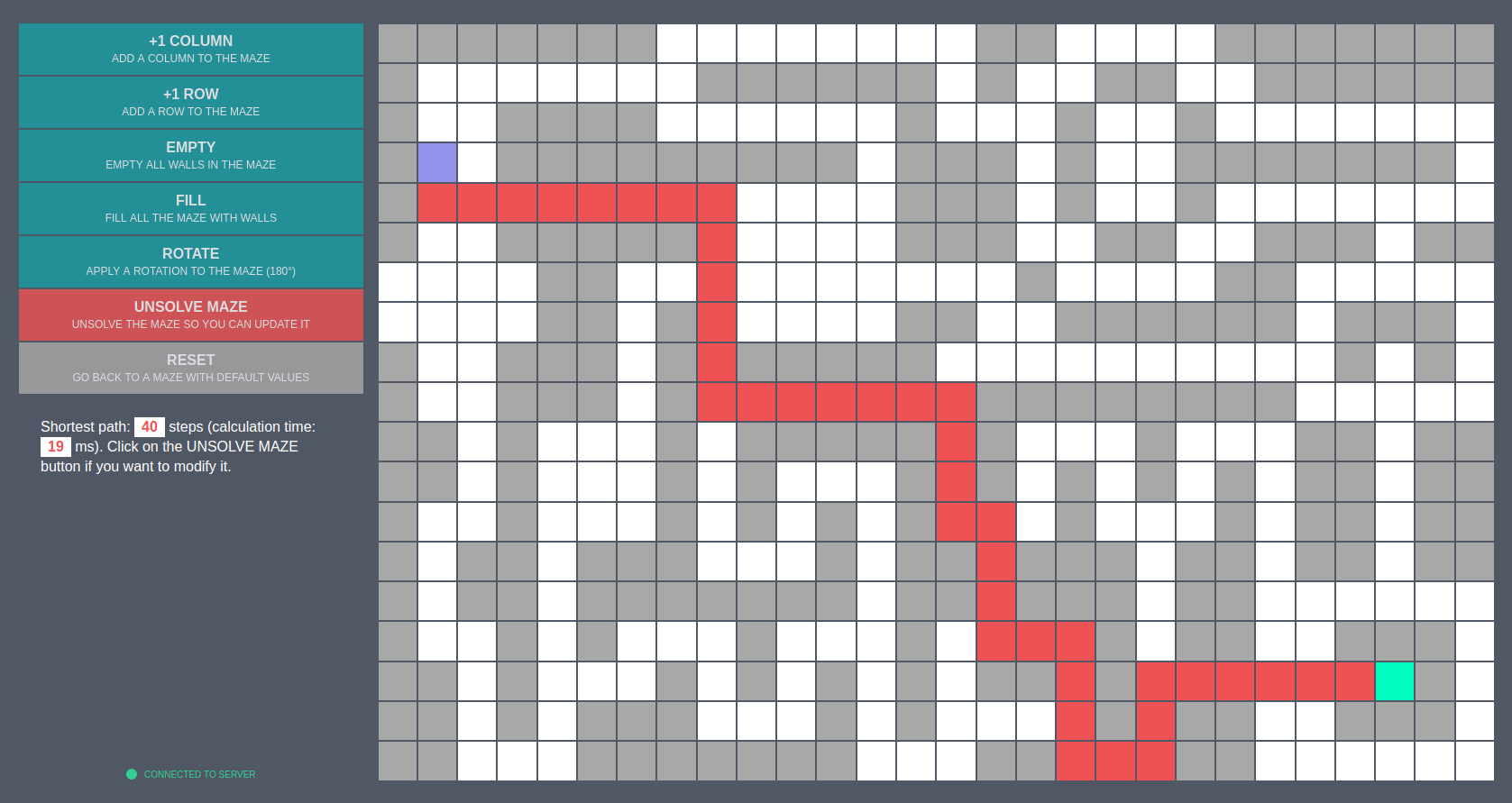
TINY PATHFINDER
Pathfinding prototype made with Ruby (back) and React/Redux (front)
December 2018
A tiny algorithm to find the shortest path in a maze
Want to test it?
You can use this INTERFACE MADE WITH REACT/REDUX.
Or, you can directly send requests...
Note: requests examples are made with httpie.
BASE_URL=https://tiny-pathfinder.herokuapp.com/mazes
http $BASE_URL/serverYou will receive a response when the server is awake!
{ "server": true }A maze is represented by a string and a width. The string contains 4 types of letters:
- S for start;
- F for finish;
- W for wall;
- P for path.
