A drop in replacement for slmgr.vbs script. The script is in alpha state. You can make use of it as separate commands but it is suggested not to use it within automation scripts since the API is subject to change until v1.0.0.
Versions 0.2.2 to 0.2.4 has a logic error and unlisted from PowerShell Gallery. Please update to version >=0.2.5.
NB: Beware that this is a partial implementation. The version 1.0.0 is planned to be the feature-complete version. Currently the features are limited to KMS and offline activation scenarios. See Comparison for details.
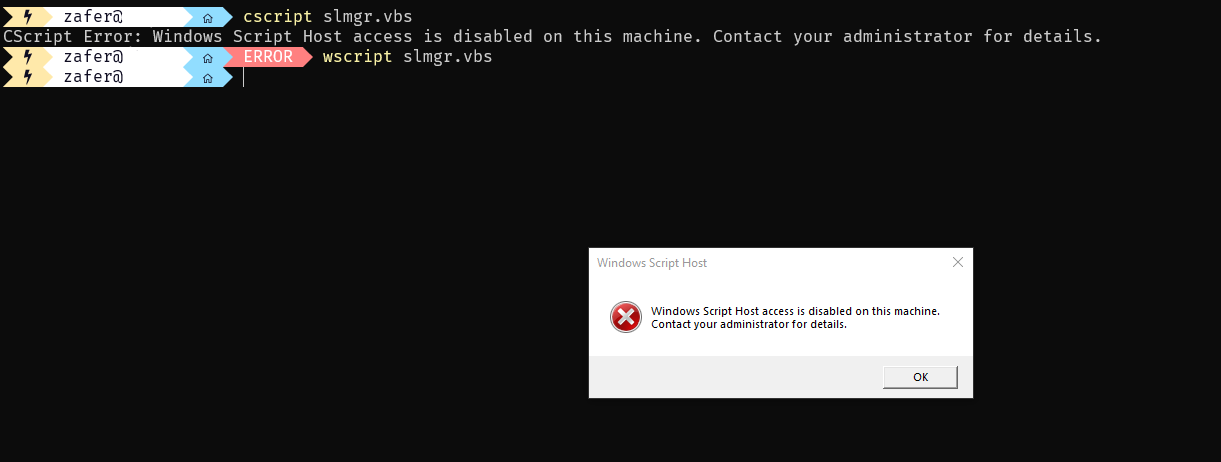
One of my hardening guideline is getting rid of vbscript in every environment.
This caused me being unable to use slmgr.vbs, OSPP.vbs, some SCCM features like MDT. I started with slmgr.vbs as it was more important for me; I was migrating Windows 7 devices to Windows 10!
I wrote a PowerShell script based on the slmgr.vbs. It's long but easy to read. You can find the old script in my gists.
I converted this simple, one-cmdlet script to a module and published it so anyone can use it easily. Ypu can find it in the Powershell Gallery.
The following tables are copied from Microsoft Docs regarding slmgr.vbs.
slmgr.vbs [<ComputerName> [<User> <Password>]] [<Options>]| Option | Description | slmgr-ps |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| [ComputerName] | Name of a remote computer (default is local computer) | -Computer | |
| [User] | Account that has the required privilege on the remote computer | -Credentials | The command uses the current user's credentials. User can pass a credential object. Reference: CWE-214: Invocation of Process Using Visible Sensitive Information |
| [Password] | Password for the account that has the required privileges on the remote computer | -Credentials | The command uses the current user's credentials. User can pass a credential object. Reference: CWE-214: Invocation of Process Using Visible Sensitive Information |
| Option | Description | slmgr-ps |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| /ipk ProductKey | Tries to install a 5×5 product key. The product key provided by the parameter is confirmed valid and applicable to the installed operating system. If not, an error is returned. If the key is valid and applicable, the key is installed. If a key is already installed, it is silently replaced. To prevent instability in the license service, the system should be restarted or the Software Protection Service should be restarted. This operation must be run from an elevated Command Prompt window, or the Standard User Operations registry value must be set to allow unprivileged users extra access to the Software Protection Service. |
Start-WindowsActivation | No need for KMS keys |
| /ato [Activation ID] | For retail editions and volume systems that have a KMS host key or a Multiple Activation Key (MAK) installed, /ato prompts Windows to try online activation. For systems that have a Generic Volume License Key (GVLK) installed, this prompts a KMS activation attempt. Systems that have been set to suspend automatic KMS activation attempts (/stao) still try KMS activation when /ato is run. Note: Starting in Windows 8 (and Windows Server 2012), the /stao option is deprecated. Use the /act-type option instead. The parameter Activation ID expands /ato support to identify a Windows edition installed on the computer. Specifying the Activation ID parameter isolates the effects of the option to the edition associated with that Activation ID. Run slmgr.vbs /dlv all to get the Activation IDs for the installed version of Windows. If you have to support other applications, see the guidance provided by that application for further instruction. KMS activation does not require elevated privileges. However, online activation does require elevation, or the Standard User Operations registry value must be set to allow unprivileged users extra access to the Software Protection Service. |
Start-WindowsActivation | No need for calling /ato separately |
| /dli [Activation ID | All] | Display license information. By default, /dli displays the license information for the installed active Windows edition. Specifying the Activation ID parameter displays the license information for the specified edition that is associated with that Activation ID. Specifying All as the parameter displays license information for all applicable installed products. This operation does not require elevated privileges. |
Get-WindowsActivation | |
| /dlv [Activation ID | All] | Display detailed license information. By default, /dlv displays the license information for the installed operating system. Specifying the Activation ID parameter displays the license information for the specified edition associated with that Activation ID. Specifying the All parameter displays license information for all applicable installed products. This operation does not require elevated privileges. |
Get-WindowsActivation -Extended | |
| /xpr [Activation ID] | Display the activation expiration date for the product. By default, this refers to the current Windows edition and is primarily useful for KMS clients, because MAK and retail activation is perpetual. Specifying the Activation ID parameter displays the activation expiration date of the specified edition that is associated with that Activation ID.This operation does not require elevated privileges. |
Get-WindowsActivation -Expiry |
