| layout | title |
|---|---|
page |
Overview |
{{ page.title }}
Contents
- What is vxlang?
- Software Protector
- Software Code obfuscation and virtualization
- Virtualization Preview
- Deploying the full version
- Latest Version
What is vxlang?
Software can be described as human-understandable mnemonics through disassamblers, and additional information can be used to convert to advanced languages such as C/C++, which are easier to understand. However, this type of analysis can also be referred to as reverse engineering, which can pose a threat to the security of the software.
vxlang is a project designed to prevent manipulations such as static or dynamic analysis, file modification, or unauthorized access by attackers, such as those described above. The vxlang project provides services for software security risks by implementing anti-tamper measures to prevent unauthorized access.
The vxlang project currently targets native binary files on x86-64 systems and Microsoft Windows operating systems, including executable files with the ".exe" extension and dynamic link library files with the ".dll" extension, kernel driver files with the ".sys". (The target binary types supported by vxlang will be expanded in future updates.)
Software Protector
Executable compression refers to the process of compressing a file into an executable format. This type of compression helps to hide source code and file information, making access more difficult. Software protectors such as vxlang can provide increased security by tampering with files, obfuscating code, and performing dynamic analysis protection to prevent unauthorized access or tampering.
Software Code obfuscation and virtualization
The software protector effectively blocks access to encryption and runtime states, however, it has a drawback in that it can expose the source code when the runtime state is dumped. To address this issue, code obfuscation is applied by adding dummy code or modulating the source code with similar code to the code exposed in the static or dynamic state. However, a more effective solution to protect the code is Code-Virtualization. Code virtualization represents real-world operational commands as virtual code, which can be executed on internal virtual machines. This approach provides a higher level of security compared to code obfuscation alone. vxlang offers these advanced obfuscation and virtualization services to ensure the protection of the code.
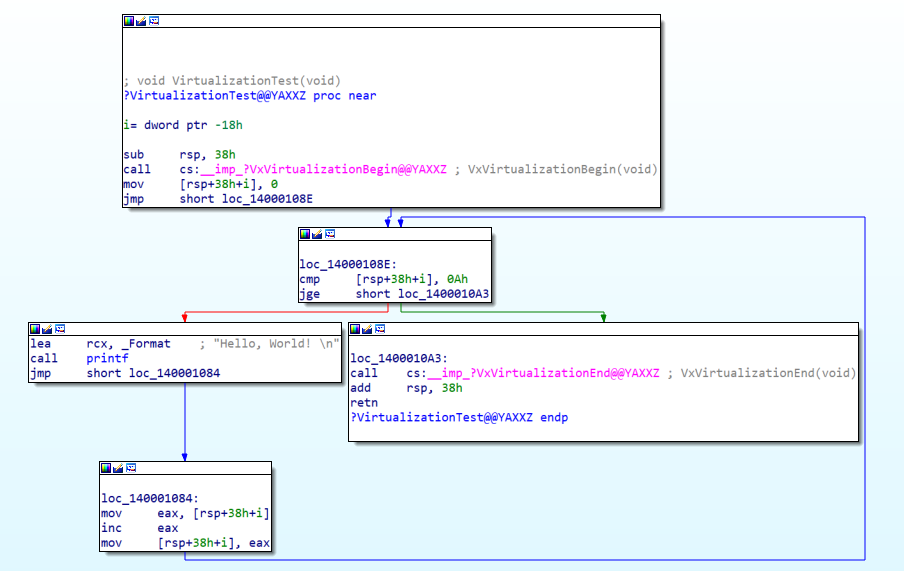
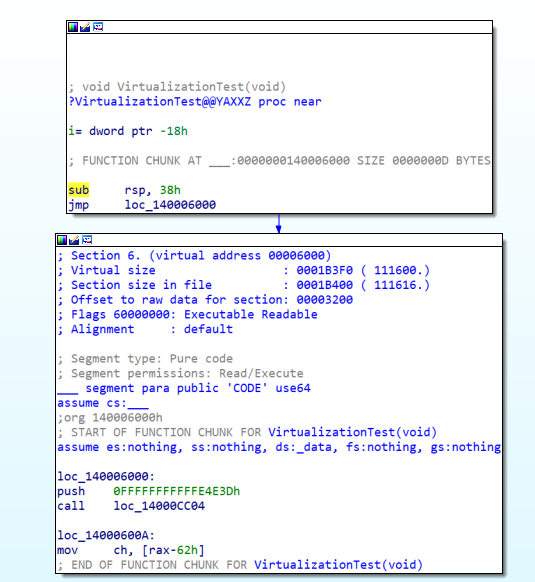
Virtualization Preview
Deploying the full version
The beta version of vxlang is free software, please request the full version via email and we will respond by creating your distribution file.
Latest Version
0.9.2
- Added code virtualization for kernel drivers.
- Removed the message box from the beta version.
- Download
0.9.1
- 2023.04.12.hotfix
- A bug has been fixed for detection.
- A bug has been fixed for the ADD-ON module.
- Change the core to Capstone Engine for ARM research.
... return cs_disasm_iter(cs_handle, (const uint8_t **)&buffer, &size, &address, insn);
- Users can add extension modules (add-ons). Extension modules allow users to take control of the
vxlangcore and add specialized functionality. - Example
#include <windows.h> #include <stdio.h> #define VXLANG_ADDON_MODULE #include "vxlib.h" BOOL WINAPI DllMain(HINSTANCE hinstDLL, DWORD fdwReason, LPVOID lpvReserved) { BOOL result = TRUE; switch (fdwReason) { case DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH: break; case DLL_THREAD_ATTACH: break; case VXLANG_LOAD_ADDON_EVENT: break; case VXLANG_DETECTED_DEBUG: case VXLANG_DETECTED_PATCH: case VXLANG_DETECTED_PATCH_SHELL: case VXLANG_DETECTED_PATCH_IMAGE: case VXLANG_DETECTED_PAUSE: case VXLANG_DETECTED_HANDLE: case VXLANG_DETECTED_SHELL: case VXLANG_DETECTED_DLL: break; case VXLANG_START_EVENT: break; case VXLANG_TERMINATE_EVENT: break; default: break; } return result; } /** * */ void NTAPI TlsCallback1(PVOID DllHandle, DWORD dwReason, PVOID) { if (dwReason == DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH) { } else if (dwReason == DLL_THREAD_ATTACH) { } } void NTAPI TlsCallback2(PVOID DllHandle, DWORD dwReason, PVOID) { if (dwReason == DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH) { } else if (dwReason == DLL_THREAD_ATTACH) { } } #ifdef _WIN64 #pragma comment (linker, "/INCLUDE:_tls_used") #pragma comment (linker, "/INCLUDE:_tls_callback_list") #else #pragma comment (linker, "/INCLUDE:__tls_used") #pragma comment (linker, "/INCLUDE:__tls_callback_list") #endif #ifdef _WIN64 #pragma const_seg(".CRT$XLC") EXTERN_C const #else #pragma data_seg(".CRT$XLC") EXTERN_C #endif PIMAGE_TLS_CALLBACK _tls_callback_list[] = { TlsCallback1, TlsCallback2 }; #ifdef _WIN64 #pragma const_seg() #else #pragma data_seg() #endif
vxlang.exe ${target-path} --add-on ${add-on-path} - If the return value of the extension module
DllMainisFALSE, the Terminate event is fired. - Download
Special Thanks
Thank you to everyone who helped with the development.