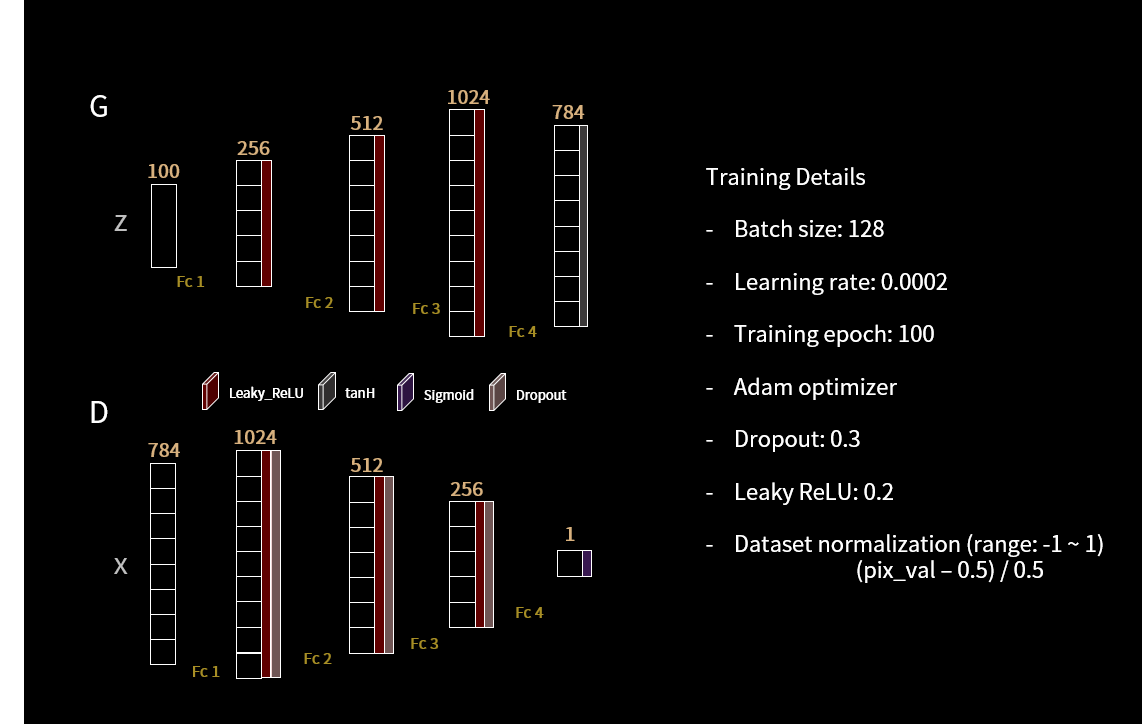
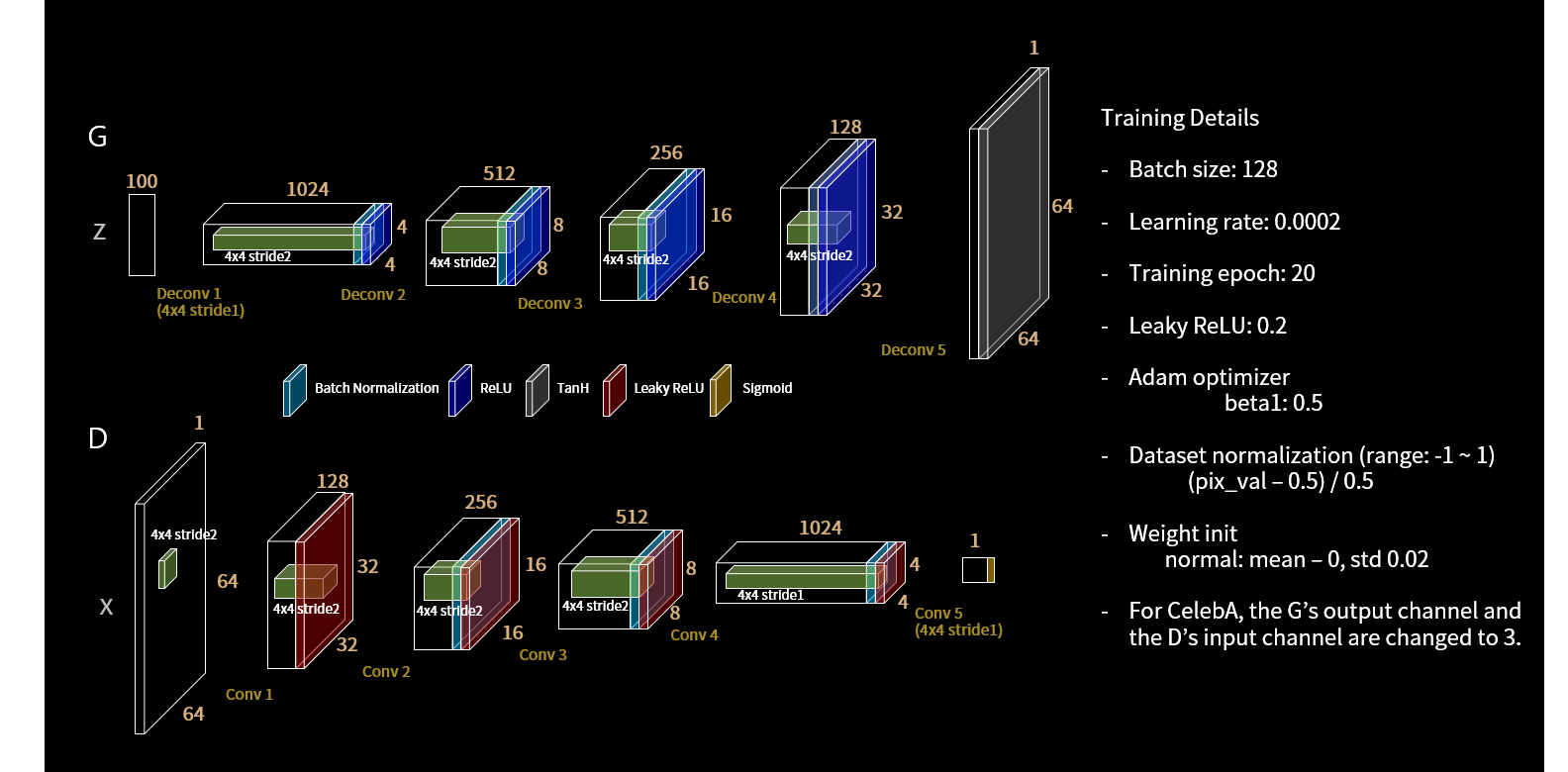
Pytorch implementation of Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) [1] and Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Networks (DCGAN) [2] for MNIST [3] and CelebA [4] datasets.
-
If you want to train using cropped CelebA dataset, you have to change isCrop = False to isCrop = True.
-
you can download
- MNIST dataset: http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/
- CelebA dataset: http://mmlab.ie.cuhk.edu.hk/projects/CelebA.html
-
pytorch_CelebA_DCGAN.py requires 64 x 64 size image, so you have to resize CelebA dataset (celebA_data_preprocess.py).
-