| Option | Description | slmgr-ps |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| /cpky | Some servicing operations require the product key to be available in the registry during Out-of-Box Experience (OOBE) operations. The /cpky option removes the product key from the registry to prevent this key from being stolen by malicious code. For retail installations that deploy keys, best practices recommend running this option. This option is not required for MAK and KMS host keys, because this is the default behavior for those keys. This option is required only for other types of keys whose default behavior is not to clear the key from the registry. This operation must be run in an elevated Command Prompt window. |
not implemented | |
| /ilc license_file | This option installs the license file specified by the required parameter. These licenses may be installed as a troubleshooting measure, to support token-based activation, or as part of a manual installation of an on-boarded application. Licenses are not validated during this process: License validation is out of scope for Slmgr.vbs. Instead, validation is handled by the Software Protection Service at runtime. This operation must be run from an elevated Command Prompt window, or the Standard User Operations registry value must be set to allow unprivileged users extra access to the Software Protection Service. |
not implemented | |
| /rilc | This option reinstalls all licenses stored in %SystemRoot%\system32\oem and %SystemRoot%\System32\spp\tokens. These are "known-good" copies that were stored during installation. Any matching licenses in the Trusted Store are replaced. Any additional licenses—for example, Trusted Authority (TA) Issuance Licenses (ILs), licenses for applications—are not affected. This operation must be run in an elevated Command Prompt window, or the Standard User Operations registry value must be set to allow unprivileged users extra access to the Software Protection Service. |
not implemented | |
| /rearm | This option resets the activation timers. The /rearm process is also called by sysprep /generalize. This operation does nothing if the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\SoftwareProtectionPlatform\SkipRearm registry entry is set to 1. See Registry Settings for Volume Activation for details about this registry entry. This operation must be run in an elevated Command Prompt window, or the Standard User Operations registry value must be set to allow unprivileged users extra access to the Software Protection Service. |
Start-WindowsActivation -Rearm | |
| /rearm-app Application ID | Resets the licensing status of the specified app. | not implemented | |
| /rearm-sku Application ID | Resets the licensing status of the specified SKU. | not implemented | |
| /upk [Application ID] | This option uninstalls the product key of the current Windows edition. After a restart, the system will be in an Unlicensed state unless a new product key is installed. Optionally, you can use the Activation ID parameter to specify a different installed product. This operation must be run from an elevated Command Prompt window. |
not implemented | |
| /dti [Activation ID] | Displays installation ID for offline activation. | Get-WindowsActivation -Offline | |
| /atp Confirmation ID | Activate product by using user-provided confirmation ID. | Start-WindowsActivation -Offline -ConfirmationID |
| Option | Description | slmgr-ps |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| /skms Name[:Port] | : port [Activation ID] | This option specifies the name and, optionally, the port of the KMS host computer to contact. Setting this value disables auto-detection of the KMS host. If the KMS host uses Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) only, the address must be specified in the format hostname:port. IPv6 addresses contain colonsV, which the Slmgr.vbs script does not parse correctly. This operation must be run in an elevated Command Prompt window. |
Start-WindowsActivation -KMSServerFQDN activationservername -KMSServerPort port | |
| /skms-domain FQDN [Activation ID] | Sets the specific DNS domain in which all KMS SRV records can be found. This setting has no effect if the specific single KMS host is set by using the /skms option. Use this option, especially in disjoint namespace environments, to force KMS to ignore the DNS suffix search list and look for KMS host records in the specified DNS domain instead. | not implemented | |
| /ckms [Activation ID] | This option removes the specified KMS host name, address, and port information from the registry and restores KMS auto-discovery behavior. This operation must be run in an elevated Command Prompt window. |
not implemented | |
| /skhc | This option enables KMS host caching (default). After the client discovers a working KMS host, this setting prevents the Domain Name System (DNS) priority and weight from affecting further communication with the host. If the system can no longer contact the working KMS host, the client tries to discover a new host. This operation must be run in an elevated Command Prompt window. |
Start-WindowsActivation -CacheEnabled $true | KMS cache is enabled by default |
| /ckhc | This option disables KMS host caching. This setting instructs the client to use DNS auto-discovery each time it tries KMS activation (recommended when using priority and weight). This operation must be run in an elevated Command Prompt window. |
Start-WindowsActivation -CacheEnabled $false |
