go语言微服务
目前的项目结构看起来像是一个独立的项目,实际真实的项目结构不是这样的,本项目为了简单使用而故意为之。
实际情况是micro-service下的每一个目录都是一个独立的微服务,需要独立部署在不同的服务器上,每个服务都需要自己
的go.mod,proto等文件和目录。
grpc v1.25.1,
v1.27.1会有类型这样的错误undefined: resolver.BuildOption,undefined: resolver.ResolveNowOption
生成*.pb.go代码
$ protoc --proto_path=. --micro_out=. --go_out=. proto/user/user.protogo run service/main.gogo run client/main.gogo run service/main.gogo run api/main.gomicro api --handler=apicurl "http://localhost:8080/user/say/hello?name=huohuo"返回 {"id":"123","password":"dslhgfoif40u9b9","username":"huohuo"}
API模块,它的身份其实就是一个网关或者代理层,它的能力就是让一个单一的入口可以去访问微服务。API工作在我们的软件服务架构的边缘。
v2.0版本默认使用的服务注册发现是mdns。 Micro内置了mDNS组播系统,这是一种零依赖的服务注册发现机制,它是区别于有注册中心的替代方案。 通过在启动指令中传入--registry=mdns 或者在环境变量中设置MICRO_REGISTRY=mdns。 其实也可以不传,早期版本的go-micro默认注册中心是consul,现在换成了mdns mDNS(多播DNS)是一种局域网内使用的DNS机制,他的大致原理如下:当有新的节点加入局域网的时候,如果打开了mDNS,就主动向局域网其他所有节点广播,自己提供的服务(域名是什么、ip地址是什么、端口号是什么), 这样我们任何一个节点都知道局域网提供了什么服务。 所以生产环境需要其他中间件,如consul,etcd。
go-micro v2弃用了consul,推荐使用的是etcd。 使用方法:
go run service/main.go --registry=etcdgo run api/main.go --registry=etcdmicro --registry=etcd api --handler=api在启动的时候加上--registry=etcd参数即可,启动日志如下:
2020-03-14 16:17:07 Starting [service] go.micro.srv.user
2020-03-14 16:17:07 Server [grpc] Listening on [::]:10507
2020-03-14 16:17:07 Registry [etcd] Registering node: go.micro.srv.user-332fd9a8-f241-4c20-bf93-ee832b487261
Registry [mdns]变成了Registry [etcd]。
.\etcd.exe --name etcd01 ^
--data-dir .\data\etcd01 ^
--advertise-client-urls http://127.0.0.1:2379 ^
--listen-client-urls http://127.0.0.1:2379 ^
--listen-peer-urls http://127.0.0.1:2380 ^
--initial-advertise-peer-urls http://127.0.0.1:2380 ^
--initial-cluster-token etcd-cluster-1 ^
--initial-cluster etcd01=http://127.0.0.1:2380,etcd02=http://127.0.0.1:2381,etcd03=http://127.0.0.1:2382 ^
--initial-cluster-state new
pause.\etcd.exe --name etcd02 ^
--data-dir .\data\etcd02 ^
--advertise-client-urls http://127.0.0.1:3379 ^
--listen-client-urls http://127.0.0.1:3379 ^
