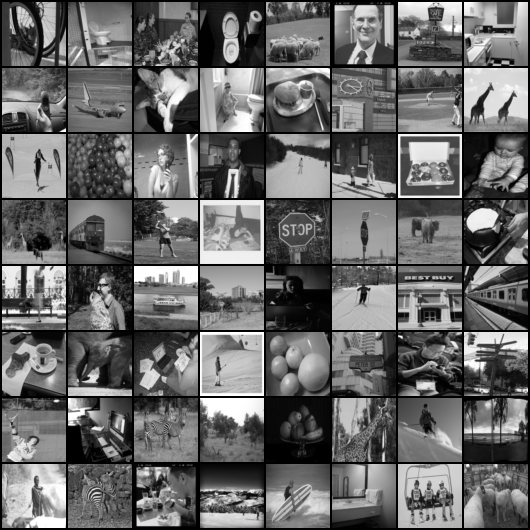
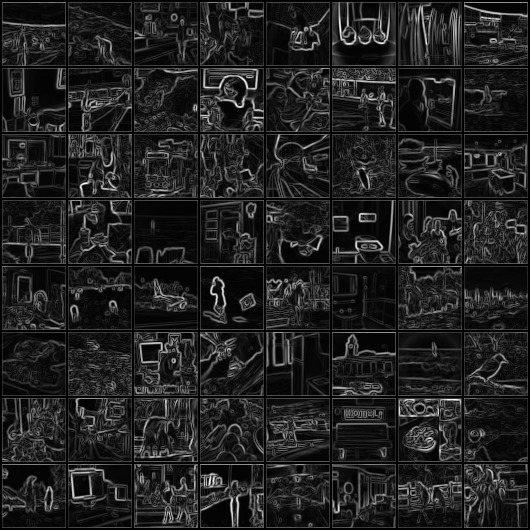
This repository contains the PyTorch code for the implementation of a sobel filter using neural networks on COCO dataset.
function train(input):
// Step 1: Initialize loss functions, train and val dataset, network
// Step 2: Loop over epochs
for epochs in num_epochs:
// Step 3: Loop through the dataset
for batch in input:
// Step 4: Compute model output
// Step 5: Compute loss between output and GT
// Step 6: Backprop and update weights
// Step 7: Run Steps 3-6 for validation dataset and log the loss
// Step 8: Save model if the validation loss is lower than that at previous epoch
// Step 9: Stop training if the decrease in validation loss falls below a certain percentages or epochs are complete
return modelfunction generateData(input):
// Step 1: Load COCO dataset
// Step 2: Compute Sobel filter on each sample
// Step 3: Wrap this dataset around a dataloader
return dataloaderIn order to build a conda environment for running our model, run the following command:
conda env create -f environment.yml