The maze should contain one start 'S' and one finish 'F' and should be rectangular. The width indicates where to cut this string in order to get rows and columns. For example, if you want to solve a maze like this one (where '#' is a wall and '.' is a path for readability):
#S#......#
#.#.####.#
#...#.....
...##.###.
...#...F..
You need to serialized it, so replace '#' by 'W' and '.' by 'P' and put everything in a single line:
SERIAL='WSWPPPPPPWWPWPWWWWPWWPPPWPPPPPPPPWWPWWWPPPPWPPPFPP'Now, you just have to send it with the width (here 10):
http POST $BASE_URL/solve serial=$SERIAL width=10This will render a json with the shortest path and some other informations:
{
"calculation_time": 1,
"error": null,
"path_found": true,
"path_length": 18,
"path_positions": [1, 11, 21, 22, 23, 13, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 18, 28, 29, 39, 49, 48, 47],
"path_serialized": "WSWXXXXXXWWXWXWWWWXWWXXXWPPPXXPPPWWPWWWXPPPWPPPFXX"
}calculation_time: time to calculate the shortest path (in ms);error: contains a message if the maze is unsolvable;path_found: true if a path has been found, false otherwise;path_length: length of the shortest path (number of steps);path_steps: shortest path steps from start to finish (positions);path_serialized: serialized path with 'X'' for the shortest path.
Note: path_steps length equals path_length + 1 because the starting node is included (but is not a step).
If there is no path from start to finish, the json will look like:
{
"calculation_time": 1,
"error": "unsolvable maze: finish can not be reached",
"path_found": false,
"path_length": null,
"path_positions": null,
"path_serialized": "WSWPPPPPPWWPWPWWWWPWWPPPWPPPPPPPPWWPWWWPPPPWPPWFWP"
}Note: path_serialized returns the serial input if no path has been found.
The algorithm
Validation class
app/services/validation.rb (readable code)
This class validates that the request is readable and check if:
- serial and width are present;
- serial is a string or respond to
to_s; - width is an integer or respond to
to_iand is positive; - serial contains only allowed characters ('S', 'F', 'W', 'P');
- there is exactly one 'S' and exactly one 'F'' character;
- the maze is rectangle (serial length modulo width returns zero).
Each error is added to the errors list.
Errors messages and regex are listed in the ValidationHelper module.
app/services/validation_helper.rb (readable code)
For example, a request with no parameter will return:
[
{
"error": "missing or invalid serial",
"text": "Serial is missing or is not a string."
},
{
"error": "missing or invalid width",
"text": "Width is missing or is not a positive integer."
},
{
"error": "forbidden characters",
"text": "Forbidden characters found in the serial. You should use only S (for start),
F (for finish), W (for wall) and P (for path)."
},
{
"error": "error with start and/or finish",
"text": "You should indicate one only one start (S) and finish (F)."
},
{
"error": "not rectangle",
"text": "The maze is not rectangle. Width should be a dividor of the serial length.
For example, if you want a maze of 8 columns and 6 rows,
provide a serial with 48 (8 * 6) characters and a width of 8."
}
]Solver class
app/services/solver.rb (readable code)
Finally, if there is no error, the Solver class will calculate the shortest path.
The public method solve launch the calculation, calculates the time taken, and returns the appropriate response with the methods response_solved or response_unsolvable.
The main method is the recursive method measure_distances which calculates and updates if necessary the distance from the start for each node in the maze, and the parent that gives the shortest path to this node:
- finds all reachable nodes around the current node (begin with start node 'S');
- for each node found:
- skips it if it's in the
@closed_list; - if the node is the finish node 'F', updates the
@finishvalue (parent and distance) if it is nil or if the distance is lower than the last one found; - if the node is a classic node, updates the distance and the parent if it's in the
@open_listwith a higher distance; - otherwise adds it to the
@open_listotherwise;
- skips it if it's in the
- returns nil if
@open_listis empty (all nodes have been analyzed); - finds the next node the analyze (first one in the
@open_list); - calls itself.
All the other methods are here to help this one: reachable_positions to find node available around, update_finish to update the @finish value if necessary, update_open_list to define if the node should be added or updated, create_node to add a node to the @open_list, update_node top update a node in the @open_list if necessary, update_current_node to find the next node to analyze.
When the shortest path is found, generate_path renders this path from start to finish (all positions to pass by) and serialized_path renders a seriliazed path (with 'X' for shortest path).
Specs
spec (spec directory)
There is 3 specs to check returns for:
- invalid params (12 errors tested);
- solvable mazes (9 mazes tested);
- unsolvable mazes (4 mazes tested).
The MazeSpecHelper module imports datas from CSV and generates mazes to test.