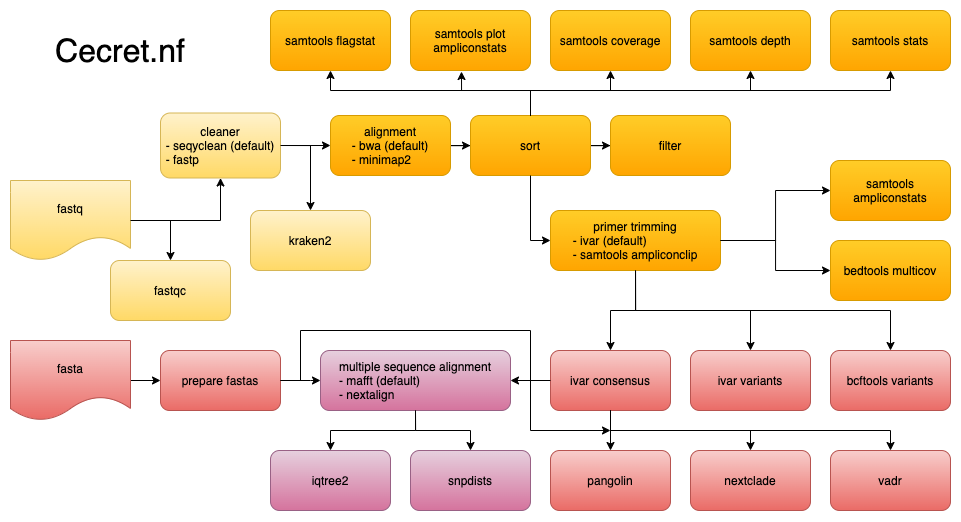
Named after the beautiful Cecret lake
Location: 40.570°N 111.622°W , 9,875 feet (3,010 m) elevation
Cecret is a workflow developed by @erinyoung at the Utah Public Health Laborotory for SARS-COV-2 sequencing with the artic/Illumina hybrid library prep workflow for MiSeq data with protocols here and here. Built to work on linux-based operating systems. Additional config options are needed for cloud batch usage.
It is possible to use this workflow to simply annotate fastas generated from any workflow with pangolin, nextclade, and vadr. Another utility is to find consensus fasta files from fastq files, and add in fasta files that were generated previously or downloaded from GISAID or NCBI for multiple sequence alignment (MSA) and phylogenetic tree.
Cecret is also part of the staphb-toolkit.
- Nextflow
- Nextflow version 20+ is required (
nextflow -vto check)
- Nextflow version 20+ is required (
- Singularity or Docker - set the profile as singularity or docker during runtime
- Git
# using singularity
nextflow run UPHL-BioNGS/Cecret -profile singularity
# using docker
nextflow run UPHL-BioNGS/Cecret -profile docker
git clone https://github.com/UPHL-BioNGS/Cecret.git
# using singularity
nextflow run Cecret.nf -c configs/singularity.config
# using docker
nextflow run Cecret.nf -c configs/docker.config
(can be adjusted with 'params.reads', 'params.single_reads', and 'params.fastas')
Paired-end fastq.gz (ending with 'fastq', 'fastq.gz', 'fq', or 'fq.gz') reads as follows or designate directory with 'params.reads' or '--reads'
directory
└── reads
└── *fastq.gz
WARNING : Sometimes nextflow does not catch every name of paired-end fastq files. This workflow is meant to be fairly agnostic, but if paired-end fastq files are not being found it might be worth renaming them to some sort of sample_1.fastq.gz format.
Single-end fastq.gz reads as follows or designate directory with 'params.single_reads' or '--single_reads'
directory
└── single_reads
└── *fastq.gz
WARNING : single and paired-end reads cannot be in the same directory
Fasta files (ending with 'fa', 'fasta', or 'fna') as follows or designate directory with 'params.fastas' or '--fastas'
directory
└── fastas
└── *fasta
MultiFasta files (ending with 'fa', 'fasta', or 'fna') as follows or designate directory with 'params.multifastas' or '--multifastas'
directory
└── multifastas
└── *fasta
WARNING : fastas and multifastas cannot be in the same directory. If no fasta preprocessing is necessary, just put the single fastas in the multifastas directory.
For the sake of simplicity, processes in this workflow are designated 1 CPU, a medium amount of CPUs (5), or the largest amount of CPUs (the number of CPUs of the environment launching the workflow if using the main workflow and a simple config file or 8 if using profiles and the config template). The medium amount of CPUs can be adjusted by the End User by adjusting 'params.medcpus', the largest amount can be adjusted with 'params.maxcpus', or the cpus can be specified for each process individually in a config file.
The main Cecret.nf file will attempt to determine how many cpus are available, and will set params.maxcpus to the number of cpus available. This option apparently caused havoc for running this workflow in the cloud and other resource management systems, so by default this is overridden when using a -profile to 'params.maxcpus = 8' in config template.
