pyuscope controls digital microscopes using Python. It primarily focuses on metallurgical microscopes with an emphasis on high resolution panoramas and advanced scripting.
Interested in purchasing a microscope? Please reach out to support@labsmore.com
Features:
- Argus GUI for easy imaging
- Panoramic imaging including simple 2D and advanced 3D tracking
- Focus stacking
- HDR capture
- Chain batch jobs together
- Automatic panorama image stitching CloudStitch
- CLI applications for batch jobs
- Simple Python API for advanced applications
OS: we primarily test on Ubuntu 20.04 but other versions of Linux or MacOS might work
git clone --branch stable-latest https://github.com/Labsmore/pyuscope.git
If you'd like a basic setup:
PYUSCOPE_MICROSCOPE=none ./setup_ubuntu_20.04.sh
Alternatively if you know your microscope configuration file (ie a dir in configs/) do something like this:
PYUSCOPE_MICROSCOPE=ls-hvy-2 ./setup_ubuntu_20.04.sh
After rebooting your system you can launch the PYUSCOPE_MICROSCOPE default microscope with:
./app/argus.py
If you want to explicitly specify a microscope:
./app/argus.py --microscope mock
Assuming you have no outstanding changes, do the following:
git pull --rebase
./setup_ubuntu_20.04.sh
Microscopes tend to be based on a GRBL motion controller + a Touptek USB camera. There are some older LinuxCNC and/or v4l flows but they aren't currently actively developed.
It's also possible to use the motion HAL / planner without gstreamer if you are ok launching from the CLI or writing your own GUI. Ex: we may add some basic SEM support this way
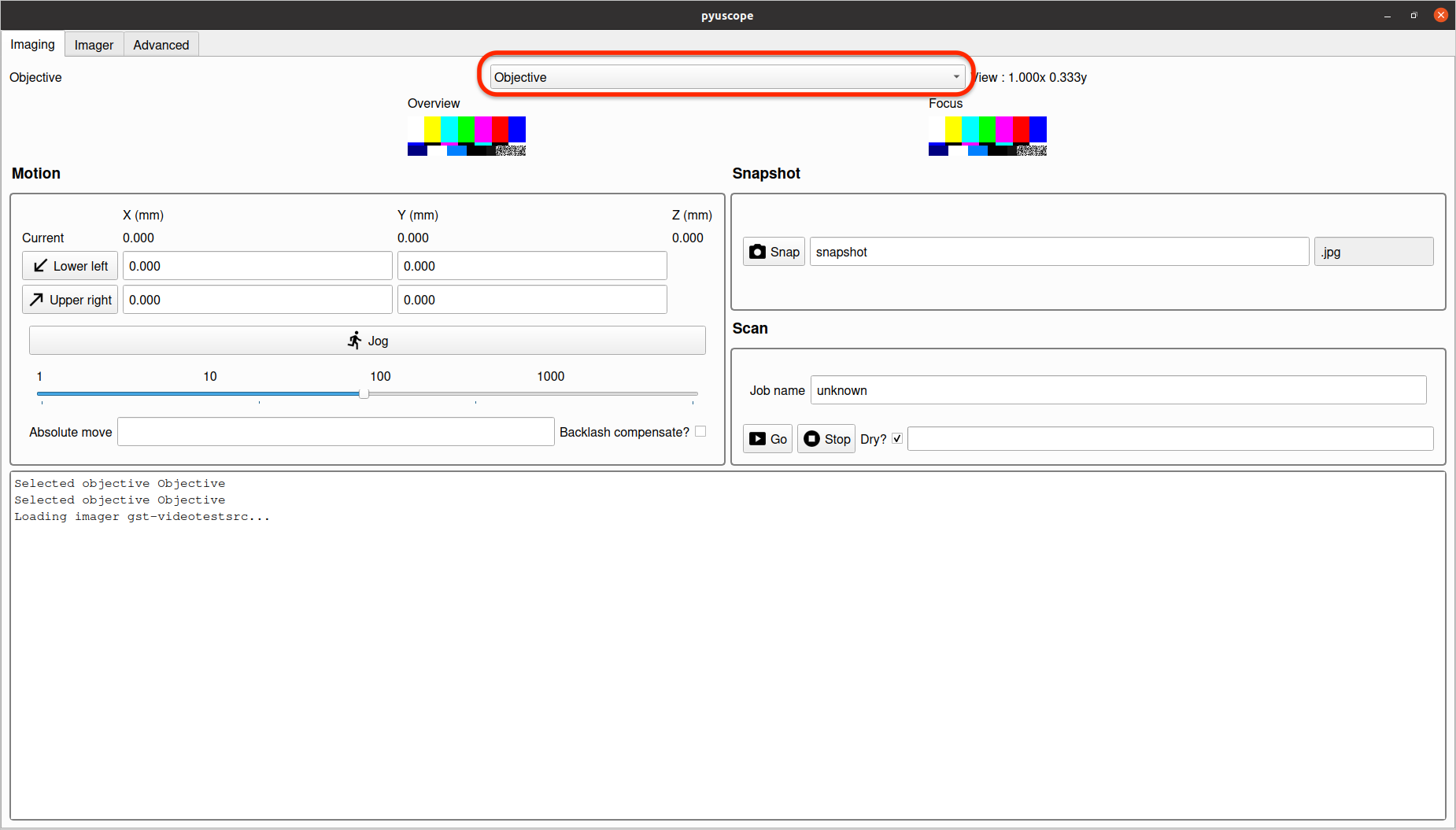
This dropdown displays a list of lens setups that exist in the configuration file used during application startup. Pick option that matches the lens currently being used to image.
