Cython wrapper for the efficient TV denoising algorithm by Laurent Condat. This wrapper wraps Condats C implementation of the algorithm for use with NumPy.
The algorithm this code uses is the improved fast total variation algorithm. The original C and MATLAB code is available on the software page of Laurent Condat's webpage.
To install these bindings, you should have a C-compiler installed on your system. Make sure you have NumPy and Cython installed beforehand (both packages come with Anaconda by default) and write
pip install condat-tv
in your terminal window. In case that does not work, you can install it directly from github by running the command
pip install git+https://github.com/yngvem/condat_tv.git
The following example is inspired by the experiments on syntetic data in [1]
import condat_tv
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltnp.random.seed(0)
N = 500 # number of samples
# Generate a sparse "derivative" vector
signal_derivative = np.random.standard_normal(N)*4
for k in range(N):
signal_derivative[k] = signal_derivative[k]*(np.random.uniform(0,1)>0.95)
# Integrate the sparse derivative vector to obtain a piecewise constant vector
signal = np.cumsum(signal_derivative)
# Add noise
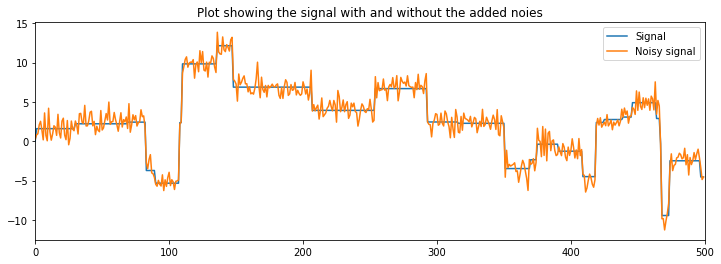
noisy_signal = signal + np.random.standard_normal(signal.shape)plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))
plt.plot(signal, label="Signal")
plt.plot(noisy_signal, label="Noisy signal")
plt.xlim(0, N)
plt.legend()
plt.title("Plot showing the signal with and without the added noies")
plt.show()plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))
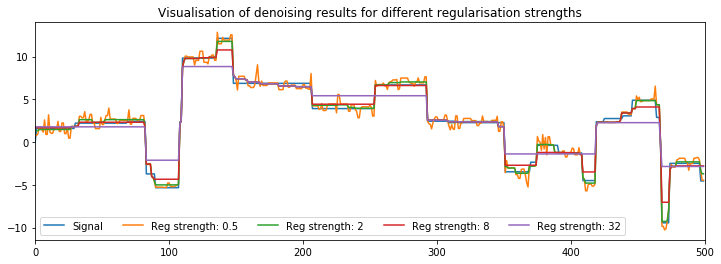
plt.plot(signal, label="Signal")
for reg_strength in [0.5, 2, 8, 32]:
# Denoise the signal with total variation minimization
denoised_signal = condat_tv.tv_denoise(noisy_signal, reg_strength)
# Visualize denoised signal
plt.plot(denoised_signal, label=f"Reg strength: {reg_strength}")
# Calculate and print RMSE
RMSE = np.linalg.norm(denoised_signal-signal)/np.sqrt(N)
print(f"Regularisation strength: {reg_strength:.1e}, RMSE: {RMSE:.2e}")
plt.xlim(0, N)
plt.legend(ncol=5)
plt.title("Visualisation of denoising results for different regularisation strengths")
plt.show()Regularisation strength: 5.0e-01, RMSE: 5.70e-01
Regularisation strength: 2.0e+00, RMSE: 3.56e-01
Regularisation strength: 8.0e+00, RMSE: 5.89e-01
Regularisation strength: 3.2e+01, RMSE: 1.52e+00
[1] Condat L. A direct algorithm for 1-D total variation denoising. IEEE Signal Processing Letters. 2013 Aug 15;20(11):1054-7. (link)