- Project Purpose
- Demo Video
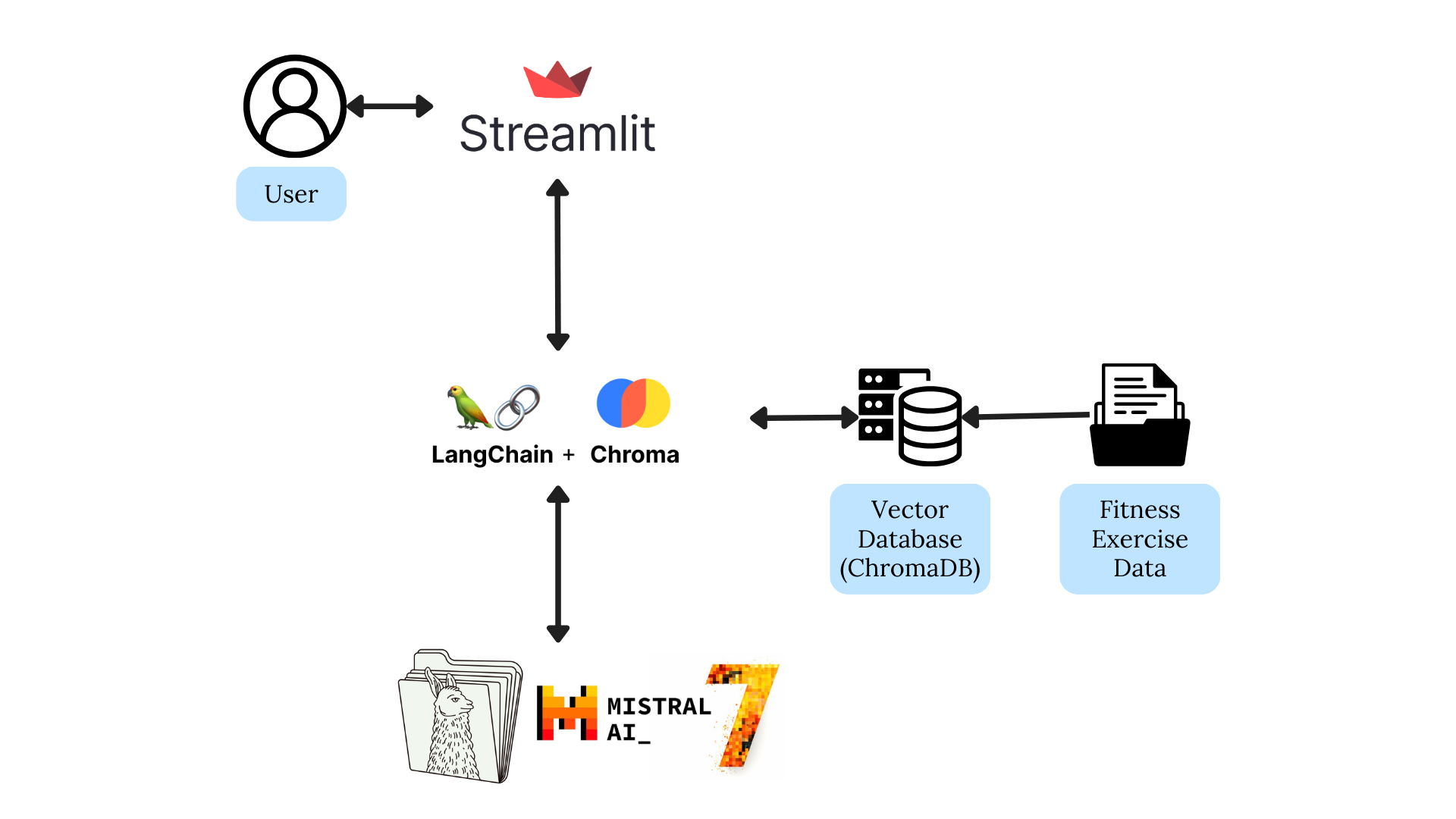
- Architecture Diagram
- Project Structure
- Setup Instructions
- Running the Application
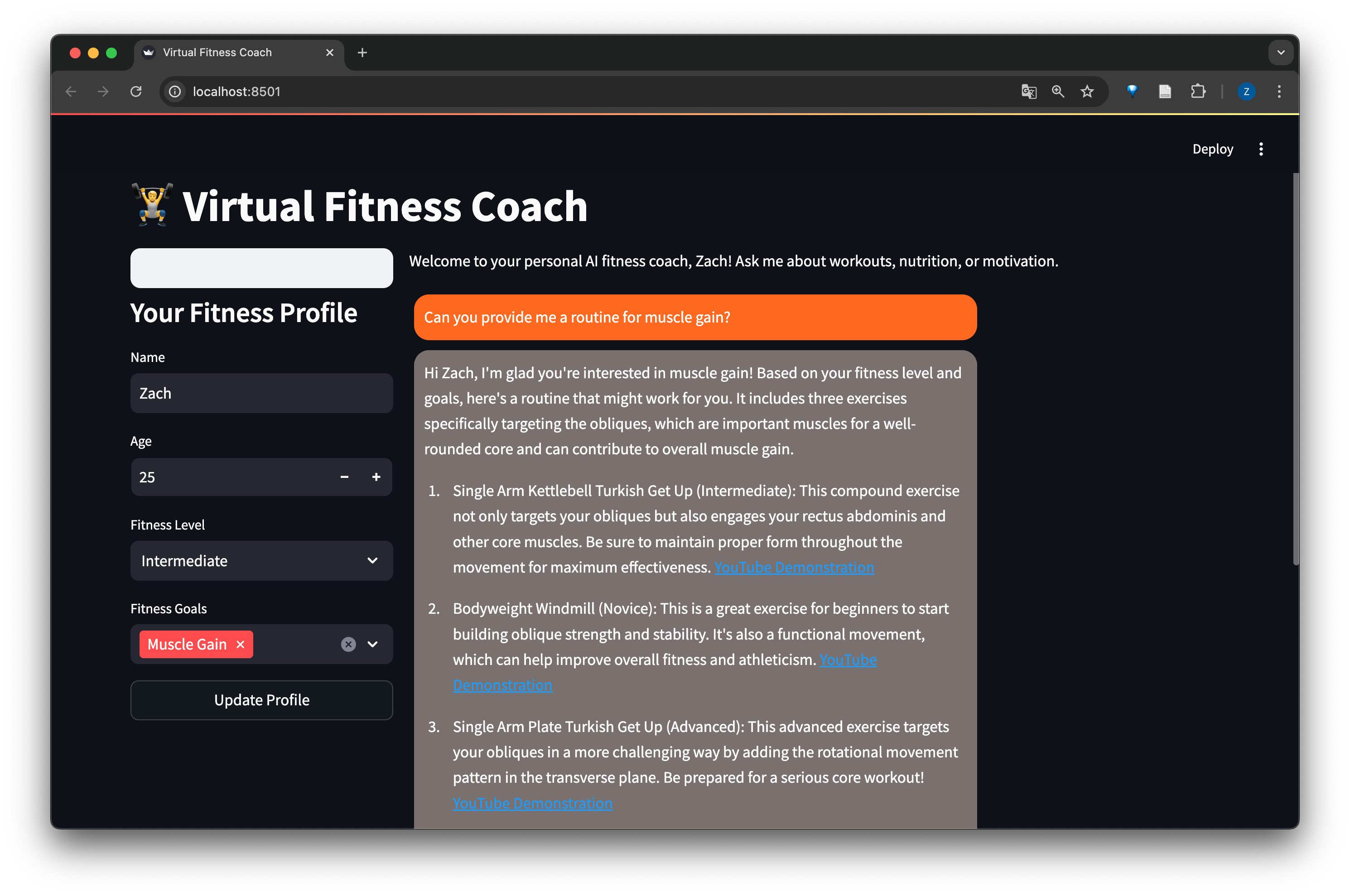
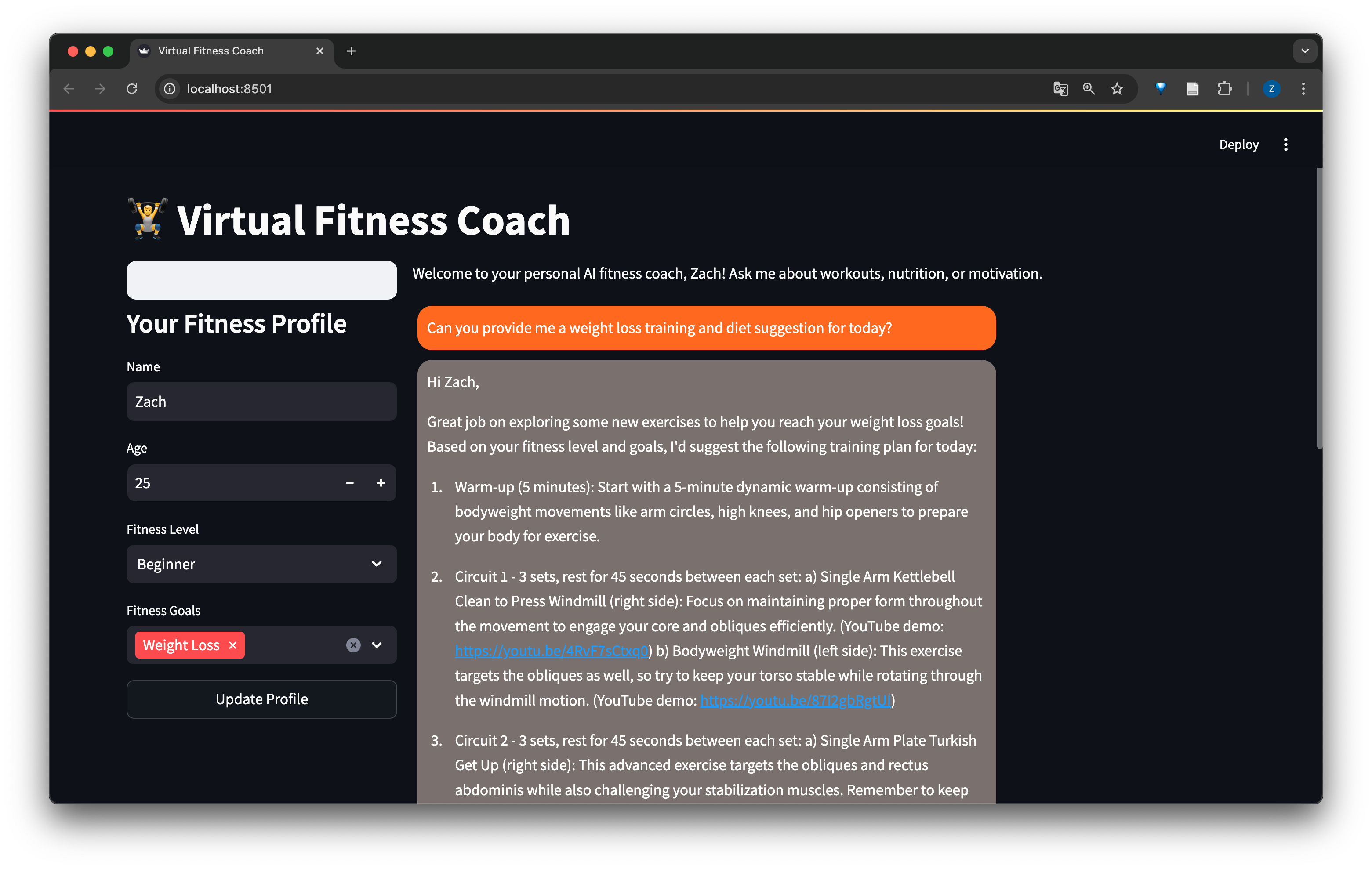
