叶树谦 115010269
The photo filename, 8-digitstudent ID and 4-digit programme code are separated by a tab in each line, and in the end of matching.txt, there should be an empty line. The shell command may not in the home directory, so $HOME is used to locate the home directory.
Use cat and while to read matching.txt line by line. And then use cut to split each line to find out the information needed included file name, student id and program code.
Verify whether the input is valid. File do not exist, ID is not 8-digit, programme code is not 4-digit, and the student ID is duplicated should be consider to ensure the robustness of the program. When meet this error, skip this turn of processing and output the error.
If all the information is right, rename and move the file into the right path using mv. If the sub folder do not exist, use mkdir to create one.
#!/bin/bash
# This is the solution to Q1
declare -a students # store the student ID to find out duplication
declare -i i
i=1
cat "$HOME/matching.txt" | while read -r line # read each line in matching.txt
do
name=`echo $line | cut -d' ' -f 1` # find out the original file name
id=`echo $line | cut -d' ' -f 2` # find out the matched ID
code=`echo $line | cut -d' ' -f 3` # find out the programme code should in
if [ ! -f "$HOME/student_photo/"$name ]; then
# check wheather the photo exist
echo "$name does not exist, so it cannot be renamed and moved."
continue
fi
if ! echo "$id" | grep -q '^[0-9]\+$'; then
# check wheather the ID is valid
echo "$id is an invalid 8-digit student ID, so $name is not renamed and moved."
