This is Chinese Version.
This is VastGaussian: Vast 3D Gaussians for Large Scene Reconstruction unofficial implementation, since this is my first time to recreate the complete code from scratch, the code may have some errors, and the code writing may seem a bit naive compared to some experts. Lack of engineering skills. But I got my foot in the door. I couldn't find any implementation of VastGaussian on the web, so I gave it a try.
If you have any experiences and feedback on any code changes, feel free to contact me, or simply raise an Issue 😀:
Email: 374774222@qq.com
QQ: 374774222
WeChat: k374774222
-
Camera-position-based region division is implemented -
Position-based data selection is implemented -
Visibility-based camera selection is implemented -
Coverage-based point selection is implemented -
Decoupled Appearance Modeling is implemented -
Seamless Merging is implemented -
Parallel training of
$m\times n$ regions on a single GPU is implemented after dividing the point cloud -
Experiments are carried out on UrbanScene3D and Mill-19 datasets
-
Fix bugs, and bugs, and bugs ...
- I made some changes to the original 3DGS. First of all, I took the hyperparameters of 3DGS from
arguments/__init__.pyand put them intoarguments/parameters.pyfile to make it easier to read and understand the hyperparameters - In order not to change the original directory structure of 3DGS, I added a new
VastGaussian_scenemodule to store VastGaussian. Part of the code I called the existing functions in thescenefolder. Also to fix theimporterror, I moved the Scene class into the datasets.py folder
- The naming of the files is consistent with the method mentioned in the paper for easy reading
datasets.pyI have rewritten the Scene class in 3DGS into BigScene and PartitionScene. The former represents the original scene BigScene, and the latter represents the PartitionScene of each small scene after Partition.data_partition.pycorresponding to theProgressive Data Partitioningin the paper.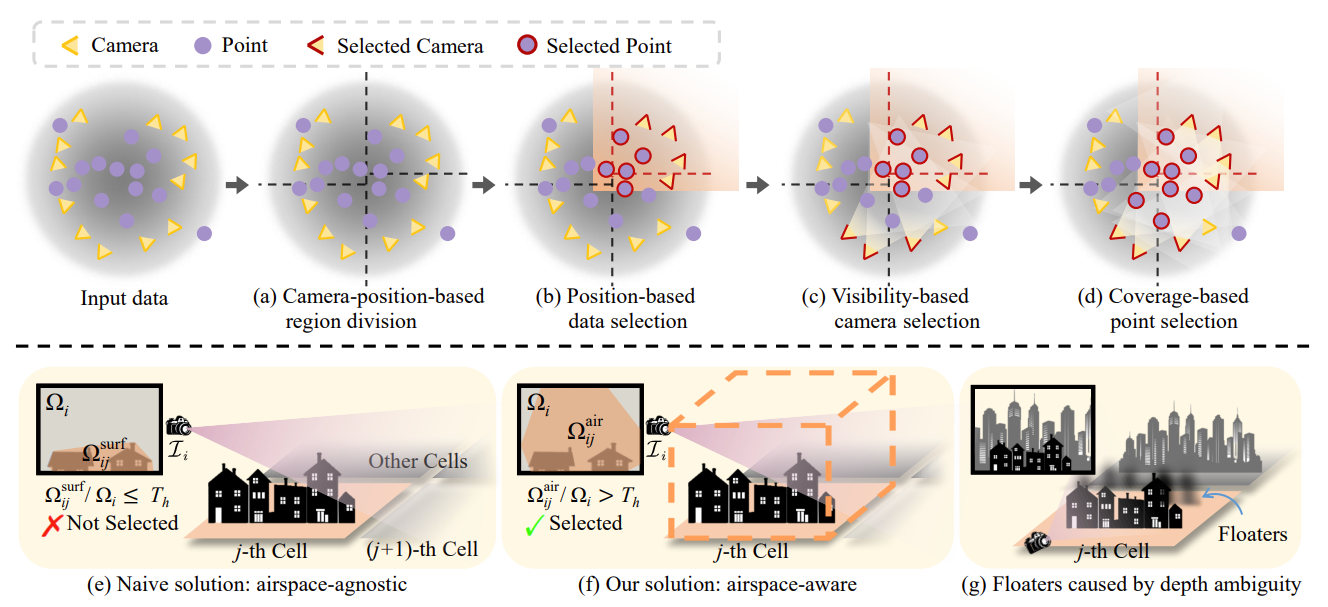
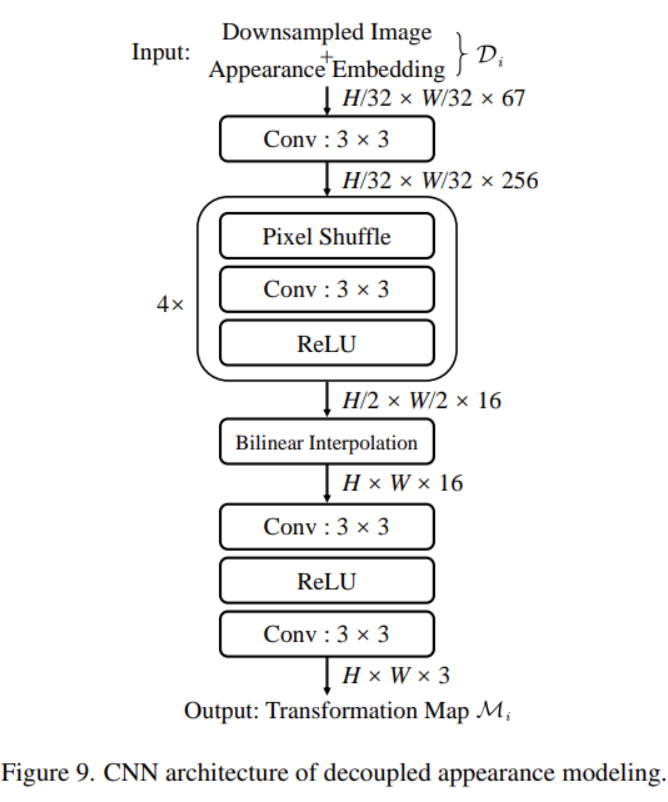
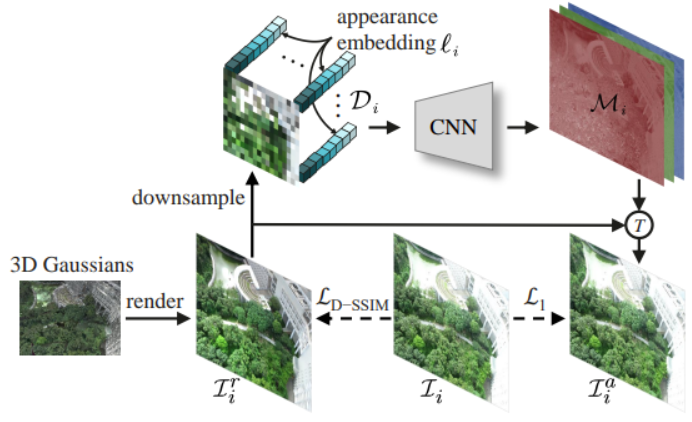
decouple_appearance_model.pycorresponding to theDecoupled Appearance Modelingin the paper.
graham_scan.pyconvex hull calculation is used to project the partition cube onto the camera plane and calculate the intersection of the projected region and the image region when implementing Visibility based camera selection.
seamless_merging.pycorresponding to theSeamless Mergingin the paper.
