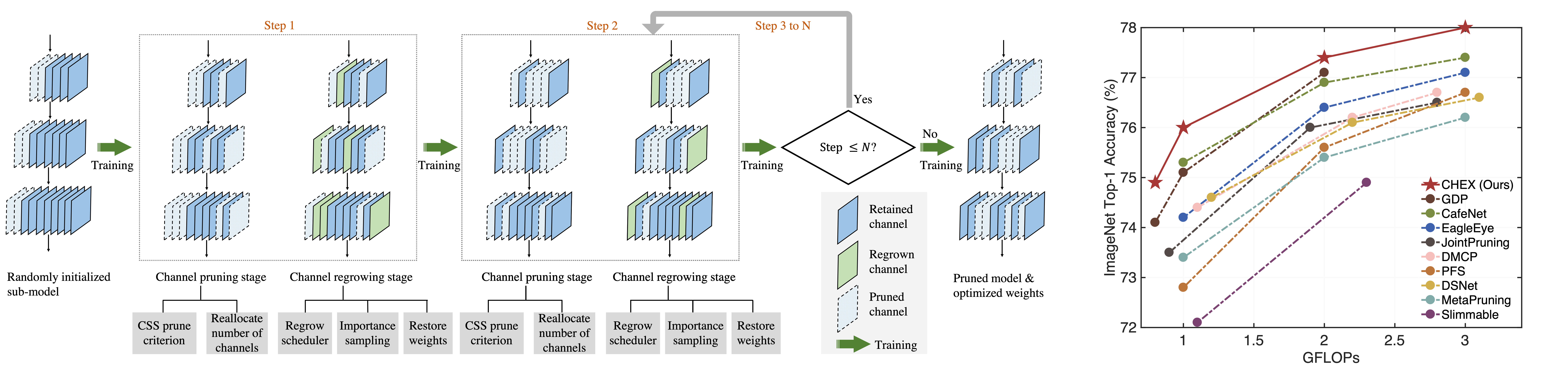
This repository contains the implementation of the paper CHEX: CHannel EXploration for CNN Model Compression (CVPR 2022).
Channel pruning has been broadly recognized as an effective technique to reduce the computation and memory cost of deep convolutional neural networks. However, conventional pruning methods have limitations in that: they are restricted to pruning process only, and they require a fully pre-trained large model. Such limitations may lead to sub-optimal model quality as well as excessive memory and training cost. In this paper, we propose a novel Channel Exploration methodology, dubbed as CHEX, to rectify these problems. As opposed to pruning-only strategy, we propose to repeatedly prune and regrow the channels throughout the training process, which reduces the risk of pruning important channels prematurely. More exactly: From intra-layer’s aspect, we tackle the channel pruning problem via a well-known column subset selection (CSS) formulation. From inter-layer’s aspect, our regrowing stages open a path for dynamically re-allocating the number of channels across all the layers under a global channel sparsity constraint. In addition, all the exploration process is done in a single training from scratch without the need of a pre-trained large model. Experimental results demonstrate that CHEX can effectively reduce the FLOPs of diverse CNN architectures on a variety of computer vision tasks, including image classification, object detection, instance segmentation, and 3D vision. For example, our compressed ResNet-50 model on ImageNet dataset achieves 76% top-1 accuracy with only 25% FLOPs of the original ResNet-50 model, outperforming previous state-of-the-art channel pruning methods.
cd ./CLS- We use ImageNet-1K, a widely used image classification dataset from the ILSVRC challenge.
- Download the images.
- Extract the training data:
mkdir train && mv ILSVRC2012_img_train.tar train/ && cd train
tar -xvf ILSVRC2012_img_train.tar && rm -f ILSVRC2012_img_train.tar
find . -name "*.tar" | while read NAME ; do mkdir -p "${NAME%.tar}"; tar -xvf "${NAME}" -C "${NAME%.tar}"; rm -f "${NAME}"; done
cd ..- Extract the validation data and move the images to subfolders:
mkdir val && mv ILSVRC2012_img_val.tar val/ && cd val && tar -xvf ILSVRC2012_img_val.tar
wget -qO- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/soumith/imagenetloader.torch/master/valprep.sh | bash- Docker setup:
docker build . -t nvidia_resnet50
nvidia-docker run --rm -it -v <path to imagenet>:/data/imagenet -v <path to where CHEX folder is saved>/CHEX:/workspace/rn50 --ipc=host nvidia_rn50We provide the checkpoints of the compressed ResNet models on ImageNet. You can download and evaluate them directly.
| Model | FLOPs | FLOPs reduction | Top-1 | Download |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet-18 | 1.03G | 43% | 69.6% | resnet18_1gflops_69.6top1 ckpt |
| ResNet-34 | 2G | 46% | 73.5% | resnet34_2gflops_73.5top1 ckpt |
| ResNet-50 | 3G | 27% | 78.0% | resnet50_3gflops_78top1 ckpt |
| 2G | 50% | 77.4% | resnet50_2gflops_77.4top1 ckpt | |
| 1G | 75% | 76% | resnet50_1gflops_76top1 ckpt | |
| 0.8G | 80% | 74.9% | resnet50_0.8gflops_74.9top1 ckpt | |
| ResNet-101 | 3.4G | 55% | 78.8% | resnet101_3.4gflops_78.8top1 ckpt |
| 1.9G | 75% | 77.6% | resnet101_1.9gflops_77.6top1 ckpt |
Start inference:
python ./main.py --data-backend pytorch --arch ${model name} --evaluate --epochs 1 -b 100 /data/imagenet --pretrained-weights /workspace/rn50/checkpoints/${checkpoint name}.pth.tar ${model name} can be resnet18, resnet34, resnet50, and resnet101. ${checkpoint name} can be any one of the checkpoints we provide in the table above.