continue
else
if [ ! ${#id} -eq 8 ] ; then
echo "$id is an invalid 8-digit student ID, so $name is not renamed and moved."
continue
fi
fi
if ! echo "$code" | grep -q '^[0-9]\+$'; then
# check wheather the programme code is valid
echo "$code is an invalid 4-digit programme code, so $name is not renamed and moved."
continue
else
if [ ! ${#code} -eq 4 ]; then
echo "$code is an invalid 4-digit programme code, so $name is not renamed and moved."
continue
fi
fi
if ! echo "${students[@]}" | grep -w $id &>/dev/null; then
# check wheather the ID is repeated
students[$i]=$id
i=i+1
else
echo "$id is a duplicate student ID, so $name is not renamed and moved."
continue
fi
name="$HOME/student_photo/"$name
# the original path
students[$i]=id
code="$HOME/student_photo/"$code
if [ ! -d $code ]; then
# if the folder do not exist, creat it
mkdir $code
fi
path=$code"/"$id".jpg"
mv $name $path # move to the new folder and rename
done-
There is no error.
The text in
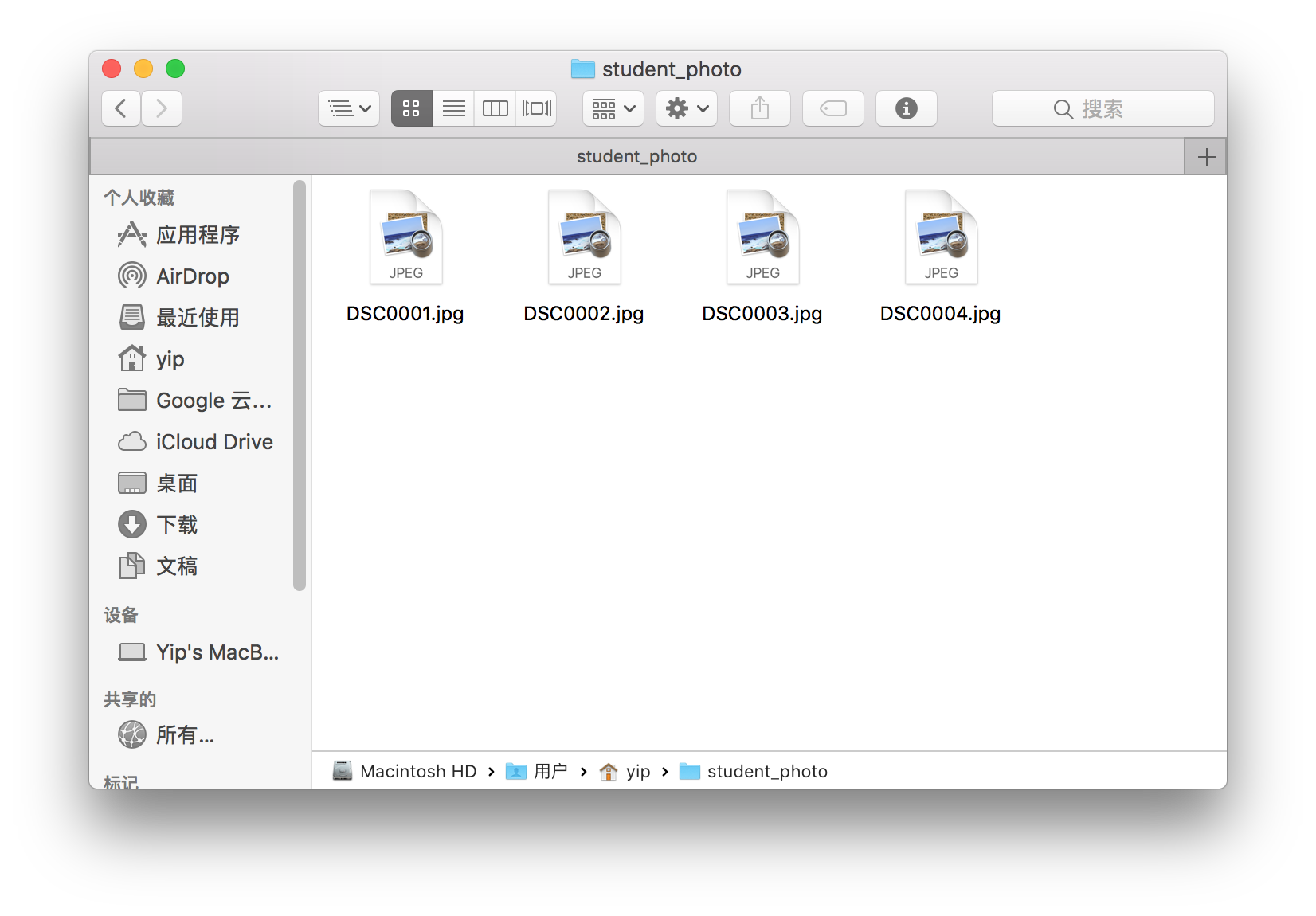
matching.txtis below.DSC0001.jpg 05123456 1561
DSC0002.jpg 05135554 1543
DSC0003.jpg 05468871 1286
DSC0004.jpg 05978585 1561
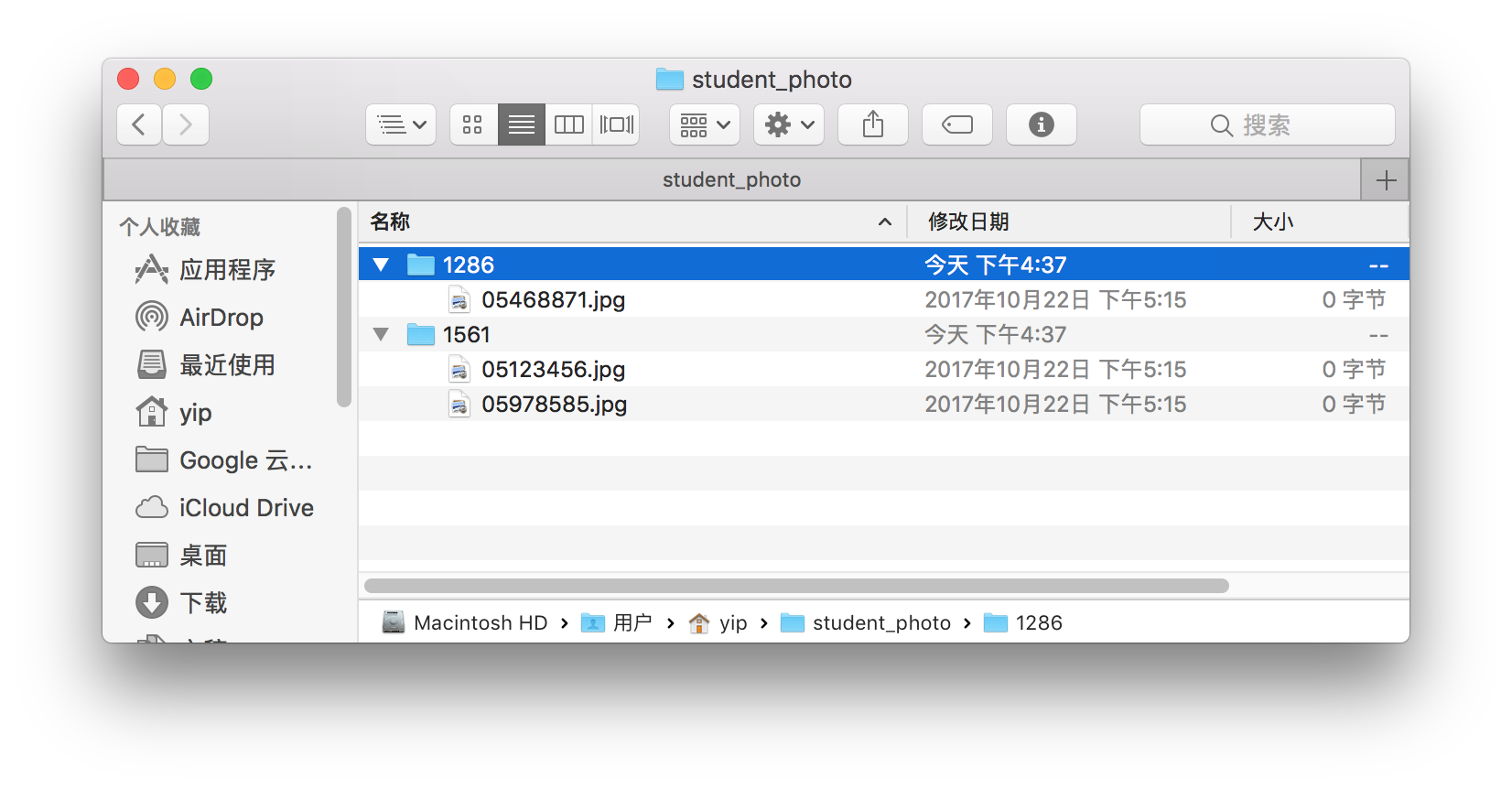
The files in the folder
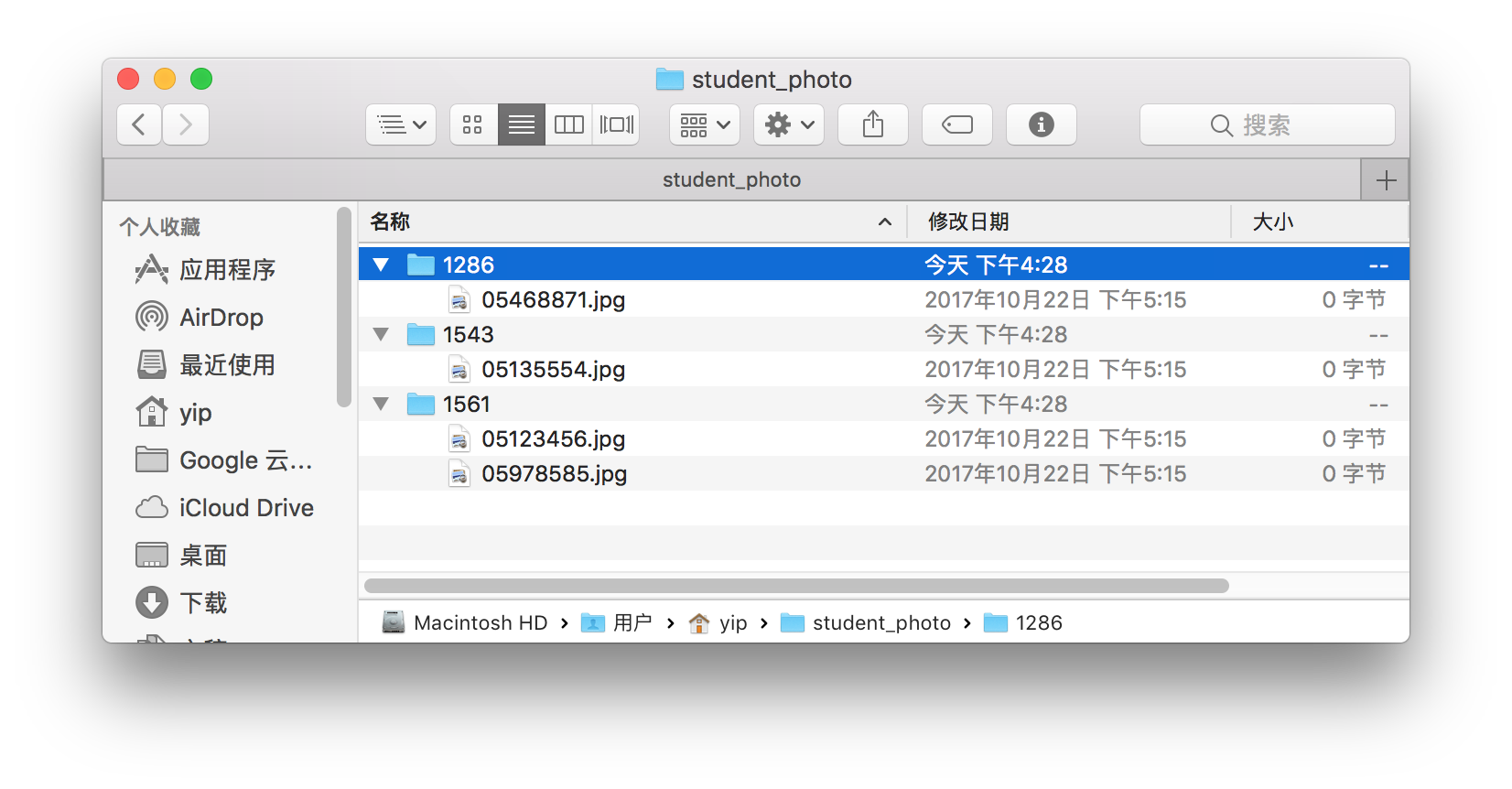
student_photobefore running the code is liked below.After running in the shell command in terminal, there is no error.
And the photos are renamed and removed successfully.
-
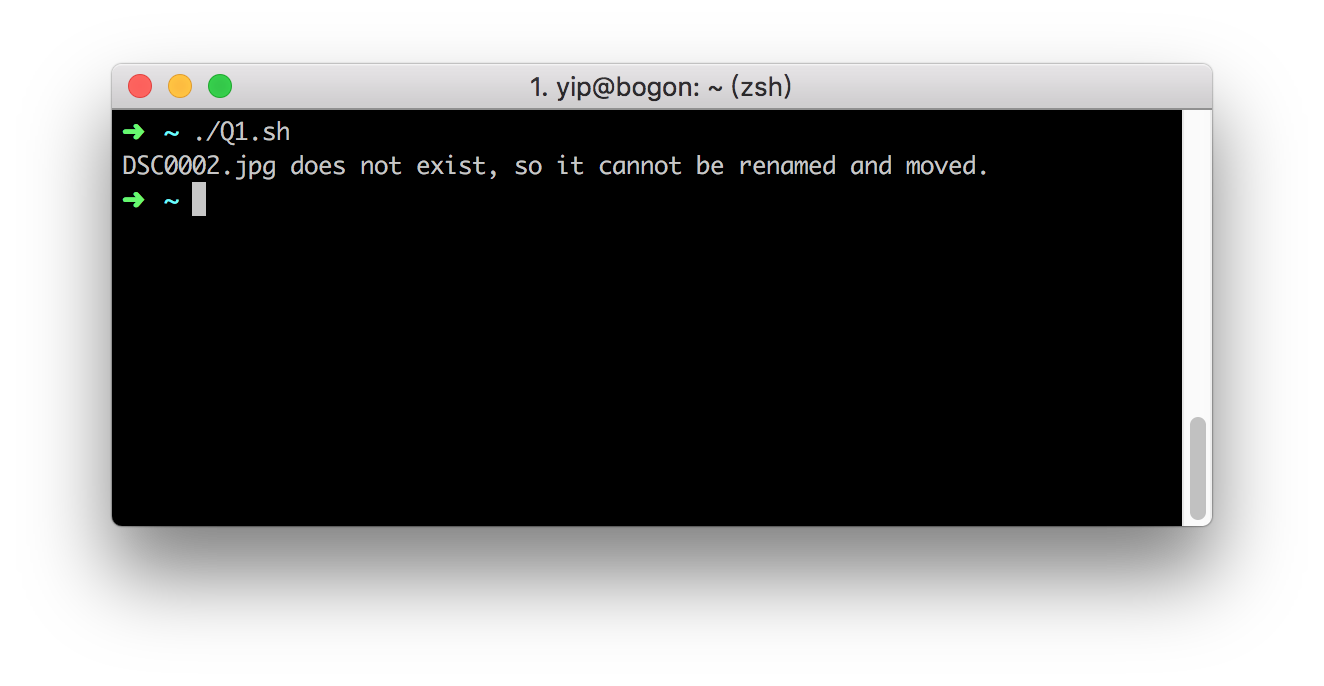
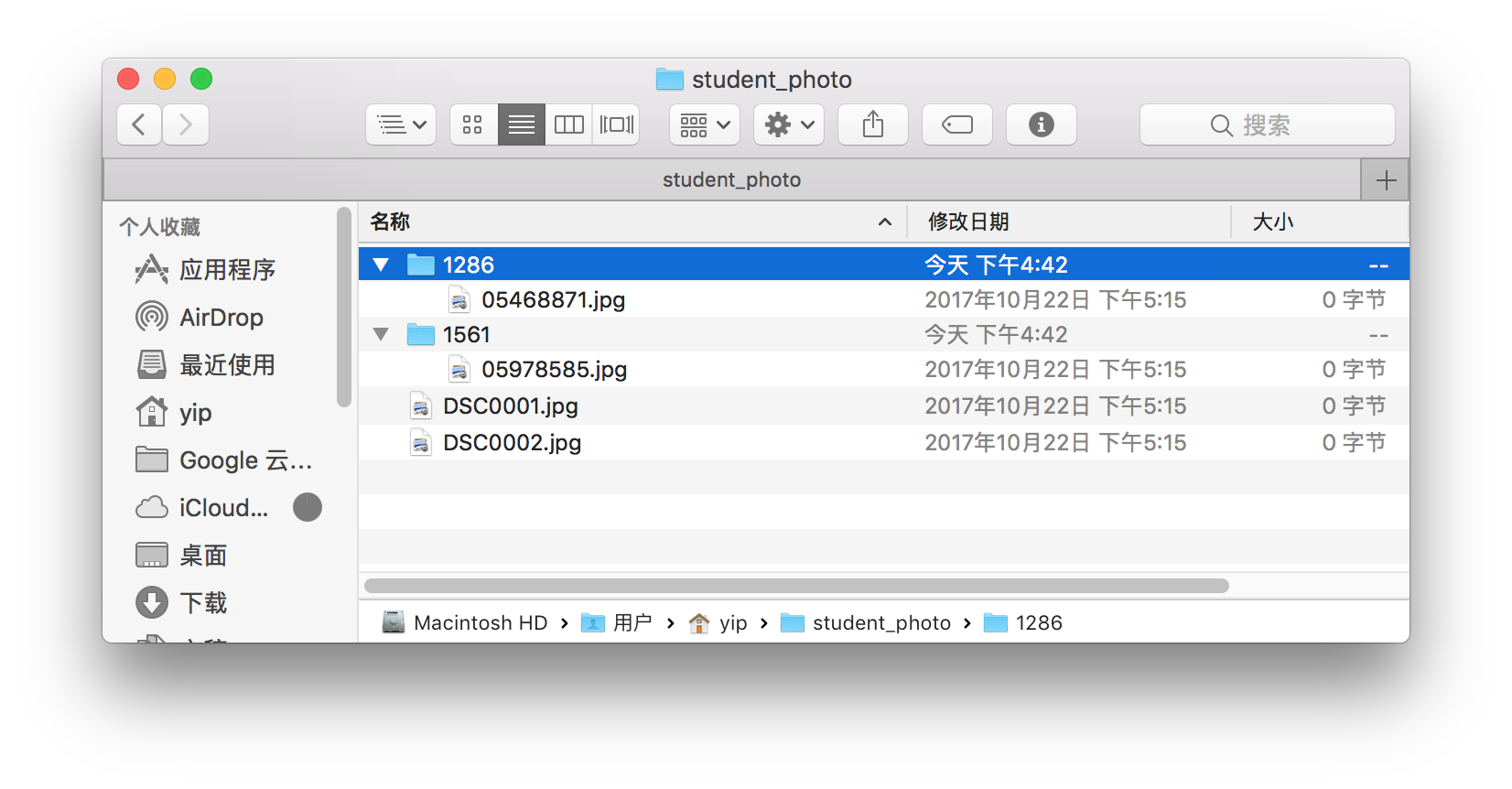
There is a photo file that do not exist.
