OMOP CDM v5 Bootstrap
This will help you get a simple OMOP CDM v5 up and running using Azure SQL Server. The Terraform files will automate the creation of necessary resources (i.e. SQL Server, SQL database) to stand up an OHDSI OMOP CDM v5 (along with its web tools such as - Atlas, R and Achilles), and also optionally import a vocabulary and/or data to get you started.
Prerequisites
- Install
sqlcmd:- If on Mac:
You can also visit herebrew tap microsoft/mssql-release https://github.com/Microsoft/homebrew-mssql-release brew update brew install mssql-tools- If on Windows, visit here
- Install
bcp. If you followed the instructions from Step 1, you may skip this step. - Clone this repository.
- Download the CMD Vocabulary and move them into the
vocab/directory of this repo. You can do this by visiting Athena. - If you would like to install the OMOP CDM with sample data from SynPuf, then unzip the
/synpuf_data/synpuf1k_omop_cdm_5.x.x.zipand make sure thesynpuf_data_import.shin thescripts/directory is pointing to the unzipped version. - Install Terraform version
v0.14.6(or greater) locally
Azure Authentication and Subscription Selection
Open a terminal, the first thing we need to do is log into our subscription.
az login
Then we can list the subscriptions we have access to.
az account list -o table
Set you subscription appropriately.
az account set --subscription <your_subscription_id>
Set environment variables
You can either set your environment variables during runtime or leverage a tfvars file to prepopulate the values before the run. For this walk through we will use the .tfvars file.
Take the terraform.sample.tfvars, make a copy and rename it to terraform.tfvars. Terraform will automatically pick up these environment variables. Populate the values in the .tfvars file.
Run Terraform
terraform initterraform plan- Provide a password for SQL Server
omop_admin. (Must contain uppercase, lowercase, and special character.) - Provide a prefix name. For example "yvonne". (Note: this is not the same as environment name (i.e.
dev)). - This could also be done using a
.tfvarsfile.
- Provide a password for SQL Server
terraform apply- Provide similar input for
terraform planif not using a.tfvarsfile.
- Provide similar input for
- BE PATIENT - it can take OHDSI WebAPI and Atlas ~5-10 minutes to boot up normally.
DISCLAIMER: The execution of terraform apply can take about 45-60 minutes if importing the vocabulary set due to the size of the vocabulary csv files, which are often a total of a few gigabytes.
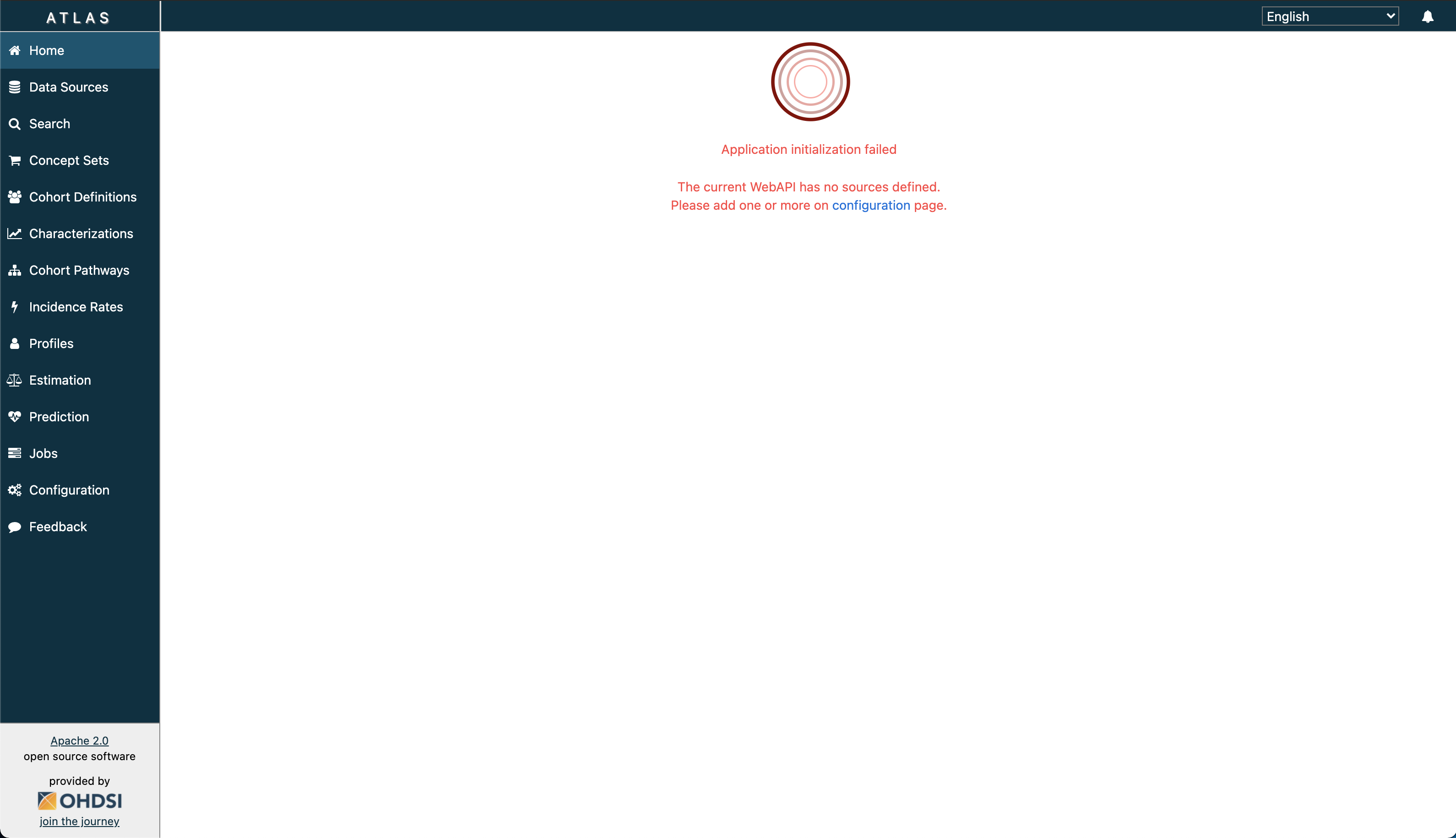
ANOTHER DISCLAIMER: If you are able to access Atlas, but are seeing the following error:
This means that you have not given the deployment enough time to configure data sources for WebAPI. Please wait about 15 minutes, and if you are still seeing this error, you can configure the source manually:
- Connect to the SQL database. You can use various database IDEs like Azure Data Studio.
- Run the query in
../sql/source_sourcce_daimon.sqlagainst your database. - Go to browser, and navigate to
https://{prefix}-{environment}-omop-broadsea.azurewebsites.net/WebAPI/source/refresh.
If you got to http://{prefix}-{environment}-omop-broadsea.azurewebsites.net/atlas/#/configure, you should now see a new source entry. Refresh Atlas, and you will no longer be prompted with the error.
Vocabulary and Data Import
You can also import the vocabulary outside of Terraform, which can drastically improve infrastructure deployment time. This is the recommended approach in case Terraform deployment errors out, and in which case, the state of the Terraform resource(s) may become "tainted". It may be challenging to resume the deployment when this occurs, and you may need to start over (i.e. perform a terraform destroy and reapply).
To import the vocabulary and synthetic data manually, be sure to comment out the vocab and data import in the Terraform main.tf script (lines 153-156 and lines 163-166, respectively) and use the script vocab_import.sh and synpuf_data_import.sh, respectively, in the \scripts directory. You may need to modify the path to CSV_FILES to point to the path of your vocabulary csv files.
Loading Clinical Data
Staging Tables SQL Script is currently executed in the Terraform to aid in loading clinical data into the OMOP CDM database, where, new clinical data can be added to the target staging table and eventually migrated to the permanent clinical table using a SQL Stored Procedure or an alternative approach. You can comment out this import in the Terraform main.tf script (lines 154-156) if this isn't desired.
Using Achilles
Running the Achilles R package on your CDM database is currently a requirement in order to characterize the datasaet and generate results that can be consumed by Atlas Data Sources. To do this:
-
Navigate to
http://{prefix}-{environment}-omop-webtools.azurewebsites.net/. -
Provide username and password. By default, they should be: username: ohdsi password: ohsi
-
Load Achilles library.
-
Create a connection:
connectionDetails <- createConnectionDetails(dbms = "sql server", connectionString = "jdbc:sqlserver://{prefix}-{environment}-omop-sql-server.database.windows.net:1433;database={prefix}_{environment}_omop_db;user=omop_admin@{prefix}-{environment}-omop-sql-server;password={password};encrypt=true;trustServerCertificate=false;hostNameInCertificate=*.database.windows.net;loginTimeout=30;", user = "omop_admin", password = {password}) -