Example of applying CHEX to ResNet-50:
python ./multiproc.py --nproc_per_node 8 ./main.py /data/imagenet --data-backend pytorch --raport-file raport.json -j8 -p 100 --lr 1.024 --optimizer-batch-size 1024 --warmup 8 --arch resnet50 -c fanin --label-smoothing 0.1 --lr-schedule cosine --mom 0.875 --wd 3.0517578125e-05 -b 128 --amp --static-loss-scale 128 --epochs 250 --mixup 0.2 --grow_prune --delta_T 2 --T_max 180 --init_channel_ratio 0.3 --channel_sparsity 0.7cd ./DET-
We use COCO 2017 dataset, a widely used object detection dataset.
-
Extract the COCO 2017 dataset with
download_dataset.sh $COCO_DIR. Data will be downloaded to the$COCO_DIRdirectory. -
Docker setup:
docker build . -t nvidia_ssd
nvidia-docker run --rm -it --ulimit memlock=-1 --ulimit stack=67108864 -v $COCO_DIR:/coco -v <path to where CHEX folder is saved>/CHEX:/workspace --ipc=host nvidia_ssdNote: the default mount point in the container is /coco.
We provide the checkpoints of the compressed SSD models on COCO2017. You can download and evaluate them directly.
| Model | Backbone | FLOPs reduction | AP | AP-50 | AP-75 | AP-S | AP-M | AP-L | Download |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSD | ResNet-50 | 50% | 25.9 | 43.0 | 26.8 | 7.8 | 27.8 | 41.7 | ssd_50%flops_25.9ap ckpt |
| 75% | 24.3 | 41.0 | 24.9 | 7.1 | 25.6 | 40.1 | ssd_25%flops_24.3ap ckpt |
Start inference:
python ./main.py --backbone resnet50 --mode evaluation --checkpoint /workspace/checkpoints/${checkpoint name}.pth.tar --data /coco${checkpoint name} can be any of the checkpoints we provide in the above table for SSD.
Example of applying CHEX to SSD:
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=8 ./main.py --backbone resnet50 --warmup 300 --bs 64 --amp --data /coco --epoch 650 --multistep 430 540 --grow_prune --channel_sparsity 0.5 --init_channel_ratio 0.2 --delta_T 2 --T_max 470 --save ./logscd ./SEG- We use COCO 2014, a widely used instance segmentation dataset.
- We provide scripts to download and extract the COCO 2014 dataset. Data will be downloaded to the current working directory on the host and extracted to a user-defined directory. To download, verify, and extract the COCO dataset, use the following scripts:
./download_dataset.sh <data/dir>- By default, the data is organized into the following structure:
<data/dir>
annotations/
instances_train2014.json
instances_val2014.json
train2014/
COCO_train2014_*.jpg
val2014/
COCO_val2014_*.jpg- Docker setup:
cd pytorch/
bash scripts/docker/build.sh
bash scripts/docker/interactive.sh <path/to/dataset/>The interactive.sh script requires that the location of the dataset is specified.
We provide the checkpoints of the compressed Mask R-CNN models on COCO2014. You can download and evaluate them directly.
| Model | Backbone | FLOPs reduction | Task | AP | AP-50 | AP-75 | AP-S | AP-M | AP-L | Download |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mask R-CNN | ResNet-50 | 63% | bbox | 37.3 | 58.5 | 40.4 | 21.7 | 39.0 | 49.5 | maskrcnn_37%flops_37.3apbox_34.5apmask ckpt |
| segm | 34.5 | 55.7 | 36.7 | 15.9 | 36.1 | 51.2 | maskrcnn_37%flops_37.3apbox_34.5apmask ckpt |
Copy checkpoint maskrcnn_37%flops_37.3apbox_34.5apmask.pth.tar to /workspace/object_detection/results/ and start inference by running:
bash scripts/eval.shExample of applying CHEX to Mask R-CNN:
bash scripts/train.shThis work was supported by Alibaba Group through Alibaba Research Intern Program. This repository is built using DeepLearningExamples.
If you find this repository helpful, please consider citing CHEX:
@inproceedings{hou2022chex,
title={CHEX: CHannel EXploration for CNN Model Compression},
author={Hou, Zejiang and Qin, Minghai and Sun, Fei and Ma, Xiaolong and Yuan, Kun and Xu, Yi and Chen, Yen-Kuang and Jin, Rong and Xie, Yuan and Kung, Sun-Yuan},
booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition},
pages={12287--12298},
year={2022}
}