This selection is required for correctly performing motion and imaging tasks and should be set when switching lenses, or performing any operations.
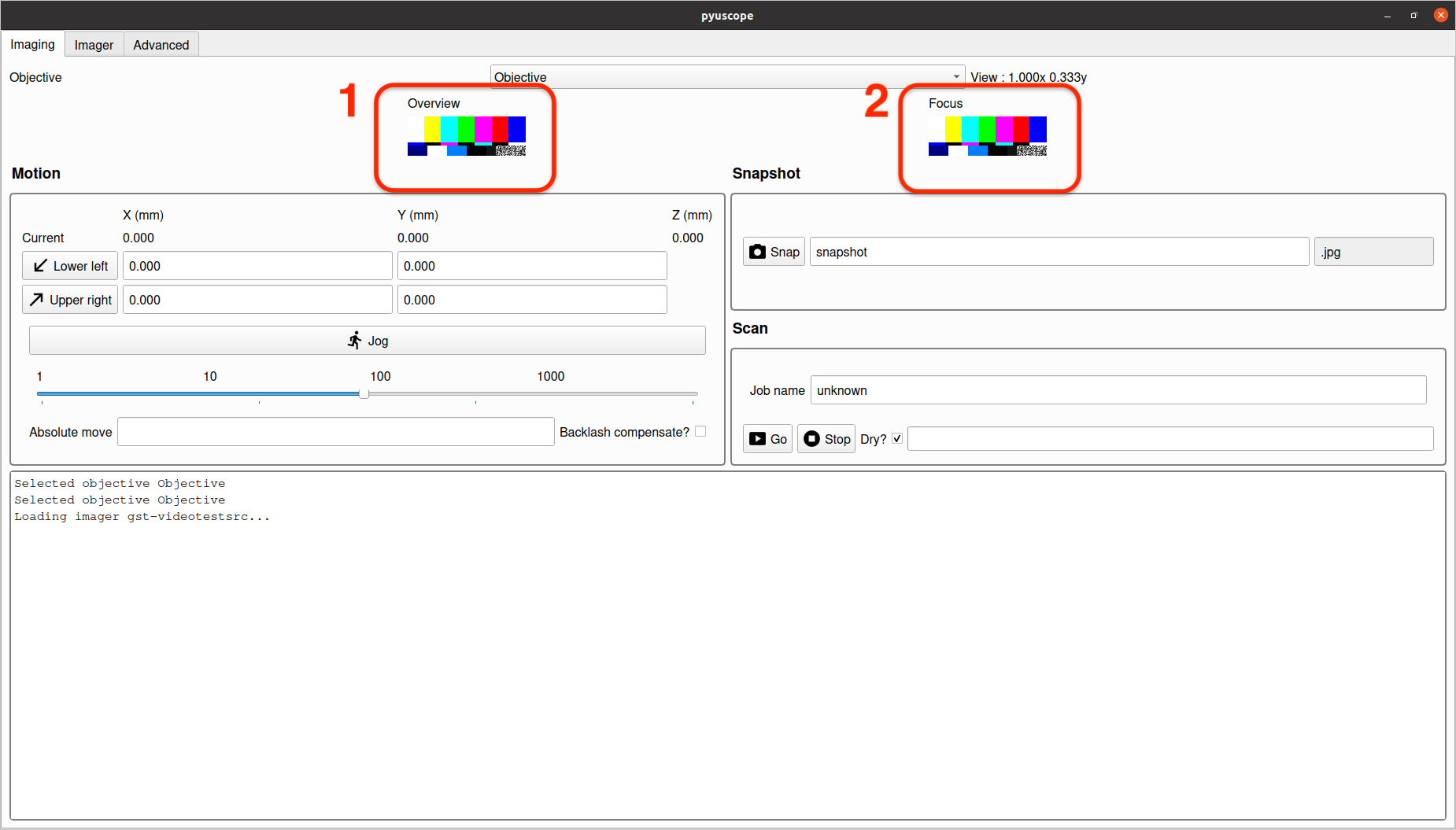
The view in section 1 provides a video feed from the camera.
