565636 0.606
Epoch 37, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.562469 0.6088
Epoch 38, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.52209 0.6106
Epoch 39, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.478937 0.618
Epoch 40, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.454209 0.6242
Now that you got a good accuracy with a single CIFAR-10 batch, try it with all five batches.
"""
DON'T MODIFY ANYTHING IN THIS CELL
"""
save_model_path = './image_classification'
print('Training...')
with tf.Session() as sess:
# Initializing the variables
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
# Training cycle
for epoch in range(epochs):
# Loop over all batches
n_batches = 5
for batch_i in range(1, n_batches + 1):
for batch_features, batch_labels in helper.load_preprocess_training_batch(batch_i, batch_size):
train_neural_network(sess, optimizer, keep_probability, batch_features, batch_labels)
print('Epoch {:>2}, CIFAR-10 Batch {}: '.format(epoch + 1, batch_i), end='')
print_stats(sess, batch_features, batch_labels, cost, accuracy)
# Save Model
saver = tf.train.Saver()
save_path = saver.save(sess, save_model_path)Training...
Epoch 1, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 2.17418 0.258
Epoch 1, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 1.89131 0.3228
Epoch 1, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 1.64358 0.377
Epoch 1, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 1.58045 0.42
Epoch 1, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 1.56963 0.4292
Epoch 2, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 1.54586 0.4666
Epoch 2, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 1.42333 0.4674
Epoch 2, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 1.31083 0.4686
Epoch 2, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 1.31937 0.5128
Epoch 2, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 1.32095 0.526
Epoch 3, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 1.33398 0.5416
Epoch 3, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 1.23915 0.5372
Epoch 3, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 1.14554 0.5422
Epoch 3, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 1.12836 0.5546
Epoch 3, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 1.21002 0.5658
Epoch 4, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 1.21794 0.5702
Epoch 4, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 1.14143 0.5704
Epoch 4, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 1.05564 0.5798
Epoch 4, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 1.00022 0.6014
Epoch 4, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 1.08161 0.5978
Epoch 5, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 1.12696 0.603
Epoch 5, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 1.01754 0.6042
Epoch 5, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.949764 0.6148
Epoch 5, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.923416 0.6146
Epoch 5, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 1.01087 0.6198
Epoch 6, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 1.05416 0.6142
Epoch 6, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.950968 0.6322
Epoch 6, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.872351 0.63
Epoch 6, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.865606 0.6376
Epoch 6, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.914406 0.6468
Epoch 7, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.962058 0.6478
Epoch 7, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.912675 0.6268
Epoch 7, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.86336 0.6404
Epoch 7, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.83486 0.6438
Epoch 7, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.849887 0.6598
Epoch 8, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.926978 0.6496
Epoch 8, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.833552 0.6654
Epoch 8, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.76524 0.6634
Epoch 8, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.731668 0.6704
Epoch 8, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.795204 0.6678
Epoch 9, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.875858 0.6724
Epoch 9, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.80453 0.6646
Epoch 9, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.735106 0.677
Epoch 9, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.701202 0.6728
Epoch 9, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.739197 0.6792
Epoch 10, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.78771 0.6786
Epoch 10, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.758499 0.6826
Epoch 10, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.677896 0.691
