Argo Workflows工作流定义蛮复杂的,学习与使用成本很高,大部分伙伴很难学会,因此创作了ArgoFlowBoot工具,支持通过简化版的yaml配置来生成argo最终的工作流定义文件,yaml的代码量大大缩小;
框架通过编写简单的yaml, 就可以执行一系列复杂的操作步骤, 如打印变量/生成wf/cwf/wft/cwft等工作流文件,极大的简化了伙伴编写argo工作流定义文件的工作量与工作难度,大幅提高人效;
框架通过提供类似pythonfor/if/break语义与变量赋值等步骤动作,赋予伙伴极大的开发能力,让工作流定义文件的编写工作更具灵活性,能适用于广泛的应用场景。
框架提供include机制,用来加载并执行其他的步骤yaml,一方面是功能解耦,方便分工,一方面是功能复用,提高效率与质量,从而推进脚本整体的工程化。
- 支持通过yaml来配置执行的步骤,简化了生成代码的开发: 每个步骤可以有多个动作,但单个步骤中动作名不能相同(yaml语法要求); 动作代表argo的某个工作流或模板定义,如wf/cwf/wft/cwft等等;
- 支持类似python
for/if/break语义的步骤动作,灵活适应各种场景 - 支持
include引用其他的yaml文件,以便解耦与复用 - yaml的代码量大大缩小,ArgoFlowBoot的yaml代码量相当于argo原生yaml的1/2~1/7
- 支持以函数形式来定义模板与调用模板,让argo工作流定义更加切合面向函数编程的方式
- wf(steps-test):
- templates:
whalesay(msg): # 定义模板(函数形式),带参数
container:
command: cowsay $msg
main(): # 定义入口模板(函数形式)
steps:
- - whalesay(hello1) # 调用模板(函数调用形式)
- - whalesay(hello2)
- whalesay(hello3)k8scmd之简化argo命令:对argo的复杂命令做了大量简化
- HttpBoot yaml驱动http接口自动化测试+性能测试
- SeleniumBoot yaml驱动Selenium测试
- AppiumBoot yaml驱动Appium测试
- MiniumBoot yaml驱动Minium测试
- ExcelBoot yaml驱动Excel生成
- MonitorBoot yaml驱动linux系统监控与jvm性能监控与告警
- SparkBoot yaml驱动Spark开发
- K8sBoot 简化k8s资源定义文件
- ArgoFlowBoot 简化Argo Workflows工作流定义文件
- 支持更多的动作
pip3 install ArgoFlowBoot
安装后会生成命令ArgoFlowBoot;
注: 对于深度deepin-linux系统,生成的命令放在目录~/.local/bin,建议将该目录添加到环境变量PATH中,如
export PATH="$PATH:/home/shi/.local/bin"
# 1 执行单个文件
ArgoFlowBoot 步骤配置文件.yml
# 2 执行多个文件
ArgoFlowBoot 步骤配置文件1.yml 步骤配置文件2.yml ...
# 3 执行单个目录, 即执行该目录下所有的yml文件
ArgoFlowBoot 步骤配置目录
# 4 执行单个目录下的指定模式的文件
ArgoFlowBoot 步骤配置目录/step-*.yml
如执行 ArgoFlowBoot example/base/dag-test.yml -o data/,输出如下
shi@shi-PC:[~/code/python/ArgoFlowBoot]: ArgoFlowBoot example/base/dag-test.yml -o data/
/home/shi/.local/lib/python3.7/site-packages/google/auth/__init__.py:55: Python37DeprecationWarning: After January 1, 2024, new releases of this library will drop support for Python 3.7. More details about Python 3.7 support can be found at https://cloud.google.com/python/docs/python37-sunset/
warnings.warn(message, Python37DeprecationWarning)
/home/shi/.local/lib/python3.7/site-packages/google/oauth2/__init__.py:40: Python37DeprecationWarning: After January 1, 2024, new releases of this library will drop support for Python 3.7. More details about Python 3.7 support can be found at https://cloud.google.com/python/docs/python37-sunset/
warnings.warn(message, Python37DeprecationWarning)
2023-11-22 11:22:04,295 - ThreadPoolExecutor-0_0 - boot - DEBUG - Load and run step file: /home/shi/code/python/ArgoFlowBoot/example/base/dag-test.yml