The view in section 2 provides a magnified sub-area of the camera feed to aid in fine tuning focus. Note: since this view is highly magnified, it may never appear completely sharp, and is intended to be a guide to maximum achievable sharpness.
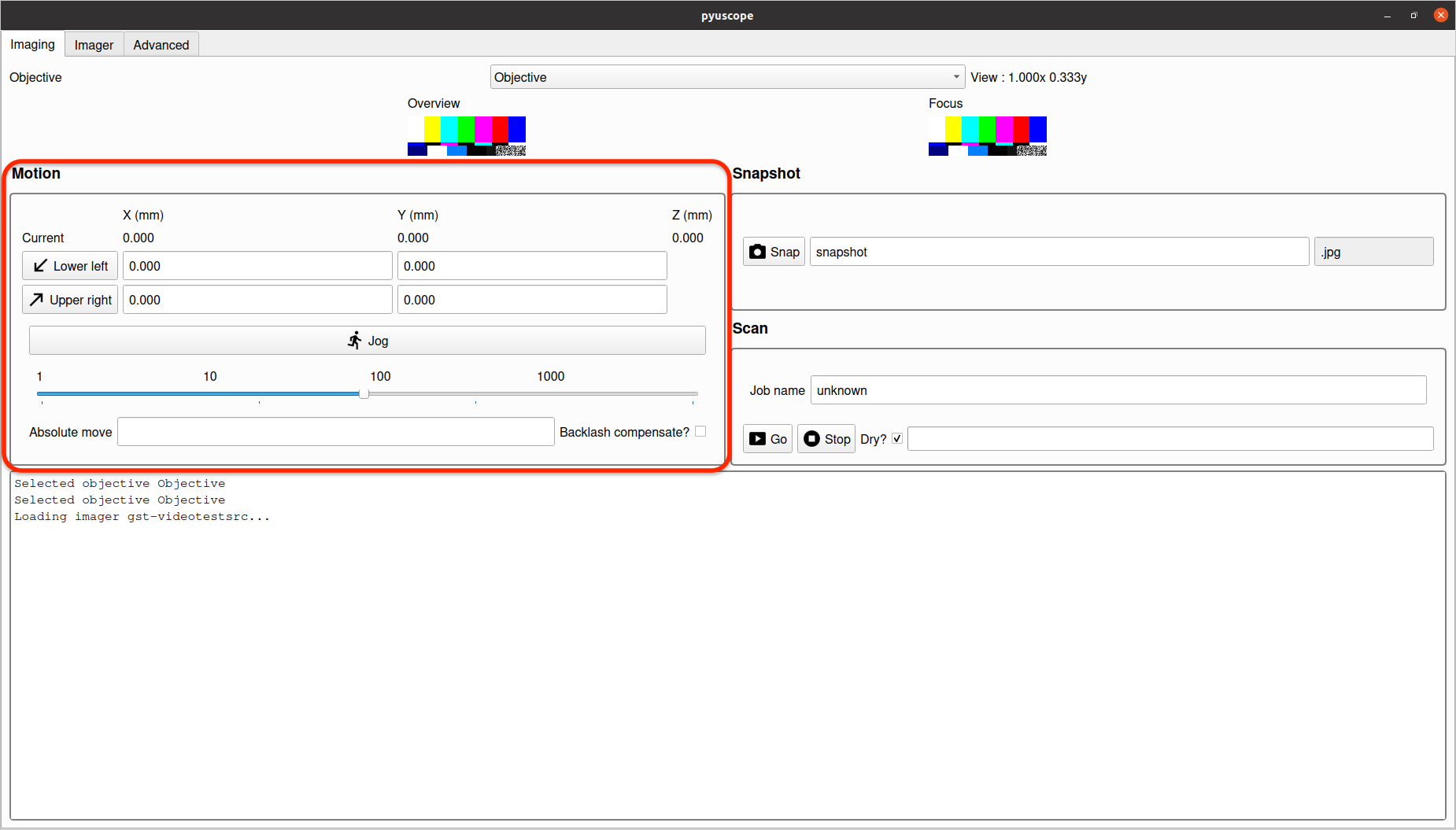
The Motion section provides controls to:
- Set the bounding box for scans.