Epoch 10, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.636346 0.6832
Epoch 10, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.703204 0.6872
Epoch 11, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.74469 0.6894
Epoch 11, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.712101 0.6886
Epoch 11, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.659332 0.6862
Epoch 11, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.619165 0.6842
Epoch 11, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.668411 0.6958
Epoch 12, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.722821 0.6962
Epoch 12, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.666356 0.6844
Epoch 12, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.648884 0.6896
Epoch 12, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.578291 0.6978
Epoch 12, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.613525 0.6992
Epoch 13, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.691871 0.702
Epoch 13, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.674262 0.6712
Epoch 13, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.617314 0.6954
Epoch 13, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.54744 0.7082
Epoch 13, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.605175 0.7018
Epoch 14, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.695072 0.683
Epoch 14, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.634088 0.696
Epoch 14, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.646989 0.6886
Epoch 14, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.515303 0.7086
Epoch 14, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.598033 0.7004
Epoch 15, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.642724 0.7036
Epoch 15, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.597932 0.7012
Epoch 15, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.570637 0.7048
Epoch 15, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.499778 0.7078
Epoch 15, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.542088 0.7058
Epoch 16, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.647928 0.7008
Epoch 16, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.596136 0.6972
Epoch 16, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.589553 0.6982
Epoch 16, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.491102 0.7102
Epoch 16, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.511343 0.7108
Epoch 17, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.628615 0.6992
Epoch 17, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.590861 0.6938
Epoch 17, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.514383 0.715
Epoch 17, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.465944 0.7198
Epoch 17, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.487415 0.72
Epoch 18, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.581234 0.7102
Epoch 18, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.528197 0.7082
Epoch 18, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.517984 0.7158
Epoch 18, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.448379 0.7244
Epoch 18, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.466885 0.719
Epoch 19, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.557558 0.7158
Epoch 19, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.485483 0.7176
Epoch 19, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.466662 0.7118
Epoch 19, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.432227 0.719
Epoch 19, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.449991 0.7208
Epoch 20, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.542111 0.7226
Epoch 20, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.507359 0.699
Epoch 20, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.450182 0.7198
Epoch 20, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.398063 0.726
Epoch 20, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.416526 0.7272
Epoch 21, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.519584 0.7102
Epoch 21, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.467399 0.7084
Epoch 21, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.433236 0.7142
Epoch 21, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.391417 0.7226
Epoch 21, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.42498 0.7218
Epoch 22, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.516996 0.7216
Epoch 22, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.4438 0.7234
Epoch 22, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.397908 0.7256
Epoch 22, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.365478 0.7238
Epoch 22, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.401759 0.7214
