This repository contains my Computer Graphics Lab Finals experiments and code.
- 3rd Year 2nd Semester, Computer Science & Engineering, University of Rajshahi
- GitHub: @akifislam | Gmail: iamakifislam@gmail.com
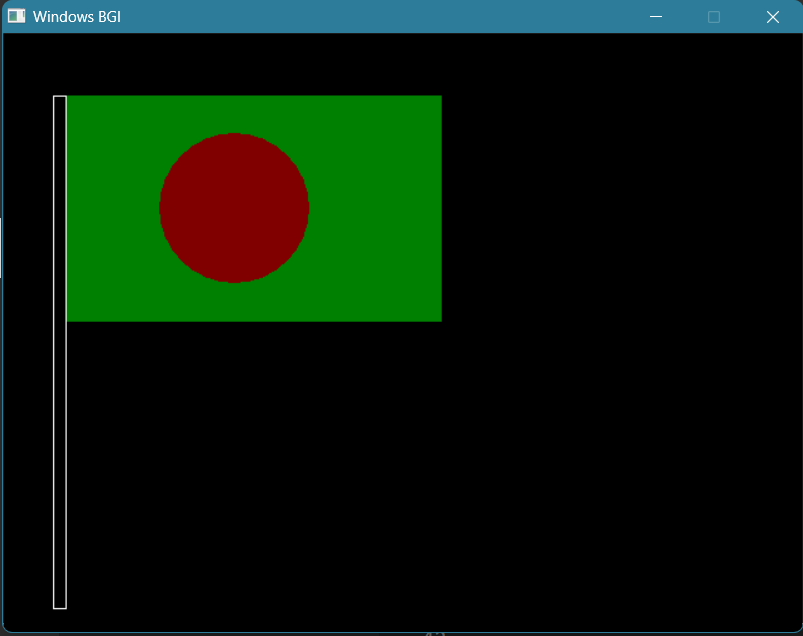
- Draw the National Flag of Bangladesh ✓
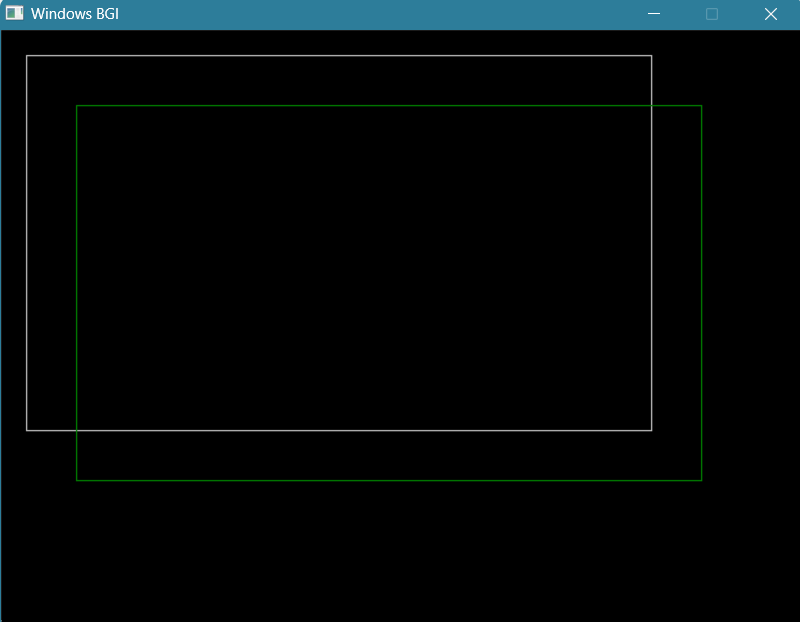
- Simulate two dimensional geometric Translation, Rotation & Scaling ✓
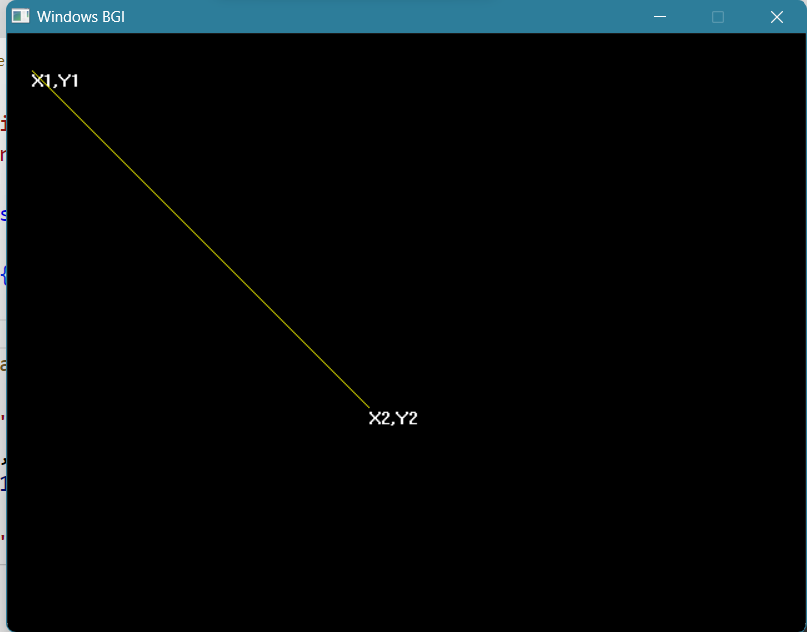
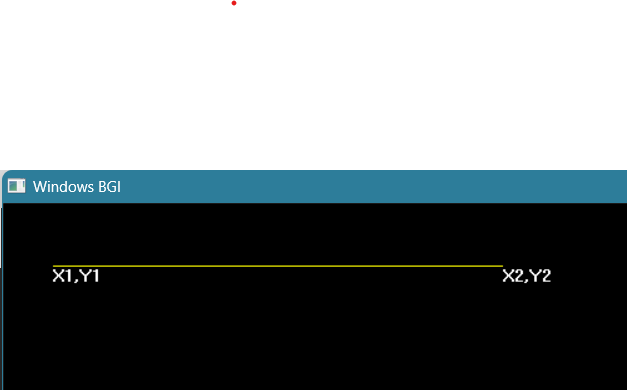
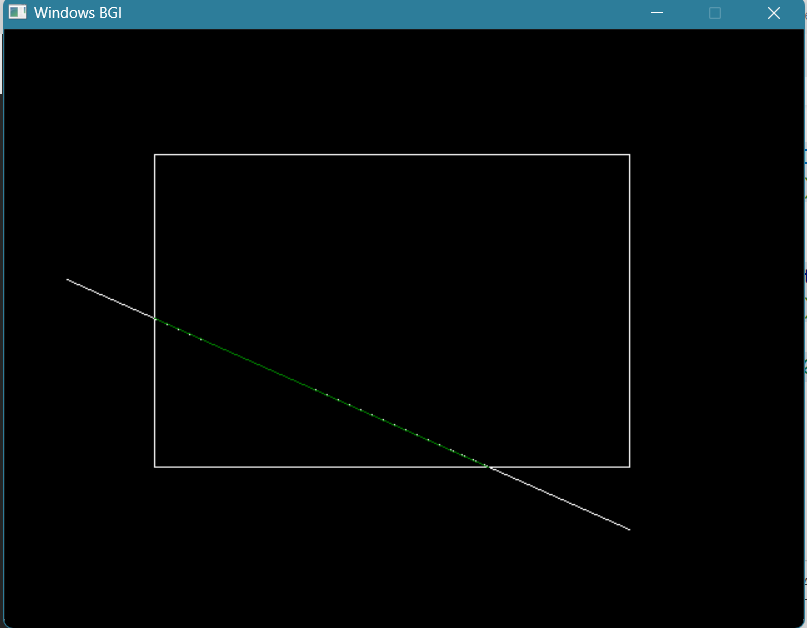
- Draw a line with the Bresenham Line Drawing algorithm ✓
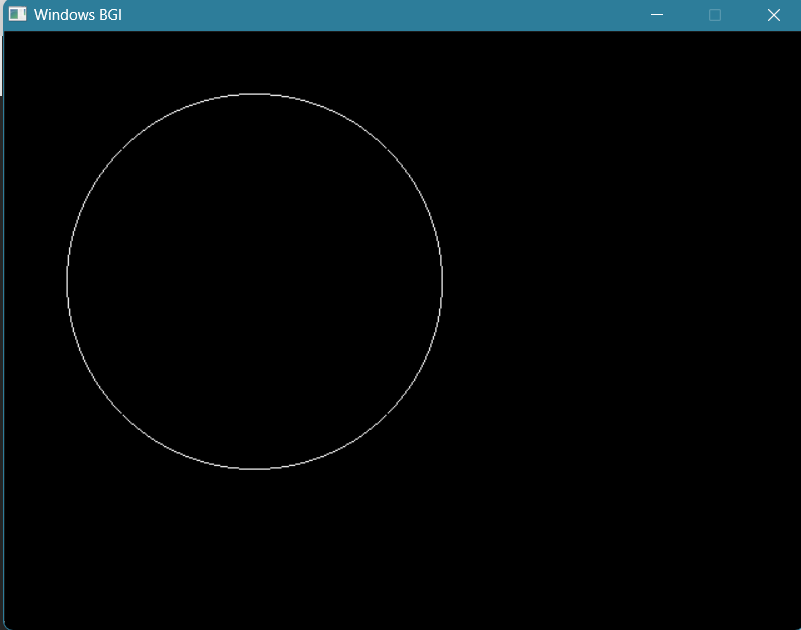
- Draw a circle with the Bresenham Circle Drawing algorithm ✓
- Simulate Hidden Surface Elimination or Visual Surface Detection ✓
- Implement the Cohen Sutherland Line Clipping algorithm ✓
- Implement the Sutherland Hodgman Polygon Clipping algorithm✓
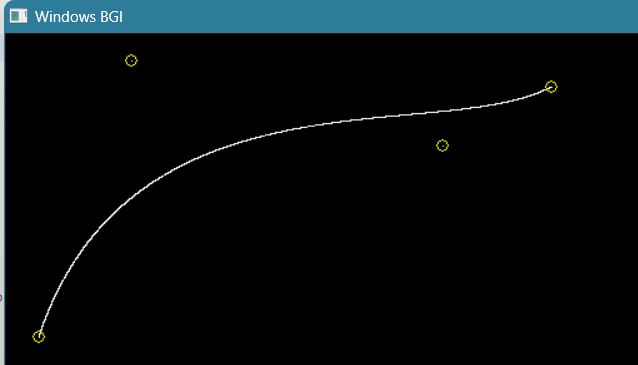
- Create the Bejier Curve ✓
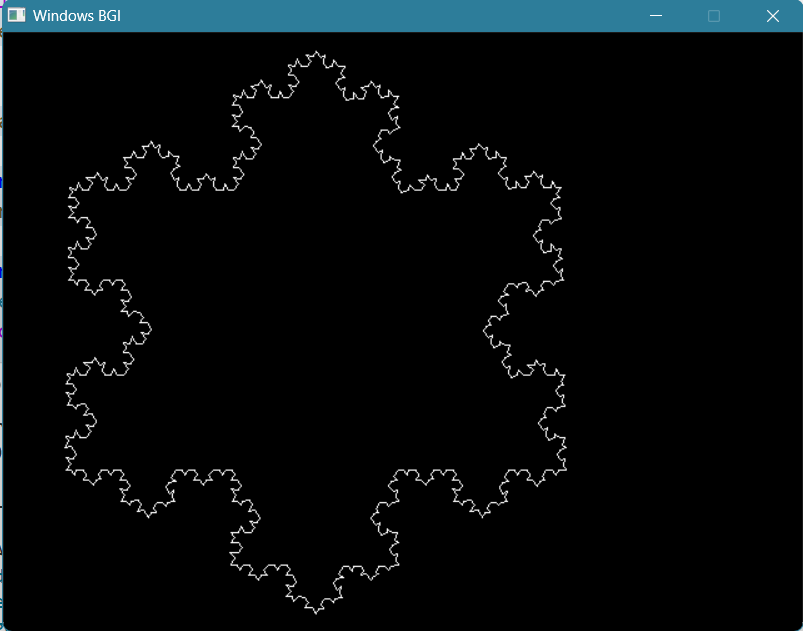
- Draw the Snowflake Pattern with Fractal Geometry✓
- Download TDM GCC 32 Bit Compiler from this link: https://jmeubank.github.io/tdm-gcc/
- Download Graphics Library: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1z19xxKm2YseQi7QGxqCCdJ-lLfiEGuCm/view
- Extract Graphics Library
- Copy graphics.h & winbgim.h and paste it in "C:\TDM-GCC-32\include"
- Copy libbgi.a and paste it in "C:\TDM-GCC-32\lib"
- Now go to CodeBlocks -> Settings -> Compiler
- Go to "Toolchain executables" & change Compiler's installation directory to "C:\TDM-GCC-32"
- Go to "Linker Settigns" -> Other linker options & add "-lbgi -lgdi32 -lcomdlg32 -luuid -loleaut32 -lole32"
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<graphics.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int gd = DETECT;
int gm = DETECT;
initgraph(&gd,&gm,"");