- Enable
Jogmode to move the microscope and in X, Y and Z directions.
Jog mode allows moving the microscope along the X, Y and Z axis.
Enter and exit Jog mode by toggling the "Jog" button.
The slider controls the speed and amount of each motion command. Use slider value 1 for fine grained motion, and increase the slider for a larger movement amount.
Enter Jog mode, by clicking the "Jog" button, then move the microscope via the following hotkeys:
AandDfor the X-axis motionWandSfor the Y-axis motionQandEfor the Z-axis motionZandCto change rateFto toggle fine mode
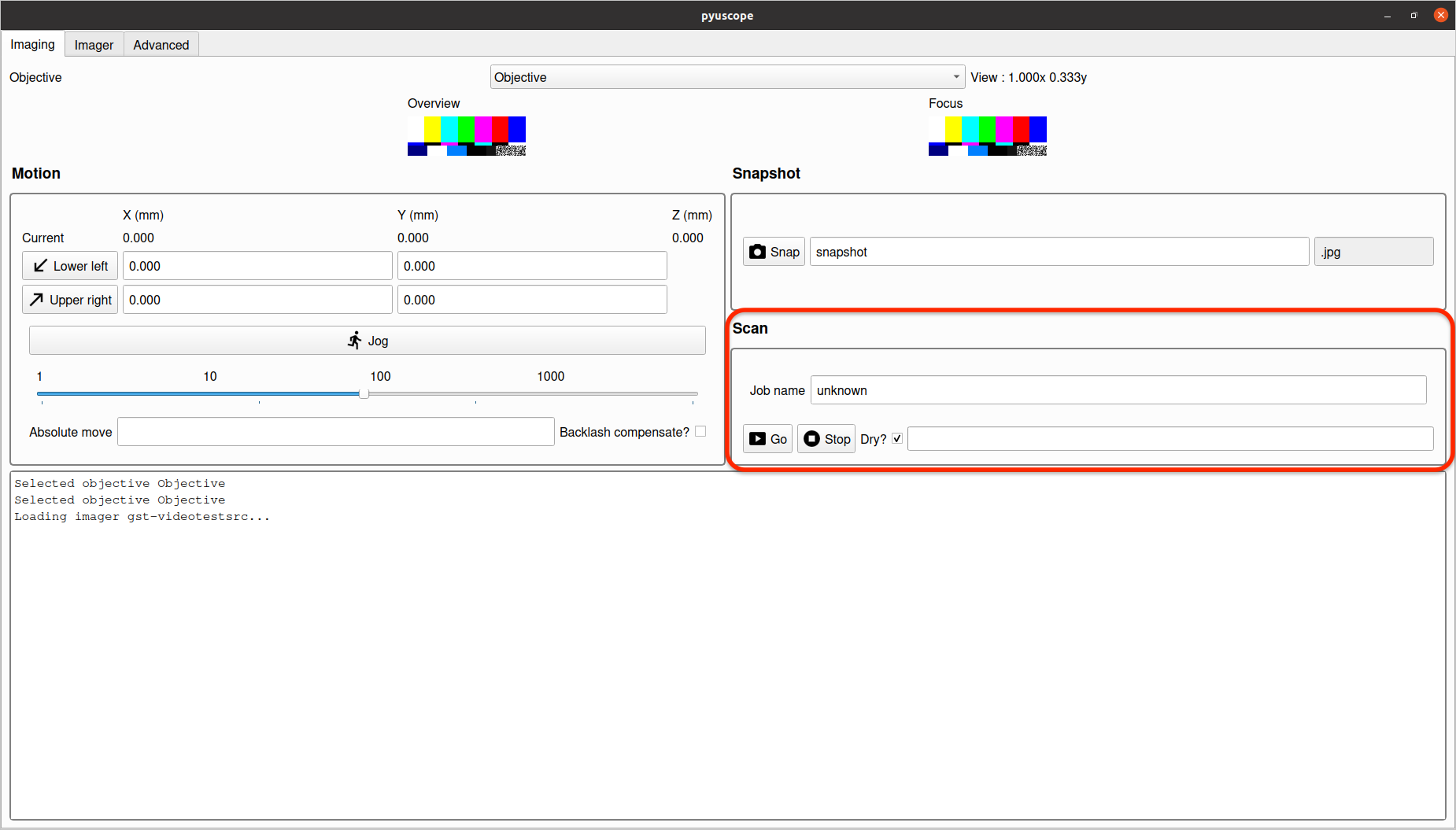
The two buttons Lower left and Upper right provide coordinates to define the area for a scan. To set either, move the microscope to the desired location, and click the button to set the current coordinate as that point.