Epoch 23, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.526016 0.7132
Epoch 23, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.451511 0.7196
Epoch 23, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.385383 0.7204
Epoch 23, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.36932 0.7208
Epoch 23, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.381374 0.7292
Epoch 24, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.517261 0.7204
Epoch 24, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.404438 0.7268
Epoch 24, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.418854 0.7182
Epoch 24, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.366863 0.721
Epoch 24, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.3707 0.7194
Epoch 25, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.46969 0.7174
Epoch 25, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.383327 0.7256
Epoch 25, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.358435 0.7294
Epoch 25, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.358246 0.7166
Epoch 25, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.356147 0.7236
Epoch 26, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.445827 0.7256
Epoch 26, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.402569 0.72
Epoch 26, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.360069 0.73
Epoch 26, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.347298 0.7152
Epoch 26, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.347091 0.7248
Epoch 27, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.453929 0.723
Epoch 27, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.351294 0.7322
Epoch 27, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.329644 0.7398
Epoch 27, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.345249 0.7226
Epoch 27, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.323675 0.7316
Epoch 28, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.415203 0.721
Epoch 28, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.371486 0.7228
Epoch 28, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.340016 0.7334
Epoch 28, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.319217 0.7262
Epoch 28, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.334795 0.7242
Epoch 29, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.428957 0.7106
Epoch 29, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.370579 0.7168
Epoch 29, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.378746 0.7388
Epoch 29, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.32033 0.7232
Epoch 29, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.311448 0.7318
Epoch 30, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.419881 0.708
Epoch 30, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.322512 0.736
Epoch 30, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.31532 0.7312
Epoch 30, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.278237 0.7322
Epoch 30, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.290007 0.7312
Epoch 31, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.38046 0.7234
Epoch 31, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.339483 0.7314
Epoch 31, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.284596 0.738
Epoch 31, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.256927 0.7408
Epoch 31, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.264829 0.7328
Epoch 32, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.353531 0.7196
Epoch 32, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.344512 0.7264
Epoch 32, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.275394 0.7372
Epoch 32, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.250398 0.7348
Epoch 32, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.263489 0.7318
Epoch 33, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.341413 0.722
Epoch 33, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.349035 0.7186
Epoch 33, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.294038 0.7286
Epoch 33, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.278225 0.7366
Epoch 33, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.250861 0.7402
Epoch 34, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.324521 0.7234
Epoch 34, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.369276 0.7194
Epoch 34, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.306543 0.7272
Epoch 34, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.284653 0.7214
Epoch 34, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.263262 0.7314
Epoch 35, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.323842 0.7224
Epoch 35, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.376572 0.7226
Epoch 35, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.325775 0.714
