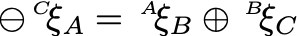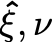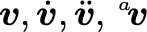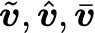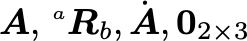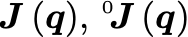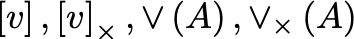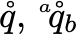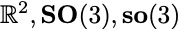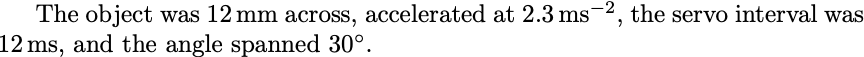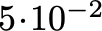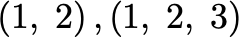LaTeX macros for Robotics, Vision and Control
This file includes macros to create equations in the style of those used in the textbook "Robotics, Vision & Control", all editions.
\include{rvc-notation}Make sure that rvc-notation.tex is in your LaTeX path.
A PDF version of the cheatsheet is available here.
Poses
\poseabstract pose, greek letter ξ\pose[f]pose with respect to a frame\pose_Ais the pose of frame A\pose[B]_Ais the pose of frame A with respect to frame B\estposeestimated pose, greek letter ξ with hat\posedotderivative of abstract pose, greek letter ν A leading superscript, the reference frame, is specified in square brackets. A trailing subscript, the target frame, is specified in the standard LaTeX way using_.
The operators ⊕ and ⊖ which are given by the LaTeX commands \oplus and \ominus respectively.
$\ominus \pose[C]_A = \pose[A]_B \oplus \pose[B]_C$
We can apply a pose to a vector, which linearly transforms it by
$\pose_b \sbullet \vec{b}_P$
You can tweak the size of the bullet by giving it a relative scale argument, ie. \sbullet[2] is very large.
There are also estimated pose and derivative of pose or spatial velocity
$\estpose, \posedot$
Coordinate frames
\cframe{A}is coordinate frame A which renders as {A}
\cframe{A}Points
\point{A}is point A which renders in Roman bold font
\point{P}Vectors
Vectors are displayed in bold italic font
\vec{t}is a vector t\vec[A]{t}is a vector t with respect to frame A\dvec{t}is vector of\dot{t}\dvec[A]{t}is vector of\dot{t}with respect to frame A\ddvec[f]{x} a double dotted vector\hvech[f]{x}a homogeneous vector (tilde above)\bvec[f]{x}a vector with an over bar, eg. for mean value\evec[f]{x}an estimated vector with a hat
$\vec{v}, \dvec{v}, \ddvec{v}, \vec[a]{v}$$ \hvec{v}, \evec{v}, \bvec{v}$Matrices
Matrices are displayed in bold Roman font
\mat{x}a matrix\mat[f]{x}a matrix with a coordinate frame\dmat[f]{x}a matrix derivative\zeroa zero matrix\matfn{f}{x}matrix function f of x
$\mat{A}, \mat[a]{R}_b, \dmat{A}, \emat{A}, \zero_{2\times 3}$$\matfn{J}{\vec{q}}, \matfn[0]{J}{\vec{q}}$Skew symmetric matrices
\skx{v}-> [v]x skew symmetric matrix\sk{v}-> [v] augmented skew symmetric matrix\iskx{v}-> inverse skew symmetric matrix, vex operator\isk{v}-> inverse augmented skew symmetric matrix
$\sk{v}, \skx{v}, \isk{A}, \iskx{A}$Unit Quaternion
\qdisplays as q with a bubble on top
$\q, \q[a]_b$Mathematial Groups
Displayed in Roman font
\Ris the group of real numbers, an R in blackboard font\SO{n}special orthogonal group: SO(n)\SE{n}special Euclidean group: SE(n)\so{n}Lie algebra of SO(n): so(n)\se{n}Lie algebra of SE(n): se(n)
$\R^2, \SO{3}, \so{3}$MATLAB code
Display a block of code in blue fixed-width font
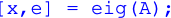
\begin{Code}
[x,e] = eig(A);
\end{Code}For multi-line code blocks with line numbering
\begin{CodeNum}
[x,e] = eig(A);
z = x(:,2);
\end{CodeNum}Miscellaneous
Smallest angular difference
The symbol ⊝ is used to represent the difference of two angles wrapped into the interval [-π π), which is produced by the LaTeX command \circleddash.
$\theta_1 \circleddash \theta_2$Units
\unit{U}sets the contents in math mode with a preceding half space, eg.\unit{m s^{-2})\mm,\um,\nm\Hz,\kHz,\MHz\ms\deg
The object was 12\mm\ across,
accelerated at 2.3\unit{m s^{-2}},
the servo interval was 12\ms,
and the angle spanned 30\deg.Scientific notation
\sci{m}{e}scientific notation with mantissa and exponent
\sci{5}{-2}Coordinates and vectors
$\coord{1}{2}, \vector{1}{2}{3}$Other symbols
\cspaceconfiguration space, caligraphic C