The End User can adjust this by specifying the maximum cpus that one process can take in the config file 'params.maxcpus = <new value>' or on the command line
nextflow run UPHL-BioNGS/Cecret -profile singularity --maxcpus <new value>
It is important to remember that nextflow will attempt to utilize all CPUs available, and this value is restricted to one process. As a specific example, the prcoess 'bwa' will be allocated 'params.maxcpus'. If there are 48 CPUs available and 'params.maxcpus = 8', then 6 samples can be run simultaneously.
nextflow run UPHL-BioNGS/Cecret -profile singularity --cleaner fastp
Or set params.cleaner = 'fastp' in a config file
nextflow run UPHL-BioNGS/Cecret -profile singularity --trimmer samtools
Or set params.trimmer = 'samtools' in a config file
nextflow run UPHL-BioNGS/Cecret -profile singularity --trimmer none
Or set params.trimmer = 'none' in a config file
nextflow run UPHL-BioNGS/Cecret -profile singularity --aligner minimap2
Or set params.aligner = 'minimap2' in a config file
To create a multiple sequence alignment and corresponding phylogenetic tree and SNP matrix, set params.relatedness = true or
nextflow run UPHL-BioNGS/Cecret -profile singularity --relatedness true
nextflow run UPHL-BioNGS/Cecret -profile singularity --relatedness true --msa nextalign
Or set params.msa = 'nextalign' and params.relatedness = true in a config file
Using the aligned fasta from nextclade to for multiple sequence alignement instead of mafft or nextalign
nextflow run UPHL-BioNGS/Cecret -profile singularity --relatedness true --msa nextclade
Or set params.msa = 'nextclade' and params.relatedness = true in a config file.
WARNING : the aligned fasta from nextclade does not include a reference sequence. If this is desired for iqtree2, a fasta of the reference MUST be included with the input files and the outgroup CAN be specified with params.iqtree2_options = '-ninit 2 -n 2 -me 0.05 -m GTR -o <YOUR OUTGROUP>'. Specifying the outgroup via 'params.iqtree2_outgroup' will not be used.
To classify reads with kraken2 to identify reads from human or the organism of choice
mkdir kraken2_db
cd kraken2_db
wget ftp://ftp.ccb.jhu.edu/pub/data/kraken2_dbs/old/minikraken2_v2_8GB_201904.tgz
tar -zxvf minikraken2_v2_8GB_201904.tgz
params.kraken2 = true
params.kraken2_db = 'kraken2_db'
params.kraken2_organism = "Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus"
- seqyclean - for cleaning reads
- fastp - for cleaning reads ; optional, faster alternative to seqyclean
- bwa - for aligning reads to the reference
- minimap2 - an alternative to bwa
- ivar - calling variants and creating a consensus fasta; optional primer trimmer
- samtools - for QC metrics and sorting; optional primer trimmer; optional converting bam to fastq files
- fastqc - for QC metrics
- bedtools - for depth estimation over amplicons
- kraken2 - for read classification
- pangolin - for lineage classification
- nextclade - for clade classification
- vadr - for annotating fastas like NCBI
- mafft - for multiple sequence alignment (optional, relatedness must be set to "true")
- snp-dists - for relatedness determination (optional, relatedness must be set to "true")
- iqtree2 - for phylogenetic tree generation (optional, relatedness must be set to "true")
- nextalign - for phylogenetic tree generation (optional, relatedness must be set to "true", and msa must be set to "nextalign")
- bamsnap - to create images of SNPs
It came to my attention that some processes (like bcftools) do not work consistently. Also, they might take longer than wanted and might not even be needed for the end user. Here's the processes that can be turned off with their default values:
params.bcftools_variants = false # the container gets a lot of traffic which can error when attempting to download
params.fastqc = true # qc on the sequencing reads
params.ivar_variants = true # itemize the variants identified by ivar
params.samtools_stats = true # stats about the bam files
params.samtools_coverage = true # stats about the bam files
params.samtools_depth = true # stats about the bam files
params.samtools_flagstat = true # stats about the bam files
params.samtools_ampliconstats = true # stats about the amplicons
params.samtools_plot_ampliconstats = true # images related to amplicon performance
params.kraken2 = false # used to classify reads and needs a corresponding params.kraken2_db and organism if not SARS-CoV-2
params.bedtools_multicov = true # bedtools multicov for coverage approximation of amplicons
params.nextclade = true # SARS-CoV-2 clade determination
params.pangolin = true # SARS-CoV-2 lineage determination
params.vadr = false # NCBI fasta QC
params.relatedness = false # create multiple sequence alignments with input fastq and fasta files
params.snpdists = true # creates snp matrix from mafft multiple sequence alignment
params.iqtree2 = true # creates phylogenetic tree from mafft multiple sequence alignement
params.bamsnap = false # can be really slow. Works best with bcftools variants. An example bamsnap image is below.
params.rename = false # needs a corresponding sample file and will rename files for GISAID and NCBI submission
params.filter = false # takes the aligned reads and turns them back into fastq.gz files
This requires a comma-delimted file set with params.sample_file file with a row for each sample and a comma-delimited column for each item to add to the GenBank submission header. Additionally, adjust params.rename = true.