Note: depending on the configuration of your specific microscope, these points might be flipped (e.g. "Upper left" vs. "Lower left").
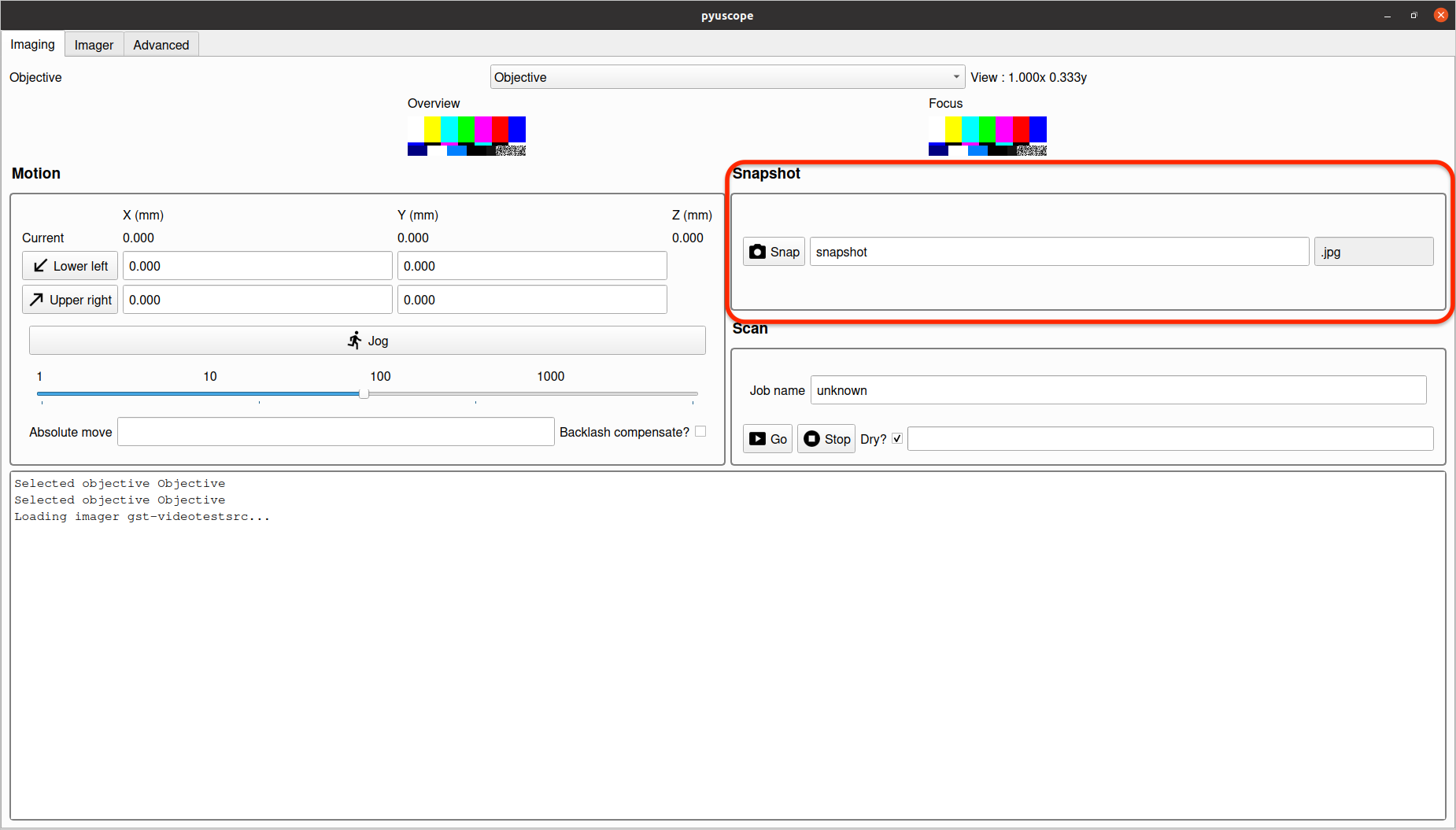
Snapshot saves the current image to the filename specified with a datetime postfix.
A scan performs a motion controlled capture over the area that has been defined by the bounding box points set in the "Motion" section.
If the Dry checkbox is selected, clicking Go will output the expected images that will be taken for the scan.
This area provides logging output and debug information.
Originally I needed to support specialized hardware and wasn't enthusiastic to use Java for MicroManager, the flagship FOSS microchip software. In general the security and lab automation communities continue to revolve around Python which makes integrating various instruments easy into my workflows.
See VERSION.md