The text in
matching.txtis the same as in part 1.The files in the folder
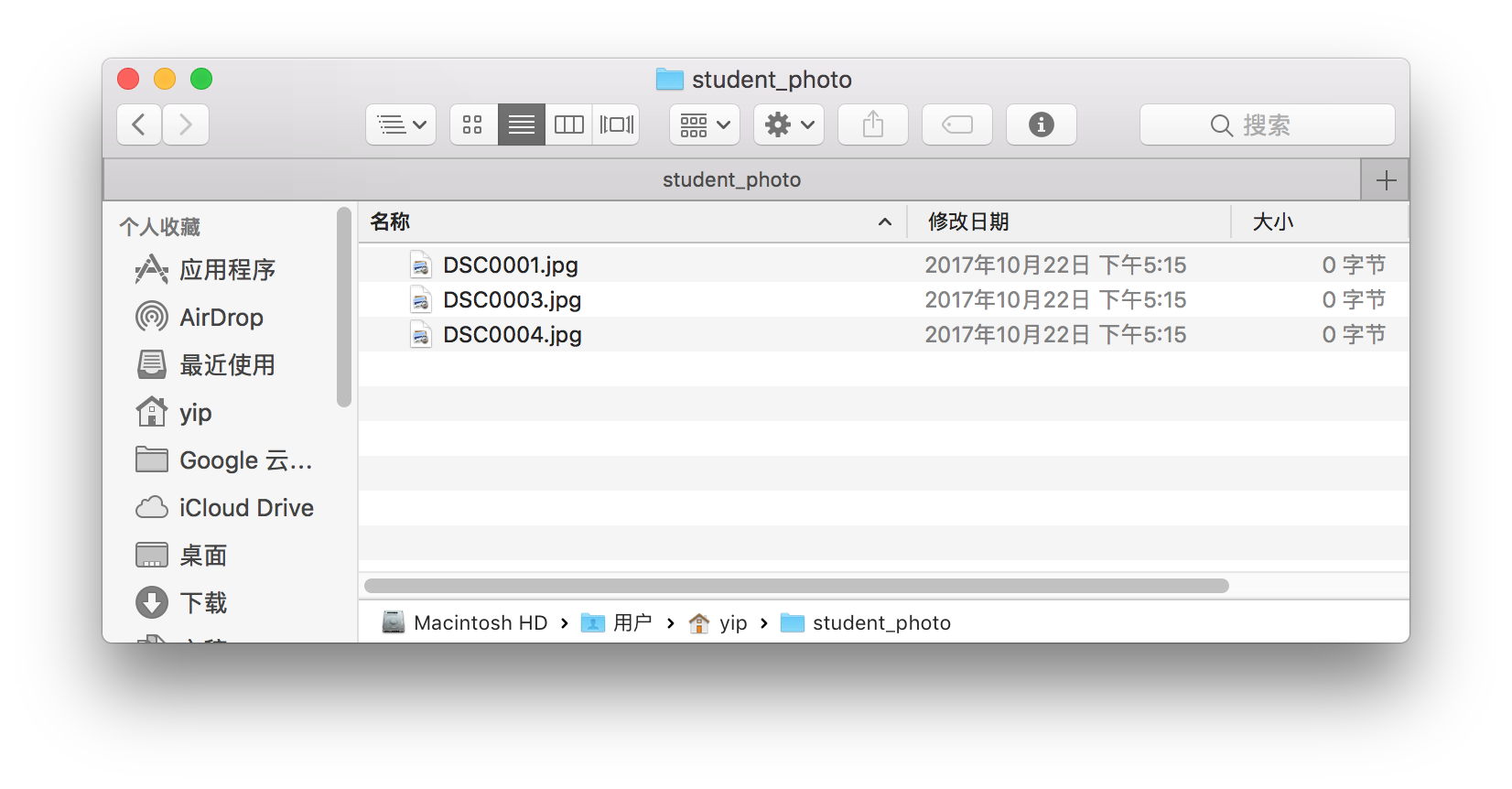
student_photobefore running the code is liked below.After running in the shell command in terminal, an error was shown liked below, and other photo has been managed.
-
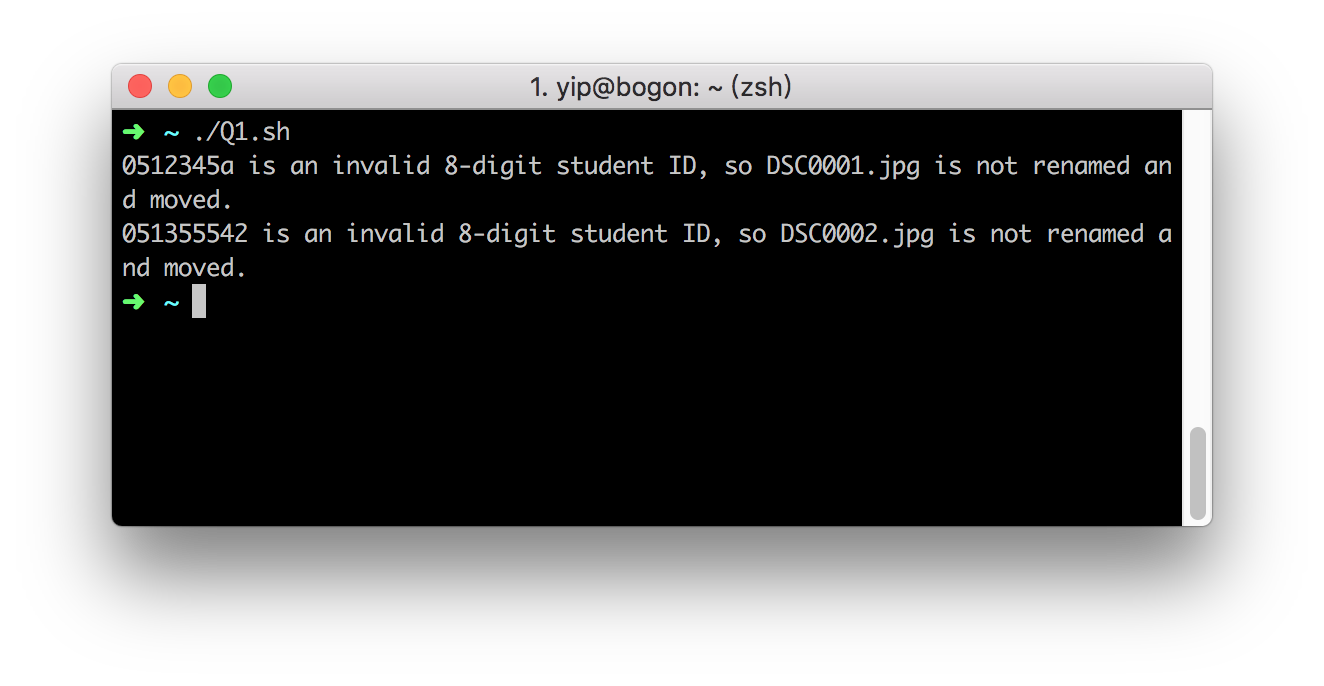
There is an invalid 8-digit student ID.
