The aim of this project is to integrate several sub-systems of a self-driving car using the robotics framework Robot Operative System (ROS). The overall system should be able to drive across a simulation at a constant speed following the lane and stopping whenever a traffic light is red. The car will slow down when approaching a red traffic light and accelerate again whenever it turns green. In particular, the components of this project were implementing ROS nodes for:
- The drive-by-wire (DBW) system, as a part of the control module. Implemented in the
/src/waypoint_updater/waypoint_updater.py - The control of the steering, the brakes and the velocity/acceleration, as a part of the control module. Implemented in the
/src/twist_controller/twist_controller.pyfile. - The waypoint updates, as a part of the planning module. Implemented in the `
- The traffic light processing, as a part of the perception module. Implemented in the `
This project uses the Capstone Project CarND Simulator in order to provide data to the ROS environment and to visualize the car behavior, points of the generated trajectory and data from the vehicle.
Further details are exposed in the Technical Details section. The result can be visualized in the following YouTube demo, where the green dots are the 200 next car positions and some information is shown on the right, such as velocity, accelerations and acceleration derivative (jerk).
This work will be followed by a brief documentation/overview contained in this file. This project is a completed version of the sample project template provided by the Self-Driving Car Engineer Udemy's Nanodegree. The un-completed original version is this repository.
The car tries to drive at 24 MPH in the center lane. When a traffic light in red is detected in the next 200 waypoints, the car will start adapting the velocity of each waypoint in order to be able to stop in the stop line. If the state of the traffic light switches to green, the car will accelerate smoothly to reach the configured speed limit. The changes in the velocity are done following a square root function depending on the distance from the car to the stop line. This way, the braking will be smooth when the car is far (and the speed is higher) and it will be harder as it approaches the stop line.
As mentioned before, the development of this project is formed by the implementation of the following ROS nodes:
- waypoint_updater: Planning module. Gets the base waypoints and combines them with the traffic light information to create and send the final waypoints in sets of 200. Implemented in the
/src/waypoint_updater/waypoint_updater.pyfile. - dbw_node: Drive-by-wire module, implemented in the
/src/twist_controller/dbw_node.pyfile. It uses the controllers defined in theControllerclass of the /src/twist_controller/twist_controller.pyfile. - tl_detector: It provides the system with the waypoints of the traffic lights stop lines and their states (red, yellow or green). It is in the
/src/tl_detector/tl_detector.pyfile.
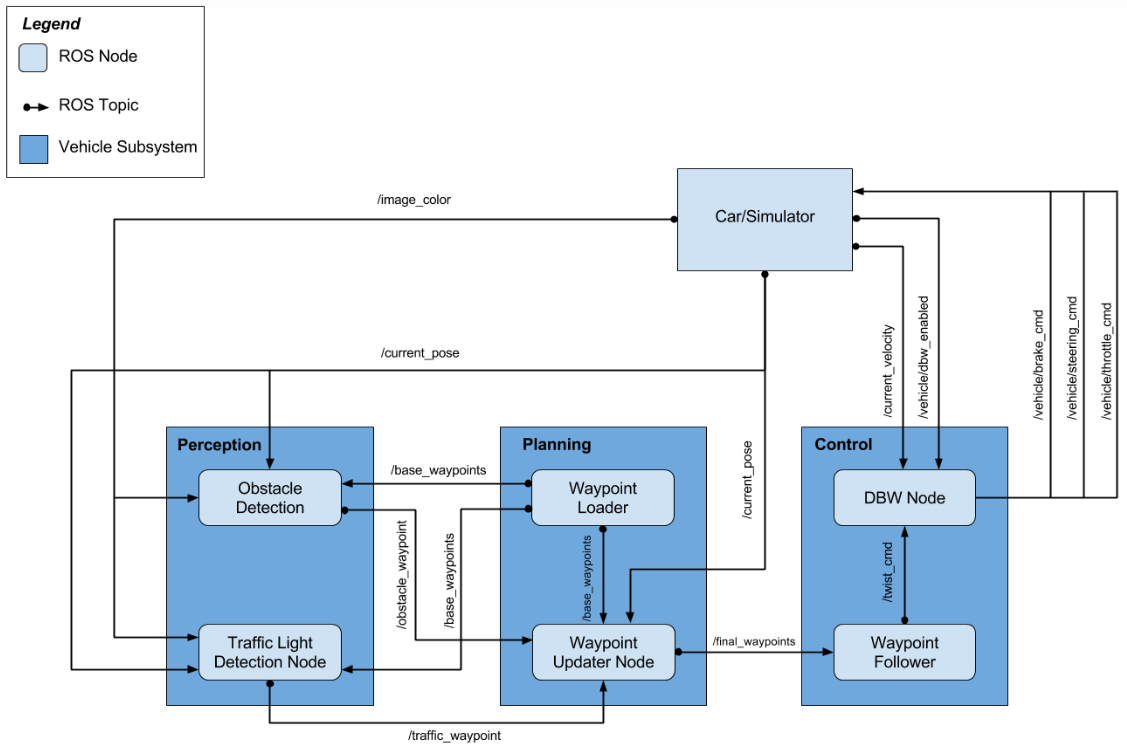
The system architecture is described in the following diagram:
