Extended Coherent Point Drift algorithm for point set registration with prior information.
This is an efficient C++ implementation of the ECPD algorithms for n-dimensional point set registration. The goal of point set registration algorithms in computer vision is 1) to find correspondences between two point sets X and Y and 2) to compute a transformation mapping from one to the other. Finding correspondences between points along with a suitable transformation makes this class of algorithms especially usefull. While the original CPD introduced by A. Myronenko and X. Song does not consider any prior knowledge regarding point correspondences, the extended version introduced by V. Golyanik et al. incorporates (sparse) correspondence pairs as constraints.
This implementation provides rigid, affine and non-rigid transformations T(Y) between two point sets X and Y.
- rigid: T(Y) = sYRT +1tT, i.e. transformation can be described by rotation, translation and a scaling factor (3 rot + 3 trans + 1 scal = 7 DoF).
- affine: T(Y) = YBT +1tT, i.e. affine matrix B is unconstrained, allowing any scalings and sheer (3 rot + 3 trans + 3 scal + 3 sheer = 12 DoF).
- non-rigid: T(Y) = Y + GW, with G a Gaussian kernel and W a coefficient matrix depending on smootheness and regularization parameters.
CPD: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/47544556_Point_Set_Registration_Coherent_Point_Drift
// Read test data set
const Matrix Y = parseXYZData("bunny.xyz");
// Apply some known rigid transformation
const Matrix R = AngleAxis(Pi_4, Vector3::UnitZ()).toRotationMatrix(); // rotate 45 deg around z-axis
const Vector3 t = Vector3(1, 2, 3); // shift
const ScalarType s = 4; // scale
const Matrix X = s * Y * R.transpose() + Vector::Ones(Y.rows()) * t.transpose();
// Let's see if we can find it
const auto res = ECPD<Rigid>::compute(X, Y, ECPD<Rigid>::Config());
std::cout << "R = \n" << res.first.R << std::endl; // found rotation matrix
std::cout << "t = " << res.first.t.transpose() << std::endl; // found translation vector
std::cout << "s = " << s << std::endl; // found scaling factor// Apply some non-rigid transformation
Matrix X = Y;
const Matrix W = 0.005 * Matrix::Random(X.rows(), X.cols());
X += W + Vector::Ones(Y.rows()) * Vector3(0, 0, 0.1).transpose();
// Permutate rows, i.e. destroy correspondences, to make it a bit harder
X = permutateRows(X);
// Let's see if we can find it
const auto res = ECPD<NonRigid>::compute(X, Y, ECPD<NonRigid>::Config());
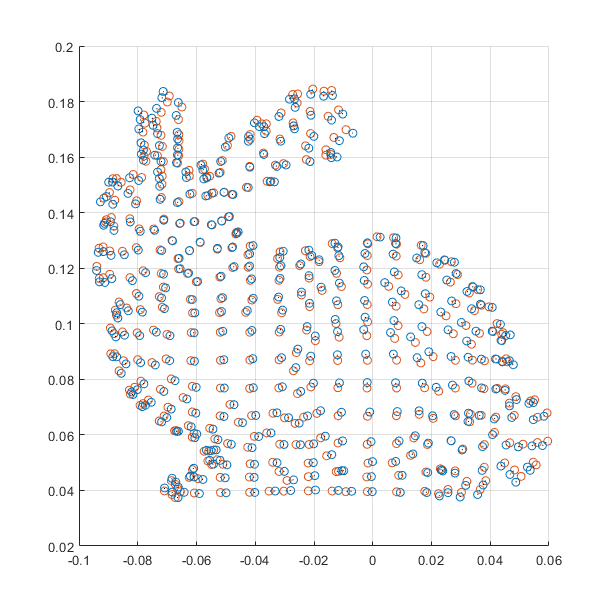
showPCs(res.second.T, Y);- Eigen3
- (optional: OpenMP)