The text in
matching.txtis below.DSC0001.jpg 0512345a 1561
DSC0002.jpg 051355542 1543
DSC0003.jpg 05468871 1286
DSC0004.jpg 05978585 1561
The files in the folder
student_photobefore running the code is the same as in part 1.After running in the shell command in terminal, an error was shown liked below, and other photo has been managed.
-
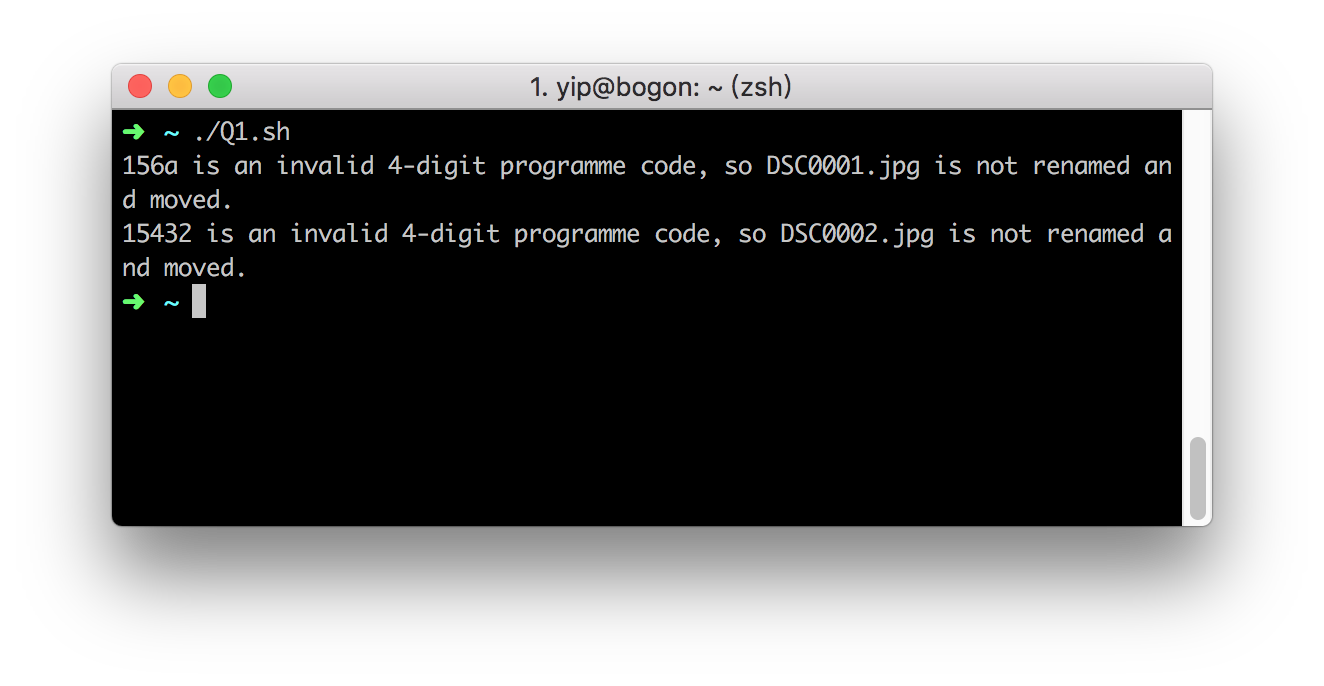
There is an invalid 4-digit programme code.