--listen-peer-urls http://127.0.0.1:2381 ^
--initial-advertise-peer-urls http://127.0.0.1:2381 ^
--initial-cluster-token etcd-cluster-1 ^
--initial-cluster etcd01=http://127.0.0.1:2380,etcd02=http://127.0.0.1:2381,etcd03=http://127.0.0.1:2382 ^
--initial-cluster-state new
pause.\etcd.exe --name etcd03 ^
--data-dir .\data\etcd03 ^
--advertise-client-urls http://127.0.0.1:4379 ^
--listen-client-urls http://127.0.0.1:4379 ^
--listen-peer-urls http://127.0.0.1:2382 ^
--initial-advertise-peer-urls http://127.0.0.1:2382 ^
--initial-cluster-token etcd-cluster-1 ^
--initial-cluster etcd01=http://127.0.0.1:2380,etcd02=http://127.0.0.1:2381,etcd03=http://127.0.0.1:2382 ^
--initial-cluster-state new
pause查看etcd节点状态
./etcdctl.exe --write-out=table --endpoints=http://127.0.0.1:2379,http://127.0.0.1:3379,http://127.0.0.1:4379 endpoint status+-----------------------+------------------+---------+---------+-----------+------------+-----------+------------+--------------------+--------+
| ENDPOINT | ID | VERSION | DB SIZE | IS LEADER | IS LEARNER | RAFT TERM | RAFT INDEX | RAFT APPLIED INDEX | ERRORS |
+-----------------------+------------------+---------+---------+-----------+------------+-----------+------------+--------------------+--------+
| http://127.0.0.1:2379 | bf9071f4639c75cc | 3.4.4 | 115 kB | true | false | 13 | 99 | 99 | |
| http://127.0.0.1:3379 | e7b968b9fb1bc003 | 3.4.4 | 115 kB | false | false | 13 | 99 | 99 | |
| http://127.0.0.1:4379 | 19ac17627e3e396f | 3.4.4 | 106 kB | false | false | 13 | 99 | 99 | |
+-----------------------+------------------+---------+---------+-----------+------------+-----------+------------+--------------------+--------+
启动两个新的服务并注册到etcd中
go run service/main.go --registry=etcd --registry_address=http://127.0.0.1:3379 go run service/main.go --registry=etcd --registry_address=http://127.0.0.1:4379多次请求http://localhost:8080/user/say/hello?name=huohuo
会在三个服务轮询接收请求
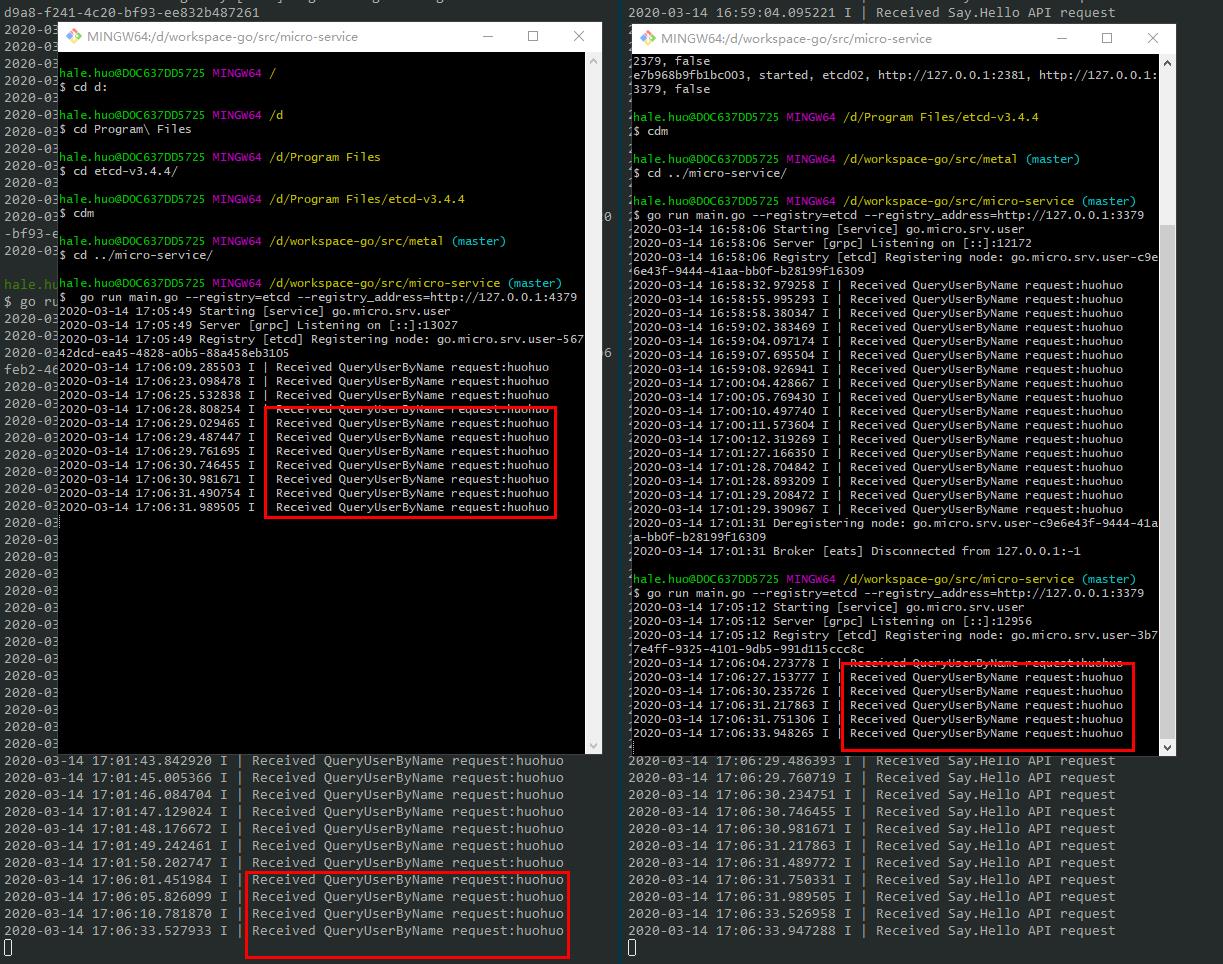 停止某个服务并不会中断服务,以此实现了服务注册发现。