// Setting Rectangle Parameter by maintaining width:height = 10:6 ratio
int scale_factor = 30;
int x1;
int y1;
cout<<"Enter the start point of the flag (x1,y1):";
cin>>x1;
cin>>y1;
int x2 = x1+10*scale_factor;
int y2 = y1+6*scale_factor;
// Drawing Rectangle
setcolor(GREEN);
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL,GREEN);
rectangle(x1,y1,x2,y2);
floodfill(x1+1,y1+1,GREEN);
//Drawing Circle
setcolor(RED);
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL,RED);
circle(x1+(x2-x1)*0.45,y1+(y2-y1)*0.5, 2*scale_factor);
floodfill(x1+(x2-x1)*0.45+1,y1+(y2-y1)*0.5+1,RED);
//Drawing a Handle
setcolor(WHITE);
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL,WHITE);
rectangle(x1-max(scale_factor/3,10),y1,x1,y2*2);
getch();
}
/*
AKIF ISLAM
1910776135
*/#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<graphics.h>
using namespace std;
void draw_polygon(vector<pair<int,int>> poly,int color){
setcolor(color);
for (int i = 0; i < poly.size(); i++)
line(poly[i].first,poly[i].second,poly[(i+1)%poly.size()].first,poly[(i+1)%poly.size()].second);
}
int main(){
int gd = DETECT;
int gm = DETECT;
initgraph(&gd,&gm,"");
// Taking No of Sides of a Polygon
cout<<"Enter No of Side : ";
int no_of_side;
cin>>no_of_side;
// Taking co-ordinates of the sides
vector<pair<int,int>> coordinates;
for (int i = 0; i < no_of_side; i++)
{
int x,y;
cout<<"Enter (X"<<i+1<<",Y"<<i+1<<"):";
cin>>x>>y;
coordinates.push_back({x,y});
}
//Taking Translation Factor
cout<<"Enter Translation Factor (Tx,Ty) :";
int tx,ty;
cin>>tx>>ty;
draw_polygon(coordinates,7);
//Translate all points
for (int i = 0; i < coordinates.size(); i++)
{
coordinates[i].first+=tx;
coordinates[i].second+=ty;
}
draw_polygon(coordinates,2);
getch();
}#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<graphics.h>
using namespace std;
double to_radian(int degree){
return (degree*3.1416)/180;