Activate environment using:
conda activate sobel
To train our model, run the following command:
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=ID python train.py
You can choose to modify the hyperparameters for training in config.json. Here, you can change various parameters like batch size, number of epochs, image size, learning rate, etc. The code can be run on GPU or CPU depending on your hardware so feel free to change that.
In the same file, you can modify the filter you would want to us (variable for that is called filter). The possible values it can take are sobel, sym_sobel, avg, blur, and custom.
You can also add your own custom filter that you want the model to learn in the get_gt_values function in the dataset.py file.
To evaluate our model on your test image, place the image in root directory with the name test_image.jpg
The, run the following command:
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=ID python test.py
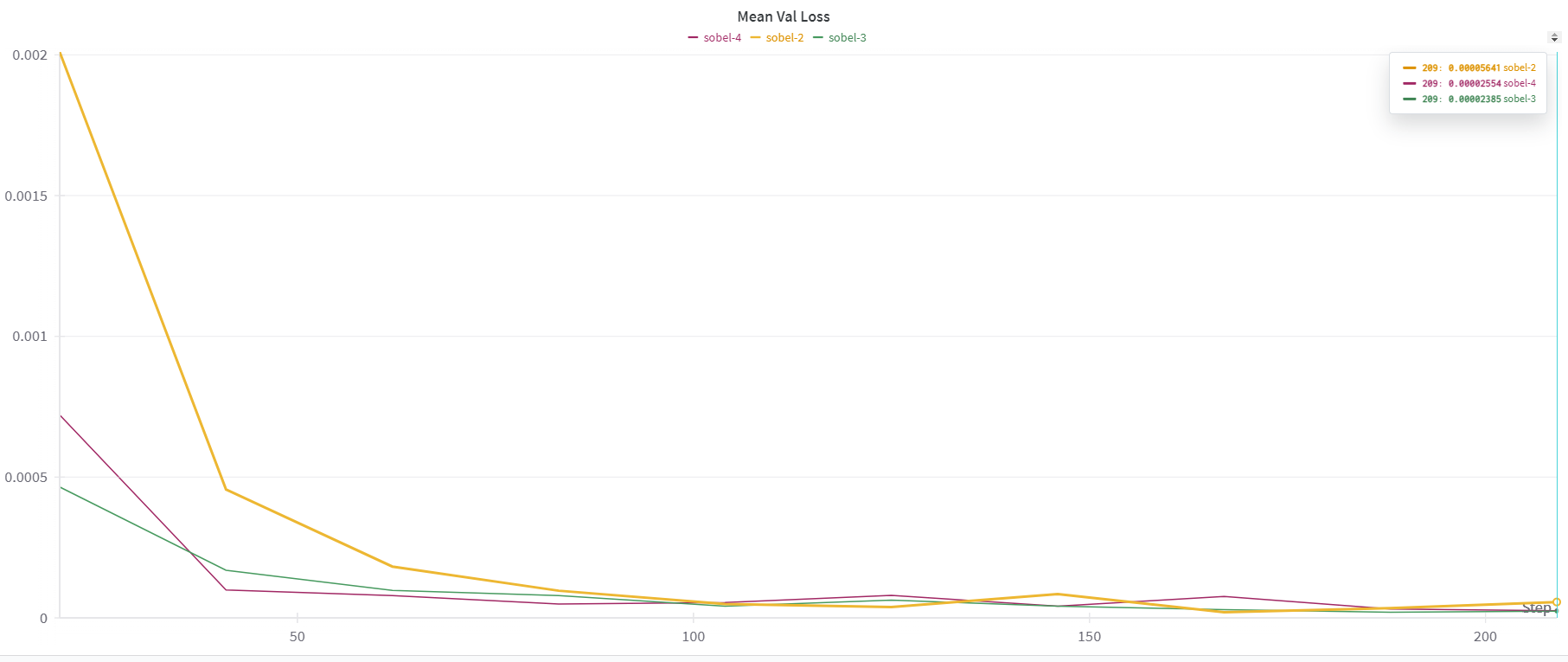
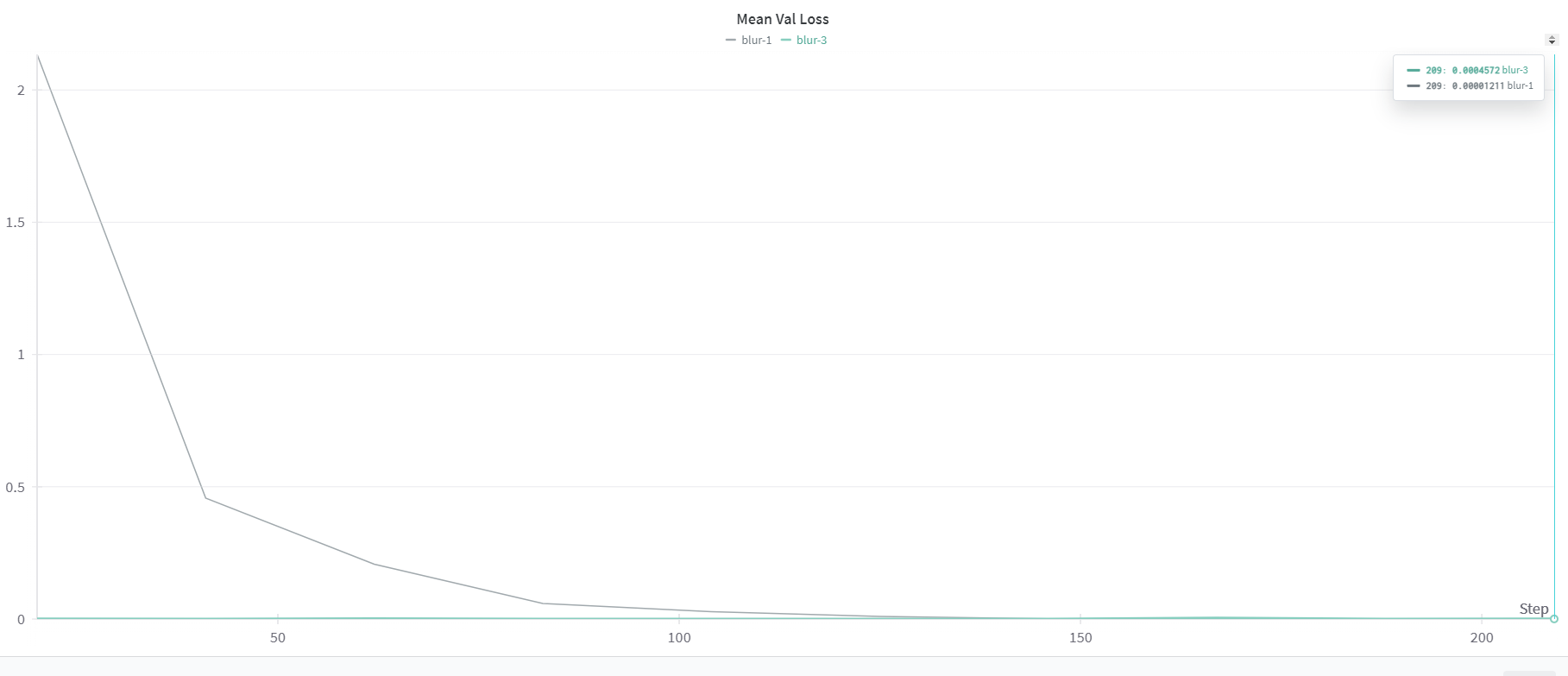
Here are some of the finding from the evaluation of the trained models.