pytorch_CelebA_DCGAN.py added learning rate decay code.
- GAN
- DCGAN
- Generate using fixed noise (fixed_z_)
| GAN | DCGAN |

| 
|
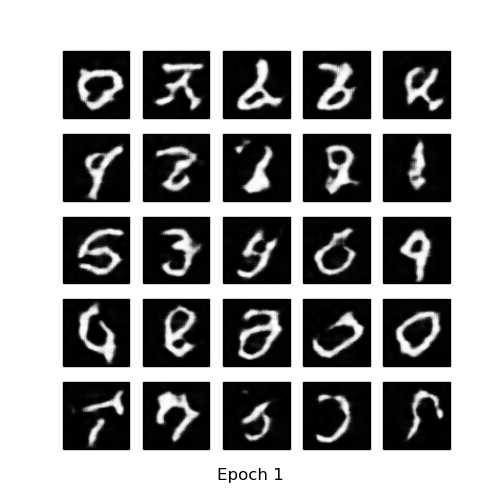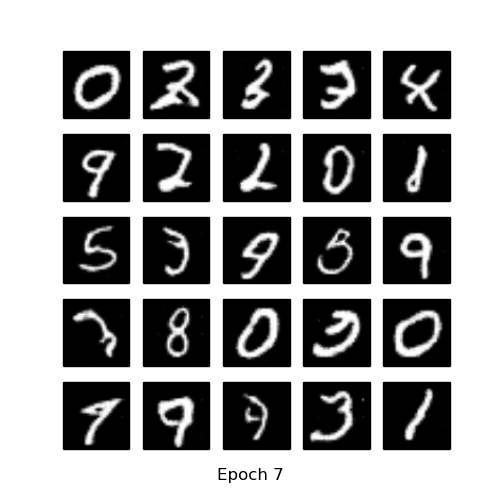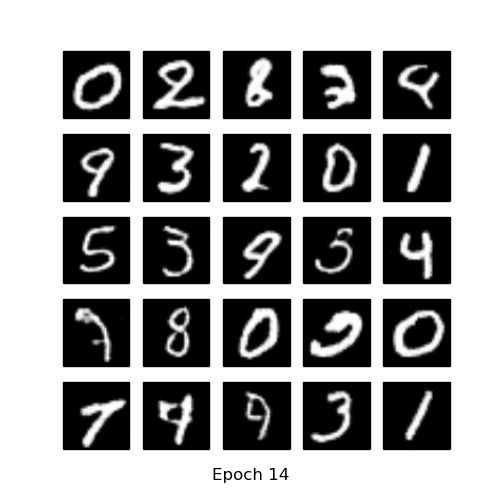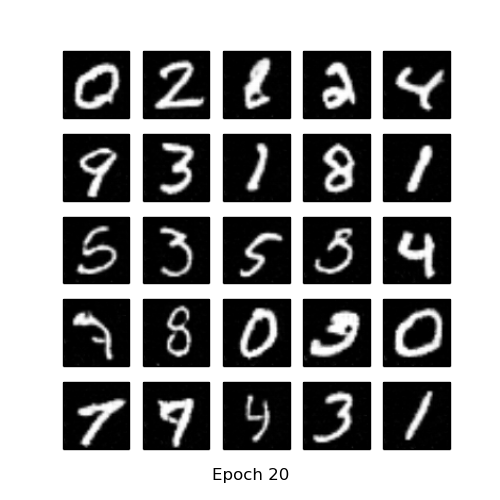
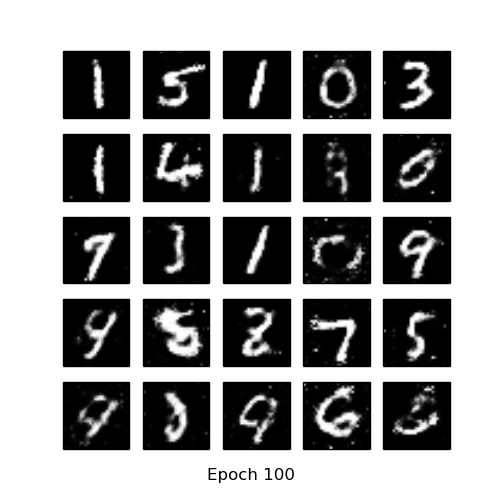
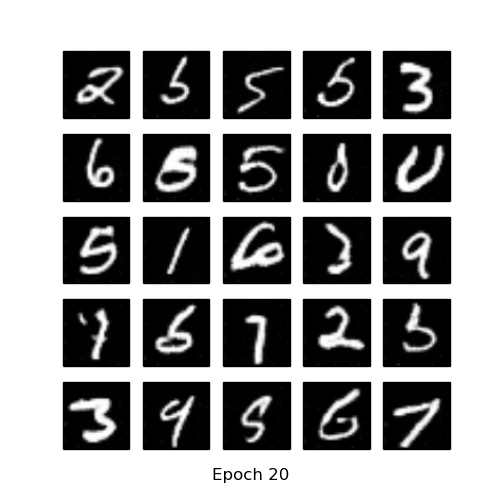
- MNIST vs Generated images
| MNIST | GAN after 100 epochs | DCGAN after 20 epochs |
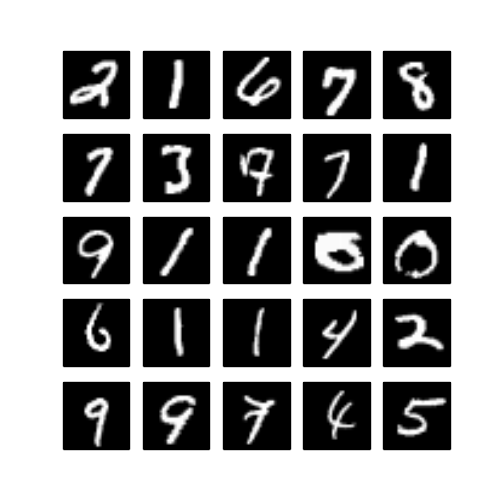
| 
| 
|
-
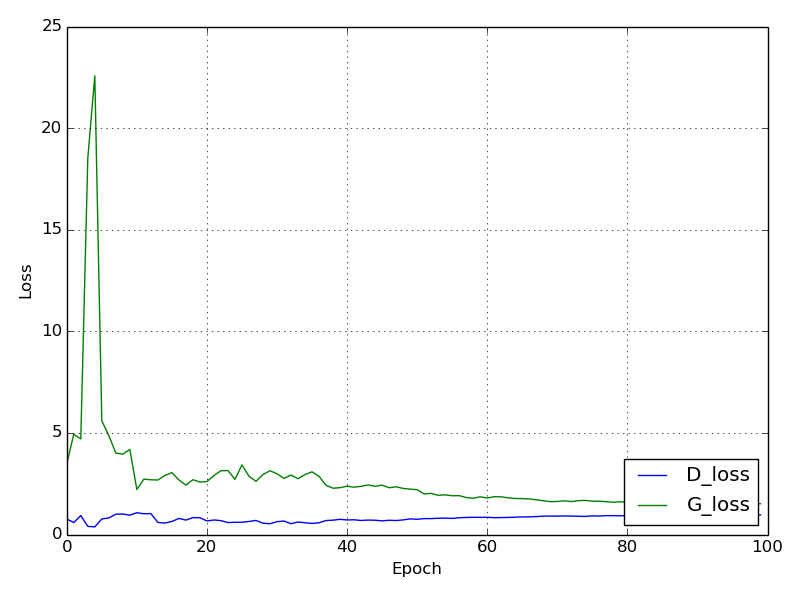
Training loss
-
Learning Time
- MNIST DCGAN - Avg. per epoch: 197.86 sec; (if you want to reduce learning time, you can change 