NCI-ISBI 2013 Challenge - Automated Segmentation of Prostate Structures (using Keras Data Augmentation)
In this work, I used deep learning methods in automated segmentation of prostate gland.
The data was originally posted on Cancer Imaging Archive website in 2013 for NCI-ISBI competition. More info on this NCI-ISBI competition can be found on Cancer Imaging Archive website.
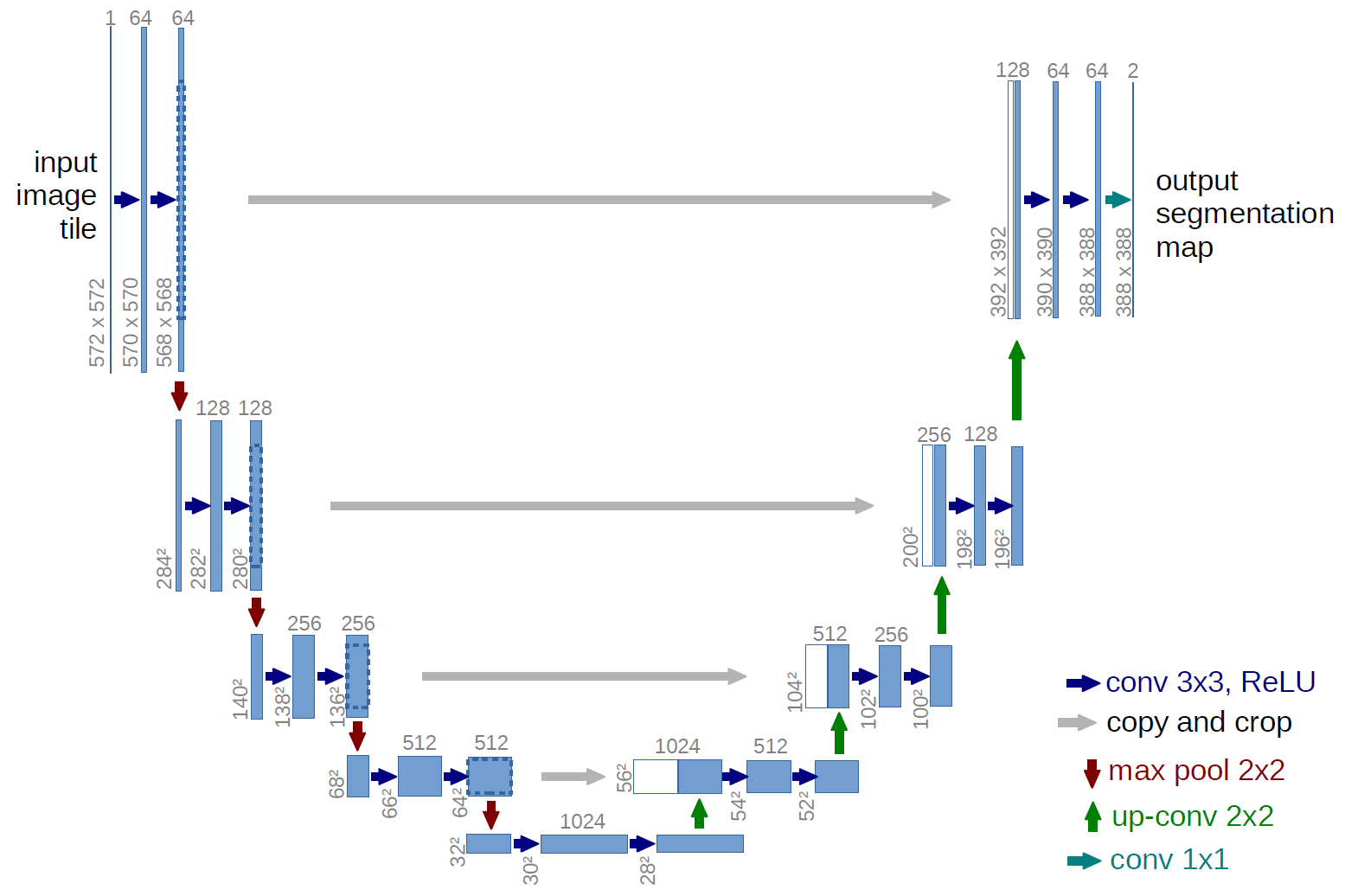
The network architecture was inspired by U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation and by Keras implementation of the model by Marko Josic
This deep neural network (which I call simple U-net) achieves ~0.70 Dice coefficient (max Dice similarity coefficient is 1) on the test images (10 patients and ~300 images), and can be tuned further to achieve better results.
Provided data is processed by dicom_to_array function. After downloading the data extract the files in the following directory structure:
-codes
|
-data
|
---- train
| |
| ---- PatientID
| | |
| | ---- 00001.dcm
| |---- PatientID.nrrd
| |---- ....
---- test
| |
| ---- PatientID
| | |
| | ---- 00001.dcm
| |---- PatientID.nrrd
| |---- ....
