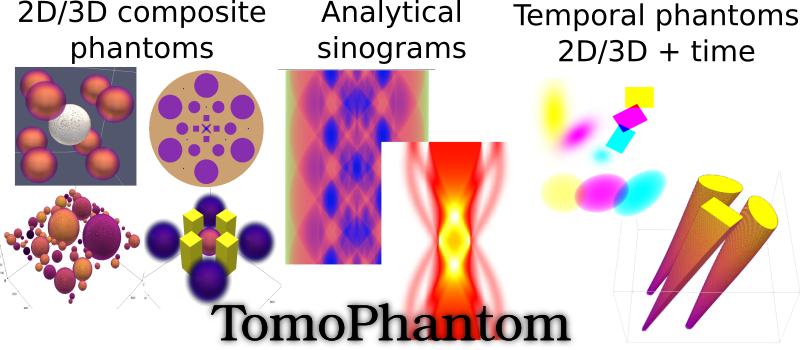
| TomoPhantom [1] is a toolbox written in C language to generate customisable 2D-4D phantoms (with a temporal capability) and their analytical projection data (parallel-beam geometry) for various image processing (e.g. tomographic reconstruction, denoising, deblurring, segmentation, etc.) and machine/deep learning tasks (e.g. segmentation, classification, clustering, etc.). |
| Master | Development | Anaconda binaries | Binder |
|---|---|---|---|
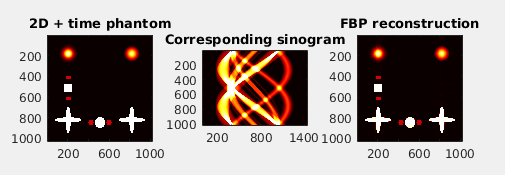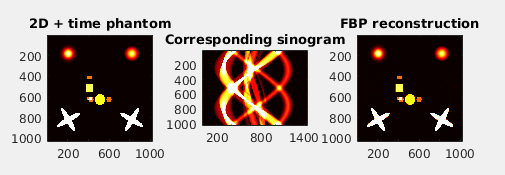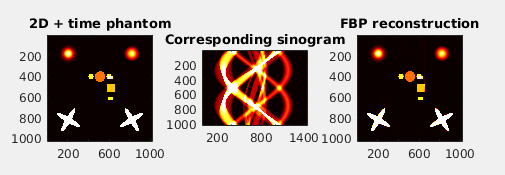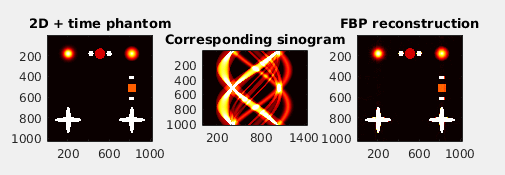
TomoPhantom is recommended for various image processing tasks that require extensive numerical testing: image reconstruction, denoising, deblurring, etc. Specifically, TomoPhantom is best-suited for testing various tomographic image reconstruction (TIR) methods. For TIR algorithms testing, the popular Shepp-Logan phantom is not always a good choice due to its piecewise-constant nature. This toolbox provides a simple modular approach to efficiently build customisable 2D-4D phantoms consisting of piecewise-constant, piecewise-smooth, and smooth analytical objects.
- Generate 2D synthetic phantoms made of Gaussians, parabolas, ellipses, cones and rectangulars.
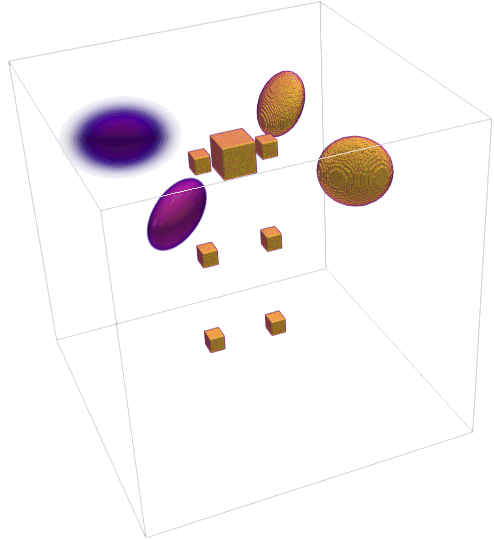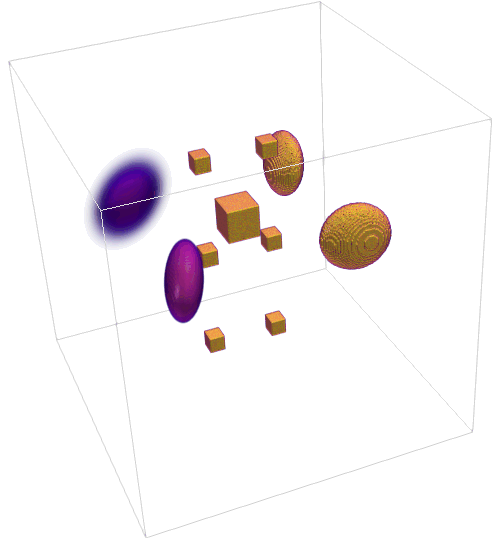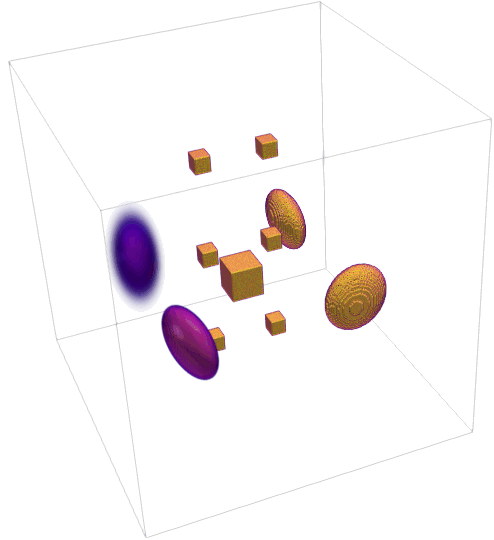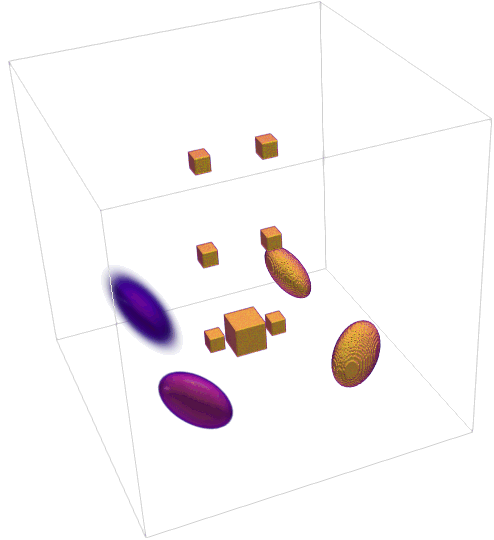
- Generate 3D synthetic phantom and 4D (temporal) extensions.