The following headers are required
- Sample_id (required, must match sample_id*.fa*)
- Submission_id (if file needs renaming)
- Collection_Date
Example covid_samples.csv file contents:
Sample_id,Submission_ID,Collection_Date,SRR
12345,UT-UPHL-12345,2020-08-22,SRR1
67890,UT-UPHL-67890,2020-08-22,SRR2
23456,UT-UPHL-23456,2020-08-22,SRR3
78901,UT-UPHL-78901,2020-08-18,SRR4
Where the files named 12345-UT-M03999-200822_S9_L001_R1_001.fastq.gz, 12345-UT-M03999-200822_S9_L001_R2_001.fastq.gz will be renamed UT-UPHL-12345.R1.fastq.gz and UT-UPHL-12345.R2.fastq.gz. A GISAID and GenBank friendly multifasta files ready for submission are also generated. The GenBank multifasta uses the input file to create fasta headers like
>12345 [Collection_Date=2020-08-22][organism=Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2][host=human][country=USA][isolate=SARS-CoV-2/human/USA/12345/2020][SRR=SRR1]
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Sometimes sequencing fails, so there are parameters for how many non-ambiguous bases a fasta needs in order to get incorporated into the final file. This can be set with params.gisaid_threshold (Default is 'params.gisaid_threshold = '25000'') and params.genbank_threshold (Default is 'params.genbank_threshold = '15000'').
Final File Tree after running cecret.nf
covid_samples.csv # only if supplied initially - used to rename files for submission
cecret # results from this workflow
├── aligned # aligned (with aligner) but untrimmed bam files with indexes
│ ├── SRR13957125.sorted.bam
│ ├── SRR13957125.sorted.bam.bai
│ ├── SRR13957170.sorted.bam
│ ├── SRR13957170.sorted.bam.bai
│ ├── SRR13957177.sorted.bam
│ └── SRR13957177.sorted.bam.bai
├── bamsnap # images for variants (if it works, default is 'false' for a reason)
│ └── sample
├── bcftools_variants # set to false by default; VCF files of variants identified
│ ├── SRR13957125.vcf
│ ├── SRR13957170.vcf
│ └── SRR13957177.vcf
├── bedtools_multicov # coverage for each amplicon
│ ├── SRR13957125.multicov.txt
│ ├── SRR13957170.multicov.txt
│ └── SRR13957177.multicov.txt
├── cecret_results.csv # comma-delimeted summary of results
├── cecret_results.txt # tab-delimited summary of results
├── consensus # the likely reason you are running this workflow
│ ├── SRR13957125.consensus.fa
│ ├── SRR13957170.consensus.fa
│ └── SRR13957177.consensus.fa
├── fastp # optional tools for cleaning reads when 'params.cleaner = fastp'
│ ├── SRR13957125_clean_PE1.fastq.gz
│ ├── SRR13957125_clean_PE2.fastq.gz
│ ├── SRR13957125_fastp.html
│ ├── SRR13957125_fastp.json
│ ├── SRR13957170_clean_PE1.fastq.gz
│ ├── SRR13957170_clean_PE2.fastq.gz
│ ├── SRR13957170_fastp.html
│ ├── SRR13957170_fastp.json
│ ├── SRR13957177_clean_PE1.fastq.gz
│ ├── SRR13957177_clean_PE2.fastq.gz
│ ├── SRR13957177_fastp.html
│ └── SRR13957177_fastp.json
├── fastqc # QC metrics for each fasta sequence
│ ├── SRR13957125_1_fastqc.html
│ ├── SRR13957125_1_fastqc.zip
│ ├── SRR13957125_2_fastqc.html
│ ├── SRR13957125_2_fastqc.zip
│ ├── SRR13957170_1_fastqc.html
│ ├── SRR13957170_1_fastqc.zip
│ ├── SRR13957170_2_fastqc.html
│ ├── SRR13957170_2_fastqc.zip
│ ├── SRR13957177_1_fastqc.html
│ ├── SRR13957177_1_fastqc.zip
│ ├── SRR13957177_2_fastqc.html
│ └── SRR13957177_2_fastqc.zip
├── filter # fastq.gz files from reads that were aligned to the reference genome
│ ├── SRR13957125_filtered_R1.fastq.gz
│ ├── SRR13957125_filtered_R2.fastq.gz
│ ├── SRR13957125_filtered_unpaired.fastq.gz
│ ├── SRR13957170_filtered_R1.fastq.gz
│ ├── SRR13957170_filtered_R2.fastq.gz
│ ├── SRR13957170_filtered_unpaired.fastq.gz
│ ├── SRR13957177_filtered_R1.fastq.gz
│ ├── SRR13957177_filtered_R2.fastq.gz
│ └── SRR13957177_filtered_unpaired.fastq.gz
