Controlling complex (directed) networks using Reinforcement Learning frameworks. Problem is framed as discrete time
linear system over a finite (Galois) field, defined as:
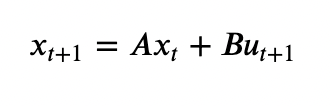
Where states and inputs of are over a finite field.
import numpy as np
from network_control_rl.rl import QLearning
from network_control_rl.algebra import BaseNumber
from network_control_rl.network import Network
network = Network()
network.from_edges([(0, 1), (1, 2), (2, 3)]) # Network can be build from (directed) links
input_matrix = {0: 0} # mapping order of driver nodes
q = 4 # order of the finite field and base of the number system
n = network.nodes # number of nodes / state vector size
initial_state = BaseNumber(n, q)
initial_state.from_array(np.array([1, 2, 3, 1]))
end_state = BaseNumber(n, q)
end_state.from_array(np.array([1, 3, 2, 1]))
model = QLearning(
initial_state,
end_state,
network,
input_matrix,
num_episodes=50,
max_iteration=10
)
model.train(seed=6)
model.get_signals(vector=True)
>>> array([[2], [3], [1]]) # ordered list of signals for each time stepIn this repo we use a few tools to keep the code clean, styled and properly tested:
make lint # runs flake8, Bandit and Black check
make format # runs Black formating
make typecheck # runs mypy
make test # runs unit [py]testsWe are using Poetry.
[1] Sutton, R. S., & Barto, A. G. (2018), "Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction", The MIT Press.
[2] Newman, M. E. J. (2010), "Networks: an introduction", Oxford University Press, Oxford; New York
[3] Diestel, R. (2002), "Graph Theory, Springer", Volume 173 of Graduate texts in mathematics, ISSN 0072-5285
[4] Brunton, S., & Kutz, J. (2019). "Data-Driven Science and Engineering: Machine Learning", Dynamical Systems, and Control. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/9781108380690
[5] Liu, Y. Y., & Barabasi, A. L. (2016), "Control Principes of Complex Networks", 10.1103/RevModPhys.88.035006
[6] Liu, Y. Y., & Slotine, J. J., & Barabási, A. L. (2011), "Controllability of complex networks". Nature 473, 167–173. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10011
[7] John Kerl, (2004), "Computation in finite fields", https://johnkerl.org/doc/ffcomp.pdf
This package was created with Cookiecutter from matejker / cookiecutter-poetry project template.