Software for β-Imbalance (BIM): Robust detection of natural selection using a probabilistic model of tree imbalance
Our method can use Tree split sizes or Site Frequency Spectrum as a statistic to infer tree imbalance. To use our program, just clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/jthlab/bim.git
cd bimIn your python session follow the steps.
from Bimbalance import bTree, bSFS #our methods
from utils import Colless, Neutrality_Tests #for comparable statistics
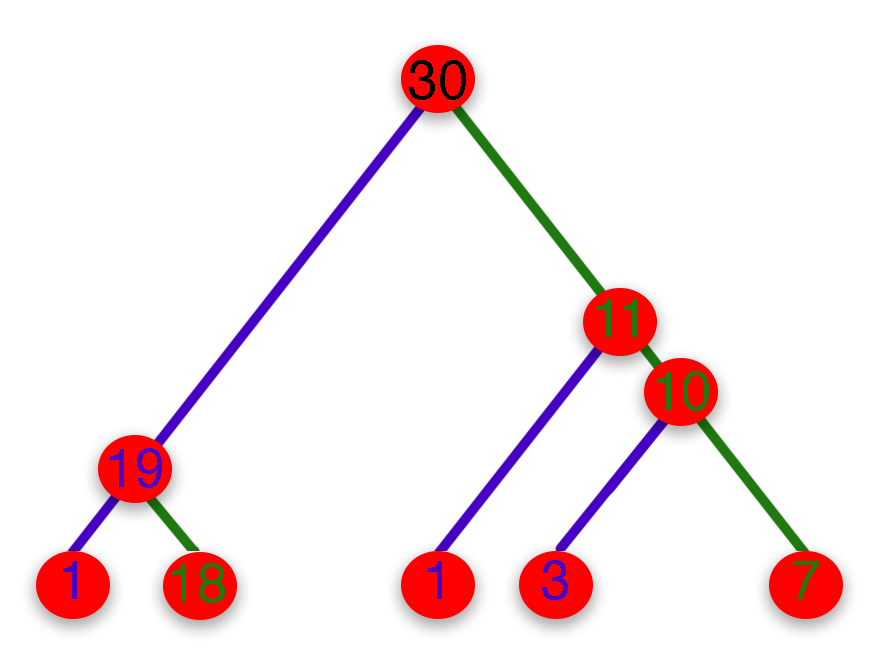
import tskit #for handling tree sequencesWe will use the tree in the figure. Statistic we have is the split sizes. n stores the number of leaves the parent subtends to and k stores the number of leaves that left child subtends to.
In the below, first node subtends 30 leaves (total sample), and its left child subtends 19, n[i] = 30 and k[i] = 19. This figure represents the first
4 splits. Each tree with sample size N have N-1 splits. For this tree at level 5 will experience 25 more splits. So both n and k are arrays with
size N-1.
Our method accepts 2 different tree types, Tskit trees and
Newick string.
- Using Tree-Sequences:
ts = tskit.load('test.trees')
N = ts.num_samples
btree = bTree(N = N) # This will initialize the optimizer for a bifurcating tree with 30 nodes
Tree = ts.first() # Get the first tree from the tree-sequence
n, k = btree.tree_to_splits(Tree)['splits'] # Get the bifurcating tree split sizes from tskit.Tree (see the figure)
bt = btree.predict(n, k, w = n-2) # This will return the optimization result
cl = Colless(n, k) # This will return the Colless statistic for the same tree
print('btree:', '{:.3f}'.format(bt.x[0]),'\nColless:', '{:.3f}'.format(cl))btree: -8.062
Colless: 0.256- Using Newick representation:
nwck = '((12,(9,((23,(10,11)),(((1,((6,(13,(17,18))),((25,(20,21)),(29,30)))),(16,26)),(15,19))))),(5,((24,(3,22)),((14,28),((2,4),(27,(7,8)))))));'
n, k = btree.newick_to_splits(nwck)['splits'] # Get the bifurcating tree split sizes from nwck representation
bt = btree.predict(n, k, w = n-2) # This will return the optimization result
cl = Colless(n, k) # This will return the Colless statistic for the same tree
print('btree:', '{:.3f}'.format(bt.x[0]),'\nColless:', '{:.3f}'.format(cl))btree: -8.062
Colless: 0.256You can use split_predict method to combine split and predict parts.
btree.split_predict(Tree)
btree.split_predict(nwck)This method takes Site Frequency Spectrum as the input. sfs is need to be an array
where sfs[i] = number of mutation which has i+1 copies in the sample
ts = tskit.load('test.trees')
N = ts.num_samples
bsfs = bSFS(N = N)
sfs = ts.allele_frequency_spectrum(polarised=True, span_normalise=False)[1:-1] # Calculate SFS
bs = bsfs.predict(sfs)
print('bsfs:', '{:.3f}'.format(bs.x[0]))bsfs: 0.976We also provided several sfs based statistics. To use them:
nt = Neutrality_Tests(N) # initalize the neutrality class with the given sample size.
print('TajD:', '{:.3f}'.format(nt.TajD(sfs))) # Tajima (1989)
print('FulD:', '{:.3f}'.format(nt.FulD(sfs))) # Fu and Li (1993)
print('FayH:', '{:.3f}'.format(nt.FayH(sfs))) # Fay and Wu (2000)
print('ZngE:', '{:.3f}'.format(nt.ZngE(sfs))) # Zeng et al. (2006)
print('FerL:', '{:.3f}'.format(nt.FerL(sfs))) # Feretti et al. (2017)TajD: 0.370
FulD: -0.213
FayH: 0.043
ZngE: 0.081
FerL: 0.130See this example.