| Option | Description | slmgr-ps |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| /sai Interval | This option sets the interval in minutes for unactivated clients to try to connect to KMS. The activation interval must be between 15 minutes and 30 days, although the default value (two hours) is recommended. The KMS client initially picks up this interval from registry but switches to the KMS setting after it receives the first KMS response. This operation must be run in an elevated Command Prompt window. |
not implemented | |
| /sri Interval | This option sets the renewal interval in minutes for activated clients to try to connect to KMS. The renewal interval must be between 15 minutes and 30 days. This option is set initially on both the KMS server and client sides. The default value is 10,080 minutes (7 days). The KMS client initially picks up this interval from the registry but switches to the KMS setting after it receives the first KMS response. This operation must be run in an elevated Command Prompt window. |
not implemented | |
| /sprt Port | This option sets the port on which the KMS host listens for client activation requests. The default TCP port is 1688. This operation must be run from an elevated Command Prompt window. |
not implemented | |
| /sdns | Enable DNS publishing by the KMS host (default). This operation must be run in an elevated Command Prompt window. |
not implemented | |
| /cdns | Disable DNS publishing by the KMS host. This operation must be run in an elevated Command Prompt window. |
not implemented | |
| /spri | Set the KMS priority to normal (default). This operation must be run in an elevated Command Prompt window. |
not implemented | |
| /cpri | Set the KMS priority to low. Use this option to minimize contention from KMS in a co-hosted environment. Note that this could cause KMS starvation, depending on what other applications or server roles are active. Use with care. This operation must be run in an elevated Command Prompt window. |
not implemented | |
| /act-type [Activation-Type] [Activation ID] | This option sets a value in the registry that limits volume activation to a single type. Activation Type 1 limits activation to Active Directory only; 2 limits it to KMS activation; 3 to token-based activation. The 0 option allows any activation type and is the default value. | not implemented |
| Option | Description | slmgr-ps |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| /lil | List the installed token-based activation issuance licenses. | not implemented | |
| /ril ILID ILvID | Remove an installed token-based activation issuance license. This operation must be run from an elevated Command Prompt window. |
not implemented | |
| /stao | Set the Token-based Activation Only flag, disabling automatic KMS activation. This operation must be run in an elevated Command Prompt window. This option was removed in Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows 8.1. Use the /act–type option instead. |
not implemented | |
| /ctao | Clear the Token-based Activation Only flag (default), enabling automatic KMS activation. This operation must be run in an elevated Command Prompt window. This option was removed in Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows 8.1. Use the /act–type option instead. |
not implemented | |
| /ltc | List valid token-based activation certificates that can activate installed software. | not implemented | |
| /fta Certificate Thumbprint [PIN] | Force token-based activation by using the identified certificate. The optional personal identification number (PIN) is provided to unlock the private key without a PIN prompt if you use certificates that are protected by hardware (for example, smart cards). | not implemented |
| Option | Description | slmgr-ps |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| /ad-activation-online Product Key [Activation Object name] | Collects Active Directory data and starts Active Directory forest activation using the credentials that the command prompt is running. Local administrator access is not required. However, Read/Write access to the activation object container in the root domain of the forest is required. | not implemented | |
| /ad-activation-get-IID Product Key | This option starts Active Directory forest activation in phone mode. The output is the installation ID (IID) that can be used to activate the forest over the telephone if internet connectivity is not available. Upon providing the IID in the activation phone call, a CID is returned that is used to complete activation. | not implemented | |
| /ad-activation-apply-cid Product Key Confirmation ID [*Activation Object name>] | When you use this option, enter the CID that was provided in the activation telephone call to complete activation | not implemented | |
| [/name: AO_Name] | Optionally, you can append the /name option to any of these commands to specify a name for the activation object stored in Active Directory. The name must not exceed 40 Unicode characters. Use double quotation marks to explicitly define the name string. In Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows 8.1, you can append the name directly after /ad-activation-online Product Key and /ad-activation-apply-cid without having to use the /name option. |
not implemented | |
| /ao-list | Displays all of the activation objects that are available to the local computer. | not implemented | |
| /del-ao AO_DN /del-ao AO_RDN |
Deletes the specified activation object from the forest. | not implemented |
- You can provide an array of computer names, and it is up to you how you get them. It's just PowerShell.
