Spark太复杂了,特别是涉及到scala与python开发,学习与使用成本很高,因此创作了SparkBoot工具,开发人员仅编写yaml与sql即可实现复杂的Spark编程,为其屏蔽了底层开开发细节,减轻了开发难度,让其更专注于大数据ETL与分析的逻辑;
框架通过编写简单的yaml与sql, 就可以执行一系列复杂的spark操作步骤, 如读数据/写数据/sql查询/打印变量等,压根不用写scala或python代码,极大的简化了伙伴Spark编程的工作量与工作难度,大幅提高人效;
框架通过提供类似pythonfor/if/break语义的步骤动作,赋予伙伴极大的开发能力与灵活性,能适用于广泛的应用场景。
框架提供include机制,用来加载并执行其他的步骤yaml,一方面是功能解耦,方便分工,一方面是功能复用,提高效率与质量,从而推进脚本整体的工程化。
- 底层基于 pyspark 库来实现
- 支持通过yaml来配置执行的步骤,简化了生成代码的开发: 每个步骤可以有多个动作,但单个步骤中动作名不能相同(yaml语法要求); 动作代表spark上的一种操作,如read_csv/run_sql/run_python等等;
- 支持类似python
for/if/break语义的步骤动作,灵活适应各种场景 - 支持
include引用其他的yaml配置文件,以便解耦与复用; - 支持用
schedule动作来实现定时处理. - sql优先,用sql来实现数据转换是相对简单的,同时相较于找一个会scala的开发伙计,找一个会sql的人更为容易。
- HttpBoot yaml驱动http接口自动化测试+性能测试
- SeleniumBoot yaml驱动Selenium测试
- AppiumBoot yaml驱动Appium测试
- MiniumBoot yaml驱动Minium测试
- ExcelBoot yaml驱动Excel生成
- MonitorBoot yaml驱动linux系统监控与jvm性能监控与告警
- SparkBoot yaml驱动Spark开发
- K8sBoot 简化k8s资源定义文件
- ArgoFlowBoot 简化Argo Workflows工作流定义文件
- 支持更多的动作
pip3 install SparkBoot
安装后会生成命令SparkBoot;
注: 对于深度deepin-linux系统,生成的命令放在目录~/.local/bin,建议将该目录添加到环境变量PATH中,如
export PATH="$PATH:/home/shi/.local/bin"
# 以local模式来执行 步骤配置文件中定义的spark作业
SparkBoot 步骤配置文件.yml
# 生成spark作业的相关文件,用于cluster/yarn模式中给spark-submit提交作业
# 生成文件包含: 1 submit.sh spark-submit的提交作业的命令 2 run.py python入口文件 3 步骤配置文件
# 提交作业命令如: spark-submit --master spark://192.168.62.209:7077 run.py 步骤配置文件
SparkBoot 步骤配置文件.yml -o 作业文件的生成目录
如执行 SparkBoot example/test.yml,输出如下
2023-09-25 12:34:22,578 - ThreadPoolExecutor-0_0 - boot - DEBUG - handle action: set_vars={'outdir': '../data'}
2023-09-25 12:34:22,578 - ThreadPoolExecutor-0_0 - boot - DEBUG - handle action: else=[{'init_session': {'app': 'test'}, 'set_vars': {'outdir': '/output'}}]
2023-09-25 12:34:22,578 - ThreadPoolExecutor-0_0 - boot - DEBUG - handle action: read_jdbc={'user': {'url': 'jdbc:mysql://192.168.62.209:3306/test', 'table': 'user', 'properties': {'user': 'root', 'password': 'root', 'driver': 'com.mysql.jdbc.Driver'}}}
+---+--------+--------+------+---+------+
| id|username|password| name|age|avatar|
+---+--------+--------+------+---+------+
| 1| | | shi-1| 1| null|
| 2| | | shi-2| 2| null|
| 3| | | shi-3| 3| null|
+---+--------+--------+------+---+------+
only showing top 20 rows
2023-09-25 12:34:27,231 - ThreadPoolExecutor-0_0 - boot - DEBUG - handle action: write_csv={'user': {'path': '$outdir/user.csv', 'mode': 'overwrite'}}
2023-09-25 12:34:27,783 - ThreadPoolExecutor-0_0 - boot - DEBUG - handle action: read_csv={'user2': {'path': '$outdir/user.csv'}}
......