For the sobel filter, 3 convolutional layers seem to be optimal. We also use ReLU activations between layers. Performance with 2 and 4 convolutional layers also saturate to a similar loss (both train and validation) but with 3 layers, the convergence is faster. Sobel filter does not work well with just one layer (loss converges to 0.3 which is significantly higher than that of >1 layers).
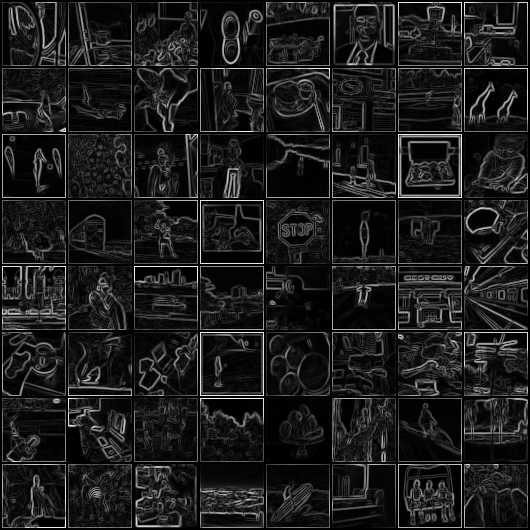
These are the images I got from the trained models. These are input images (left), target images after applying the sobel filter (middle), and the output images from our model (right), respectively.
For blurring filter, again 3 convolutional layers lead to faster convergence but eventually, the one layer network reaches a slightly lower loss (both train and validation). This is because effectively we are just applying one convolutional filter to the image which can be learnt by the neural network with one layer. This enables us to compute the filter output very efficiently since we are using a GPU for computations. A larger network optimizes faster due to its capacity to learn more complex behaviors and since there are multiple ways to represent a filter, it converges faster to a solution.
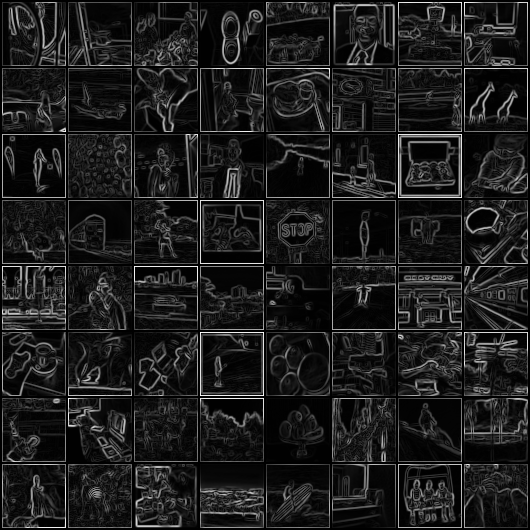
These are the images I got from the trained models. These are input images (left), target images after applying the blur filter (middle), and the output images from our model (right), respectively.
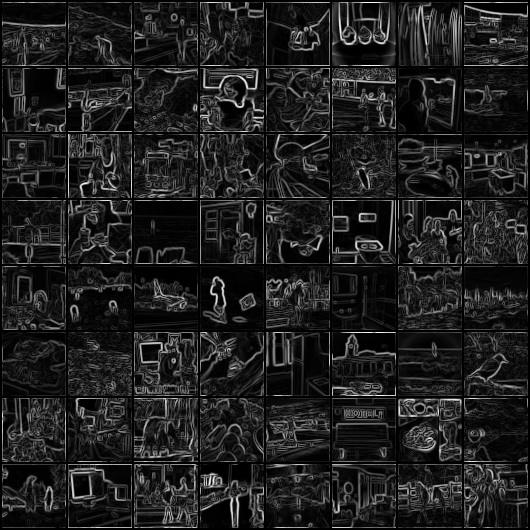
At the boundaries of the output images of sobel filter, we can see artifacts because we will obtain a gradient at the boundary. Hence, I also tested out a sobel filter that uses wrap boundaries (mirroring) to reduce artifacts at the boundaries of the image. The loss for the model with wrap boundaries is a little higher because the convolutional layers inherently use zero value paddings. This one works well for any number of layers >= 3.
These are the images I got from the trained models. These are input images (left), target images after applying the sobel (with mirroring) filter (middle), and the output images from our model (right), respectively.
Neural networks (using CNNs) are learning various filters (other than Sobel and blur). So, we provide the feature to manually input a filter in the dataset.py file and add your filter there. You can then train your model following the training instructions.