2023-11-22 11:22:04,303 - ThreadPoolExecutor-0_0 - boot - DEBUG - handle action: wf(dag-test)=[{'templates': {'echo(msg)': {'container': {'command': 'echo $msg'}}, 'main()': {}}}]
2023-11-22 11:22:04,303 - ThreadPoolExecutor-0_0 - boot - DEBUG - handle action: templates={'echo(msg)': {'container': {'command': 'echo $msg'}}, 'main()': {}}
2023-11-22 11:22:04,303 - ThreadPoolExecutor-0_0 - boot - INFO - 流程[dag-test]的定义文件已生成完毕, 如要提交到到集群中请手动执行: argo submit /home/shi/code/python/ArgoFlowBoot/data/dag-test.yml
命令会自动操作并生成argo工作流文件
shi@shi-PC:[~/code/python/ArgoFlowBoot]: tree data
data
└── dag-test.yml
支持通过yaml文件来配置执行的步骤;
每个步骤可以有多个动作,但单个步骤中动作名不能相同(yaml语法要求);
动作代表argo上的一种资源或动作,如wf/cwf/wft/cwft等等;
下面详细介绍每个动作
- ns:设置当前 namespace
ns: 命名空间名- wf:定义流程,并执行子步骤
wf(流程名):
# 子步骤
templates: ...- wft:定义流程模板,并执行子步骤
wft(流程模板名):
# 子步骤
templates: ...- cwft:定义集群级流程模板,并执行子步骤
cwft(流程模板名):
# 子步骤
templates: ...- cwf:定义定时流程,并执行子步骤;注意其下必须包含
cron子动作
cwf(定时流程名):
# 子步骤
templates: ...
cron: ...- bind_event: 流程绑定事件
# 流程绑定事件(绑定名) -- 触发流程模板
- bind_event(test-event):
# discriminator与selector二选一
# discriminator: test-event # 事件鉴别器,用于区分事件类型,可省,默认为绑定名
# selector: discriminator == "test-event" # 事件选择器,与discriminator只能存在一个
wft: my-wft(payload.message) # 事件触发的流程模板测试,参考event文档
ARGO_TOKEN="Bearer $(kubectl get secret default.service-account-token -n argo -o=jsonpath='{.data.token}' | base64 --decode)"
curl https://10.105.1.242:2746/api/v1/events/argo/test-event \
-H "Authorization: $ARGO_TOKEN" \
-d '{"message": "hello"}'
-k
- include_argo_wft: 加载argo流程模板原生文件,主要是为了获知其入参
include_argo_wft: ./hello-wft.yml- print: 打印, 支持输出变量/函数;
# 调试打印
print: "总申请数=${dyn_data.total_apply}, 剩余份数=${dyn_data.quantity_remain}"- set_vars: 设置变量;
set_vars:
name: shi
password: 123456
birthday: 5-27- print_vars: 打印所有变量;
print_vars:- for: 循环;
for动作下包含一系列子步骤,表示循环执行这系列子步骤;变量
for_i记录是第几次迭代(从1开始),变量for_v记录是每次迭代的元素值(仅当是list类型的变量迭代时有效)
# 循环3次
for(3) :
# 每次迭代要执行的子步骤
- print: $for_v
# 循环list类型的变量urls
for(urls) :
# 每次迭代要执行的子步骤
- print: $for_v
# 无限循环,直到遇到跳出动作
# 有变量for_i记录是第几次迭代(从1开始)
for:
# 每次迭代要执行的子步骤
- break_if: for_i>2 # 满足条件则跳出循环
print: $for_v- once: 只执行一次,等价于
for(1); once 结合 moveon_if,可以模拟 python 的if语法效果
once:
# 每次迭代要执行的子步骤
- moveon_if: for_i<=2 # 满足条件则往下走,否则跳出循环
print: $for_v- break_if: 满足条件则跳出循环; 只能定义在for/once循环的子步骤中
break_if: for_i>2 # 条件表达式,python语法- moveon_if: 满足条件则往下走,否则跳出循环; 只能定义在for/once循环的子步骤中
moveon_if: for_i<=2 # 条件表达式,python语法- if/else: 满足条件则执行if分支,否则执行else分支
