REXUP: I REason, I EXtract, I UPdate with Structured Compositional Reasoning for Visual Question Answering
Luo, S.*, Han, S. C.*, Sun, K., & Poon, J. (2020). ICONIP 2020
REXUP: I REason, I EXtract, I UPdate with Structured Compositional Reasoning for Visual Question Answering (BEST PAPER AWARD - ICONIP2020)
For any issue related to code, pls first search for solution in Issues section, if there is no result, pls post a comment in "Issues" section, we will help soon.
This is an implementation of the REXUP network to take advantage of scene graph from the the GQA dataset. GQA is a new dataset for real-world visual reasoning, offrering 20M diverse multi-step questions, all come along with short programs that represent their semantics, and visual pointers from words to the corresponding image regions. Here we extend the MAC network to work over VQA and GQA, and provide multiple baselines as well.
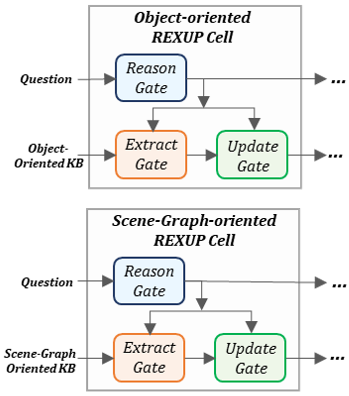
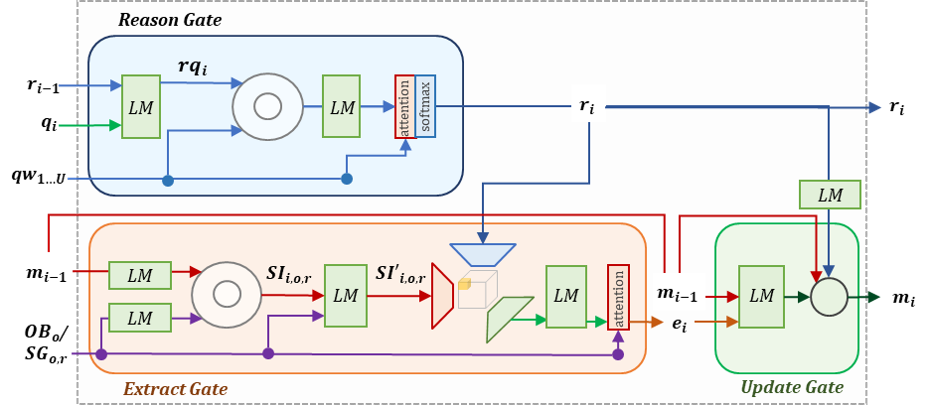
decription for REXUP NETWORK The REXUP network contains two parallel branches, object-oriented branch and scene-graph oriented branch. Each branch contains a sequence of REXUP cells where each cell operates for one reasoning step for the answer prediction.
Please cite the following if you use any of our code
@article{siwen2020rexup,
title={REXUP: I REason, I EXtract, I UPdate with Structured Compositional Reasoning for Visual Question Answering},
author={Siwen Luo, Soyeon Caren Han, Kaiyuan Sun and Josiah Poon},
conference={International Conference on Neural Information Processing},
year={2020}
}
Note: To make sure that you can reimplement our model and result, we recommand you to use Dockerfile and Makefile we provide in this github to create a same environment as we conduct.
- We have performed experiments on Titan RTX GPU with 24GB of GPU memory, from experiments, our model needs around 20GB GPU memory with 128 batch size, you can reduce the batch size to reduce the total memory you need.
Let's begin from cloning this reponsitory branch:
git clone https://github.com/usydnlp/REXUP.git
- run
pip install dockerto install docker in your server. - cd into the folder, run
sudo build maketo create an image of the location. - use
sudo maketo start a docker image. (if you have any issue related to GPU-support dokcer image, pls refer to docker GPU website)
Before training the model, you have to download the GQA dataset and extracted features for the images.
To download and unpack the data, run the following commands:
mkdir data
cd data
wget https://nlp.stanford.edu/data/gqa/data1.2.zip
unzip data1.2.zip
wget http://nlp.stanford.edu/data/glove.6B.zip
unzip glove.6B.zip
cd ../
- The data zip file here contains only the minimum information and splits needed to run the model in this repository. To access the full version of the dataset with more information about the questions as well as the test/challenge splits please download the questions from the
official download page.
mkdir data
cd data
wget http://nlp.stanford.edu/data/glove.6B.zip
unzip glove.6B.zip -d glove
mkdir gqa
cd gqa
wget https://nlp.stanford.edu/data/gqa/sceneGraphs.zip
unzip sceneGraphs.zip -d sceneGraphs
wget https://nlp.stanford.edu/data/gqa/questions1.3.zip
unzip questions1.3.zip -d questions
Alternatively, if you have the latest version of the GQA dataset already downloaded, use symlinks to link to the dataset items.
cd data
wget http://nlp.stanford.edu/data/gqa/objectFeatures.zip
unzip objectFeatures.zip
cd ../
python merge.py --name objects
To train the model, run the following command:
python main.py --expName "gqaExperiment" --train --testedNum 10000 --epochs 25 --netLength 4 @configs/gqa/gqa_ensemble.txt
First, the program preprocesses the GQA questions. It tokenizes them and maps them to integers to prepare them for the network. It then stores a JSON with that information about them as well as word-to-integer dictionaries in the data directory.
Then, the program trains the model. Weights are saved by default to ./weights/{expName} and statistics about the training are collected in ./results/{expName}, where expName is the name we choose to give to the current experiment.
- The number of examples used for training and evaluation can be set by
--trainedNumand--testedNumrespectively. - You can use the
-rflag to restore and continue training a previously pre-trained model. - We recommend you to try out varying the number of REXUP cells used in the network through the
--netLengthoption to explore different lengths of reasoning processes. - Good lengths for GQA are in the range of 2-6.
See config.py for further available options (Note that some of them are still in an experimental stage).
To evaluate the trained model, and get predictions and attention maps, run the following:
python main.py --expName "gqaExperiment" --finalTest --testedNum 10000 --netLength 4 -r --getPreds --getAtt @configs/gqa/gqa_ensemble.txt
The command will restore the model we have trained, and evaluate it on the validation set. JSON files with predictions and the attention distributions resulted by running the model are saved by default to ./preds/{expName}.
- In case you are interested in getting attention maps (
--getAtt), and to avoid having large prediction files, we advise you to limit the number of examples evaluated to 5,000-20,000.