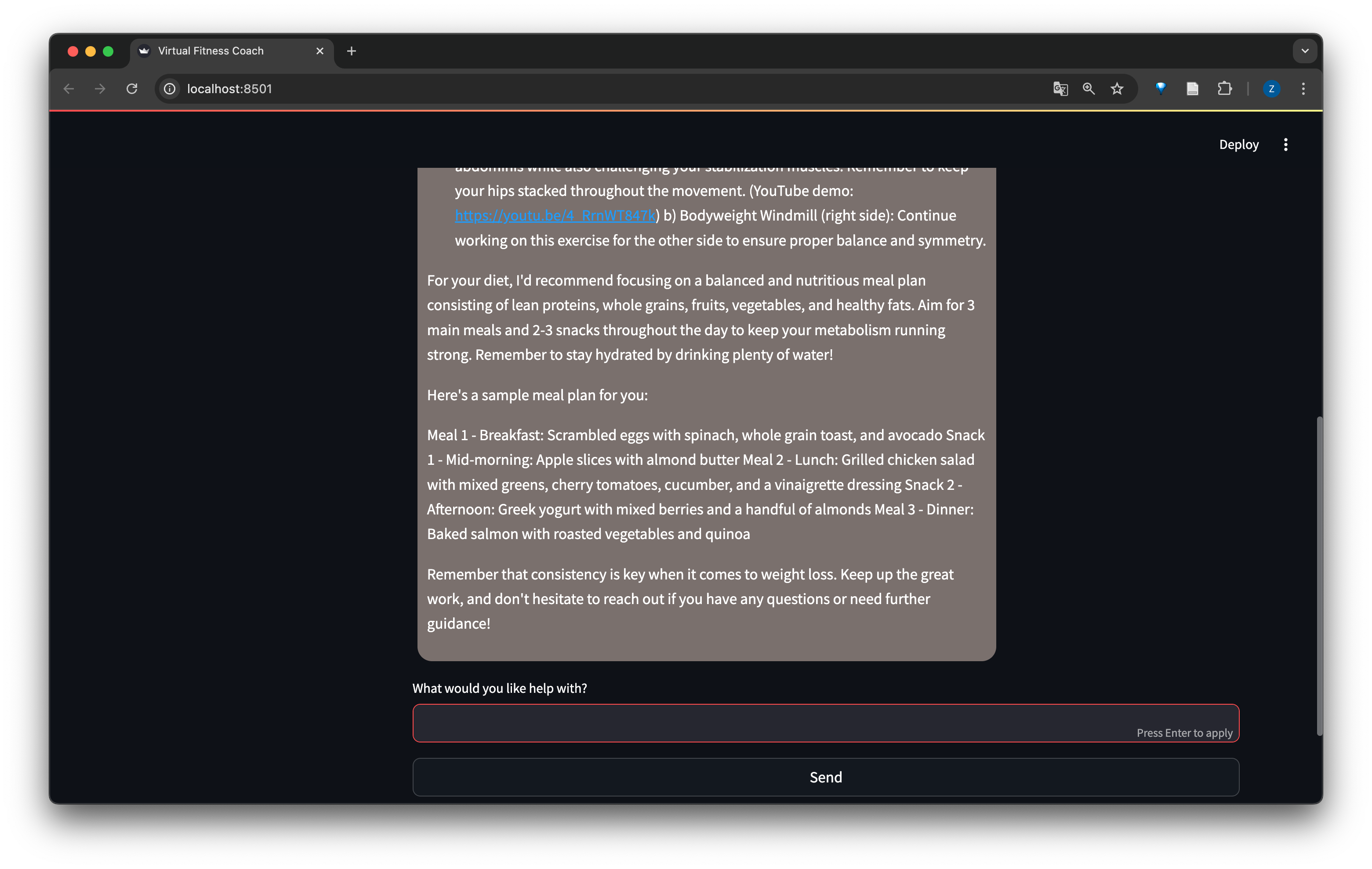
- Examples and Screenshots
- Performance Evaluation
- Unit Tests
- CI/CD Pipeline
- Model Selection
The Virtual Fitness Coach project aims to provide personalized fitness coaching using an local LLM based on llamafile. The application allows users to interact with the virtual coach, receive tailored workout plans with detailed demonstration guides (including videos), based on their fitness goals and preferences. The project leverages the Mozilla Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2 model to generate workout plans and instructions for users.
Please click to view the demo video: Demo Video
Or you can find in under the assets folder.
.