命令会自动执行test.yaml文件中定义的spark任务
- 生成作业文件
SparkBoot udf-test.yml -u udf-test.py -o gen生成文件如下
shi@shi-PC:[~/code/python/SparkBoot/example]: tree gen
gen
├── run.py -- python入口文件
├── submit.sh -- 提交命令,其中master要根据实际情况调整
├── udf-test.py -- udf定义文件
└── udf-test.yml -- 步骤配置文件
- 将生成文件目录上传到spark master节点
- 执行
submit.sh来提交作业
用于指定多个步骤, 示例见源码 example 目录下的文件;
顶级的元素是步骤;
每个步骤里有多个动作(如read_csv/run_sql/run_python),如果动作有重名,就另外新开一个步骤写动作,这是由yaml语法限制导致的,但不影响步骤执行。
简单贴出3个demo
- 基本api测试: 详见 example/test.yml
- 简单的单词统计: 详见 example/word-count.yml
- 复杂的订单统计: 详见 example/order-stat.yml
支持通过yaml来配置执行的步骤;
每个步骤可以有多个动作,但单个步骤中动作名不能相同(yaml语法要求);
动作代表spark上的一种操作,如read_csv/run_sql/run_python等等;
下面详细介绍每个动作:
- init_session: 初始化spark session
- init_session:
app: test
#master: local[*] # master: 对local仅在本地调试时使用,如果是在集群中运行,则需要删掉本行,并在spark-submit命令中指定master
log_level: error # 日志级别- read_csv: 读csv数据
read_csv:
# key是表名, value是csv文件路径
user: /data/input/user.csv- read_json: 读json数据
read_json:
# key是表名, value是json文件路径
user: /data/input/user.json
order: http://127.0.0.1:8080/minimini.json # 对远程文件, 先下载到本地- read_orc: 读orc数据
read_orc:
# key是表名, value是orc文件路径
user: /data/input/user.orc- read_parquet: 读parquet数据
read_parquet:
# key是表名, value是parquet文件路径
user: /data/input/user.parquet- read_text: 读文本数据
read_text:
# key是表名, value是文本文件路径
lines: /data/input/words.txt- read_jdbc: 读jdbc数据
read_jdbc:
# key是表名, value是jdbc连接配置
user:
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.62.209:3306/test
table: user # 表
# table: (SELECT * FROM user WHERE id <= 10) AS tmp # 查询sql
properties:
user: root
password: root
driver: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver # 需要提前复制好mysql驱动jar,参考pyspark.md- read_table: 读表数据
# 接收字典参数
read_table:
# key是新表名, value是旧表名
user2: user
# 接收数组参数
read_table:
- user- reads_rate: 读模拟流数据
reads_rate:
# key是表名, value是参数
user:
rowsPerSecond: 10 # 每秒产生10行- reads_socket: 读socket流数据
reads_socket:
# key是表名, value是socket server的ip端口
user: localhost:9999- reads_kafka: 读kafka流数据
reads_kafka:
# key是表名, value是kafka brokers+topic
user:
brokers: localhost:9092 # 多个用逗号分割