Run Achilles:
achilles(connectionDetails = connectionDetails, cdmDatabaseSchema = "{databaseName}.{schema}", resultsDatabaseSchema = "{databaseName}.{schema}", vocabDatabaseSchema = "{databaseName}.{schema}", sourceName = "OHDSI CDM V5 Database", cdmVersion = 5.3, numThreads = 1, runHeel = FALSE, outputFolder = "output")
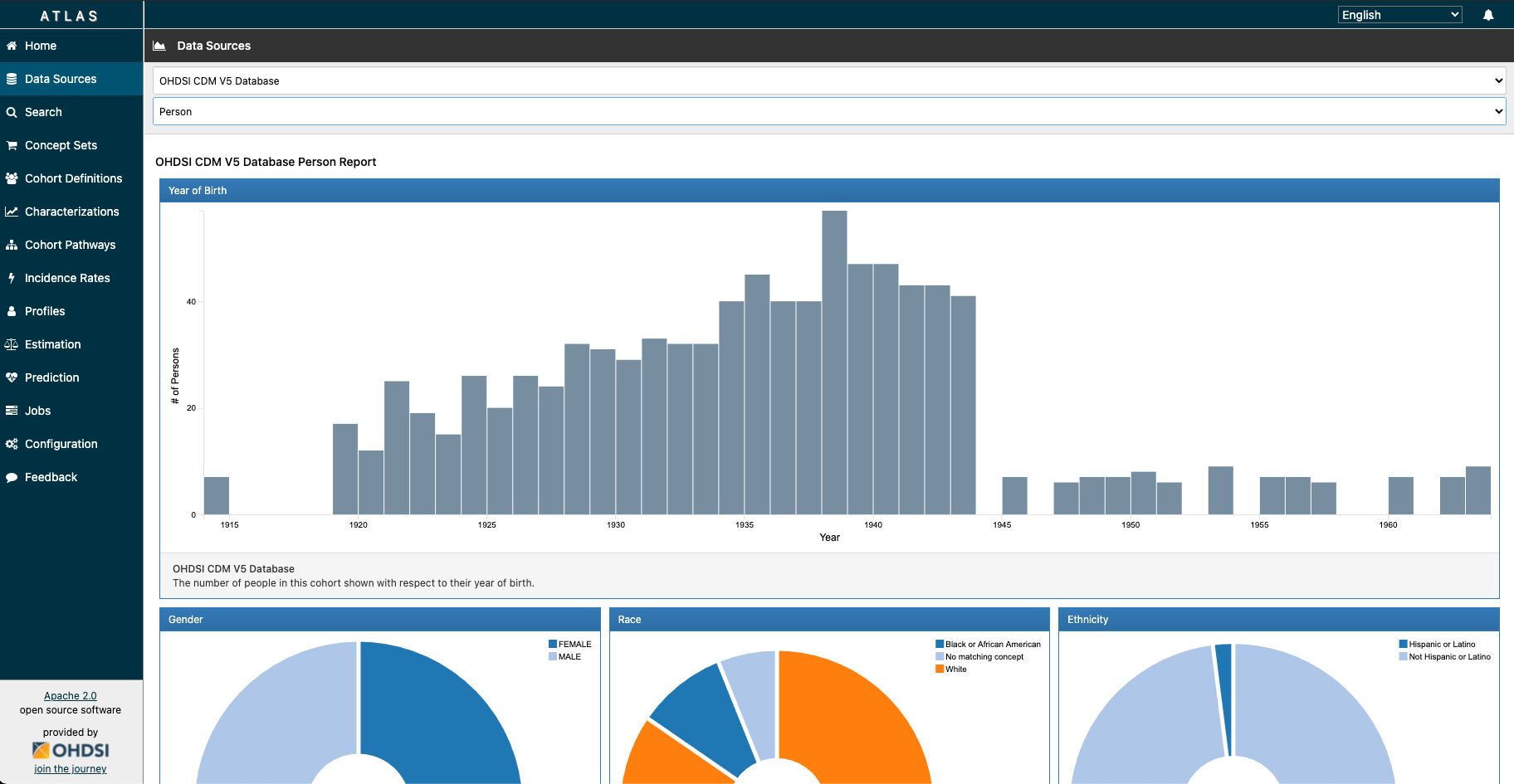
If you navigate to Atlas Data Sources, you should be able to see reports for the drop down menu items:
Troubleshooting
Error: Error running command '../scripts/synpuf_data_import.sh test-dev-omop-sql-server.database.windows.net test-dev-omop-db omop_admin omop_password': exit status 126. Output: /bin/sh: ../scripts/synpuf_data_import.sh: Permission denied
This could mean that the script has restricted access. You can change permissions by running:
chmod +x /scripts/synpuf_data_import.sh
You may be required to change permissions for the file vocab_import.sh as well.
Error: Msg 40544, Level 17, State 12, Line 1 The database 'test-dev-omop-db' has reached its size quota. Partition or delete data, drop indexes, or consult the documentation for possible resolutions.
This message is in regards to the omop_db_size. If you are having problems with performing SQL queries, you may need to increase the SQL database maximum storage size.
Error: sqlcmd: command not found
If you have installed sqlcmd and bcp but you still run into a command not found error it may be because you do not have a proper symlink created. See this page on how to fix this issue.
r: Error executing SQL: com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerException: Incorrect syntax near 'analysis_id'. An error report has been created at /home/ohdsi/errorReport.txt Error in rJava::.jcall(metaData, "Ljava/sql/ResultSet;", "getCatalogs") : com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerException: Connection reset
You may see this error message in R when you attempt to load the Achilles function described in Using Achilles. Because the syntax “drop index if exists” doesn’t work for all OHDSI SQL platforms, when the “drop index” step fails if you do not already have an index, it throws an error message. For now, this is a harmless error. Similar to a bug described here.
Footnotes
- Package Tomcat Server, WebAPI, Atlas - Deploying docker container in Azure App Service
- Azure Key vault support for App Service secrets
- R Server + Achilles
- Implementation of CI/CD in Azure DevOps pipelines to build custom Docker images
- ETL
- Testing and managing multiple databases
- Observability
- Authentication