}
void draw_polygon(vector<pair<int,int>> poly,int color){
setcolor(color);
for (int i = 0; i < poly.size(); i++)
line(poly[i].first,poly[i].second,poly[(i+1)%poly.size()].first,poly[(i+1)%poly.size()].second);
}
int main(){
int gd = DETECT;
int gm = DETECT;
initgraph(&gd,&gm,"C:\\Users");
// Taking No of Sides of a Polygon
cout<<"Enter No of Side : ";
int no_of_side;
cin>>no_of_side;
// Taking co-ordinates of the sides
vector<pair<int,int>> coordinates;
for (int i = 0; i < no_of_side; i++)
{
int x,y;
cout<<"Enter (X"<<i+1<<",Y"<<i+1<<"):";
cin>>x>>y;
coordinates.push_back({x,y});
}
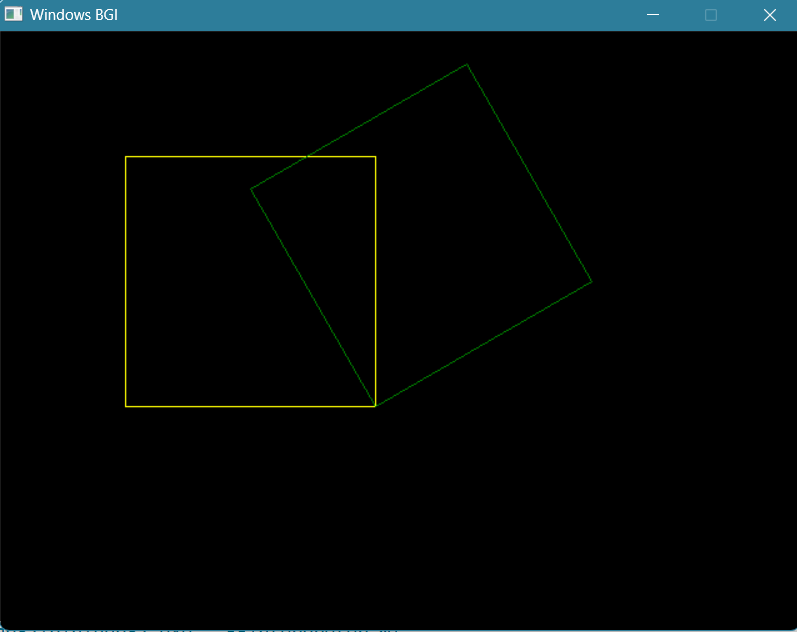
cout<<"Rotation Angle in Degree : ";
int angle;
cin>>angle;
//Taking Scaling Factor
cout<<"Enter Pivot Point for Rotation (rx,ry) :";
int rx,ry;
cin>>rx>>ry;
draw_polygon(coordinates,14);
//Translate to Origin, Then Rotate, Then Back to Pivot Point
for (int i = 0; i < coordinates.size(); i++)
{
double x = coordinates[i].first;
double y = coordinates[i].second;
//Move to Origin
int x_shift=x-rx;
int y_shift=y-ry;
//Rotate
x = x_shift*cos(to_radian(angle))-y_shift*sin(to_radian(angle));
y = x_shift*sin(to_radian(angle))+y_shift*cos(to_radian(angle));
//Back to Pivot Point
x+=rx;
y+=ry;
coordinates[i].first = x;
coordinates[i].second = y;
}
draw_polygon(coordinates,2);
getch();
}#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<graphics.h>
using namespace std;
void draw_polygon(vector<pair<int,int>> poly,int color){
setcolor(color);
for (int i = 0; i < poly.size(); i++)
line(poly[i].first,poly[i].second,poly[(i+1)%poly.size()].first,poly[(i+1)%poly.size()].second);
}
int main(){
int gd = DETECT;
int gm = DETECT;
initgraph(&gd,&gm,"");
// Taking No of Sides of a Polygon
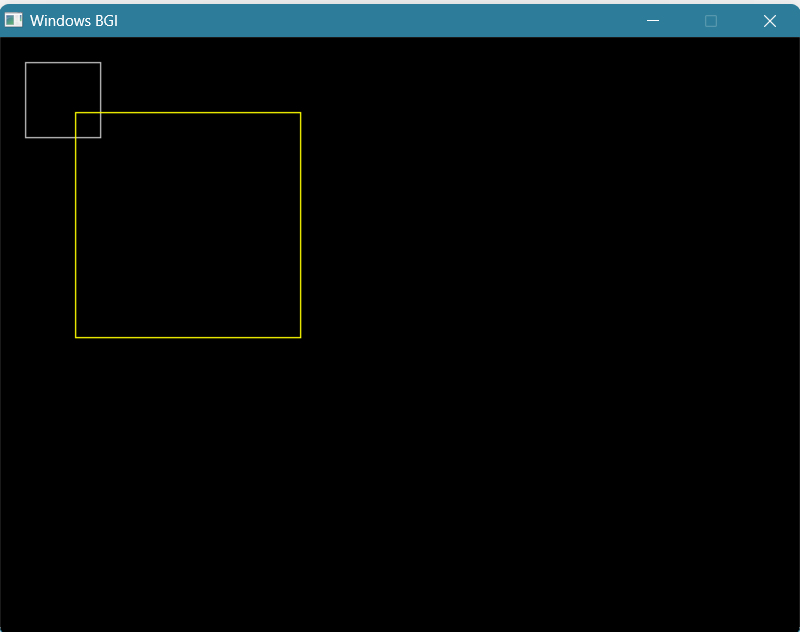
cout<<"Enter No of Side : ";
int no_of_side;
cin>>no_of_side;