- It works on PowerShell version 5.0 and above. It means PowerShell 7.0 is ok, too.
- It uses WinRM for remote computers. Check if remote computers are accessible over WinRM.
- It includes a list of KMS keys, so that you don't have to for most of them. It covers some of the versions though, not all of them.
- It works even if you disabled
cscriptandwscript- it's PowerShell! - The code is documented and readable, so that you can improve according to your needs.
Install-Module slmgr-psStart-WindowsActivation -WhatIf
# Activates the local computer
Start-WindowsActivation -Verbose
# Activates the computer named WS01
Start-WindowsActivation -Computer WS01
# Activates the computer named WS01 using different credentials
Start-WindowsActivation -Computer WS01 -Credentials (Get-Credential)
# Disabled the KMS cache for the computers named WS01 and WS02. Cache is enabled by default.
Start-WindowsActivation -Computer WS01, WS02 -CacheEnabled $false
# Activates the computer named WS01 against server.domain.net:2500
Start-WindowsActivation -Computer WS01 -KMSServerFQDN server.domain.net -KMSServerPort 2500
# ReArm the trial period. ReArming already licensed devices can break current license issues.
# Guard clauses wil protect 99% but cannot guarantee 100%.
Start-WindowsActivation -ReArm
# Used for offline -aka phone- activation
Start-WindowsActivation -Offline -ConfirmationID <confirmation ID># Collects basic license information of local computer, equal to slmgr.vbs /dli
Get-WindowsActivation
# Collects extended license information of local computer, equal to slmgr.vbs /dlv
Get-WindowsActivation -Extended
# Collects license expiration information of local computer, equal to slmgr.vbs /xpr
Get-WindowsActivation -Expiry
# Collects basic license information of computer WS01 over WinRM
Get-WindowsActivation -Computer WS01
# Collects basic license information of computer WS01 over WinRM using different credentials
Get-WindowsActivation -Computer WS01 -Credentials (Get-Credential)
# Get the offline installation ID for offline -aka phone- activation
Get-WindowsActivation -OfflineThis module allows users to activate computers remotely as well as reporting.
$computers = @('WS01', 'WS02', 'WS03')
# Iterate over the list and activate
Start-WindowsActivation -Computer $computers -Verbose
# Generate a report of activation status
$report = $computers | ForEach-Object {
$status = Get-WindowsActivation -Computer $_
[PSCustomObject]@{
Computer = $_
Status = $status.LicenseStatus
}
}
$report | Format-Table -AutoSizeFor secure communication when using WinRM for remote management, consider enabling HTTPS for WinRM. Detailed instructions can be found in the official Microsoft documentation:
If you encounter issues, use the -Verbose or -Debug parameters to get detailed logs:
# Enable verbose logging
Start-WindowsActivation -Computer WS01 -Verbose
# Enable debug logging
Start-WindowsActivation -Computer WS01 -DebugIn case of any problems, feel free to create an issue.
The target is to be a feature complete alternative to the slmgr.vbs script. Therefore, any PR adding new features adding new features out of this scope until version 1.0.0 will be kept on hold. Please refer to the comparison table when developing features. Any issues and PRs about fixing the bugs are always welcome.
Please refer to the CONTRIBUTING.MD for PR guidelines.