├── iqtree2 # phylogenetic tree that is generated with 'params.relatedness = true'
│ ├── iqtree2.iqtree
│ ├── iqtree2.log
│ ├── iqtree2.mldist
│ └── iqtree2.treefile
├── ivar_trim # bam files after primers have been trimmed off the reads with ivar
│ ├── SRR13957125.primertrim.sorted.bam
│ ├── SRR13957125.primertrim.sorted.bam.bai
│ ├── SRR13957170.primertrim.sorted.bam
│ ├── SRR13957170.primertrim.sorted.bam.bai
│ ├── SRR13957177.primertrim.sorted.bam
│ └── SRR13957177.primertrim.sorted.bam.bai
├── ivar_variants # tsv and vcf files of variants identified in sample
│ ├── SRR13957125.ivar_variants.vcf
│ ├── SRR13957125.variants.tsv
│ ├── SRR13957170.ivar_variants.vcf
│ ├── SRR13957170.variants.tsv
│ ├── SRR13957177.ivar_variants.vcf
│ └── SRR13957177.variants.tsv
├── kraken2 # kraken2 report of the organisms the reads may be from
│ ├── SRR13957125_kraken2_report.txt
│ ├── SRR13957170_kraken2_report.txt
│ └── SRR13957177_kraken2_report.txt
├── logs # divided log and err files for QC and troubleshooting pleasures
│ └── processes*
│ ├── sample.run_id.err
│ └── sample.run_id.log
├── mafft # multiple sequence alignment created when 'params.relatedness = true'
│ └── mafft_aligned.fasta
├── nextclade # nextclade reports
│ ├── combined.fasta
│ ├── nextclade.aligned.fasta
│ ├── nextclade.auspice.json
│ ├── nextclade.csv
│ ├── nextclade.errors.csv
│ ├── nextclade.gene.E.fasta
│ ├── nextclade.gene.M.fasta
│ ├── nextclade.gene.N.fasta
│ ├── nextclade.gene.ORF1a.fasta
│ ├── nextclade.gene.ORF1b.fasta
│ ├── nextclade.gene.ORF3a.fasta
│ ├── nextclade.gene.ORF6.fasta
│ ├── nextclade.gene.ORF7a.fasta
│ ├── nextclade.gene.ORF7b.fasta
│ ├── nextclade.gene.ORF8.fasta
│ ├── nextclade.gene.ORF9b.fasta
│ ├── nextclade.gene.S.fasta
│ ├── nextclade.insertions.csv
│ ├── nextclade.json
│ └── nextclade.tsv
├── pangolin # pangolin results
│ ├── combined.fasta
│ └── lineage_report.csv
├── samtools_ampliconstats # amplicon statistics and metrics as determined by samtools
│ ├── SRR13957125_ampliconstats.txt
│ ├── SRR13957170_ampliconstats.txt
│ └── SRR13957177_ampliconstats.txt
├── samtools_coverage # coverage and metrics as determined by samtools
│ └── aligned
│ ├── SRR13957125.cov.hist
│ ├── SRR13957125.cov.txt
│ ├── SRR13957170.cov.hist
│ ├── SRR13957170.cov.txt
│ ├── SRR13957177.cov.hist
│ └── SRR13957177.cov.txt
├── samtools_depth # the number of reads
│ ├── aligned
│ │ ├── SRR13957125.depth.txt
│ │ ├── SRR13957170.depth.txt
│ │ └── SRR13957177.depth.txt
│ └── trimmed
│ ├── SRR13957125.depth.txt
│ ├── SRR13957170.depth.txt
│ └── SRR13957177.depth.txt
├── samtools_flagstat # flag information
│ ├── aligned
│ │ ├── SRR13957125.flagstat.txt
│ │ ├── SRR13957170.flagstat.txt
│ │ └── SRR13957177.flagstat.txt
│ └── trimmed
│ ├── SRR13957125.flagstat.txt
│ ├── SRR13957170.flagstat.txt
│ └── SRR13957177.flagstat.txt
├── samtools_plot_ampliconstats # plots of the ampliconstats for troubleshooting purposes
│ ├── SRR13957125
│ ├── SRR13957125-combined-amp.gp
│ ├── SRR13957125-combined-amp.png
│ ├── SRR13957125-combined-coverage-1.gp
│ ├── SRR13957125-combined-coverage-1.png
│ ├── SRR13957125-combined-depth.gp
│ ├── SRR13957125-combined-depth.png
│ ├── SRR13957125-combined-read-perc.gp
│ ├── SRR13957125-combined-read-perc.png
│ ├── SRR13957125-combined-reads.gp
│ ├── SRR13957125-combined-reads.png
│ ├── SRR13957125-combined-tcoord.gp
│ ├── SRR13957125-combined-tcoord.png
│ ├── SRR13957125-combined-tdepth.gp
│ ├── SRR13957125-combined-tdepth.png
│ ├── SRR13957125-heat-amp-1.gp
│ ├── SRR13957125-heat-amp-1.png
│ ├── SRR13957125-heat-coverage-1-1.gp
│ ├── SRR13957125-heat-coverage-1-1.png
│ ├── SRR13957125-heat-read-perc-1.gp
