Sparsity and Linearity-Exploiting Interior-Point solver - Now Internally Readable
Named after Odin's eight-legged horse from Norse mythology, Sleipnir is a linearity-exploiting sparse nonlinear constrained optimization problem solver that uses the interior-point method.
#include <fmt/core.h>
#include <sleipnir/OptimizationProblem.hpp>
int main() {
// Find the x, y pair with the largest product for which x + 3y = 36
sleipnir::OptimizationProblem problem;
auto x = problem.DecisionVariable();
auto y = problem.DecisionVariable();
problem.Maximize(x * y);
problem.SubjectTo(x + 3 * y == 36);
problem.Solve();
// x = 18.0, y = 6.0
fmt::print("x = {}, y = {}\n", x.Value(), y.Value());
}Sleipnir's internals are intended to be readable by those who aren't domain experts with links to explanatory material for its algorithms.
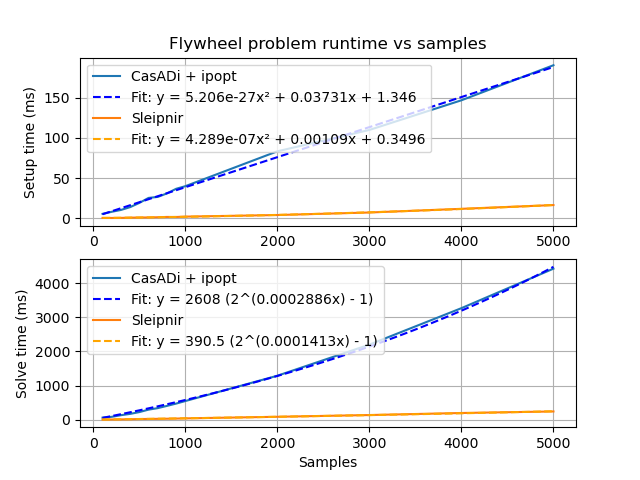 |
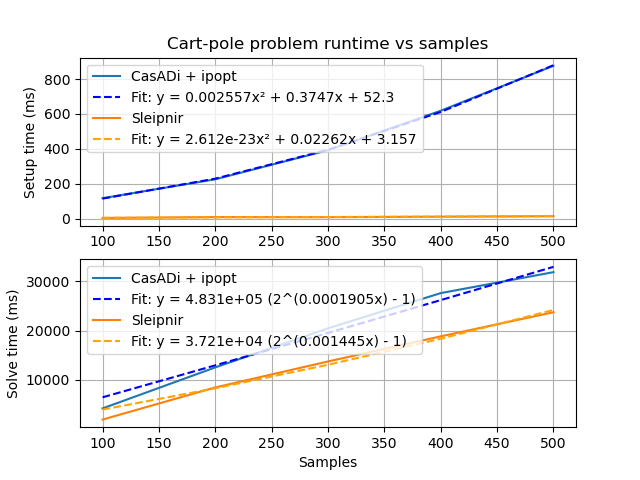 |
Generated by tools/generate-scalability-results.sh from benchmarks/scalability source on a i5-8350U with 16 GB RAM.
During problem setup, equality and inequality constraints are encoded as different types, so the appropriate setup behavior can be selected at compile time via operator overloads.
The autodiff library automatically records the linearity of every node in the computational graph. Linear functions have constant first derivatives, and quadratic functions have constant second derivatives. The constant derivatives are computed in the initialization phase and reused for all solver iterations. Only nonlinear parts of the computational graph are recomputed during each solver iteration.
For quadratic problems, we compute the Lagrangian Hessian and constraint Jacobians once with no problem structure hints from the user.
Eigen provides these. It also has no required dependencies, which makes cross compilation much easier.
This promotes fast allocation/deallocation and good memory locality.
We could mitigate the solver's high last-level-cache miss rate (~42% on the machine above) further by breaking apart the expression nodes into fields that are commonly iterated together. We used to use a tape, which gave computational graph updates linear access patterns, but tapes are monotonic buffers with no way to reclaim storage.
Benchmark projects are in the benchmarks folder. To compile and run the flywheel scalability benchmark, run the following in the repository root:
# Install CasADi first
cmake -B build -S .
cmake --build build
./build/FlywheelScalabilityBenchmark
# Install matplotlib, numpy, and scipy pip packages first
./tools/plot_scalability_results.py --filename flywheel-scalability-results.csv --title FlywheelSee the examples and optimization unit tests.
- C++20 compiler
- On Linux, install GCC 11 or greater
- On Windows, install Visual Studio Community 2022 and select the C++ programming language during installation
- On macOS, install the Xcode command-line build tools via
xcode-select --install
- Eigen
- fmtlib (internal only)
- googletest (tests only)
Library dependencies which aren't installed locally will be automatically downloaded and built by CMake.
If CasADi is installed locally, the benchmark executables will be built.
Starting from the repository root, run the configure step:
cmake -B build -S .This will automatically download library dependencies.
Run the build step:
cmake --build buildRun the tests:
cd build
ctestThe following build types can be specified via -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE:
- Debug
- Optimizations off
- Debug symbols on
- Release
- Optimizations on
- Debug symbols off
- RelWithDebInfo (default)
- Release build type, but with debug info
- MinSizeRel
- Minimum size release build
- Asan
- Enables address sanitizer
- Tsan
- Enables thread sanitizer
- Ubsan
- Enables undefined behavior sanitizer
- Perf
- RelWithDebInfo build type, but with frame pointer so perf utility can use it
Some test problems generate CSV files containing their solutions. These can be plotted with tools/plot_test_problem_solutions.py.
Logo: SVG, PNG (1000px)
Font: Centaur