// Taking co-ordinates of the sides
vector<pair<int,int>> coordinates;
for (int i = 0; i < no_of_side; i++)
{
int x,y;
cout<<"Enter (X"<<i+1<<",Y"<<i+1<<"):";
cin>>x>>y;
coordinates.push_back({x,y});
}
//Taking Scaling Factor
cout<<"Enter Scaling Factor (Sx,Sy) :";
int sx,sy;
cin>>sx>>sy;
draw_polygon(coordinates,7);
//Translate all points
for (int i = 0; i < coordinates.size(); i++)
{
coordinates[i].first*=sx;
coordinates[i].second*=sy;
}
draw_polygon(coordinates,14);
getch();
}Experiment 03 - Hidden Surface Elimination
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<graphics.h>
using namespace std;
void Triangle()
{
int x[] = {10, 50, 100};
int y[] = {100, 20, 100};
setcolor(YELLOW);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
line(x[i], y[i], x[(i + 1) % 3], y[(i + 1) % 3]);
}
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL, YELLOW);
floodfill(50, 25, YELLOW);
}
void Circle()
{
setcolor(RED);
circle(100, 100, 45);
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL, RED);
floodfill(101, 101, RED);
}
void Rectangle()
{
setcolor(GREEN);
rectangle(100-20, 100-20, 180, 180);
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL, GREEN);
floodfill(101, 101, GREEN);
}
int main()
{
string sequence;
cin >> sequence;
int gd = DETECT;
int gm = DETECT;
initgraph(&gd, &gm, "");
for (int i = 0; i < sequence.size(); i++)
{
if(sequence[i]=='C')
Circle();
else if(sequence[i]=='R')
Rectangle();
else
Triangle();
}
getch();
return 0;
}#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<graphics.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int gd = DETECT;
int gm = DETECT;
initgraph(&gd,&gm," ");
cout<<"Enter (x1,y1):";
int x1,y1;
cin>>x1>>y1;
cout<<"Enter (x2,y2):";
int x2,y2;
cin>>x2>>y2;
int dx = x2-x1;
int dy = y2-y1;
int cur_x = x1;
int cur_y = y1;
outtextxy(cur_x,cur_y,"X1,Y1");
putpixel(cur_x,cur_y,14);