- Calculate analytical Radon transform of 2D-4D models and also their numerical projections.
- Model Gaussian or Poisson noise and some typical acquisition artifacts (zingers, rings, shifts, partial volume effect and others)
- Perform reconstructions avoiding 'Inverse Crime' using ToMoBAR, ASTRA-toolbox or TomoPy packages.
Run TomoPhantom in Binder HERE with jupyter-notebooks in Demos/Python/jupyter-notebooks
- Python (tested ver. 3.5-3.8); Cython OR
- MATLAB
- C compilers: GCC/MinGW/TDM-GCC/Visual Studio
- CMake (if this installation route is chosen)
Tomophantom is distributed as conda package for linux-64 from the ccpi channel. To install
conda install tomophantom -c ccpi
The package comes as a CMake project so you will need CMake (v.>=3) to configure it. Additionally you will need a C compiler, and a build tool as make (on linux). The toolkit may be used with Python and/or Matlab for which we provide wrappers. TomoPhantom's core is built as shared library and it should be possible to call it directly from C/C++, but currently no C/C++ API is available.
Prerequisites:
- CMake >= 3.0
- a C compiler with OpenMP
- libm on linux
- Cython to build the Python wrappers (optional)
- MATLAB installation to build MATLAB wrappers (optional)
- Clone this repository to a directory, i.e.
TomoPhantom, - create a build directory.
- Issue
cmaketo configure (orcmake-gui, orcmake, orcmake3). Use additional flags to fine tune the configuration.
Flags used during configuration
| CMake flag | type | meaning |
|---|---|---|
BUILD_PYTHON_WRAPPER |
bool | ON|OFF whether to build the Python wrapper |
BUILD_MATLAB_WRAPPER |
bool | ON|OFF whether to build the Matlab wrapper |
CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX |
path | your favourite install directory |
PYTHON_DEST_DIR |
path | python modules install directory (default ${CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX}/python) |
MATLAB_DEST_DIR |
path | Matlab modules install directory (default ${CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX}/matlab) |
CONDA_BUILD |
bool | ON|OFF whether it is installed with setup.py install |
Matlab_ROOT_DIR |
path | Matlab directory |
PYTHON_EXECUTABLE |
path | /path/to/python/executable |
Here an example of build on Linux:
git clone https://github.com/dkazanc/TomoPhantom.git
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ../ -DCONDA_BUILD=OFF -DMatlab_ROOT_DIR=/home/algol/matlab2016/ -DBUILD_MATLAB_WRAPPER=ON \
-DBUILD_PYTHON_WRAPPER=ON -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=./install
make install
# let Python find the shared library
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=${LD_LIBRARY_PATH}:./install
# let MATLAB find the shared library and mex files
PATH="./install/matlab:$PATH" LD_LIBRARY_PATH="./install/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH" matlabSee run.sh script for additional examples on build.
git clone https://github.com/dkazanc/TomoPhantom.git
cd TomoPhantom
export CIL_VERSION=1.4.9
conda build Wrappers/Python/conda-recipe --numpy 1.15 --python 3.7
conda install -c file://${CONDA_PREFIX}/conda-bld/ tomophantom --force-reinstall
- Phantom2DLibrary.dat and Phantom3DLibrary.dat are editable text files with parametrised models (2D/3D versions of Shepp-Logan, Defrise, and QRM phantoms are included). The generation of new phantoms is highly encouraged, please submit them through pull requests or via e-mail bellow.
- See MATLAB and Python demos
TomoPhantom is released under Apache License v.2. Note that some demos where 'ASTRA-toolbox' is used are of GPLv3 license and also BSD-3 license for TomoPy package.
- xdesign XDesign is an open-source Python package for generating configurable simulation phantoms for benchmarking tomographic image reconstruction.
- syris Syris (synchrotron radiation imaging simulation) is a framework for simulations of X-ray absorption and phase contrast dynamic imaging experiments, like time-resolved radiography, tomography or laminography.
[2] D. Kazantsev, V. Pickalov "New iterative reconstruction methods for fan-beam tomography", IPSE, 2017
- TOmographic MOdel-BAsed Reconstruction (ToMoBAR)
- Joint image reconstruction method with correlative multi-channel prior for X-ray spectral computed tomography
- Deep learning segmentation of synthetic tomographic data using Pytorch U-net
Software related questions/comments please e-mail to Daniil Kazantsev at dkazanc@hotmail.com