topic: test- reads_csv: 读csv流数据
reads_csv:
# key是表名, value是csv文件路径
user: /data/input/user.csv- reads_json: 读json流数据
reads_json:
# key是表名, value是json文件路径
user: /data/input/user.json- reads_orc: 读orc流数据
reads_orc:
# key是表名, value是orc文件路径
user: /data/input/user.orc- reads_parquet: 读parquet流数据
reads_parquet:
# key是表名, value是parquet文件路径
user: /data/input/user.parquet- reads_text: 读文本流数据
reads_text:
# key是表名, value是文本文件路径
lines: /data/input/words.txt- run_sql: 执行sql
- run_sql:
# key是表名, value是查询sql
words: select explode(split(value," ")) as word from lines
word_count: select word, count(1) as cnt from words group by word- run_python: 执行python脚本
- run_python:
# key是表名, value是python脚本
test: |
user.select("id", "name", "age").filter("id <= 10")参考python-test.yml,其中user是之前代码定义过的表名对应的变量,代表一个spark DataFrame对象
- write_console: 将数据写到控制台
write_console:
# key是表名, value是参数
user:
mode: complete # append/update/complete- write_csv: 写csv数据
write_csv:
# key是表名, value是csv文件路径
user: /data/output/user.csv
# 或
write_csv:
user:
path: /data/output/user.csv
mode: overwrite # 模式:append/overwrite/ignore
#compression: none # 不压缩- write_json: 写json数据
write_json:
# key是表名, value是json文件路径
user: /data/output/user.json- write_orc: 写orc数据
write_orc:
# key是表名, value是orc文件路径
user: /data/output/user.orc- write_parquet: 写parquet数据
write_parquet:
# key是表名, value是parquet文件路径
user: /data/output/user.parquet- write_text: 写文本数据
write_text:
# key是表名, value是文本文件路径
user: /data/output/user.txt- write_jdbc: 写jdbc数据
write_jdbc:
# key是表名, value是jdbc连接配置
user:
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.62.209:3306/test
table: user
properties:
user: root
password: root
driver: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver # 需要提前复制好mysql驱动jar,参考pyspark.md- writes_console: 将流数据写到控制台
writes_console:
# key是表名, value是参数
user:
checkpointLocation: path/to/checkpoint/dir
outputMode: complete # append/update/complete
#trigger: 5 # 定时写的时间间隔,接收int(如5表示5秒)或str(如5 seconds)- writes_mem: 将流数据写到内存表中
writes_mem:
# key是表名, value是参数
user:
checkpointLocation: path/to/checkpoint/dir
