1st repository to get started with GitHub. This repo contains a set of handy git commands to enable beginners to get started with Open Source Development & Version Control.
-
git config --global user.name <your-name>This name will be displayed against the commits you create.
git config --global user.email <your-registered-email> -
git init -
git remote add origin <http-link-of-the-git-repo> -
Adding/Configuring a remote upstream repository. (Useful to keep a forked repo in sync with an upstream repo).
git remote add upstream <http-link-to-the-upstream-repo> -
Firstly, make sure you have already configured a remote upstream repo (using 3) before proceeding with the following steps:
git pull upstreamThis will create a new branch in your local repo named 'upstream/master'.
Then checkout out to your master branch.
git checkout masterThen merge the 'upstream/master' branch with the 'master' branch using the following command:
git merge upstream/masterFinally, delete the local 'upstream/master' branch after the merge using the following command:
git branch -d upstream/masterThis will sync your local repo with the upstream, if you want to reflect the changes to your remote forked repo, simply push the changes to the remote origin repo using the following command.
git push -u origin master -
git remote -v -
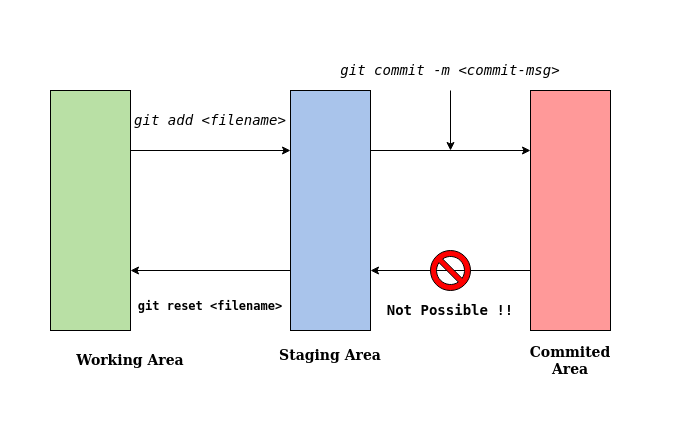
git add { <filename> | -A }Using the ' -A ' option instead of specifying a file name will transfer all the unstaged changes to the staging area.
-
git commit -m "<a-brief-message-about-the-commit>" -
git status -
git log -
git branch <branch-name> -
git branchEx:
git branch Lists all the local branches. git branch -r Lists all the branches in the Remote Repository. git branch -a Lists all local & remote branches. -
git checkout <branch-name> -
git pull origin
Go through this document for a list of best practices while using git: Best Practices
Contributions are welcome.
This guide is under active development and i will be adding newer commands as time progresses. Presently, i have only included those commands which are the bare minimum for getting started with version control. Meanwhile, if you find some other git command which you would want to include in this guide, feel free to open a pull request will all the necessary changes.