Implementation of control algorithms for the cart-pole system, including Nonlinear Model Predictive Control (NMPC), Linear Quadratic Control (LQR), and Linear Model Predictive Control (LMPC).
-
Linear Quadratic Regulator (LQR)
- Infinite-horizon using Continuous Algebraic Riccati Equation (CARE)
- Infinite-horizon using Discrete Algebraic Riccati Equation (DARE)
- Finite-horizon LQR
Infinite-horizon LQR (CARE) Infinite-horizon LQR (DARE) Finite-horizon LQR 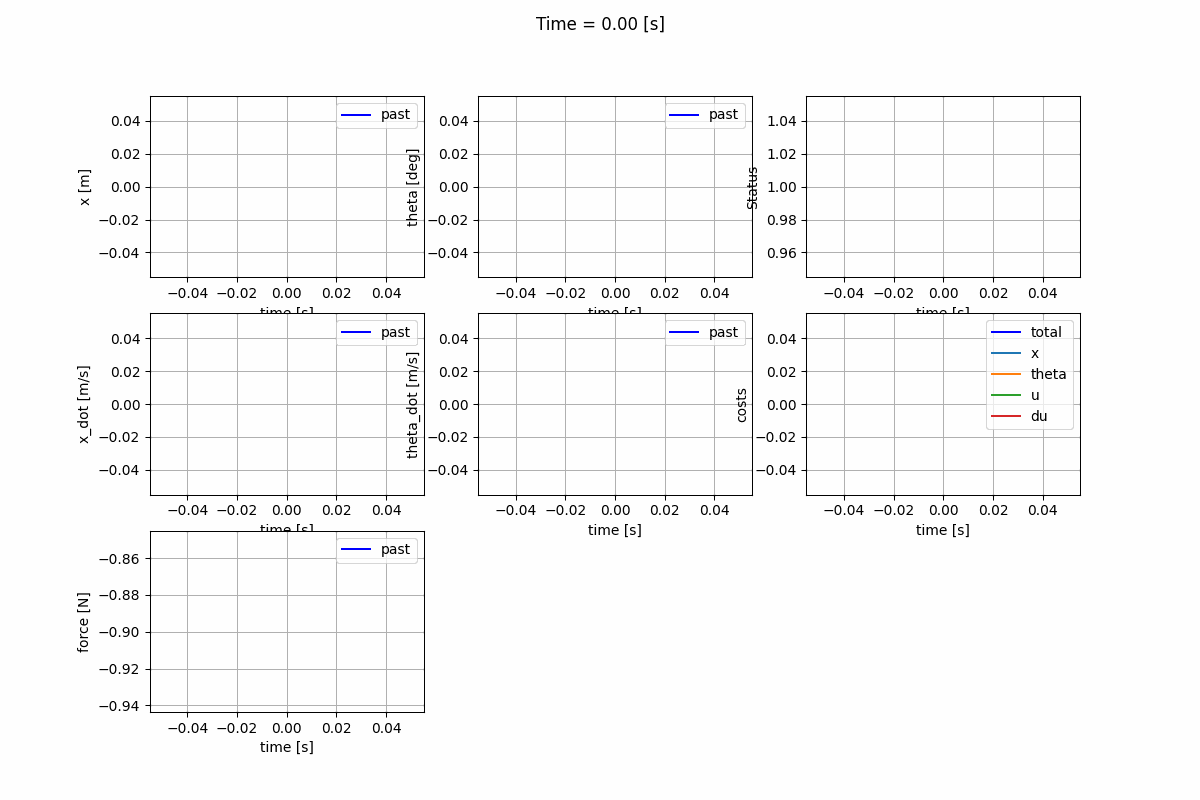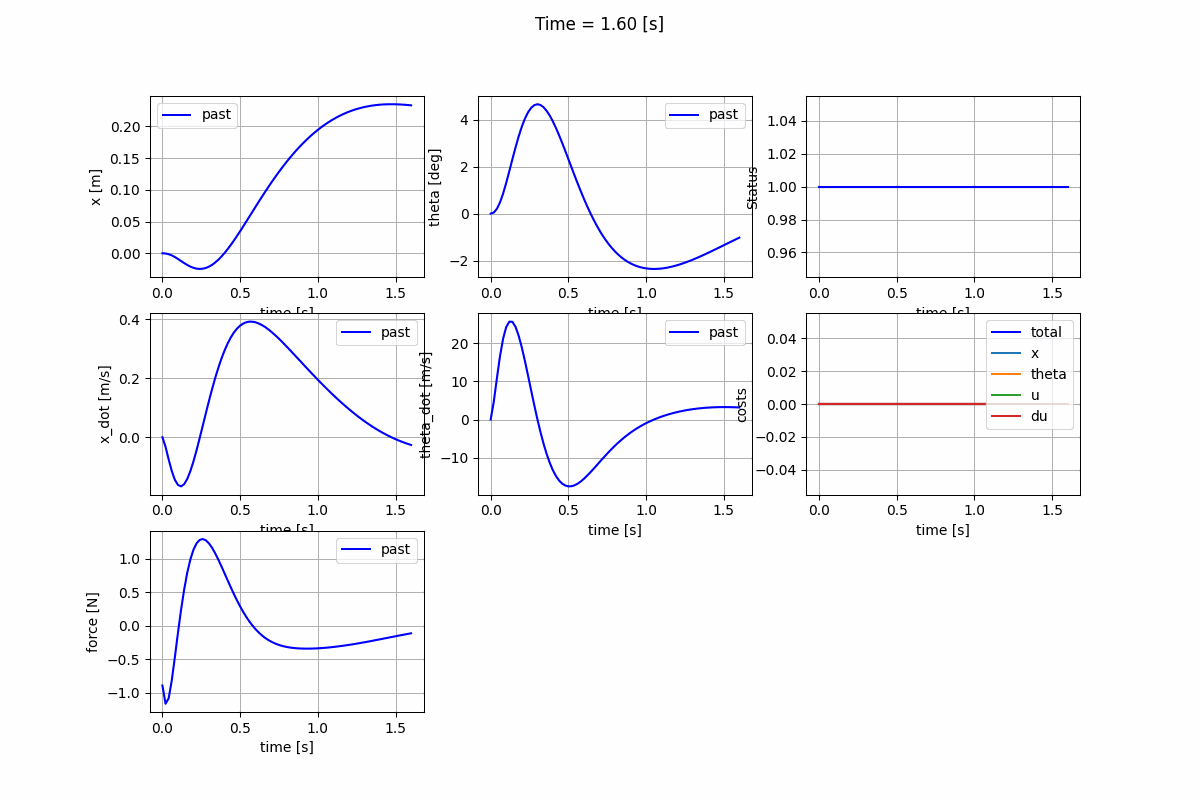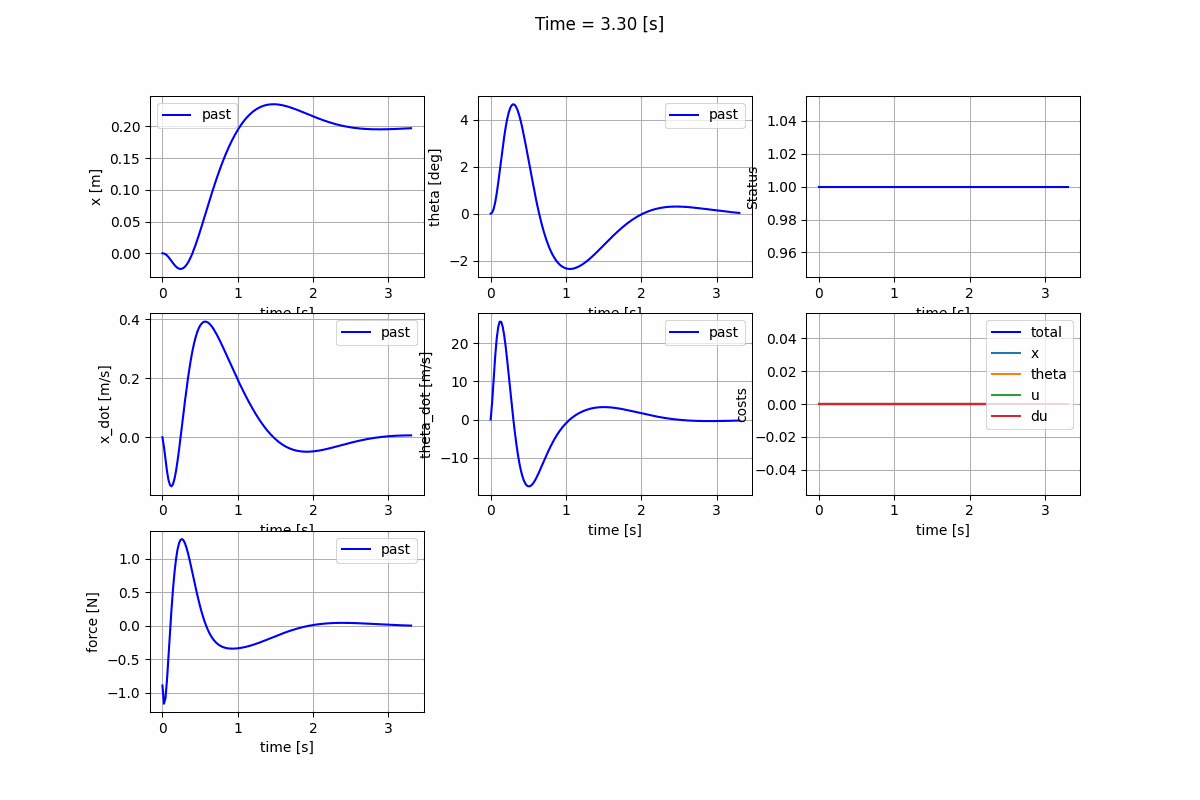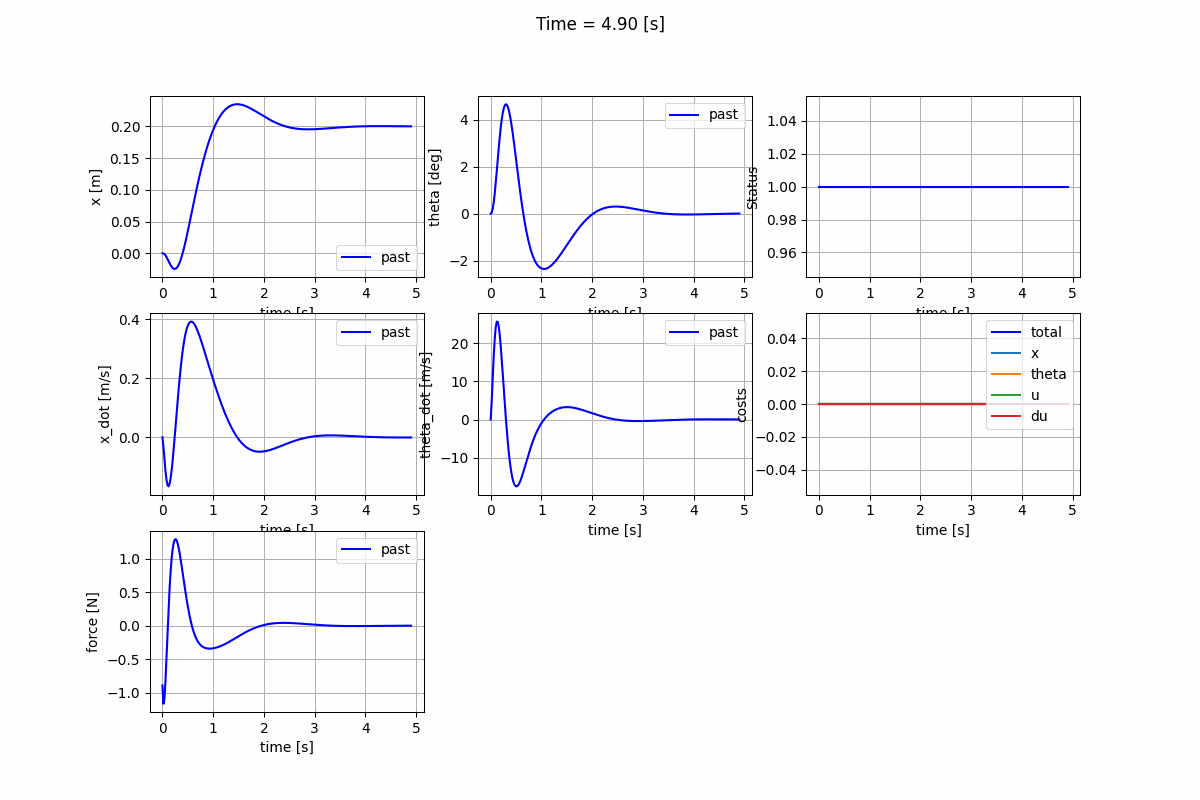

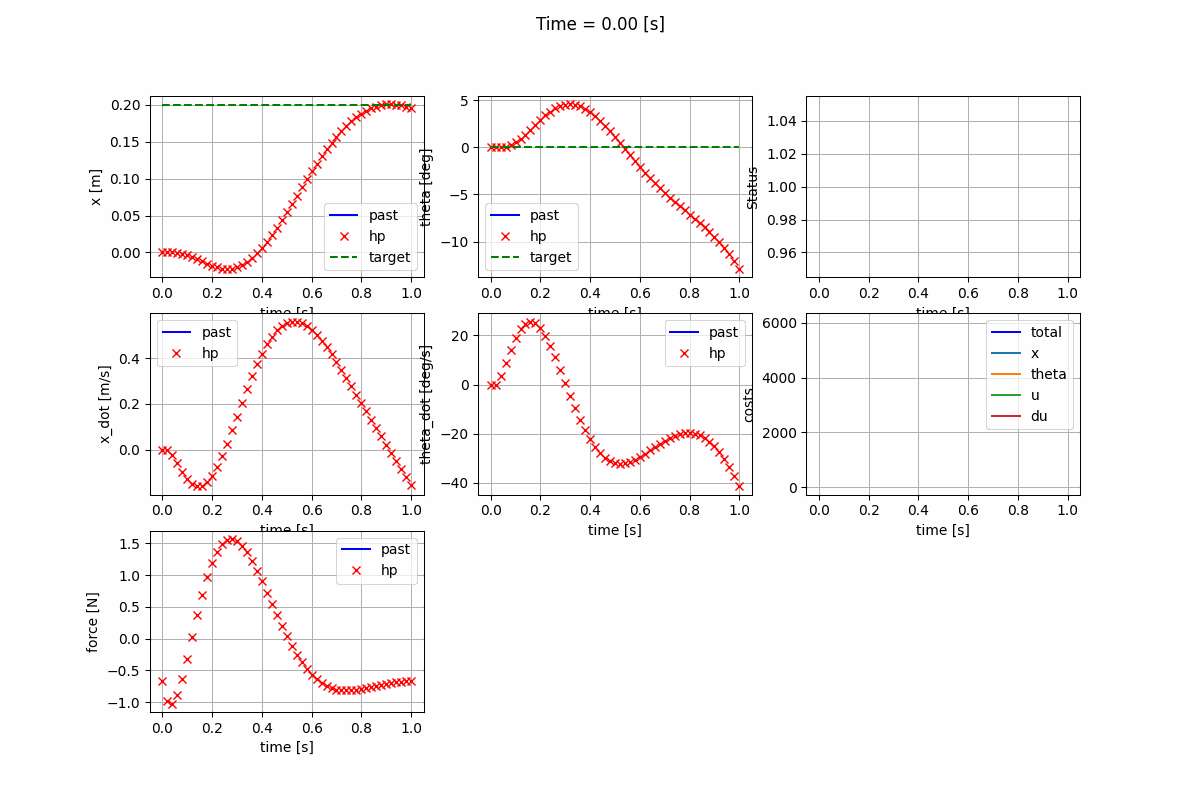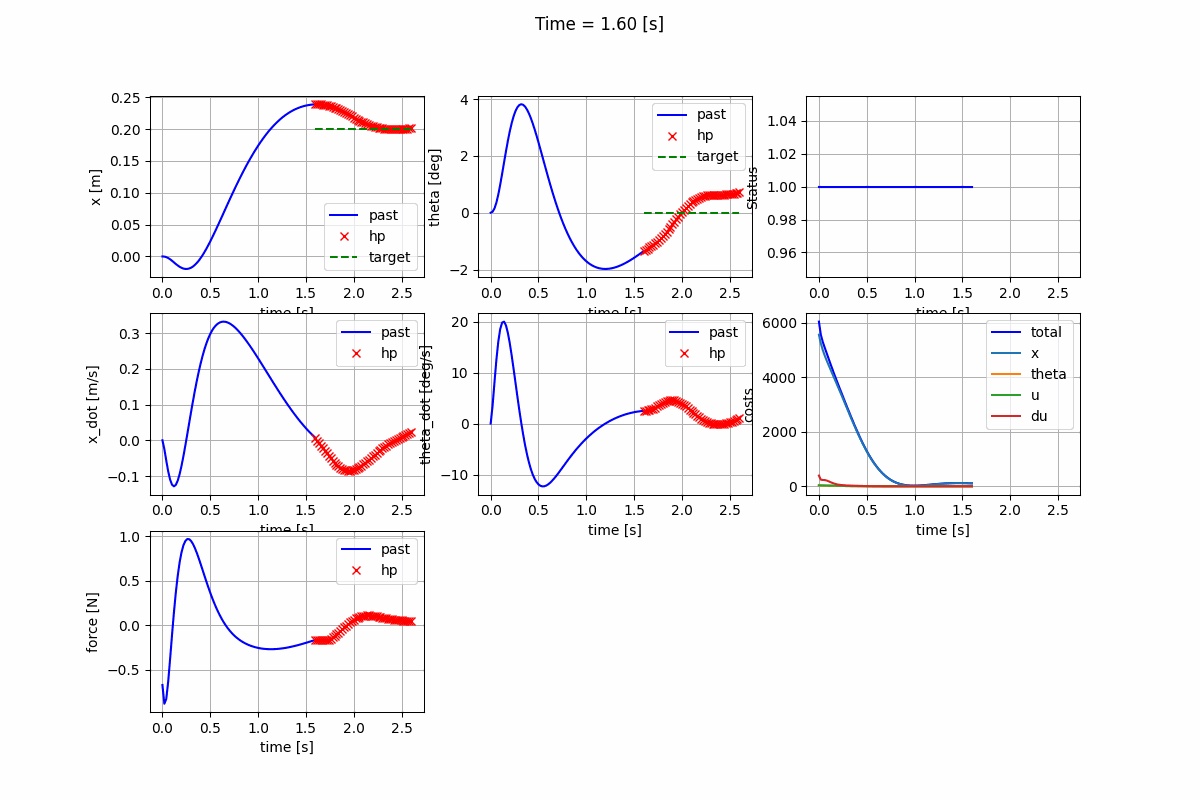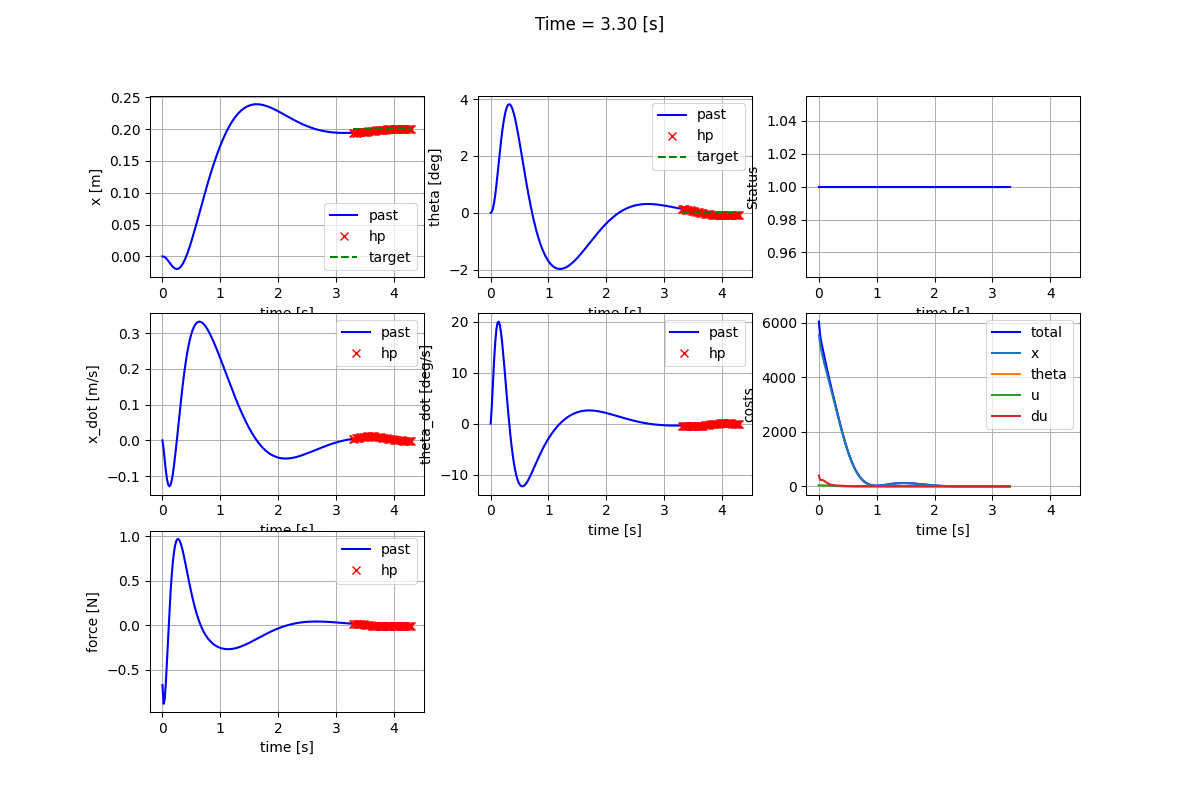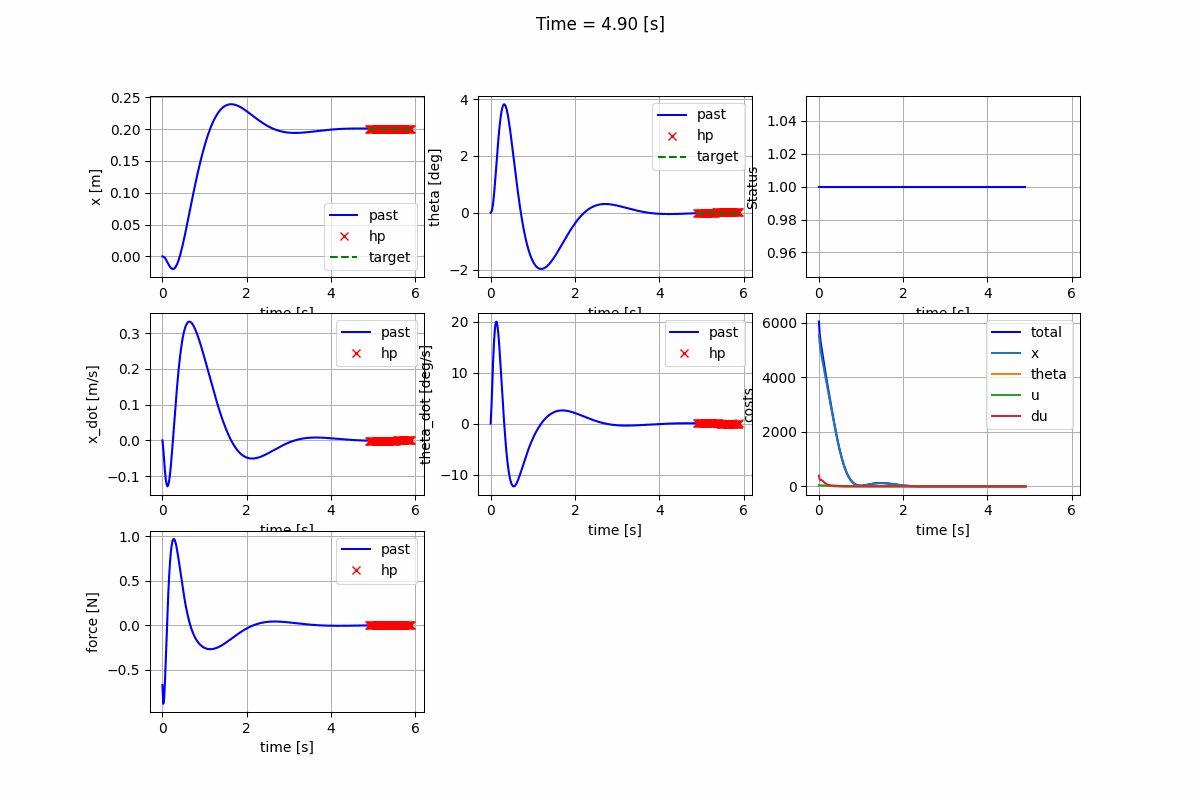
-
Linear Model Predictive Control (LMPC)
- Unconstrained LMPC with analytical solution