int P = 2*dy-dx;
while(cur_x<x2 || cur_y<y2){
if(P<0){
cur_x++;
putpixel(cur_x,cur_y,14);
P+=2*dy;
}
else{
cur_x++;
cur_y++;
putpixel(cur_x,cur_y,14);
P+=2*dy-2*dx;
}
}
outtextxy(cur_x,cur_y,"X2,Y2");
getch();
}#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <graphics.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int gd, gm;
gd = DETECT, gm = DETECT;
initgraph(&gd, &gm, "");
// Input Parameter
int r = 150;
int x = 200;
int y = 200;
cin>>x>>y>>r;
// Process
int P = 1 - r;
int cur_x = 0, cur_y = r;
vector<pair<int, int>> points;
while (cur_x < cur_y)
{
points.push_back({cur_x, cur_y});
points.push_back({cur_y, cur_x});
cur_x++;
if (P < 0)
{
P += 2 * cur_x + 1;
}
else
{
cur_y--;
P += 2 * (cur_x - cur_y) + 1;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++)
{
putpixel(x + points[i].first, y + points[i].second, WHITE);
putpixel(x - points[i].first, y + points[i].second, WHITE);
putpixel(x - points[i].first, y - points[i].second, WHITE);
putpixel(x + points[i].first, y - points[i].second, WHITE);
}
getch();
}#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <graphics.h>
using namespace std;
int factorial(int n)
{
if(n<2)
return 1;
return n*factorial(n-1);
}
double nCr(int n, int r)
{
return (double)(factorial(n)/(factorial(r)*factorial(n-r)));
}
double bezierFunction(int k, int n, double u)
{
return nCr(n, k) * pow(u, k) * pow((1 - u), (n - k));
}
void bezierCurve(vector<pair<int, int>> points)
{
setcolor(YELLOW);
int n = points.size() - 1;
double eps = 0.0001;
for (double u = 0; u <= 1; u += eps)
{
double x = 0, y = 0;
for (int k = 0; k <= n; k++)
{
double bez = bezierFunction(k, n, u);
x += points[k].first * bez;
y += points[k].second * bez;
}
putpixel(x, y, WHITE);
}
for (auto x: points)
{
putpixel(x.first, x.second, WHITE);
circle(x.first, x.second, 5);
}
}
int main()
{