├── Dockerfile
├── README.md
├── assets
├── chroma_langchain_db # Persistent storage for functional database
│ └── chroma.sqlite3
├── data
├── load_test.py # Load testing script
├── main_page.py # Main application file to run the service
├── performance_test.py # Performance testing script
├── requirements.txt
├── tests # Unit tests
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── test_main_page.py
└── vector_database_setup.py # Setup file for the vector database
- Docker
- Git
- Python 3.10
-
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/zihanxing/Virtual-Fitness-Coach-Project.git cd Virtual-Fitness-Coach-Project -
Set up the Python environment:
python -m venv venv source venv/bin/activate # On Windows use `venv\Scripts\activate` pip install -r requirements.txt
-
Download the model from this link: mistral-7b-instruct-v0.2.Q5_K_M.llamafile
-
Make the model executable:
chmod +x ./mistral-7b-instruct-v0.2.Q5_K_M.llamafile
-
Run the model server on port 8080, and enable embedding:
./mistral-7b-instruct-v0.2.Q5_K_M.llamafile --server --nobrowser --embedding --port 8080
-
Build the Docker image:
docker build -t virtual-fitness-coach . -
Run the container:
docker run -p 8000:8000 virtual-fitness-coach
-
Access the application at
http://localhost:8000.
By running the performance_test.py script, I evaluate the model's performance using the following metrics:
- Average Speed: 15.06 tokens/second
To compare the performance with a different model, here is the similar metrics for GPT-4 API:
- Average Output Speed: 25.1 tokens/second.
The performance of the model is satisfactory for the application's requirements, providing a good user experience.
Using load_test.py, we conducted load testing to evaluate the scalability and performance of the Virtual Fitness Coach chatbot under various conditions. The tests were run on a machine with the following specifications:
- Python Version: 3.10.14
- Operating System: Darwin 23.5.0
- Machine: arm64
| Test Configuration | Requests | Concurrent Workers | Total Time (s) | Successful Requests | Requests per Second | Average Latency (s) | Average Speed (tokens/s) | Average Tokens per Response | Min Latency (s) | Max Latency (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test 1 | 2 | 2 | 40.58 | 2 | 0.05 | 39.88 | 7.50 | 299.50 | 39.18 | 40.58 |
| Test 2 (Timeout Errors) | 4 | 4 | N/A | 0 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Test 3 | 4 | 2 | 99.75 | 4 | 0.04 | 45.70 | 8.67 | 384.00 | 32.70 | 60.51 |
-
Test 1: Successfully handled 2 requests with 2 concurrent workers, achieving an average latency of 39.88 seconds and an average speed of 7.50 tokens per second.
-
Test 2: With 4 requests and 4 concurrent workers, all requests timed out, indicating limitations in handling multiple simultaneous requests on the current hardware setup.
-
Test 3: With 4 requests and 2 concurrent workers, the system processed all requests successfully. The average latency increased to 45.70 seconds, and the average speed improved to 8.67 tokens per second.
-
Scalability: The system performs well with a smaller number of concurrent requests but encounters timeouts with higher concurrency.
-
Performance Consistency: As the number of concurrent workers increases, latency becomes a significant factor affecting performance. Deploying the model server on a more powerful machine or utilizing cloud resources could help address these challenges.
The unit tests are located in the tests directory and include the following:
- Profile Update Test: Verifies that user profile details (name, age, fitness level, and goals) can be updated correctly.
- Chat History Test: Ensures that user messages are properly added to the chat history.
- Response Generation Test: Simulates the language model's response generation and checks that the assistant's messages are correctly formatted and stored.
By running pytest tests at the root of the project, you can execute all unit tests and view the results:
$ pytest tests/test_main_page.py
============================================================================================= test session starts ==============================================================================================
platform darwin -- Python 3.10.14, pytest-8.3.2, pluggy-1.5.0
rootdir: /Users/xzh/Desktop/AIPI561/Virtual-Fitness-Coach-Project
plugins: asyncio-0.23.8, cov-5.0.0, anyio-4.4.0, mock-3.14.0
asyncio: mode=strict
collected 3 items
tests/test_main_page.py ... [100%]
============================================================================================== 3 passed in 0.74s ===============================================================================================The CI/CD pipeline is implemented using GitHub Actions and includes the following stages:
- Installing Dependencies: Sets up Python and Docker toolchains.
- Formatting: Ensures code is properly formatted.
- Linting: Checks code quality using linters.
- Running Unit Tests: Executes all tests to ensure functionality.
- Building Docker Image: Creates the Docker image.
- Pushing to Container Registry: Publishes the image to GitHub Packages.
The application uses the Mozilla Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2 model to generate workout plans and instructions for users. It is the smallest model available that provides the necessary functionality for the Virtual Fitness Coach application, while maintaining a decent output speed and performance (compared to Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct and larger models).