'generator(128)' and 'discriminator(128)' to 'generator(64)' and 'discriminator(64)' ... then Avg. per epoch: about 67sec in my development environment.)
- Generate using fixed noise (fixed_z_)
| DCGAN | DCGAN crop |

| 
|
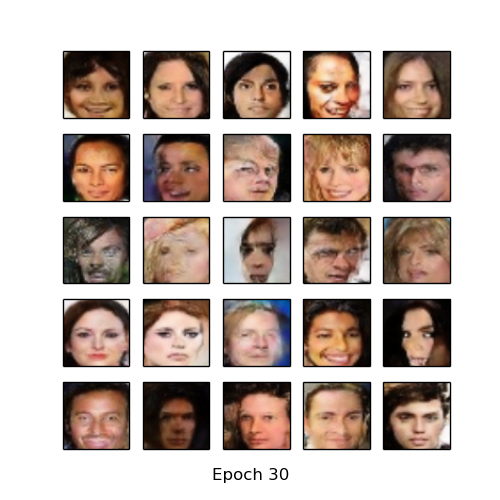
- CelebA vs Generated images
| CelebA | DCGAN after 20 epochs | DCGAN crop after 30 epochs |

| 
| 
|
- Learning Time
- CelebA DCGAN - Avg. per epoch: 732.54 sec; total 20 epochs ptime: 14744.66 sec
- Ubuntu 14.04 LTS
- NVIDIA GTX 1080 ti
- cuda 8.0
- Python 2.7.6
- pytorch 0.1.12
- torchvision 0.1.8
- matplotlib 1.3.1
- imageio 2.2.0
- scipy 0.19.1
[1] Goodfellow, Ian, et al. "Generative adversarial nets." Advances in neural information processing systems. 2014.
(Full paper: http://papers.nips.cc/paper/5423-generative-adversarial-nets.pdf)
[2] Radford, Alec, Luke Metz, and Soumith Chintala. "Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks." arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.06434 (2015).
(Full paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1511.06434.pdf)
[3] Y. LeCun, L. Bottou, Y. Bengio, and P. Haffner. "Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition." Proceedings of the IEEE, 86(11):2278-2324, November 1998.
[4] Liu, Ziwei, et al. "Deep learning face attributes in the wild." Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 2015.