int gd = DETECT, gm = DETECT;
initgraph(&gd, &gm, "");
vector<pair<int, int>> points = {{27, 243}, {101, 22}, {350, 90}, {437, 43}};
bezierCurve(points);
getch();
closegraph();
return 0;
}#include <graphics.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
double x_left = 120, x_right = 500, y_bottom = 100, y_top = 350; //... Clipping window
int Left = 1, Right = 2, Bottom = 4, Top = 8; //... Region code
int regionCode(int x, int y)
{
int code = 0;
if (x > x_right) code |= Right;
else if (x < x_left) code |= Left;
if (y > y_top) code |= Top;
else if (y < y_bottom) code |= Bottom;
return code;
}
void cohenSutherland(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2)
{
int code1 = regionCode(x1, y1);
int code2 = regionCode(x2, y2);
while (true)
{
double x, y;
if (!(code1 | code2)) //... Line is completely inside
{
line(x1, y1, x2, y2);
return;
}
else if (code1 & code2) break; //... Line is completely outside
else //... Line is partially inside
{
int code = code1 ? code1 : code2;
if (code & Top)
{
y = y_top;
x = x1 + (x2 - x1) / (y2 - y1) * (y - y1);
}
else if (code & Bottom)
{
y = y_bottom;
x = x1 + (x2 - x1) / (y2 - y1) * (y - y1);
}
else if (code & Left)
{
x = x_left;
y = y1 + (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1) * (x - x1);
}
else if (code & Right)
{
x = x_right;
y = y1 + (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1) * (x - x1);
}
if (code == code1)
{
x1 = x;
y1 = y;
code1 = regionCode(x1, y1);
}
else
{
x2 = x;
y2 = y;
code2 = regionCode(x2, y2);
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int gd = DETECT, gm = DETECT;
initgraph(&gd, &gm, "");
setcolor(WHITE);
rectangle(x_left, y_bottom, x_right, y_top);
line(50, 200, 500, 400);
setcolor(GREEN);
cohenSutherland(50, 200, 500, 400);
getch();
closegraph();
return 0;
}#include<iostream>
#include<graphics.h>