- Constrained LMPC using Quadratic Programming (QP) solver
Unconstrained LMPC Constrained LMPC 

-
Nonlinear Model Predictive Control (NMPC)
Nonlinear Model Predictive Control (NMPC) 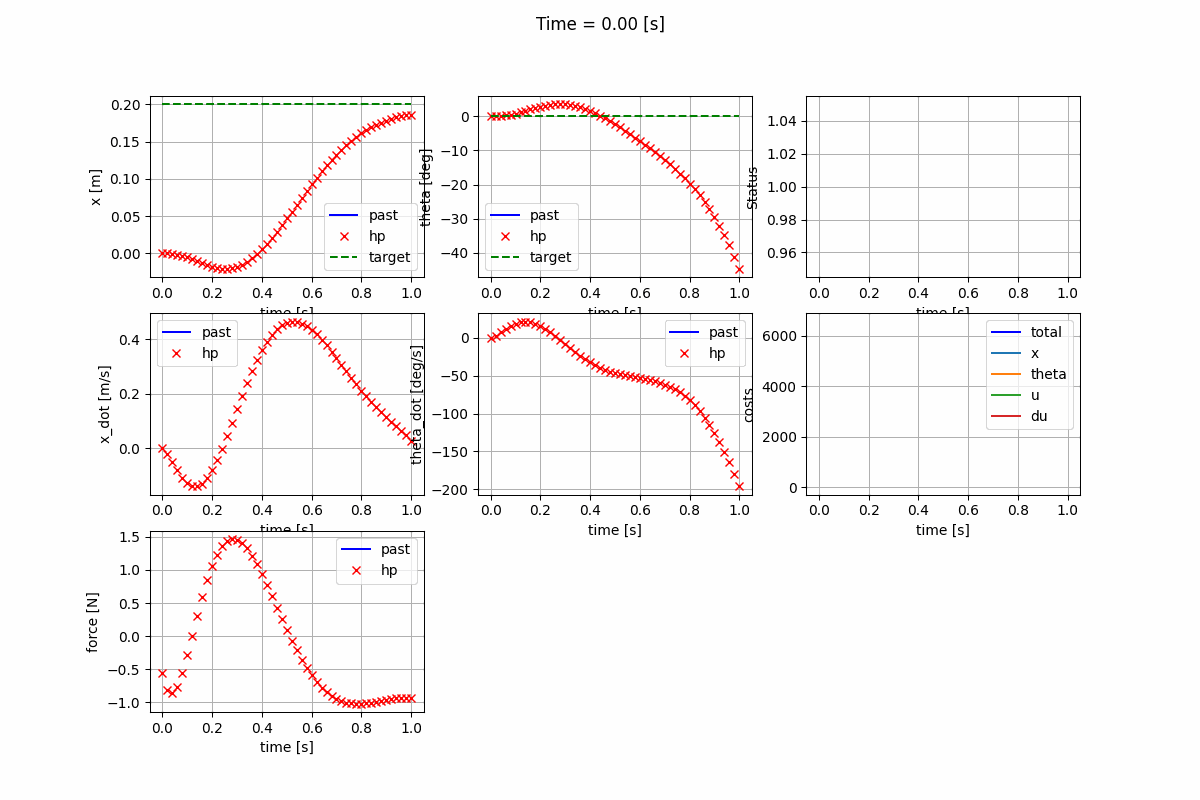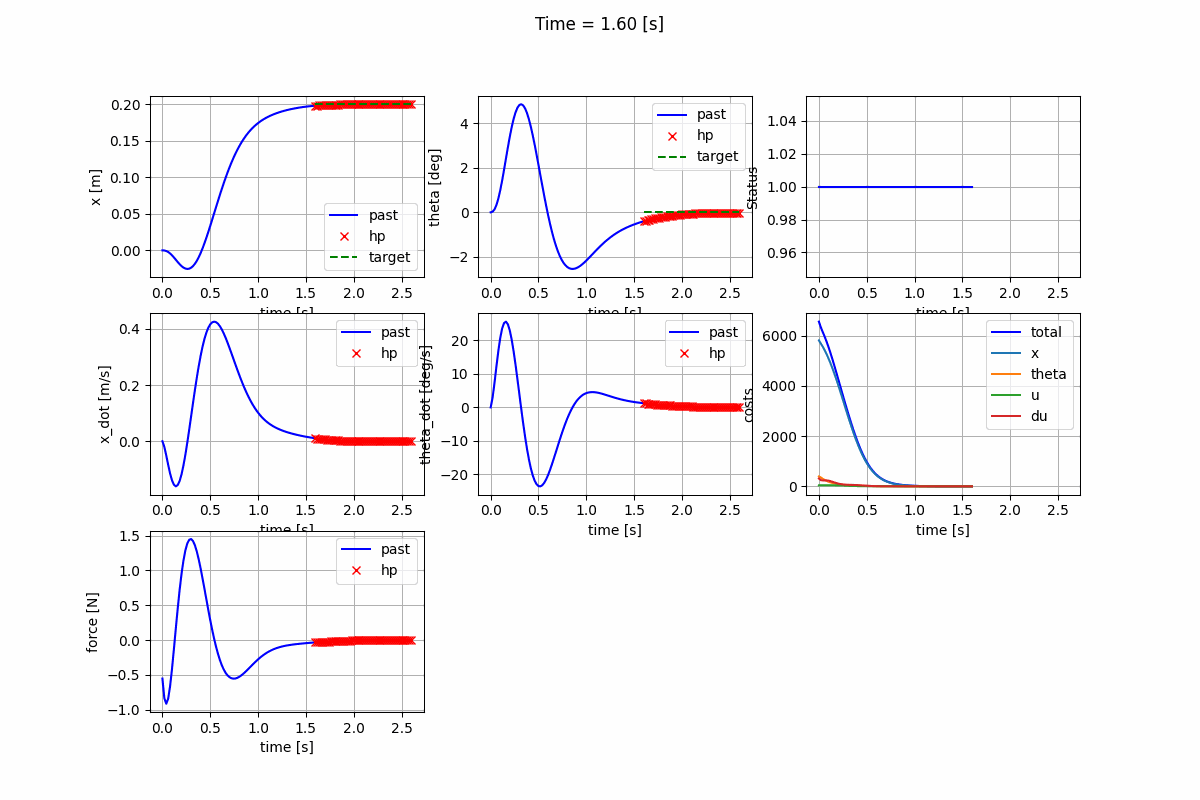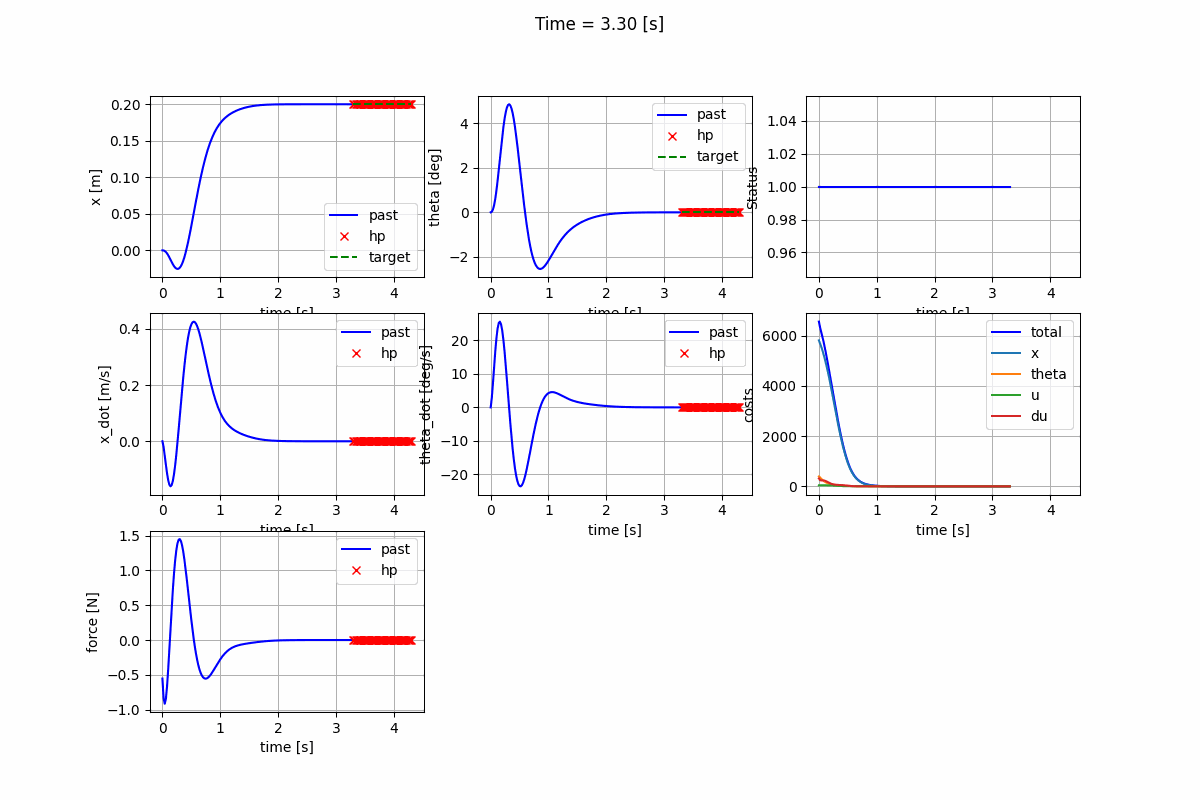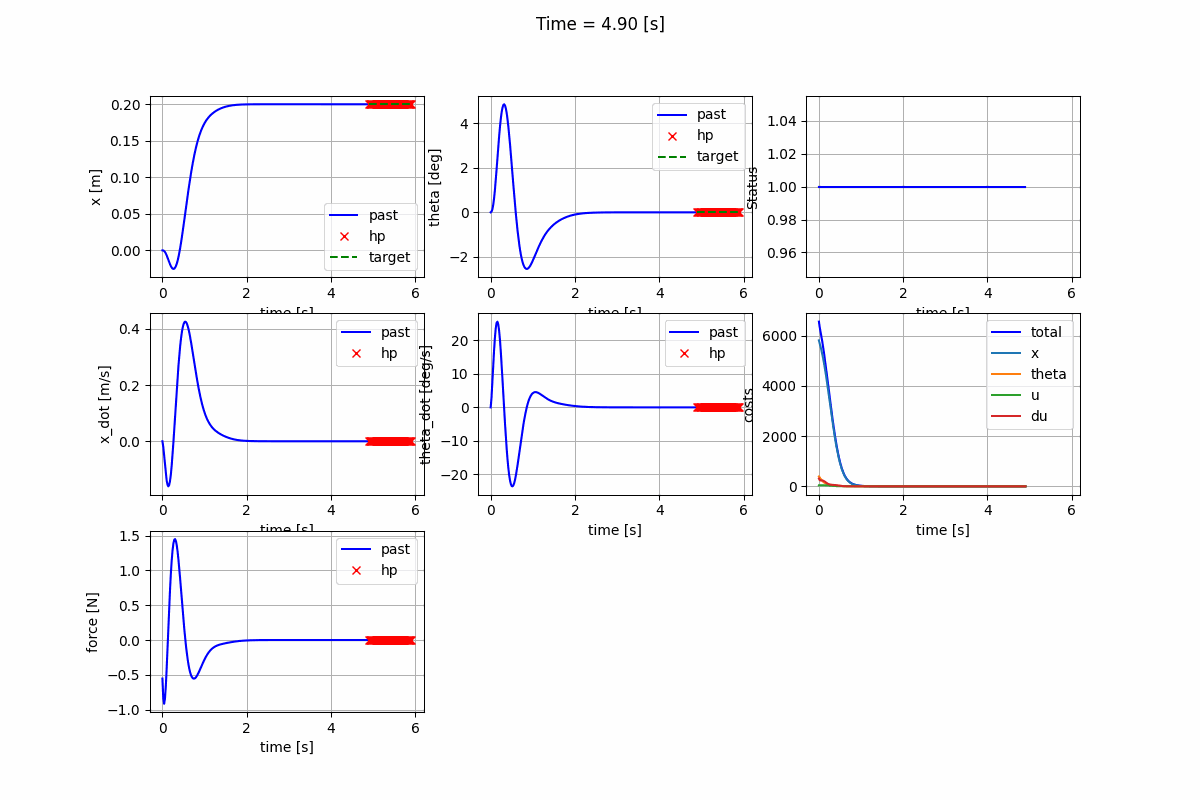
- Download
Coin-HSL Archive(free for personal use) - Install HSL solvers following instructions in