outputMode: complete # append/update/complete
#trigger: 5 # 定时写的时间间隔,接收int(如5表示5秒)或str(如5 seconds)
queryName: tmp_user # 内存表名- writes_kafka: 写kafka流数据
writes_kafka:
# key是表名, value是kafka brokers+topic
user:
brokers: localhost:9092 # 多个用逗号分割
topic: test
checkpointLocation: path/to/checkpoint/dir
outputMode: complete # append/update/complete
#trigger: 5 # 定时写的时间间隔,接收int(如5表示5秒)或str(如5 seconds)- writes_csv: 写csv数据
writes_csv:
# key是表名, value是文本文件路径
user:
path: /data/output/user.csv
mode: overwrite # 模式:append/overwrite/ignore
#compression: none # 不压缩
checkpointLocation: path/to/checkpoint/dir
outputMode: complete # append/update/complete
#trigger: 5 # 定时写的时间间隔,接收int(如5表示5秒)或str(如5 seconds)- writes_json: 写json数据
writes_json:
# key是表名, value是json文件路径
user:
path: /data/output/user.json
checkpointLocation: path/to/checkpoint/dir
outputMode: complete # append/update/complete
#trigger: 5 # 定时写的时间间隔,接收int(如5表示5秒)或str(如5 seconds)- writes_orc: 写orc数据
writes_orc:
# key是表名, value是orc文件路径
user:
path: /data/output/user.orc
checkpointLocation: path/to/checkpoint/dir
outputMode: complete # append/update/complete
#trigger: 5 # 定时写的时间间隔,接收int(如5表示5秒)或str(如5 seconds)- writes_parquet: 写parquet数据
writes_parquet:
# key是表名, value是parquet文件路径
user:
path: /data/output/user.parquet
checkpointLocation: path/to/checkpoint/dir
outputMode: complete # append/update/complete
#trigger: 5 # 定时写的时间间隔,接收int(如5表示5秒)或str(如5 seconds)- writes_text: 写文本数据
writes_text:
# key是表名, value是文本文件路径
user:
path: /data/output/user.txt
checkpointLocation: path/to/checkpoint/dir
outputMode: complete # append/update/complete
#trigger: 5 # 定时写的时间间隔,接收int(如5表示5秒)或str(如5 seconds)- list_tables: 列出所有表
list_tables: - drop_table: 删除单个表
drop_table: user # 删除表user- cache: 对子动作中产生的表进行缓存
- cache:
- run_sql:
my_order: select storeProvince,storeID,receivable,dateTS,payType from order where storeProvince != 'null' and receivable > 1000 # 读源文件 minimini.json- cache: 对子动作中产生的表进行存储
- persist:
- run_sql:
top3_province_order: select my_order.* from my_order join top3_provinces where my_order.storeProvince = top3_provinces.storeProvince- print: 打印, 支持输出变量/函数;