#include<fstream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Point{
public:
int x, y;
Point(int x, int y)
{
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
};
Point intersect_point(Point p1, Point p2,
Point p3, Point p4)
{
int xnum = (p1.x*p2.y - p1.y*p2.x) * (p3.x-p4.x) -
(p1.x-p2.x) * (p3.x*p4.y - p3.y*p4.x);
int xden = (p1.x-p2.x) * (p3.y-p4.y) - (p1.y-p2.y) * (p3.x-p4.x);
int ynum = (p1.x*p2.y - p1.y*p2.x) * (p3.y-p4.y) -
(p1.y-p2.y) * (p3.x*p4.y - p3.y*p4.x);
int yden = (p1.x-p2.x) * (p3.y-p4.y) - (p1.y-p2.y) * (p3.x-p4.x);
return Point(xnum/xden, ynum/yden);
}
vector<Point> clip(vector<Point> points, Point p1, Point p2)
{
vector<Point> new_points;
for(int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++)
{
int k = (i+1) % points.size();
int ix = points[i].x;
int iy = points[i].y;
int kx = points[k].x;
int ky = points[k].y;
int i_pos = (p2.x - p1.x) * (iy - p1.y) - (p2.y - p1.y) * (ix - p1.x);
int k_pos = (p2.x - p1.x) * (ky - p1.y) - (p2.y - p1.y) * (kx - p1.x);
// Case 1 : When both points are inside
if(i_pos < 0 && k_pos < 0)
{
new_points.push_back(Point(kx, ky));
}
// Case 2: When only first point is outside
else if(i_pos >= 0 && k_pos < 0)
{
new_points.push_back(intersect_point(p1, p2, Point(ix, iy), Point(kx, ky)));
new_points.push_back(Point(kx, ky));
}
// Case 3: When only second point is outside
else if(i_pos < 0 && k_pos >= 0)
{
new_points.push_back(intersect_point(p1, p2, Point(ix, iy), Point(kx, ky)));
}
else
{
// No points are added.
}
}
return new_points;
}
vector<Point> southHodgeClip(vector<Point> points, vector<Point> clipper)
{
for(int i = 0; i < clipper.size(); i++)
{
int k = (i+1) % clipper.size();
points = clip(points, clipper[i], clipper[k]);
}
for(int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++)
{
cout<<points[i].x<<" "<<points[i].y<<endl;
}
return points;
}