We also provided a tool to infer our imbalance statistics from command line. The first argument is the treefiles seperated by a comma and the second argument is the sample size. If sample size is less than the number of samples in the tree sequence file, program automatically subsamples.
python BIM.py <treeseq_path1,treeseq_path2,...> <sample_size>python BIM.py test.trees 30| start | end | N | SS | FerL | FulD | FayH | TajD | ZngE | bsfs | Colless | btree | path | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 10042 | 30 | 60 | 0.130262 | -0.212967 | 0.043301 | 0.370402 | 0.0806426 | 0.976254 | 0.183981 | 0.274776 | test.trees |
This will calculate all available statistics for test.trees file. For SFS based statistics (bsfs, FerL,FulD,FayH,TajD,ZngE), program first gets allele frequency spectrum of whole sequence
and calculates SFS then it uses the SFS to caclulate those statistics. For tree based statistics (btree, Colless), it calculates the statistic for each tree
then takes a weighted avarage for whole-sequence statistic. (SS is the number of segregating sites)
Note: The dataframe we return have the shell script at top. In order to load the dataframe use below script from the python:
df = pd.read_csv('bim.csv', comment = '#')From the shell, you can print the first line to see the function call that generates bim.csv:
head -n 1 bim.csv#BIM.py test.trees 30Option list:
- --stat=
stat1,stat2,...(defaultall): Enter the statistics by comma. - --wsz=
window_size(defaultNone): Window size for windowed statistic. - --ssz=
stride_size(defaultNone): Stride size for windowed statistic. - --pop=
population_id(defaultNone): See tskit page - --out=
out_path(defaultbim.csv): Output for csv file. - --eta=
eta_path(defaultNone): Path for population size estimates. See the example. - --log_pdf=
log_pdf(defaultlogfs): log pdf of a splitting function. - --r1t=
penalizer(default0): l1 penalty for beta-Tree likelihood. - --r2t=
penalizer(default0): l2 penalty for beta-Tree likelihood. - --r1s=
penalizer(default0): l1 penalty for beta-SFS likelihood. - --r2s=
penalizer(default0): l2 penalty for beta-SFS likelihood. - --treew=
likelihood_weights(defaultsplit): weighting method for beta-Tree likelihood.split,branchorNone.
- Usage with only tree statistics with windows
python BIM.py test.trees 30 --stat=btree,Colless --tsz=1Here is the head of data frame
| start | end | N | btree | Colless | path | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 127.701 | 30 | -8.06225 | 0.256158 | test.trees |
| 1 | 127.701 | 409.431 | 30 | -8.06225 | 0.256158 | test.trees |
| 2 | 409.431 | 1009.27 | 30 | -8.06225 | 0.256158 | test.trees |
| 3 | 1009.27 | 1166.91 | 30 | -2.8385 | 0.251232 | test.trees |
| 4 | 1166.91 | 1633.49 | 30 | -10.6076 | 0.300493 | test.trees |
- Usage with windowed statistics. Window size is 4000 and stride is 2000. We l2 penalize the bsfs and btree likelihoods.
python BIM.py test.trees 30 --stat=bsfs,btree,TajD,FayH --wsz=4000 --ssz=2000 --r2t=0.05 --r2s=0.1| start | end | N | SS | bsfs | FayH | TajD | btree | path | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 4000 | 30 | 25 | -0.0862302 | -0.05856 | -0.188135 | -0.601038 | test.trees |
| 1 | 2000 | 6000 | 30 | 28 | 0.181423 | 0.00457662 | 0.535885 | -0.154576 | test.trees |
| 2 | 4000 | 8000 | 30 | 22 | 0.273358 | 0.115117 | 0.519614 | -0.0365731 | test.trees |
| 3 | 6000 | 10000 | 30 | 21 | 0.266103 | 0.112546 | 0.534623 | 0.56814 | test.trees |
| 4 | 8000 | 10042 | 30 | 13 | 0.266389 | 0.122819 | 1.06633 | 1.1978 | test.trees |
- Usage with some effective population size estimate. It is located at
testeta.json.
python BIM.py test.trees 30 --stat=bsfs,btree,TajD,FayH --wsz=4000 --ssz=2000 --r2t=0.05 --r2s=0.1 --eta=testeta.json| start | end | N | SS | bsfs | TajD | FayH | btree | path | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 4000 | 30 | 25 | -0.100229 | -0.188135 | -0.05856 | -0.601038 | test.trees |
| 1 | 2000 | 6000 | 30 | 28 | 0.172588 | 0.535885 | 0.00457662 | -0.154576 | test.trees |
| 2 | 4000 | 8000 | 30 | 22 | 0.264042 | 0.519614 | 0.115117 | -0.0365731 | test.trees |
| 3 | 6000 | 10000 | 30 | 21 | 0.257641 | 0.534623 | 0.112546 | 0.56814 | test.trees |
| 4 | 8000 | 10042 | 30 | 13 | 0.264506 | 1.06633 | 0.122819 | 1.1978 | test.trees |
Population size option (--eta) only accounted in bsfs. You can see it only changed that.