The text in
matching.txtis below.DSC0001.jpg 05123456 156a
DSC0002.jpg 05135554 15432
DSC0003.jpg 05468871 1286
DSC0004.jpg 05978585 1561
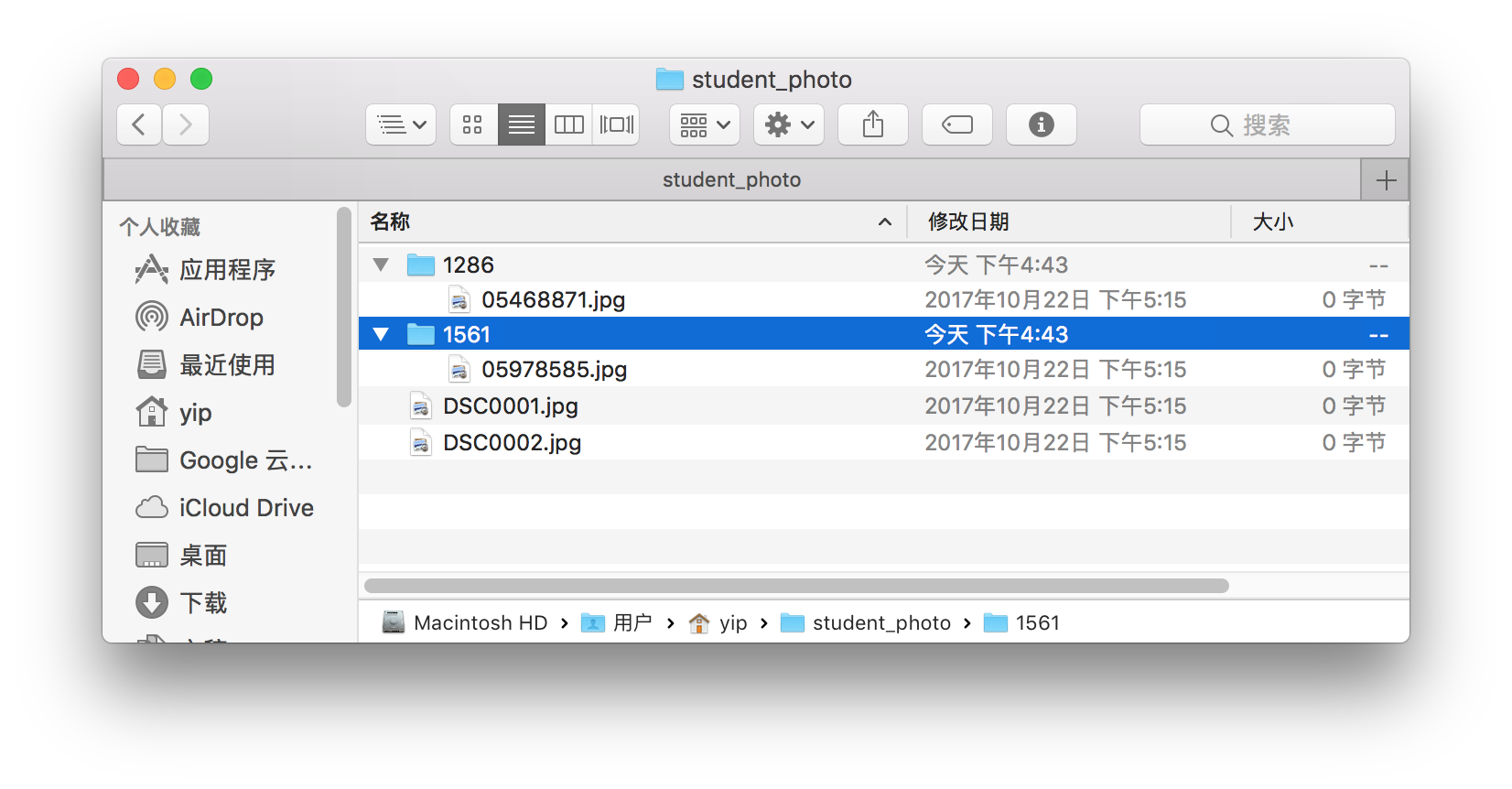
The files in the folder
student_photobefore running the code is the same as in part 1.After running in the shell command in terminal, an error was shown liked below, and other photo has been managed.
-
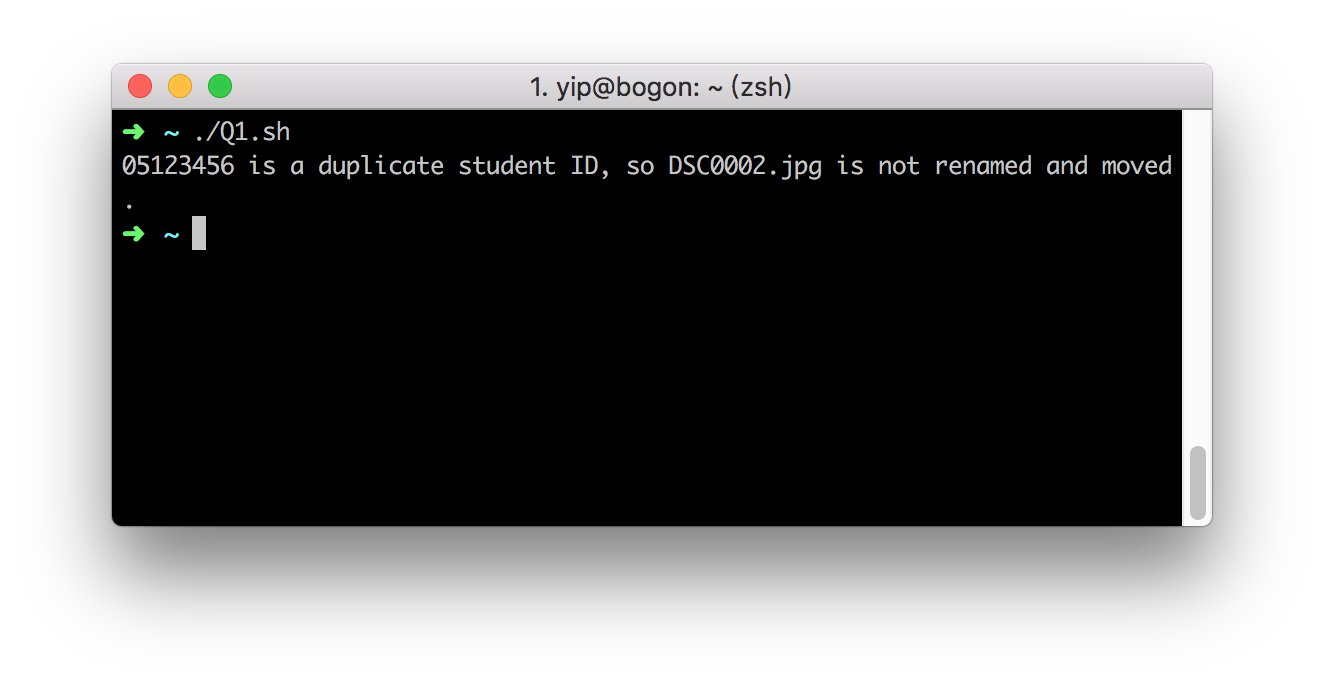
There is a duplicate student ID.
