This package lets you test different physics parameters in Gazebo to give you a better understanding of how they change the simulation e.g. friction parameters.
Additional videos demonstrating the effect of some of the physics parameters can be found here: http://gazebosim.org/tutorials?tut=physics_params
Launch Gazebo with and empty world
$ roslaunch gazebo_tests empty_gazebo.launchEnable spawning of box and ramp
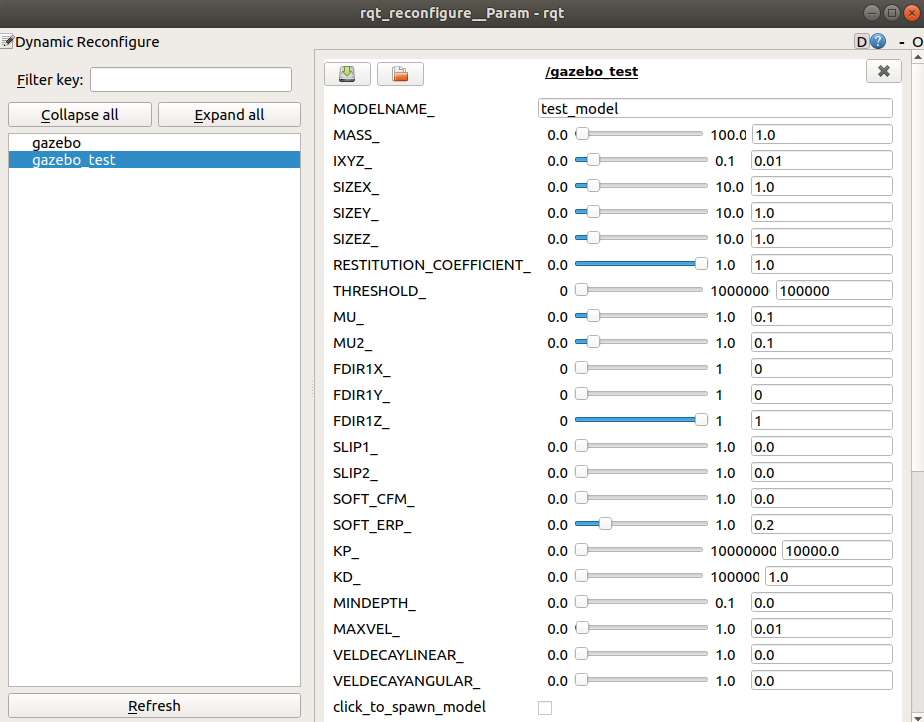
$ rosrun gazebo_tests spawn_by_params.pyOpen RQT Dynamic Reconfigure to spawn new boxes with different physics parameters. Set the parameters you would like to test and press the checkbox click_to_spawn_model to spawn a box.
$ rosrun rqt_reconfigure rqt_reconfigureOptional:
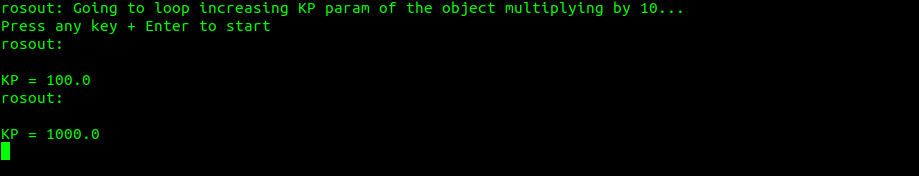
Automatic loop through one parameter multiplying by 10
$ rosrun gazebo_tests loop_parameter_example.pyhttp://gazebosim.org/tutorials?tut=modifying_world
In the World tab, select the Physics item. A list of physics properties will be displayed in the list box below.
- The
enable physicscheck-box can be used to disable physics while allowing plugins and sensors to continue running. - The
real time update rateparameter specifies in Hz the number of physics updates that will be attempted per second. If this number is set to zero, it will run as fast as it can. Note that the product of real time update rate and max step size represents the target real time factor, or ratio of simulation time to real-time. - The
max step sizespecifies the time duration in seconds of each physics update step.
In the gravity block:
- The
x,yandzparameters set the global gravity vector components inm/s^2.
In the solver block:
- The
iterationsparameter specifies the number of iterations to use for iterative LCP solvers (used by ODE and bullet). - The
SORparameter stands forsuccessive over-relaxation, which can be used to try to speed the convergence of the iterative method.
The constraints block contains several parameters related to solving constraints:
- The
CFMandERPparameters stands forConstraint Force MixingandError Reduction Parameterand are used byODEandbullet. The CFM and ERP parameters can be related to linear stiffness and damping coefficients. - The
max velocityandsurface layerparameters are used to resolve contacts with a split impulse method. Any contacts that penetrate deeper than a depth specified bysurface layerand have a normal velocity less thanmax velocitywill not bounce.
http://gazebosim.org/tutorials?tut=friction
When two object collide, such as a ball rolling on a plane, a friction term is generated. In ODE this is composed of two parts, mu and mu2, where:
-
muis the Coulomb friction coefficient for the first friction direction, and -
mu2is the friction coefficient for the second friction direction (perpendicular to the first friction direction).
ODE will automatically compute the first and second friction directions for us. Note, you can manually specify the first friction direction in SDF, but this capability is out of the scope of this tutorial.
The two objects in collision each specify mu and mu2. Gazebo will choose the smallest mu and mu2 from the two colliding objects.
The valid range of values for mu and mu2 is any non-negative number, where 0 equates to a friction-less contact and a large value approximates a surface with infinite friction. Tables of friction coefficient values for a variety of materials can be found in engineering handbooks or online references.
ODE spec: http://sdformat.org/spec?elem=collision&ver=1.4
mu: Coefficient of friction in the range of[0..1]. (default 1)mu2: Second coefficient of friction in the range of[0..1]. (default 1)fdir1: 3-tuple specifying direction of mu1 in the collision local reference frame. (default 0 0 0)slip1: Force dependent slip direction 1 in collision local frame, between the range of[0..1]. (default 0)slip2: Force dependent slip direction 2 in collision local frame, between the range of[0..1]. (default 0 )
soft_cfm: Soft constraint force mixing. (default 0)soft_erp: Soft error reduction parameter. (default 0.2)kp: Dynamically "stiffness"-equivalent coefficient for contact joints. (default 1e+12)kd: Dynamically "damping"-equivalent coefficient for contact joints. (default 1)max_vel: Maximum contact correction velocity truncation term. (default 0.01)min_depth: Minimum allowable depth before contact correction impulse is applied. (default 0)
restitution_coefficient: Bounciness coefficient of restitution, from [0..1] where 0=no bounciness. (default 1)threshold: Bounce capture velocity, below which effective coefficient of restitution is 0. (default 100000)
- A inertia matrix diagonal terms that goes lower than mass / 1000.0 makes the item unstable (w/ ground at least). Using standard inertia matrix for cubes, cylinders or spheres works good enough. I made a little program to compute them.
- KP minimum 10000. The tinier... it does not converge on getting onto a static position. Also, it must affect joint elements in gazebo, simple objects may be less affected by it (to be proven).
SOFT_CFMandSOFT_ERPdon't do anything. Gazebo Physics CFM and ERP can be tuned online from the Gazebo GUI client. They seem to slow down or not let two items in contact converge in a static position.muandmu2are (as the documentation states) in between [0.0..1.0], anything over 1.0 will be truncated to 1.0, infinite friction (like ground_plane).fdir13 element vector, are x y z, in local frame. There is some info in this gazebo answers.