- set_vars:
txt: '进入首页'
- if(txt=='进入首页'): # 括号中包含的是布尔表达式,如果表达式结果为true,则执行if动作下的子步骤,否则执行else动作下的子步骤
- print: '----- 执行if -----'
else:
- print: '----- 执行else -----'- include: 包含其他步骤文件,如记录公共的步骤,或记录配置数据(如用户名密码);
include: part-common.yml以下的动作,必须声明在 wf/wft/cwft/cwf 动作的子步骤中,动作的参数支持传递变量;
- labels:设置应用标签
labels:
flow: test
flow2: $flow # 支持传递变量- args: 定义流程级参数
- wft(hello-world-wft): # 流程模板
- args: # 流程级参数
# 参数名: 参数值
msg: hello world # 普通参数
'@art': /tmp/hello_world.txt # 工件名: 挂载路径如果参数名以@开头则为artifact参数,否则为普通参数;
你可以在模板中使用变量的方式来引用流程级参数:
变量 $msg = {{workflow.parameters.msg}}
变量 $@art = {{workflow.artifacts.art}}
- templates: 定义函数模板
- wf(steps-test):
- templates:
whalesay(msg): # 定义模板(函数形式),带参数
container:
command: cowsay $msg
main(): # 定义入口模板(函数形式),工作流入口必然是main
steps:
- - whalesay(hello1) # 调用模板(函数调用形式)
- - whalesay(hello2)
- whalesay(hello3)- vc_templates: 定义持久卷声明
- wf(vol-test):
# key是vc模板名, value是{size, mount}
- vc_templates: # 共享的pvc, 所有任务的容器都会挂载
workdir: # pvc名
size: 1Gi # 空间大小
mount: /code # 挂载路径其中mount可以是str类型,表示整体挂载到容器中的路径名;也可以是dict类型,key是pvc子路径,value是挂载到容器内路径,下面是dict类型的demo:
- wft(ci-workflowtemplate):
- args:
branch: master
- vc_templates: # 共享的pvc, 所有任务的容器都会挂载
workdir: # pvc名
size: 64Mi # 空间大小
mount: # 挂载路径
mod: /go/pkg/mod
cache: /root/.cache/go-build
src: /src
- cron: 定义定时选项,需定义在
cwf动作下作为子动作
- wf(cron-test):
- cron: # 定时选项
schedule: "* * * * *"
concurrencyPolicy: "Replace"
startingDeadlineSeconds: 0- spec: 定义流程的其他配置
- wf(timeouts-test):
- spec:
activeDeadlineSeconds: 5 # terminate workflow after 5 seconds-
入口(entrypoint)模板名必然是
main -
退出处理(exit handler)模板名必然是
onexit
- 模板是定义在
templates动作下,如
- templates: # templates动作参数是模板dict,key是模板名+参数名(函数形式),value是模板具体定义
whalesay(msg): # 定义模板(函数形式),带参数
container:
command: cowsay $msg- 基本语法:以函数形式来定义模板,格式如
模板名(参数列表)
whalesay(): # 定义模板 whalesay,不带参数
container:
command: cowsay hello
whalesay2(msg): # 定义模板 whalesay2,带参数
container:
command: cowsay $msg上面代码定义了2个模板,分别是 whalesay 与 whalesay2
- 基本语法:以函数形式来定义模板+参数,格式如
模板名(参数1,参数2),其中如果参数名以@开头则为artifact参数,否则为普通参数
whalesay(msg,@art): # 定义模板 whalesay,带2个输入参数,分别是:普通参数为msg, artifact参数为art
container:
command: cowsay $msg ; cat ${@art.path} # 用 $xxx 或 ${xxx.yyy} 形式来引用参数- 入参的默认值
whalesay2(msg=hello,@art=/tmp/message): # 定义模板 whalesay,带2个输入参数,参数都有默认值
container:
command: cowsay $msg ; cat ${@art.path} # 用 $xxx 或 ${xxx.yyy} 形式来引用参数问题:由于用函数形式来定义模板+参数+参数默认值,如果代表参数默认值包含,)等特殊字符,或如果artifact参数默认值是一个dict,这会导致不满足函数定义形式,进而导致后续解析模板失败!