│ ├── SRR13957125-heat-read-perc-1.png
│ ├── SRR13957125-heat-read-perc-log-1.gp
│ ├── SRR13957125-heat-read-perc-log-1.png
│ ├── SRR13957125-heat-reads-1.gp
│ ├── SRR13957125-heat-reads-1.png
│ ├── SRR13957125-SRR13957125.primertrim.sorted-amp.gp
│ ├── SRR13957125-SRR13957125.primertrim.sorted-amp.png
│ ├── SRR13957125-SRR13957125.primertrim.sorted-cov.gp
│ ├── SRR13957125-SRR13957125.primertrim.sorted-cov.png
│ ├── SRR13957125-SRR13957125.primertrim.sorted-reads.gp
│ ├── SRR13957125-SRR13957125.primertrim.sorted-reads.png
│ ├── SRR13957125-SRR13957125.primertrim.sorted-tcoord.gp
│ ├── SRR13957125-SRR13957125.primertrim.sorted-tcoord.png
│ ├── SRR13957125-SRR13957125.primertrim.sorted-tdepth.gp
│ ├── SRR13957125-SRR13957125.primertrim.sorted-tdepth.png
│ ├── SRR13957125-SRR13957125.primertrim.sorted-tsize.gp
│ ├── SRR13957125-SRR13957125.primertrim.sorted-tsize.png
│ ├── SRR13957170
│ ├── SRR13957170-combined-amp.gp
│ ├── SRR13957170-combined-amp.png
│ ├── SRR13957170-combined-coverage-1.gp
│ ├── SRR13957170-combined-coverage-1.png
│ ├── SRR13957170-combined-depth.gp
│ ├── SRR13957170-combined-depth.png
│ ├── SRR13957170-combined-read-perc.gp
│ ├── SRR13957170-combined-read-perc.png
│ ├── SRR13957170-combined-reads.gp
│ ├── SRR13957170-combined-reads.png
│ ├── SRR13957170-combined-tdepth.gp
│ ├── SRR13957170-combined-tdepth.png
│ ├── SRR13957170-heat-amp-1.gp
│ ├── SRR13957170-heat-amp-1.png
│ ├── SRR13957170-heat-coverage-1-1.gp
│ ├── SRR13957170-heat-coverage-1-1.png
│ ├── SRR13957170-heat-read-perc-1.gp
│ ├── SRR13957170-heat-read-perc-1.png
│ ├── SRR13957170-heat-read-perc-log-1.gp
│ ├── SRR13957170-heat-read-perc-log-1.png
│ ├── SRR13957170-heat-reads-1.gp
│ ├── SRR13957170-heat-reads-1.png
│ ├── SRR13957170-SRR13957170.primertrim.sorted-amp.gp
│ ├── SRR13957170-SRR13957170.primertrim.sorted-amp.png
│ ├── SRR13957170-SRR13957170.primertrim.sorted-cov.gp
│ ├── SRR13957170-SRR13957170.primertrim.sorted-cov.png
│ ├── SRR13957170-SRR13957170.primertrim.sorted-reads.gp
│ ├── SRR13957170-SRR13957170.primertrim.sorted-reads.png
│ ├── SRR13957170-SRR13957170.primertrim.sorted-tdepth.gp
│ ├── SRR13957170-SRR13957170.primertrim.sorted-tdepth.png
│ ├── SRR13957177
│ ├── SRR13957177-combined-amp.gp
│ ├── SRR13957177-combined-amp.png
│ ├── SRR13957177-combined-coverage-1.gp
│ ├── SRR13957177-combined-coverage-1.png
│ ├── SRR13957177-combined-depth.gp
│ ├── SRR13957177-combined-depth.png
│ ├── SRR13957177-combined-read-perc.gp
│ ├── SRR13957177-combined-read-perc.png
│ ├── SRR13957177-combined-reads.gp
│ ├── SRR13957177-combined-reads.png
│ ├── SRR13957177-combined-tcoord.gp
│ ├── SRR13957177-combined-tcoord.png
│ ├── SRR13957177-combined-tdepth.gp
│ ├── SRR13957177-combined-tdepth.png
│ ├── SRR13957177-heat-amp-1.gp
│ ├── SRR13957177-heat-amp-1.png
│ ├── SRR13957177-heat-coverage-1-1.gp
│ ├── SRR13957177-heat-coverage-1-1.png
│ ├── SRR13957177-heat-read-perc-1.gp
│ ├── SRR13957177-heat-read-perc-1.png
│ ├── SRR13957177-heat-read-perc-log-1.gp
│ ├── SRR13957177-heat-read-perc-log-1.png
│ ├── SRR13957177-heat-reads-1.gp
│ ├── SRR13957177-heat-reads-1.png
│ ├── SRR13957177-SRR13957177.primertrim.sorted-amp.gp
│ ├── SRR13957177-SRR13957177.primertrim.sorted-amp.png
│ ├── SRR13957177-SRR13957177.primertrim.sorted-cov.gp
│ ├── SRR13957177-SRR13957177.primertrim.sorted-cov.png
│ ├── SRR13957177-SRR13957177.primertrim.sorted-reads.gp
│ ├── SRR13957177-SRR13957177.primertrim.sorted-reads.png
│ ├── SRR13957177-SRR13957177.primertrim.sorted-tcoord.gp
│ ├── SRR13957177-SRR13957177.primertrim.sorted-tcoord.png
│ ├── SRR13957177-SRR13957177.primertrim.sorted-tdepth.gp
│ ├── SRR13957177-SRR13957177.primertrim.sorted-tdepth.png
│ ├── SRR13957177-SRR13957177.primertrim.sorted-tsize.gp
