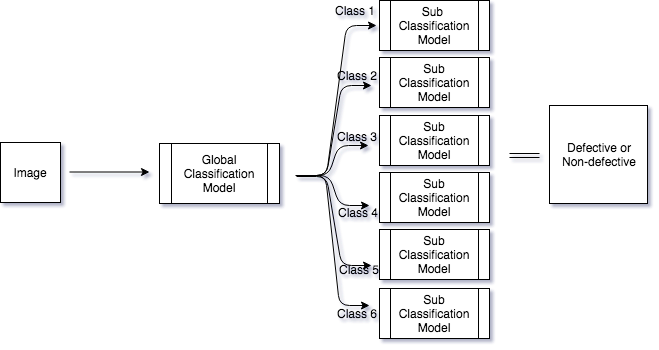
Automating the process of quality control using visual inspection by developing a deep learning model to distinguish between defective and non-defective products. Implementing model architecture as proposed in the paper.
- Python 3.3+
- Tensorflow 1.6+
- pillow (PIL)
- pickle
- Matplotlib
- DAGM Texture Databse: DAGM database used for model training
DAGM Texture database is used to train and test the model as specified in the paper. The dataset contains 6 product classes which are divided into normal and defective categories, having 1000 and 150 images respectively.
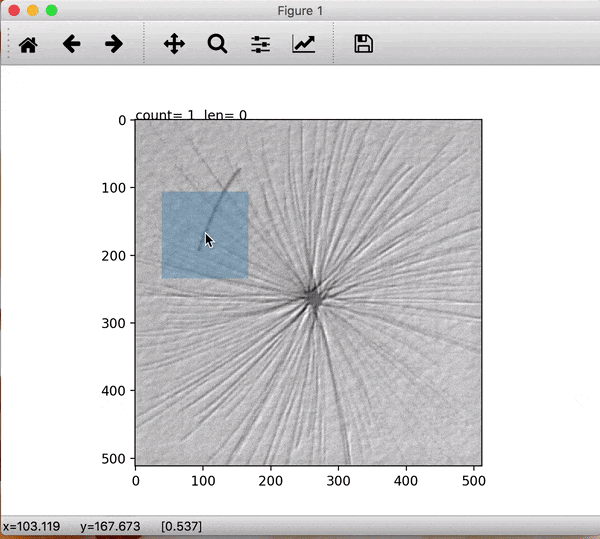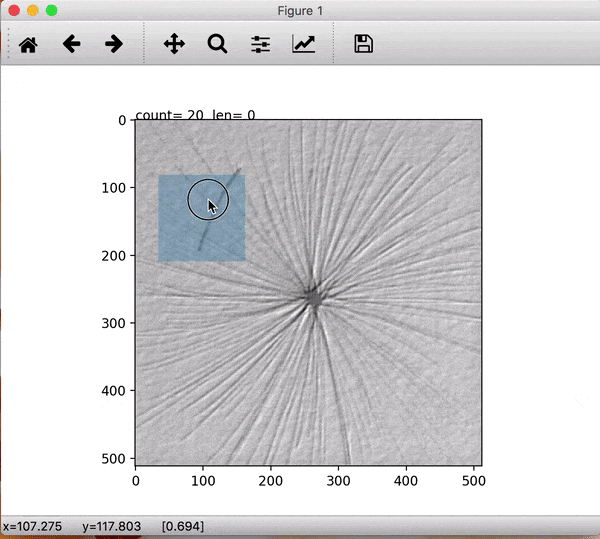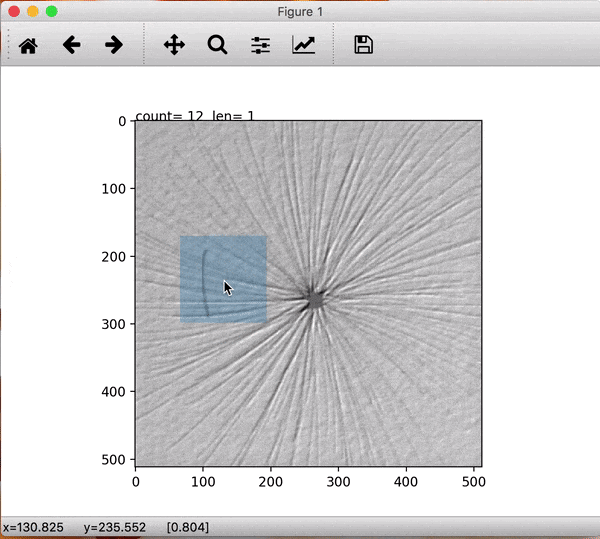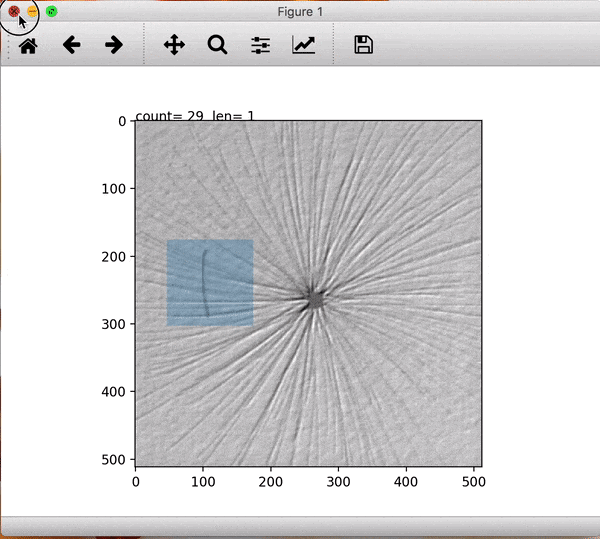
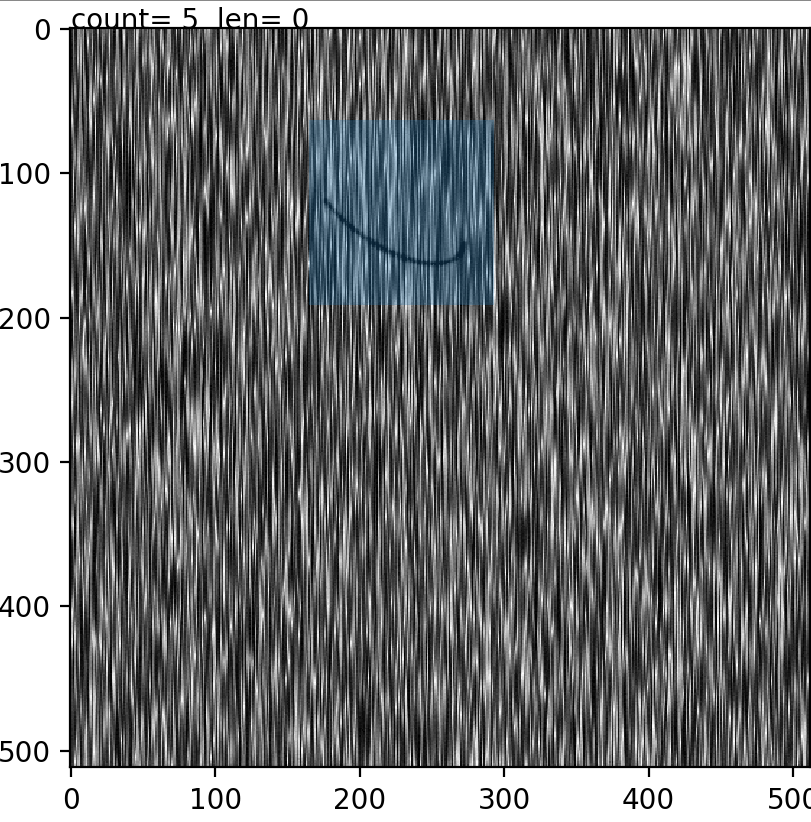
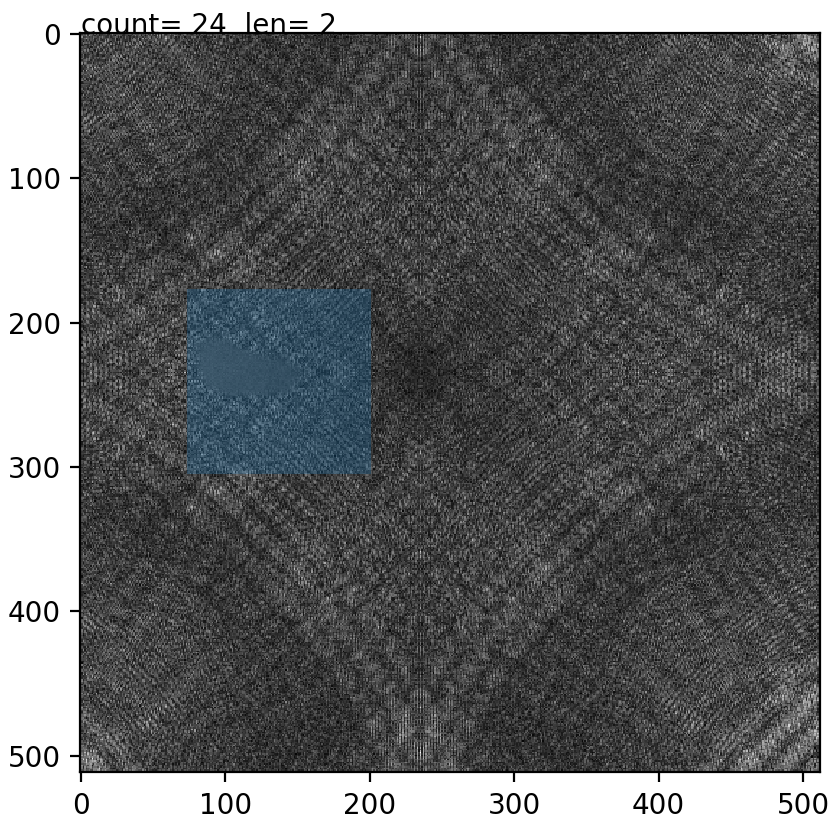