解决:用变量来做参数默认值,参考 artifact-var.yml
# artifact入参带默认值:通过变量的方式
- wf(artifact-var):
- set_vars: # 定义变量
source-opt:
path: /src # 可省,默认路径为 /tmp/artifacts/工件名
git:
repo: https://gitee.com/argoproj/argo-workflows.git
revision: "master"
- templates: # 定义模板
main(@source=$source-opt): # 变量用作采纳数默认值
container:
command: ls -l ${@source.path}- 用变量的方式来引用入参
对模板
whalesay(msg,@art):, 你可以使用以下方式来引用入参: 变量$msg={{inputs.parameters.msg}}变量$@art={{inputs.artifacts.art}}变量表达式${@art.path}= artifacts变量art挂载的路径
- 模板的输出参数是定义在
out属性中
whalesay: # 定义模板 whalesay,有2个输出参数,分别是:普通参数为msg2, artifact参数为art2
container:
command: echo -n hello world > /tmp/hello_world.txt
out:
msg2: hello world
'@art2': /tmp/hello_world.txt # 工件名: 挂载路径(路径可省,默认路径为 /tmp/artifacts/工件名)对于container/script类型模板,其中image(镜像)配置可省略,其缺省镜像的策略如下:
-
script类型模板,缺省镜像为 bash
-
对container类型模板,根据不同的command参数,有不同的缺省镜像:
bash命令: 缺省镜像为 bash
cowsay命令: 缺省镜像为 docker/whalesay
curl命令: 缺省镜像为 appropriate/curl
其他命令:缺省镜像为 'alpine'
- container类型模板
main(): # 定义模板 main
container: # container类型模板
command: cowsay hello- script类型模板
bash-random(): # 定义模板 bash-random
script: # script类型模板
source: |
cat /dev/urandom | od -N2 -An -i | awk -v f=1 -v r=100 '{printf "%i\n", f + r * $1 / 65536}'- python类型模板,相当于特殊的script模板
flip-coin(): # 定义模板 flip-coin
python3.6: # python类型模板,支持python版本有 3.6/3.7/3.8/3.9/3.10/3.11
#image: python:alpine3.6 # 镜像可省,各版本对应缺省镜像为 python:alpine3.6/python:alpine3.7/python:alpine3.8/python:alpine3.9/python:alpine3.10/python:alpine3.11
source: |
import random
result = "heads" if random.randint(0,1) == 0 else "tails"
print(result)- steps类型模板
main(): # 定义模板 main
steps: # steps类型模板
- - whalesay(hello1) # 调用模板(函数调用形式)
- - whalesay(hello2)
- whalesay(hello3)步骤之间传递参数, 即引用上一步骤的输出参数,可以用变量的方式来引用:
whalesay(): # 定义模板 whalesay,有输出参数
container:
command: cowsay hello world | tee /tmp/hello_world.txt
out:
msg: hello
'@art': /tmp/hello_world.txt
print-message(msg, @art): # 定义模板 print-message,有输入参数,用于接收上一步骤的输出参数
container:
command: echo $msg, cat ${@art.path}
main(): # 工作流入口必然是main
steps:
- - whalesay()
- - print-message(${whalesay.msg}, ${whalesay.@art}) # 将上一步骤的输出参数,作为下一步骤的输入参数
其中
${whalesay.msg} = {{steps.whalesay.outputs.parameters.msg}}
${whalesay.@art} = {{steps.whalesay.outputs.artifacts.art}}
- dag类型模板
main(): # 定义模板 main
dag: # dag类型模板
# 简写语法: 上游的模板调用 -> 下游的模板调用
# 同一级的多个模板调用用;分割
- echo(A) -> echo(B);echo(C) -> echo(D)- suspend类型模板
approve(): # 定义模板 approve