停止某个服务并不会中断服务,以此实现了服务注册发现。
在线上部署就不能使用go run service/main.go命令了,需要打包编译
linux系统需要这样编译:GOOS=linux go build -o service service/main.go
go build -o service service/main.go./service --registry=etcd --registry_address=xx.xx.xx.xx:2379go build -o api api/main.go./api --registry=etcd --registry_address=xx.xx.xx.xx:2379至于线上的restful api可以选择适合自己的web服务框架,在web服务中调用api服务。也可以像本地一样启动 web中服务中调用api层
micro --registry=etcd --registry_address=xx.xx.xx.xx:2379 api --handler=api不过要在服务器上下载micro工具。
线上etcd和本地启动有讲究了,如果etcd是单独的服务器,那么在不加任何参数的情况下直接启动,那基本是调不通的。
$ ./service --registry=etcd --registry_address=xx.xx.xx.xx:2379
2020-03-17 17:04:42 Starting [service] go.micro.srv.user
2020-03-17 17:04:42 Server [grpc] Listening on [::]:48493
2020-03-17 17:04:42 Registry [etcd] Registering node: go.micro.srv.user-f32a2950-8e59-44d4-ac86-f4e1ec103395
{"level":"warn","ts":"2020-03-17T17:04:47.849+0800","caller":"clientv3/retry_interceptor.go:61","msg":"retrying of unary invoker failed","target":"endpoint://client-e45decee-12bf-4a9b-a7ab-f92eece39420/xx.xx.xx.xx:2379","attempt":0,"error":"rpc error: code = DeadlineExceeded desc = latest connection error: connection error: desc = \"transport: Error while dialing dial tcp xx.xx.xx.xx:2379: connect: connection refused\""}
2020-03-17 17:04:47 Server register error: %!(EXTRA context.deadlineExceededError=context deadline exceeded)这就是错误示例,etcd拒绝连接。 为了能顺利看到胜利的结果,需要这样启动etcd:
$ ./etcd --listen-client-urls http://0.0.0.0:2379 --advertise-client-urls http://0.0.0.0:2379 --listen-peer-urls http://0.0.0.0:2380 --initial-advertise-peer-urls http://0.0.0.0:2380 --initial-cluster my-etcd-1=http://0.0.0.0:2380将ip为0.0.0.0可以理解为不限制连接机器(真正的生产不推荐这样设置)。
服务启动参数--registry_address=xx.xx.xx.xx:2379不能带http://。
项目中推荐使用github.com/micro/go-micro/v2/logger作为日志插件,输出的格式如:
2020-05-12 16:08:07 file=D:/workspace-go/src/micro-service/api/handler/user.handler.go:23 level=info Received Say.Hello API request
包含了时间 文件:行数 日志等级 信息