To enlarge the defective images set small patches are extracted manually after which they are augmented using rotations and mirrorings. To do this easily the prepdatalist.py file allows the user to save the centre points for the patches of every defective image and saving them to disk. Later, at the time of training, these centre points are used to create the training and validation dataset at run time.
 |
 |
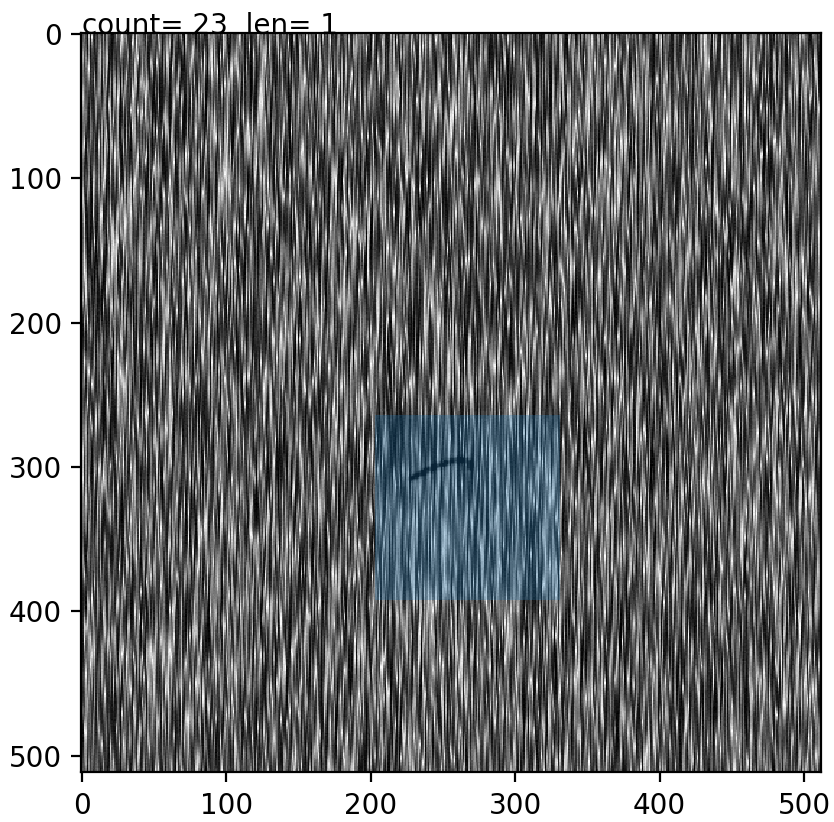 |
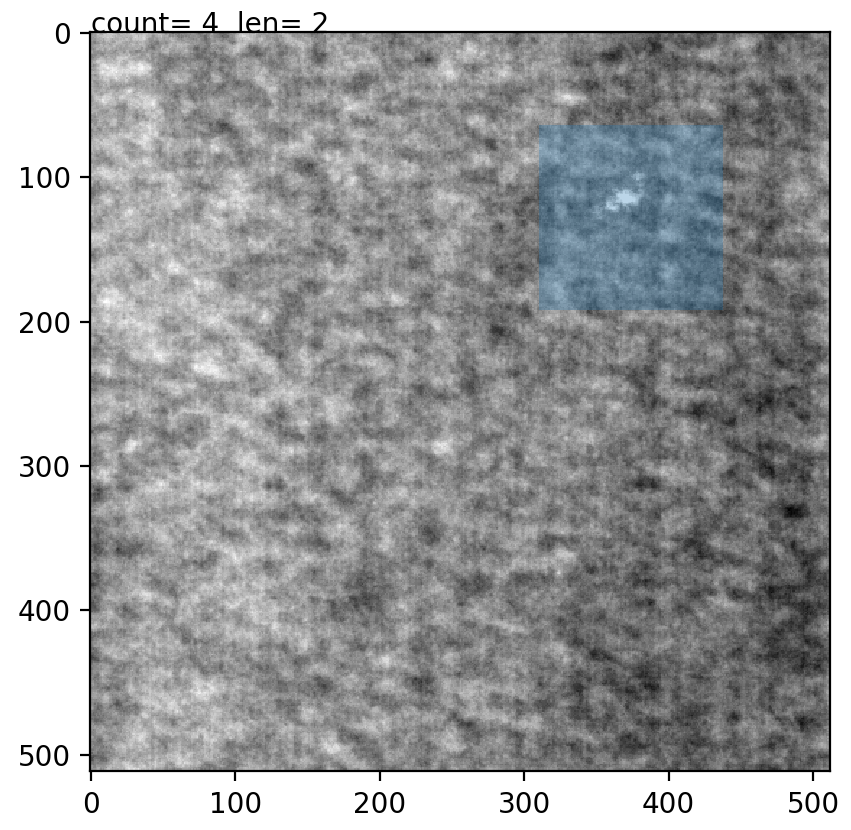
Fig1: Extracting image patch. The blue window patch shows the image which will be saved later. Count shows the image points extracted for this image and len shows the number of images processed for a specific class.
| Class 1 Defective | Class 2 Defective | Class 3 Defective |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