suspend: # 暂停, 直到被resume
delay(): # 定义模板 delay
suspend: 5 # 暂停5秒- create类型模板
main(): # 定义模板 main
create:
file: ./test-config.yml # k8s资源文件等价于
main(): # 定义模板 main
create:
# k8s资源定义,即k8s资源文件内容
manifest: |
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
generateName: test-
data:
some: value- apply类型模板
main(): # 定义模板 main
apply:
file: ./test-config.yml # k8s资源文件等价于
main(): # 定义模板 main
apply:
# k8s资源定义,即k8s资源文件内容
manifest: |
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
generateName: test-
data:
some: value- delete类型模板
main(): # 定义模板 main
delete:
file: ./test-config.yml # k8s资源文件等价于
main(): # 定义模板 main
delete:
# k8s资源定义,即k8s资源文件内容
manifest: |
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
generateName: test-
data:
some: value- create_wf_by_wft类型模板
resource-without-argument(): # 定义模板 resource-without-argument
create_wf_by_wft: hello-world-wft() # 通过流程模板来创建子流程 -- 不带参数
resource-with-argument(msg): # 定义模板 resource-with-argument
create_wf_by_wft: hello-world-wft($msg) # 通过流程模板来创建子流程 -- 带参数- http模板
req(): # 定义模板 req
# http类型模板
# 简写: curl命令
http: curl https://list.zhonghuasuan.com/search -d type=goods&key=hello等价于
req(): # 定义模板 req
# 完整写法
http:
url: https://list.zhonghuasuan.com/search
method: POST
body: type=goods&key=hello-
引用流程级输入参数 变量
$msg={{workflow.parameters.msg}}变量$@art={{workflow.artifacts.art}} -
引用模板的输入参数 如果模板为
whalesay(msg,@art):, 则你可以使用以下方式来引用入参: 变量$msg={{inputs.parameters.msg}}变量$@art={{inputs.artifacts.art}}变量表达式${@art.path}= artifacts变量art挂载的路径 -
在steps模板中引用上一步骤的输出参数 如果上一步骤调用的模板为
whalesay, 且模板的输出参数为msg与@art, 则你可以使用以下方式来引用上一步骤的输出: 变量${whalesay.msg}={{steps.whalesay.outputs.parameters.msg}}变量${whalesay.@art}={{steps.whalesay.outputs.artifacts.art}}
示例见源码 example 目录:
| 序号 | demo文件 | 作用 | 代码量缩减到原生的 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | input-test.yml | 演示输入参数 | 1/3.43 |
| 2 | steps-test.yml | 演示steps类型模板 | 1/4.0 |
| 3 | steps-async.yml | steps类型模板异步模式 | 1/3.29 |
| 4 | dag-test.yml | 演示dag类型模板 | 1/6.75 |
| 5 | artifact-test.yml | 演示artifact | 1/2.94 |
| 6 | artifact-type.yml | 演示各种类型的artifact | 1/1.76 |
| 7 | artifact-key.yml | 演示key-only artifact | 1/2.71 |
| 8 | artifact-repo-ref.yml | 演示artifact仓库引用 | 1/2.3 |
| 9 | artifact-var.yml | 演示artifact的默认值是变量 | 1/2.18 |
| 10 | script-test.yml | 演示script类型模板 | 1/2.23 |
| 11 | output-test.yml | 演示输出参数 | 1/2.76 |
| 12 | secret-env+vol-test.yml | 挂载secret与pvc | 1/2.62 |