│ └── SRR13957177-SRR13957177.primertrim.sorted-tsize.png
├── samtools_stats # stats as determined by samtools
│ ├── aligned
│ │ ├── SRR13957125.stats.txt
│ │ ├── SRR13957170.stats.txt
│ │ └── SRR13957177.stats.txt
│ └── trimmed
│ ├── SRR13957125.stats.trim.txt
│ ├── SRR13957170.stats.trim.txt
│ └── SRR13957177.stats.trim.txt
├── seqyclean # reads that have had PhiX and adapters removed
│ ├── Combined_SummaryStatistics.tsv
│ ├── SRR13957125_clean_PE1.fastq.gz
│ ├── SRR13957125_clean_PE2.fastq.gz
│ ├── SRR13957125_clean_SummaryStatistics.tsv
│ ├── SRR13957125_clean_SummaryStatistics.txt
│ ├── SRR13957170_clean_PE1.fastq.gz
│ ├── SRR13957170_clean_PE2.fastq.gz
│ ├── SRR13957170_clean_SummaryStatistics.tsv
│ ├── SRR13957170_clean_SummaryStatistics.txt
│ ├── SRR13957177_clean_PE1.fastq.gz
│ ├── SRR13957177_clean_PE2.fastq.gz
│ ├── SRR13957177_clean_SummaryStatistics.tsv
│ └── SRR13957177_clean_SummaryStatistics.txt
├── snp-dists # SNP matrix created with 'params.relatedness = true'
│ └── snp-dists.txt
├── submission_files # optional functionality that requires a key and renames files when 'params.rename = true'
│ ├── UT-UPHL-2103503681_filtered_R1.fastq.gz
│ ├── UT-UPHL-2103503681_filtered_R2.fastq.gz
│ ├── UT-UPHL-2103503681.genbank.fa
│ ├── UT-UPHL-2103503681.gisaid.fa
│ ├── UT-UPHL-2103929243_filtered_R1.fastq.gz
│ ├── UT-UPHL-2103929243_filtered_R2.fastq.gz
│ ├── UT-UPHL-2103929243.genbank.fa
│ ├── UT-UPHL-2103929243.gisaid.fa
│ ├── UT-UPHL-2103954304_filtered_R1.fastq.gz
│ └── UT-UPHL-2103954304_filtered_R2.fastq.gz
├── summary # summary files with condensed results
│ ├── SRR13957125.summary.csv
│ ├── SRR13957125.summary.txt
│ ├── SRR13957170.summary.csv
│ ├── SRR13957170.summary.txt
│ ├── SRR13957177.summary.csv
│ └── SRR13957177.summary.txt
├── summary.csv
└── vadr # QC that mimics NCBI's metrics
├── combined.fasta
├── trimmed.fasta
├── vadr.vadr.alc
├── vadr.vadr.alt
├── vadr.vadr.alt.list
├── vadr.vadr.cmd
├── vadr.vadr.dcr
├── vadr.vadr.fail.fa
├── vadr.vadr.fail.list
├── vadr.vadr.fail.tbl
├── vadr.vadr.filelist
├── vadr.vadr.ftr
├── vadr.vadr.log
├── vadr.vadr.mdl
├── vadr.vadr.pass.fa
├── vadr.vadr.pass.list
├── vadr.vadr.pass.tbl
├── vadr.vadr.rpn
├── vadr.vadr.sda
├── vadr.vadr.seqstat
├── vadr.vadr.sgm
├── vadr.vadr.sqa
└── vadr.vadr.sqc
reads # user supplied fastq files for analysis
single_reads # user supplied fastq files for analysis
fastas # user supplied fasta files for analysis
multifastas # user supplied multifasta files for analysis
work # nextflow's working directories
A FILE THAT THE END USER CAN COPY AND EDIT IS FOUND AT configs/cecret_config_template.config
This file contains all of the configurable parameters with their default values. Use '-c' to specify the edited config file. If the End User is using some sort of cloud or HPC setup, it is highly recommended that this file is copied and edited appropriately. A limited list of parameters is listed below:
- params.reads = workflow.launchDir + '/reads'
- params.single_reads = workflow.launchDir + '/single_reads'
- params.fastas = workflow.launchDir + '/fastas'
- params.outdir = workflow.launchDir + '/cecret'
- params.reference_genome = workflow.projectDir + "/configs/MN908947.3.fasta"
- params.gff_file = workflow.projectDir + "/configs/MN908947.3.gff"
- params.primer_bed = workflow.projectDir + "/configs/artic_V3_nCoV-2019.bed"
- params.amplicon_bed = workflow.projectDir + "/configs/nCoV-2019.insert.bed"
- To "resume" a workflow that use
-resumewith the nextflow command - To create a report, use
-with-reportwith the nextflow command - To use nextflow tower, use
-with-towerwith the nextflow command
TELL ME ABOUT IT!!!