void draw(vector<Point> points)
{
points.push_back(points[0]);
int n = points.size();
int arr[ 2*n ];
int j = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
arr[j] = points[i].x;
arr[j+1] = points[i].y;
j += 2;
}
drawpoly(n, arr);
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
int gd = DETECT;
int gm;
vector<Point> clipper;
clipper.push_back(Point(150, 150));
clipper.push_back(Point(150, 200));
clipper.push_back(Point(200, 200));
clipper.push_back(Point(200, 150));
initgraph(&gd, &gm, NULL);
draw(clipper);
int n;
{
ifstream cin("input.txt");
cin>>n;
}
vector<Point> points;
{
ifstream cin("input.txt");
cin>>n;
int x, y;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin>>x>>y;
points.push_back(Point(x, y));
}
}
draw(points);
getch();
cleardevice();
draw(clipper);
points = southHodgeClip(points, clipper);
setcolor(GREEN);
draw(points);
getch();
closegraph();
return 0;
}
#include <graphics.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void snowfalke(int x1, int y1, int x5, int y5, int it)
{
if (it)
{
vector<pair<int, int>> x(5);
int dx = (x5 - x1) / 3, dy = (y5 - y1) / 3;
x[0] = {x1, y1};
x[1] = {x1 + dx, y1 + dy};
x[2] = {(x1 + x5) / 2 + sqrt(3) * (y1 - y5) / 6, (y1 + y5) / 2 + sqrt(3) * (x5 - x1) / 6};
x[3] = {x1 + 2 * dx, y1 + 2 * dy};
x[4] = {x5, y5};
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
snowfalke(x[i].first, x[i].second, x[i + 1].first, x[i + 1].second, it - 1);
}
}
else line (x1, y1, x5, y5);
delay(5);
}
int main()
{
int gd = DETECT, gm = DETECT;
initgraph(&gd, &gm, "");
int iteration = 4;
vector<pair<int, int>> x = {{250, 15}, {50, 350}, {450, 350}};
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
snowfalke(x[i].first, x[i].second, x[(i + 1) % 3].first, x[(i + 1) % 3].second, iteration);
}
getch();
closegraph();
return 0;
}(I implemented an easier version with a triangle shape)