Regarding the control, the provided yaw_controller (src/twist_controller/yaw_controller.py) is used for the steering control. A low pass filter (LPF) is used to smooth the velocity changes because the readings are noisy. A PID controller is used to control the throttle. As this project was prepared to be loaded in the Udacity's real autonomous car (Carla), it provides control comands at 50Hz. This is done because it gives warnings if it is lower and switches to manual mode when it is under 10 Hz. Another relevant appreciation is that this real car is automatic, so it needs over 700 Nm of braking torque to keep it stopped, which is also considered in the code. For the rest of braking operations, the necessary torque is computed by multiplying the vehicle mass, the radio of the wheels and the desired acceleration.
About the perception module, the following repositories can be used to build a Deep Learning-based traffic light detection:
Finally, about the simulator, for performance reasons, I did the development executing it in my host system, while running ROS in a virtual machine (with Ubuntu 16.04 and ROS Kinetic). This can be done using port forwarding. i.e. opening in the virtual machine the port used by the simulator so that it can communicate with the host operative system and exchange information between the ROS ecosystem and the simulator. It can be done by following this tutorial. You will need to open the port 4567 with a TCP protocol.
In order to install and run this project, as explained in the original template repo, it can be done nativelly or using docker containers.
-
Be sure that your workstation is running Ubuntu 16.04 Xenial Xerus or Ubuntu 14.04 Trusty Tahir. Ubuntu downloads can be found here.
-
If using a Virtual Machine to install Ubuntu, use the following configuration as minimum:
- 2 CPU
- 2 GB system memory
- 25 GB of free hard drive space
The Udacity provided virtual machine has ROS and Dataspeed DBW already installed, so you can skip the next two steps if you are using this.
-
Follow these instructions to install ROS
- ROS Kinetic if you have Ubuntu 16.04.
- ROS Indigo if you have Ubuntu 14.04.
-
- Use this option to install the SDK on a workstation that already has ROS installed: One Line SDK Install (binary)
-
Download the Udacity Simulator.
Build the docker container
docker build . -t capstoneRun the docker file
docker run -p 4567:4567 -v $PWD:/capstone -v /tmp/log:/root/.ros/ --rm -it capstone- Clone the project repository
git clone https://github.com/udacity/CarND-Capstone.git- Install python dependencies
cd CarND-Capstone
pip install -r requirements.txt- Make and run styx
cd ros
catkin_make
source devel/setup.sh
roslaunch launch/styx.launch- Run the simulator
- Download training bag that was recorded on the Udacity self-driving car.
- Unzip the file
unzip traffic_light_bag_file.zip- Play the bag file
rosbag play -l traffic_light_bag_file/traffic_light_training.bag- Launch your project in site mode
cd CarND-Capstone/ros
roslaunch launch/site.launch- Confirm that traffic light detection works on real life images
Outside of requirements.txt, here is information on other driver/library versions used in the simulator and Carla:
Specific to these libraries, the simulator grader and Carla use the following:
| Simulator | Carla | |
|---|---|---|
| Nvidia driver | 384.130 | 384.130 |
| CUDA | 8.0.61 | 8.0.61 |
| cuDNN | 6.0.21 | 6.0.21 |
| TensorRT | N/A | N/A |
| OpenCV | 3.2.0-dev | 2.4.8 |
| OpenMP | N/A | N/A |
We are working on a fix to line up the OpenCV versions between the two.