- Github issue
- Email me
- Send me a message on slack
Be sure to include the command that was used, what config file was used, and what the nextflow error was.
In the history of this repository, there actually was an attempt to store fastq files here that the End User could use to test out this workflow. This made the repository very large and difficult to download.
Instead, it recommended that the End User uses the SARS-CoV-2 datasets, an effort of the CDC to provide a benchmark dataset for validating bioinformatic workflows. Fastq files from the nonviovoc, voivoc, and failed projects were downloaded from the SRA and put through this workflow. The summary files are included in the data directory under the following filenames for comparison:
- data/default_datasets_summary.csv : Using the default options
- data/toggled_datasets_summary.csv : Using fastp, minimap2, and samtools ampliconclip
- data/uphl_datasets_summary.csv : Using UPHL's profile (which is essentially the same as using the default options, but includes a kraken2 database used locally)
The expected amount of time to run this workflow with 250 G RAM and 48 CPUs, 'params.maxcpus = 8', and 'params.medcpus = 4' is ~42 minutes. This corresponded with 25.8 CPU hours.
nextflow run UPHL-BioNGS/Cecret -profile singularity --fastas <directory with fastas> --multifastas <directory with multifastas>
The End User can run mafft, snpdists, and iqtree on a collection of fastas as well with
nextflow run UPHL-BioNGS/Cecret -profile singularity --relatedness true --fastas <directory with fastas> --multifastas <directory with multifastas>
The End User can also have paired-end, singled-end, and fastas that can all be put together into one analysis.
nextflow run UPHL-BioNGS/Cecret -profile singularity --relatedness true --fastas <directory with fastas> --multifastas <directory with multifastas> --reads <directory with paire-end reads> --single_reads <directory with single-end reads>
The End User is more than welcome to look at an example here. Just remove the comments for the parameters that need to be adjusted and specify with -c.
At UPHL, our config file is small enough to be put as a profile option, but the text of the config file would be as follows:
singularity.enabled = true
singularity.autoMounts = true
params {
reads = "Sequencing_reads/Raw"
kraken2 = true
kraken2_db = '/Volumes/IDGenomics_NAS/Data/kraken2_db/h+v'
vadr = false
}
There are two ways to do this.
cecret/bedtools_multicov has a file for each sample.
This is standard bedtools multicov output, so it doesn't have a header.
- Column 1 : The reference
- Column 2 : Start of amplicon
- Column 3 : End of amplicon
- Column 4 : Amplicon number
- Column 5-6 : version number and strand from bedfile
- Column 7 : (Column G) is the depth observed for that amplicon for that sample.
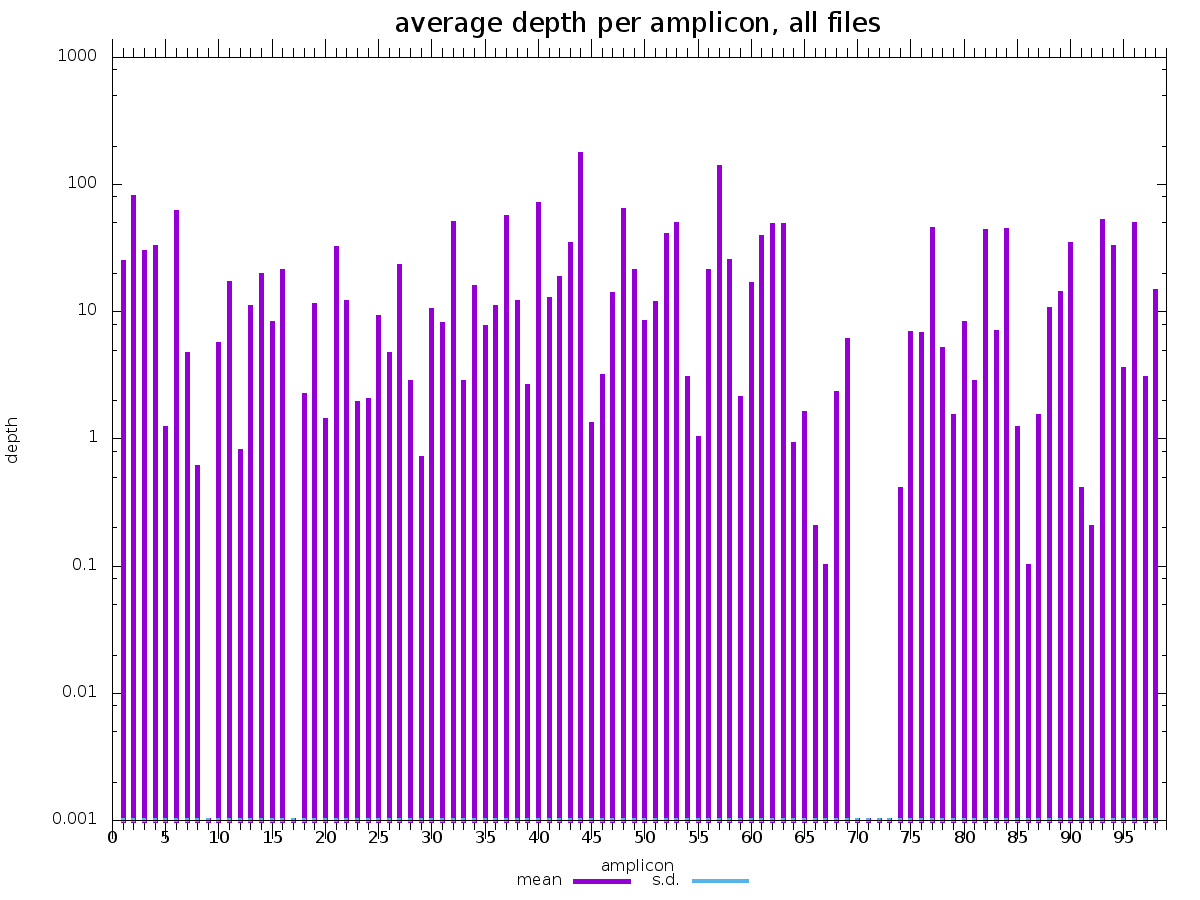
cecret/samtools_ampliconstats has a file for each sample
Row number 126 (FDEPTH) has a column for each amplicon (also without a header). To get this row for all of the samples, grep the keyword "FDEPTH" from each sample.