- I have added a new file
train_vast.pyto modify the process of training VastGaussian, if you want to train the original 3DGS, please usetrain.py - The paper mentioned
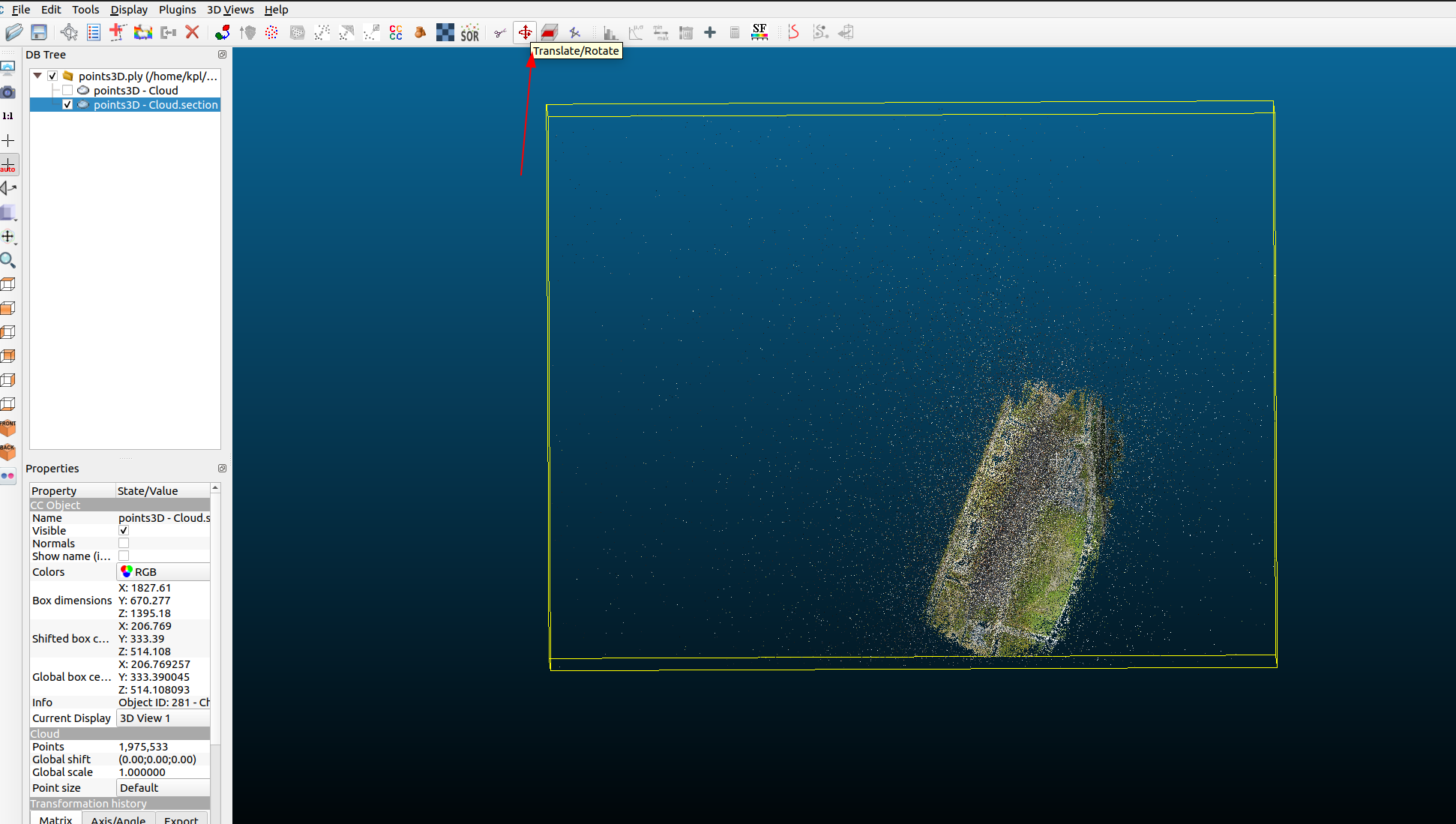
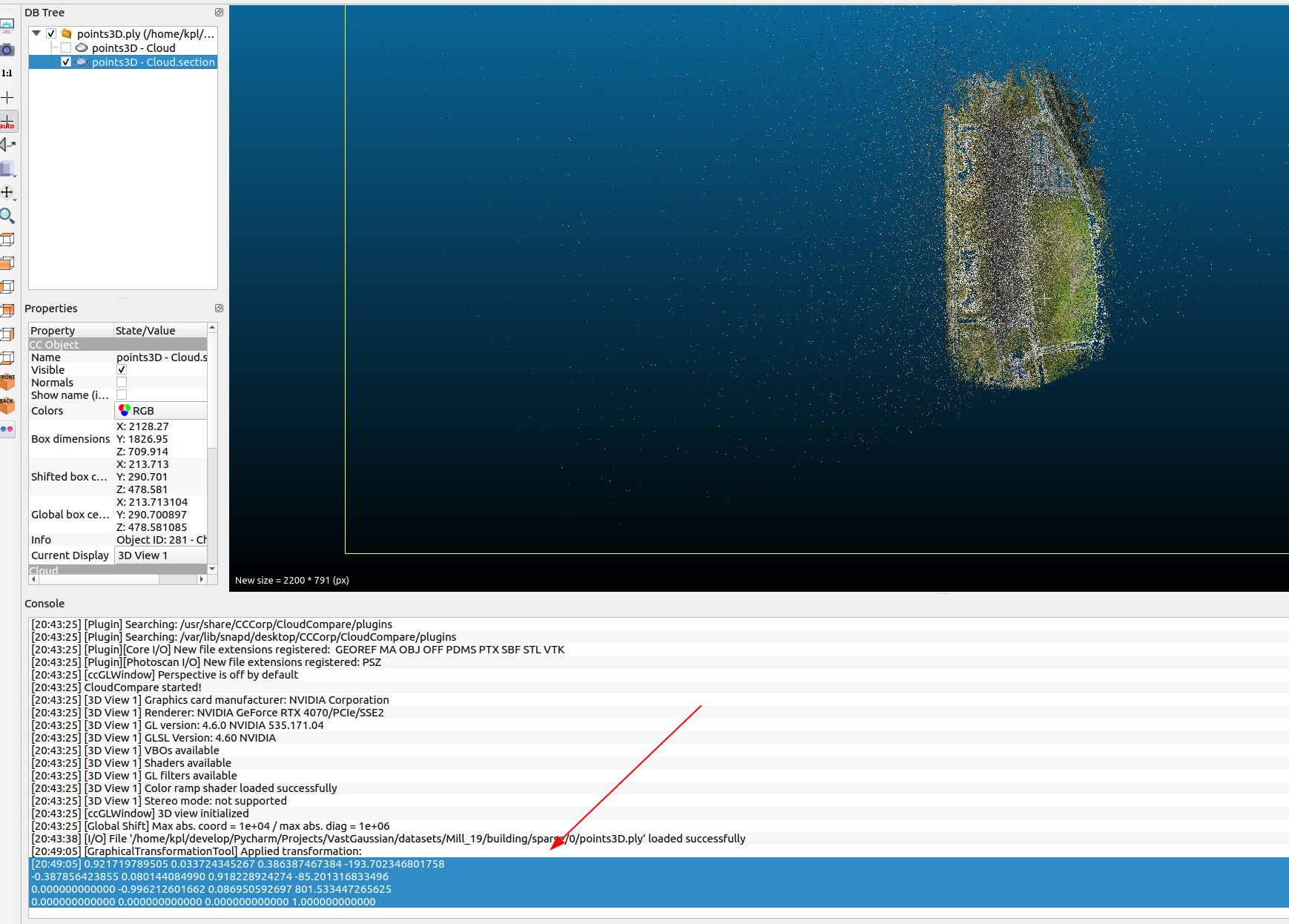
Manhattan world alignment, so that the Y-axis of the world coordinate is perpendicular to the ground plane, I asked the experts to know that this thing can be adjusted manually usingCloudCompare software, the general process is to adjust the bounding box boundary of the point cloud region to keep parallel to the overall orientation of the point cloud region. In my implementation, I assume that this step is done ahead of time.
For example, the point cloud in the following picture was originally tilted, but after adjusting it to become horizontal and vertical, the high person said that Manhattan World is the basic operation for large-scale 3D reconstruction (convenient partition), 😹
- In the process of implementation, I used a small range of data provided by 3DGS for testing. Larger data can not run on the native computer, and a large range of data requires at least 32G video memory according to the instructions of the paper
- In the implementation process, some operations in the paper, the author is not very clear about the details, so some implementation is based on my guess and understanding to complete, so my implementation may have some bugs, and some implementation may be a little stupid in the eyes of the expert, if you find problems in the use of the process, please contact me in time, progress together.
- The data format is the same as 3DGS, and the training command is basically the same as 3DGS. I didn't make too many personalized changes, you can refer to the following command (see
arguments/parameters.pyfor more parameters):
python train_vast.py -s datasets/xxx --exp_name test-
Urbanscene3D: https://github.com/Linxius/UrbanScene3D -
Mill-19: https://opendatalab.com/OpenDataLab/Mill_19/tree/main/raw -
test data for this implementation: https://repo-sam.inria.fr/fungraph/3d-gaussian-splatting/datasets/input/tandt_db.zip