ThirdParty-HSL - Alternatively, use MUMPS solver by following instructions in
ThirdParty-MUMPS - Install Ipopt following provided instructions
- Install CppAD following provided instructions
The cart-pole env in gymnasium was used for visualization. Test if visualization is set up correctly.
python3 ./vis/examples/test_vis.py
Test if the cart-pole plant (physical model) can run smoothly:
python3 -m system.plant --enable_vis
Install required Python packages:
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
Build the project with cmake:
mkdir build && cd build
cmake ..
make -j4
How to run the simulation
python3 run.py --save_gif
Settings of the controller type and parameter values are in the json file, config/control_param.json.
"type": "NMPC", // Available Types: "LQR", "LMPC", "NMPC"
"nmpc_cfg": { // Control parameters for NMPC, active when "type" is "NMPC"
"mpc_dt": 0.02, // [s], NMPC time step
"hp": 50, // Prediction Horizon
"hc": 50, // Control Horizon, hc <= hp
"Qx": 5000.0, // Weight for tracking error of x
"Qtheta": 100.0, // Weight for tracking error of theta
"R_u": 100.0, // Weight for control effort (force)
"R_du": 0.0 // Weight for control rate (force rate)
}
"lqr_cfg": { // Control parameters for LQR, active when "type" is "LQR"
"Qx": 5000.0, // Weight for tracking error of x
"Qtheta": 100.0, // Weight for tracking error of theta
"R_u": 1.0, // Weight for control effort (force)
"R_du": 0.1, // Weight for control rate (force rate)
"use_finite_lqr": true, // If true, use finite horizon LQR solver; Otherwise, use infinite horizon LQR solver
"hp": 50, // Horizon, valid only if `is_finite` is true
"lqr_dt": 0.02 // DARE step size, valid only if `is_finite` is true; Generally, `lqr_dt` = `ctrl_time_step`
"use_dare": true // For Infinite-Horizon LQR: If true, use DARE solver; Otherwise, use CARE solver
}
"lmpc_cfg": {
"mpc_dt": 0.02,
"hp": 50,
"hc": 50,
"Qx": 5000.0,
"Qtheta": 100.0,
"R_u": 1.0,
"R_du": 0.1,
"is_unconstrained": false // If true, use Analytical solution for unconstrained LMPC;
// Otherwise, use QP solver for constrained LMPC
}