| Class 4 Defective | Class 5 Defective | Class 6 Defective |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
First, the image of the texture is passed through a 'global' classification model which predicts the class for the texture after which it passes through the class specific 'sub' model which classifies it as defective or non-defective. The model architecture is the same for 'global' and 'sub' models except for the last fully connected layer.
To prepare centre point lists for the defective images:
- Change data_path variable as per your project directory in the file prepdatalist.py and execute the same.
Executing this file produces 'sub' model file lists for every class with the name- qcdlsub(Class_no)list, e.g., qcdlsub2list and a 'global' model file list containing training and validation images for the global model - qcdlglobal
To train the model: 'sub' model
> python trainqcdl.py --data_path qcdl --model_part sub --class_no 2 --model_dir qcdl/sub2
'global' model
> python trainqcdl.py --data_path qcdl --model_part global --model_dir qcdl/global
- data_path: Path to the directory containing the dataset organised in Class(Classno) and Class(Classno)_def folders, e.g., Class1, Class1_def. File lists prepared on running prepdatalist.py are stored in this folder. The folder path is then passed as data_path variable value while training the model. (No default value. Need to provide)
- model_part: global or sub to train a model. (default value: global)
- class_no: Class_no for which to train the sub model (default value: 1)
- model_dir: Path to the directory where the model would be saved after training. (default value: model_dir)
Abhishek Tandon/ @Tandon-A