Epoch 35, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.266008 0.733
Epoch 35, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.255277 0.7346
Epoch 36, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.326463 0.7228
Epoch 36, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.316385 0.7308
Epoch 36, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.269 0.7256
Epoch 36, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.251647 0.7342
Epoch 36, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.224504 0.7382
Epoch 37, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.320176 0.7266
Epoch 37, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.261291 0.7406
Epoch 37, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.24623 0.7318
Epoch 37, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.233286 0.7338
Epoch 37, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.225085 0.7356
Epoch 38, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.285046 0.731
Epoch 38, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.267369 0.7332
Epoch 38, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.288629 0.7184
Epoch 38, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.229647 0.732
Epoch 38, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.214168 0.7354
Epoch 39, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.267609 0.7278
Epoch 39, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.274509 0.7384
Epoch 39, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.264205 0.7302
Epoch 39, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.252471 0.7308
Epoch 39, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.224979 0.734
Epoch 40, CIFAR-10 Batch 1: 0.251603 0.7306
Epoch 40, CIFAR-10 Batch 2: 0.277763 0.7348
Epoch 40, CIFAR-10 Batch 3: 0.288197 0.7162
Epoch 40, CIFAR-10 Batch 4: 0.243268 0.7348
Epoch 40, CIFAR-10 Batch 5: 0.231756 0.7248
The model has been saved to disk.
Test your model against the test dataset. This will be your final accuracy. You should have an accuracy greater than 50%. If you don't, keep tweaking the model architecture and parameters.
"""
DON'T MODIFY ANYTHING IN THIS CELL
"""
%matplotlib inline
%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'retina'
import tensorflow as tf
import pickle
import helper
import random
# Set batch size if not already set
try:
if batch_size:
pass
except NameError:
batch_size = 64
save_model_path = './image_classification'
n_samples = 4
top_n_predictions = 3
def test_model():
"""
Test the saved model against the test dataset
"""
test_features, test_labels = pickle.load(open('preprocess_test.p', mode='rb'))
loaded_graph = tf.Graph()
with tf.Session(graph=loaded_graph) as sess:
# Load model
loader = tf.train.import_meta_graph(save_model_path + '.meta')
loader.restore(sess, save_model_path)
# Get Tensors from loaded model
loaded_x = loaded_graph.get_tensor_by_name('x:0')
loaded_y = loaded_graph.get_tensor_by_name('y:0')
loaded_keep_prob = loaded_graph.get_tensor_by_name('keep_prob:0')
loaded_logits = loaded_graph.get_tensor_by_name('logits:0')
loaded_acc = loaded_graph.get_tensor_by_name('accuracy:0')
# Get accuracy in batches for memory limitations
test_batch_acc_total = 0
test_batch_count = 0
for test_feature_batch, test_label_batch in helper.batch_features_labels(test_features, test_labels, batch_size):
test_batch_acc_total += sess.run(
loaded_acc,
feed_dict={loaded_x: test_feature_batch, loaded_y: test_label_batch, loaded_keep_prob: 1.0})
test_batch_count += 1
print('Testing Accuracy: {}\n'.format(test_batch_acc_total/test_batch_count))
# Print Random Samples
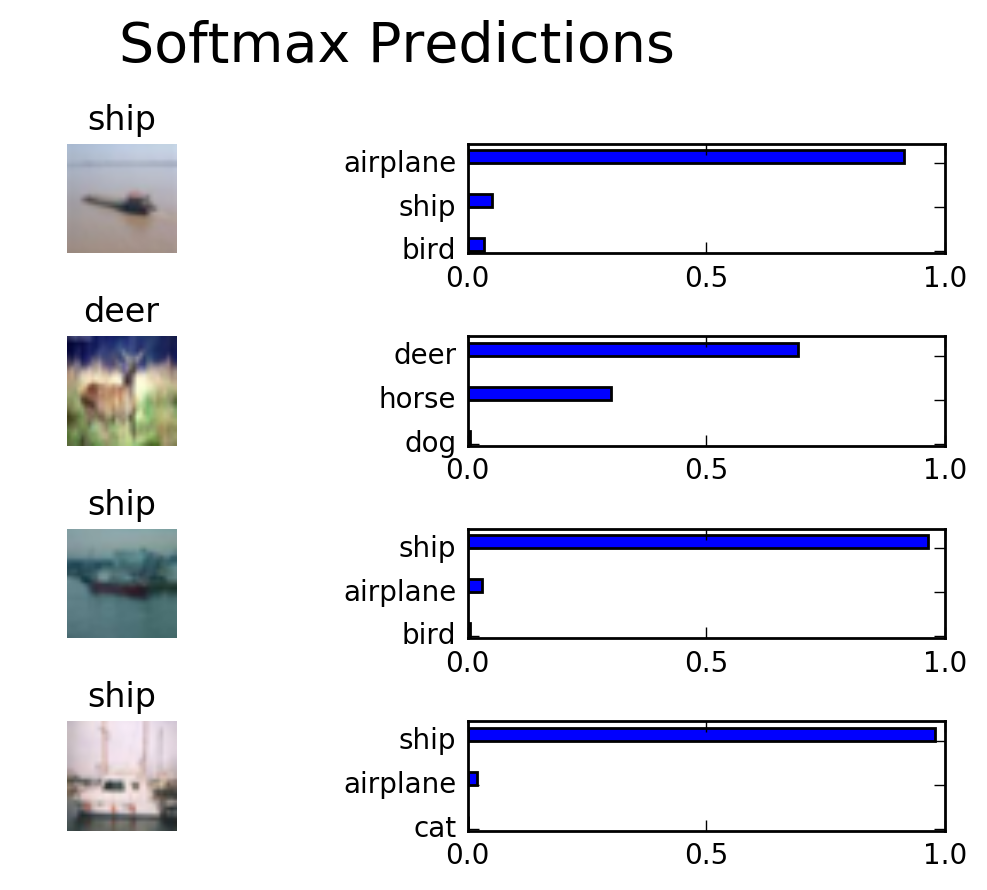
random_test_features, random_test_labels = tuple(zip(*random.sample(list(zip(test_features, test_labels)), n_samples)))
random_test_predictions = sess.run(
tf.nn.top_k(tf.nn.softmax(loaded_logits), top_n_predictions),
feed_dict={loaded_x: random_test_features, loaded_y: random_test_labels, loaded_keep_prob: 1.0})
helper.display_image_predictions(random_test_features, random_test_labels, random_test_predictions)
test_model()INFO:tensorflow:Restoring parameters from ./image_classification
Testing Accuracy: 0.7232766538858414
You might be wondering why you can't get an accuracy any higher. First things first, 50% isn't bad for a simple CNN. Pure guessing would get you 10% accuracy. However, you might notice people are getting scores well above 80%. That's because we haven't taught you all there is to know about neural networks. We still need to cover a few more techniques.
When submitting this project, make sure to run all the cells before saving the notebook. Save the notebook file as "dlnd_image_classification.ipynb" and save it as a HTML file under "File" -> "Download as". Include the "helper.py" and "problem_unittests.py" files in your submission.