---- validate
| |
| ---- PatientID
| | |
| | ---- 00001.dcm
| |---- PatientID.nrrd
| |---- ....
The histogram of the images are equalized using skimage.exposure.equalize_hist.
All the images were resized to 96x96 (better resolution will likely provide better results)
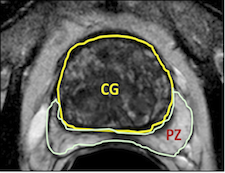
Segmentations (masks) are provided as nrrd files. Peripheral zone (PZ) of the prostate gland is masked with some value close to 1 and the less accessible central gland (CG) is masked with values close to 2. The masks are converted to binary arrays for 1 masking whole prostate gland (not differentiating between CG and PG in this particular model).
The provided model is basically modification of U-Net architecture. Original U-net has millions of weights but there only ~1000 training data available for this segmentation problem. Therefore, to avoid over-fitting, I got rid convolutional layers (both downsampling and upsampling) with 128 and 256 filters. Moreover, I have reduced number of filters in each layer. This gave me ~30k weights to be optimized.
The training set has only ~1000 images with masks. I used Keras's ImageDataGenerator to augment data with random rotations, flips, zooms and shifts. Note that I have used the same image augmentation parameters and random seed for both images and masks. Overall, I have trained the model with fit_generator for ~150k augmented dataset. The model is trained for 30 epochs with batch size 32, where each epoch took ~3 minutes on Nvidia P100 GPUs provided by Ohio Supercomputer Center. Memory footprint of the model is ~2GB.
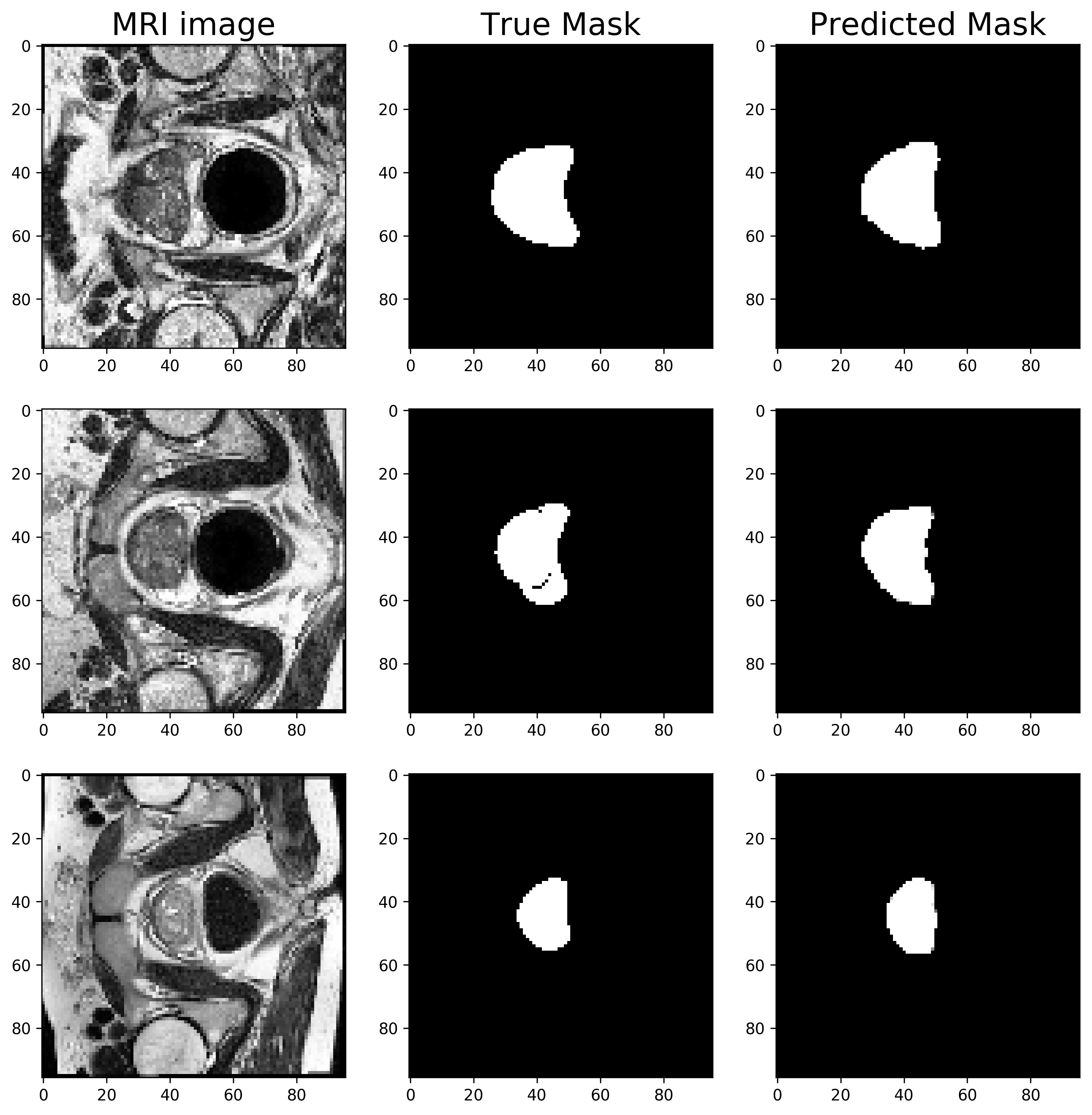
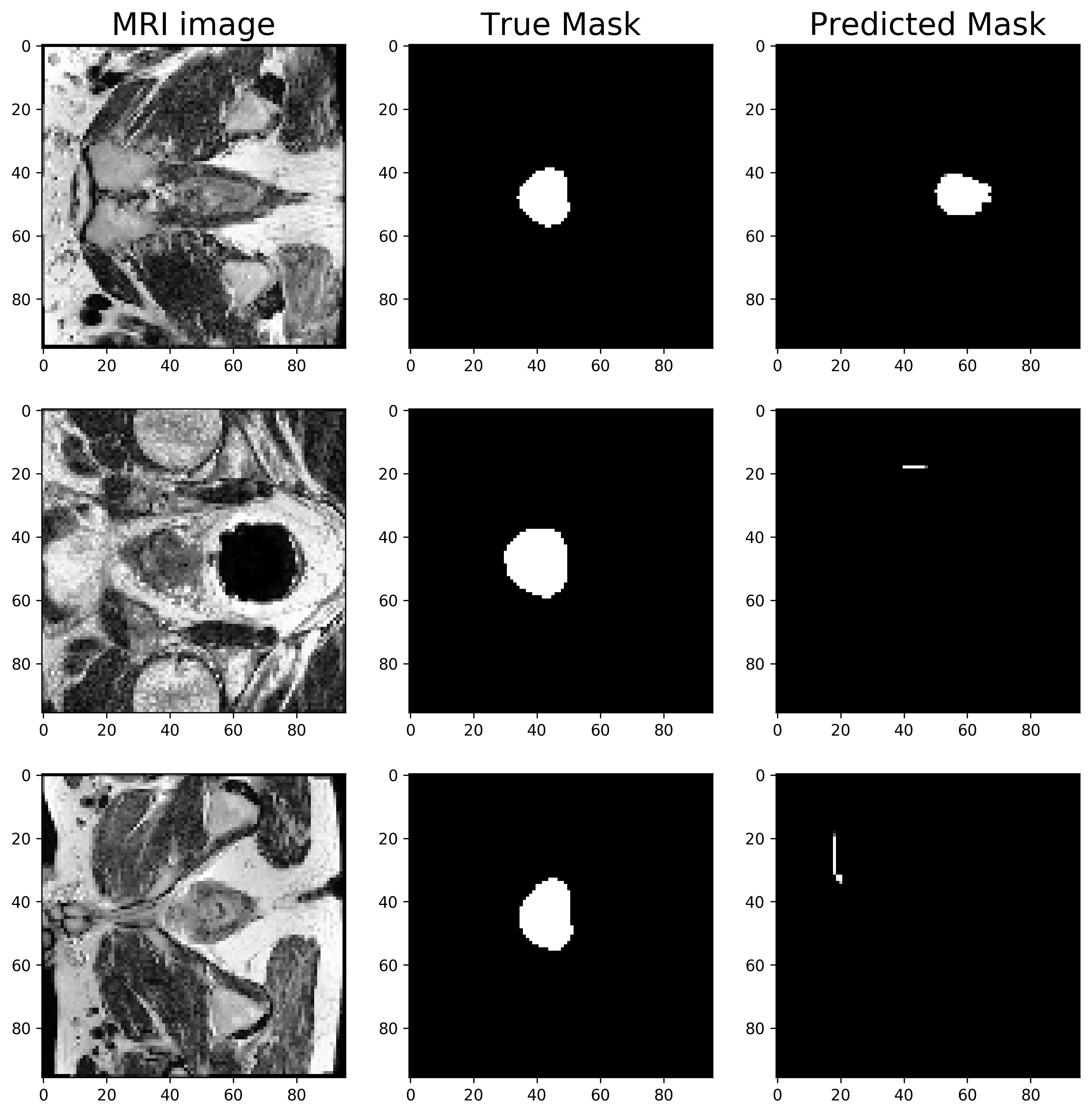
After 30 epochs, calculated Dice coefficient is ~0.70 on test images.
Top 3 predictions by Dice coefficient
Bottom 3 predictions by Dice coefficient
This tutorial depends on the following libraries:
- scikit-image, numpy, matplotlib
- pydicom
- pynrrd
- Tensorflow
- Keras >= 2.0
This code should also be compatible with Theano backend of Keras, but in my experience Theano is slower than TensorFlow.
-
Run
python train.pyto pre-process the data and train the model. Model weights are save in file../data/weights.h5. -
Run
python test.pyto test the model and generate some images with some best and worst predictions.
-
This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Agreement No. 0931642
-
Mathematical Biosciences Institute at Ohio State University