| 13 | loop-withitems.yml | 演示循环(withItems方式) | 1/2.84 |
| 14 | loop-withparam.yml | 演示循环(withParam方式) | 1/2.44 |
| 15 | loop-result.yml | 聚合循环的结果 | 1/2.3 |
| 16 | conditionals-test.yml | 演示when | 1/2.13 |
| 17 | conditionals-artifacts.yml | 演示when | 1/1.96 |
| 18 | conditionals-parameters.yml | 演示when | 1/1.96 |
| 19 | recursion-test.yml | 演示递归 | 1/2.06 |
| 20 | retry-test.yml | 演示重试 | 1/2.0 |
| 21 | exit-test.yml | 演示退出处理 | 1/2.52 |
| 22 | timeouts-test.yml | 演示超时 | 1/2.29 |
| 23 | suspend-test.yml | 演示suspend类型模板 | 1/3.5 |
| 24 | sidecars-test.yml | 演示sidecars类型模板 | 1/2.89 |
| 25 | cron-test.yml | 演示定时流程 | 1/2.67 |
| 26 | k8sres-test.yml | 演示k8s资源的创建 | 1/3.6 |
| 27 | http-test.yml | 演示http类型模板 | 1/3.71 |
| 28 | event-test.yml | 演示事件 | 1/4.1 |
| 29 | var-test.yml | 演示流程级参数 | 1/3.0 |
| 30 | vol-test.yml | 演示pvc挂载 | 1/2.88 |
| 31 | wf2wf-test.yml | 流程创建流程 | 1/3.71 |
| 32 | wftmpl-test.yml | 演示流程模板 | 1/3.8 |
| 33 | ci.yml | 演示ci | 1/2.37 |
| 34 | ci-workflowtemplate.yml | 演示ci | 1/2.09 |
接下来以 example/base/dag-test.yml 为案例讲解下 ArgoFlowBoot 与 简化版argo命令 的使用:
- 步骤yaml
main.yml
- wf(dag-test):
- templates:
echo(msg): #
container:
command: echo $msg
main(): # 工作流入口必然是main
dag: # 依赖关系
- echo(A) -> echo(B);echo(C) -> echo(D)- 生成argo工作流文件
ArgoFlowBoot example/base/dag-test.yml -o data生成argo文件 data/dag-test.yml,内容如下:
# data/dag-test.yml
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: dag-test-
labels:
flow: dag-test
spec:
entrypoint: main
templates:
- name: echo
inputs:
parameters:
- name: msg
container:
image: alpine
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
command:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- echo {{inputs.parameters.msg}}
- name: main
dag:
tasks:
- name: echo
template: echo
arguments:
parameters:
- name: msg
value: A
- name: echo2
template: echo
arguments:
parameters:
- name: msg
value: B
dependencies:
- echo
- name: echo3
template: echo
arguments:
parameters:
- name: msg
value: C
dependencies:
- echo
- name: echo4
template: echo
arguments:
parameters:
- name: msg
value: D
dependencies:
- echo2
- echo3=> ArgoFlowBoot代码量缩减到argo原生代码的1/6.75
- 提交argo工作流文件
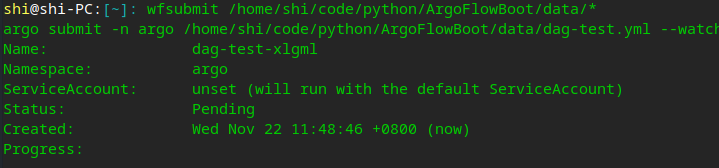
argo submit data/dag-test.yml
# 或
wfsubmit data/dag-test.yml- 查看所有流程
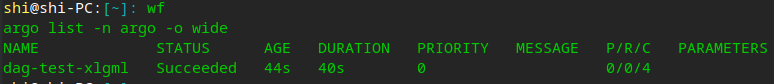
- 查看单个流程
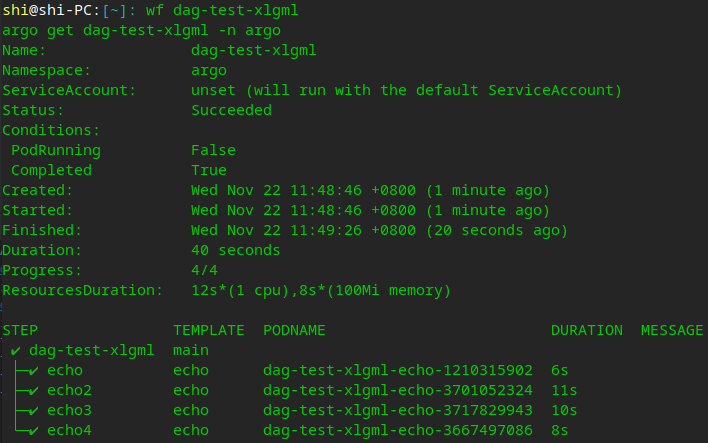
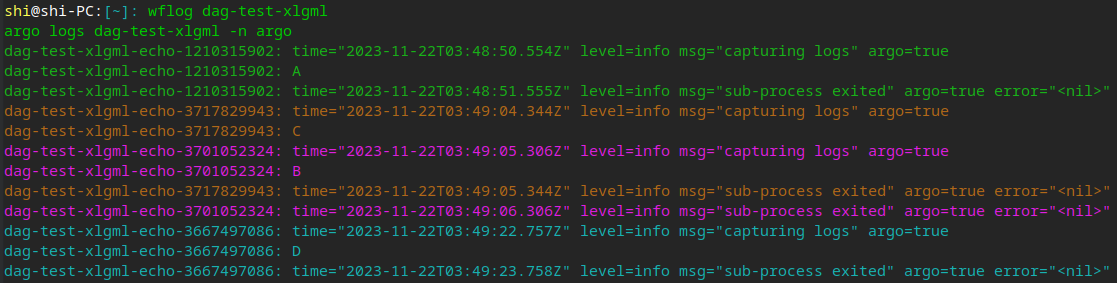
- 查看单个流程的日志