grep "^FDEPTH" cecret/samtools_ampliconstats/* > samtools_ampliconstats_all.tsv
There are corresponding images in cecret/samtools_plot_ampliconstats for each sample.
There's nothing wrong with the bcftools process, and the vcf created by bcftools is rather handy for additional analyses. The 'staphb/bcftools:latest' container is really popular, and has issues downloading during high traffic times. The maintainers of this repository don't have the time to handle issues of users not understanding why the container did not download. /Sorry
To to get the vcf of variants from bcftools, set params.bcftools_variants = true
The primer bedfile is the file with the start and stop of each primer sequence.
$ head -n 3 artic_V3_nCoV-2019.bed
MN908947.3 30 54 nCoV-2019_1_LEFT nCoV-2019_1 +
MN908947.3 385 410 nCoV-2019_1_RIGHT nCoV-2019_1 -
MN908947.3 320 342 nCoV-2019_2_LEFT nCoV-2019_2 +
The amplicon bedfile is the file with the start and stop of each intended amplicon.
$ head -n 3 nCoV-2019.insert.bed
MN908947.3 54 385 1 1 +
MN908947.3 342 704 2 2 +
MN908947.3 664 1004 3 1 +
Due to the many varieties of primer bedfiles, I determined it was best if the user supplied this file for custom primer sequences.
In a config file, change the following relevant parameters:
params.reference_genome
params.primer_bed
params.amplicon_bed or set params.bedtools_multicov = false
params.gff_file or set params.ivar_variants = false
And set
params.pangolin = false
params.nextclade = false or adjust nexclade_prep_options from '--name sars-cov-2' to the name of the relevent dataset
params.vadr = false or configure the vadr container appropriately and params.vadr_reference
Although not perfect, if 'params.filter = true', then only the reads that were mapped to the reference are returned. This should eliminate all human contamination (as long as human is not part of the supplied reference).
This workflow has too many bells and whistles. I really only care about generating a consensus fasta. How do I get rid of all the extras?
Change the parameters in a config file and set most of them to false.
params.fastqc = false
params.ivar_variants = false
params.samtools_stats = false
params.samtools_coverage = false
params.samtools_depth = false
params.samtools_flagstat = false
params.bedtools_multicov = false
params.samtools_ampliconstats = false
params.samtools_plot_ampliconstats = false
params.bedtools_multicov = false
params.pangolin = false
params.nextclade = false
params.vadr = false
And, yes, this means I added some bells and whistles so the End User could turn off the bells and whistles. /irony
Yes. Set params.bamsnap = true. This is false by default because of how long it takes. It will work with variants called by ivar_variants and bcftools_variants, although it is MUCH faster with the vcf created by bcftools.
Warning : will not work on all variants. This is due to how bamsnap runs. It is even less likely to work on indels.