# 调试打印
print: "总申请数=${dyn_data.total_apply}, 剩余份数=${dyn_data.quantity_remain}"- for: 循环;
for动作下包含一系列子步骤,表示循环执行这系列子步骤;变量
for_i记录是第几次迭代(从1开始),变量for_v记录是每次迭代的元素值(仅当是list类型的变量迭代时有效)
# 循环3次
for(3) :
# 每次迭代要执行的子步骤
- switch_sheet: test
# 循环list类型的变量urls
for(urls) :
# 每次迭代要执行的子步骤
- switch_sheet: test
# 无限循环,直到遇到跳出动作
# 有变量for_i记录是第几次迭代(从1开始)
for:
# 每次迭代要执行的子步骤
- break_if: for_i>2 # 满足条件则跳出循环
switch_sheet: test- once: 只执行一次,等价于
for(1); once 结合 moveon_if,可以模拟 python 的if语法效果
once:
# 每次迭代要执行的子步骤
- moveon_if: for_i<=2 # 满足条件则往下走,否则跳出循环
switch_sheet: test- break_if: 满足条件则跳出循环; 只能定义在for/once循环的子步骤中
break_if: for_i>2 # 条件表达式,python语法- moveon_if: 满足条件则往下走,否则跳出循环; 只能定义在for/once循环的子步骤中
moveon_if: for_i<=2 # 条件表达式,python语法- if/else: 满足条件则执行if分支,否则执行else分支
- set_vars:
txt: '进入首页'
- if(txt=='进入首页'): # 括号中包含的是布尔表达式,如果表达式结果为true,则执行if动作下的子步骤,否则执行else动作下的子步骤
- print: '----- 执行if -----'
else:
- print: '----- 执行else -----'- include: 包含其他步骤文件,如记录公共的步骤,或记录配置数据(如用户名密码);
include: part-common.yml- set_vars: 设置变量;
set_vars:
name: shi
password: 123456
birthday: 5-27- print_vars: 打印所有变量;
print_vars:- schedule: 定时处理,就是每隔指定秒数就执行下子步骤,如定时将流处理结果输出
# 定时处理
- schedule(5): # 每隔5秒
# 执行子步骤
- print: '每隔5s触发: ${now()}'- 定义 UDF: udf-test.py
from pyspark.sql.functions import udf
from pyspark.sql.types import *
@udf(returnType=DoubleType())
def add(m, n):
return float(m) + float(n)
@udf(returnType=DoubleType())
def add_one(a):
return float(a) + 1.0- 定义步骤文件: udf-test.yml
- debug: true # 遇到df就show()
# 1 初始化spark session
- init_session:
app: test
#master: local[*]
log_level: error # 日志级别
# 2 读mysql
- read_jdbc:
user:
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.62.209:3306/test
table: user
properties:
user: root
password: root
driver: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver # 需要提前复制好mysql驱动jar,参考pyspark.md
# 3 查sql: select udf
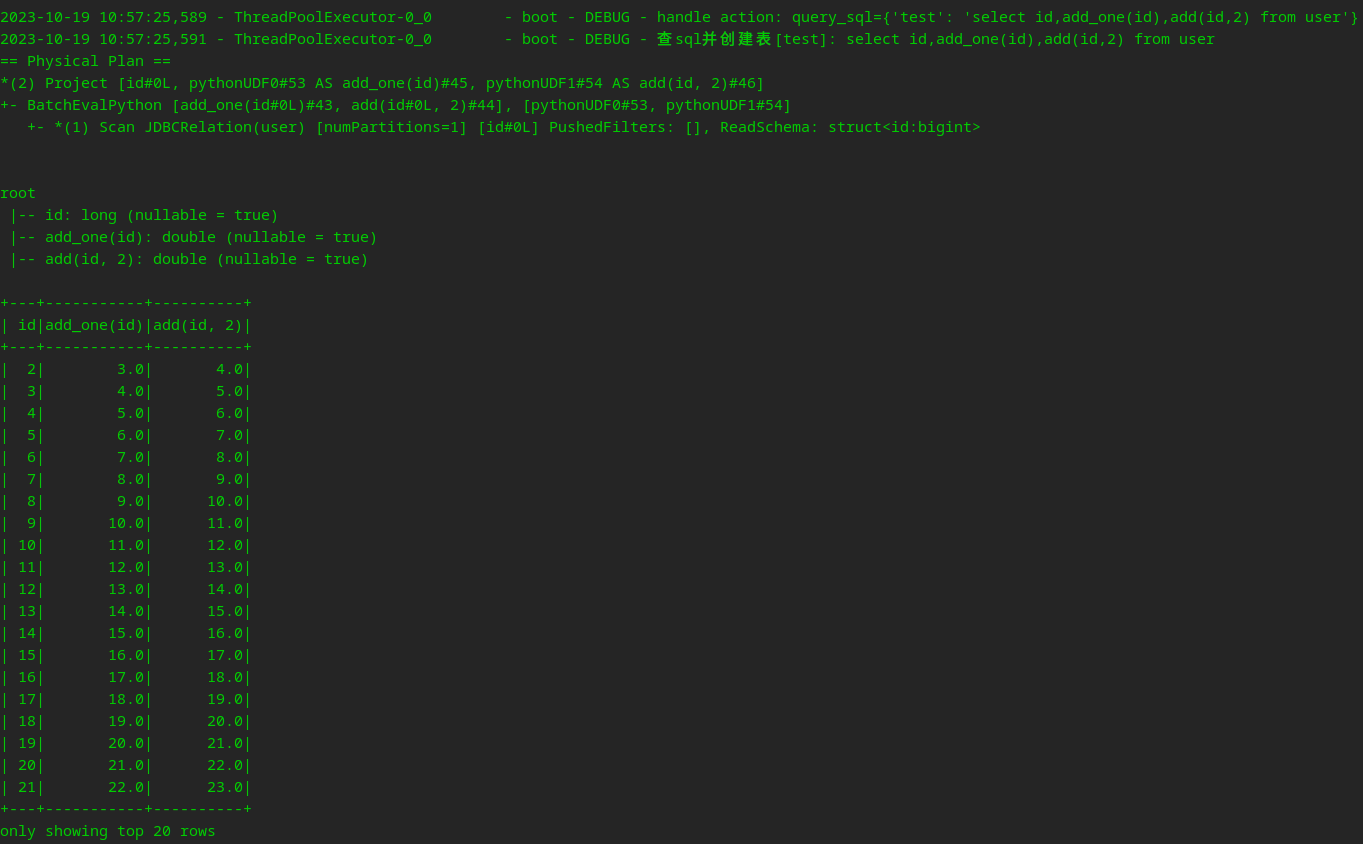
- run_sql:
test: select id,add_one(id),add(id,2) from user- 命令行执行,需用
-u来指定UDF所在的python文件
SparkBoot udf-test.yml -u udf-test.py执行结果如下