The text in
matching.txtis below.DSC0001.jpg 0512345a 1561
DSC0002.jpg 051355542 1543
DSC0003.jpg 05468871 1286
DSC0004.jpg 05978585 1561
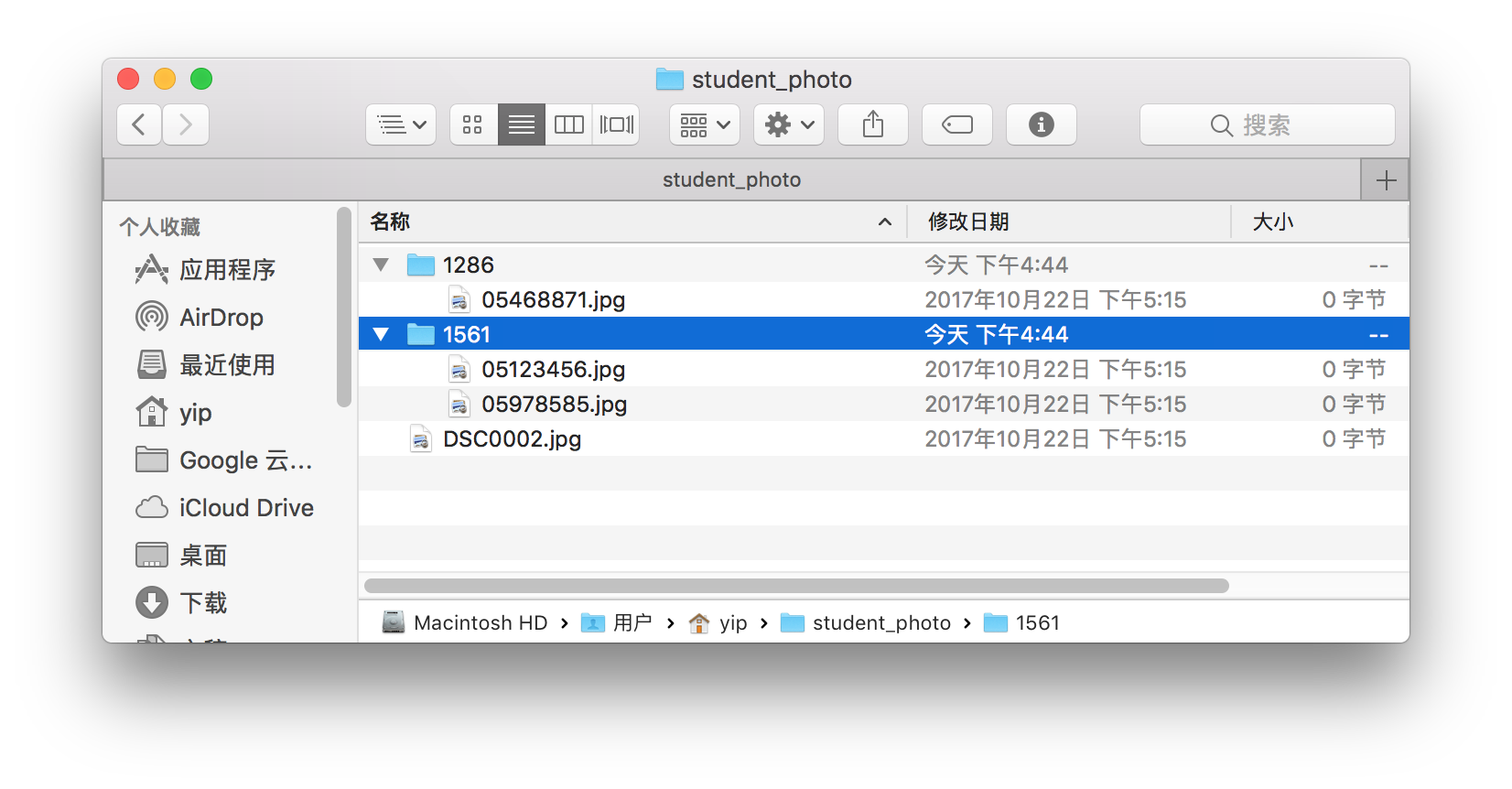
The files in the folder
student_photobefore running the code is the same as in part 1.After running in the shell command in terminal, an error was shown liked below, and other photo has been managed.
Input arguments in main() function into *argv[], and use atoi() to transfer character into interger.
Using shared memory to store the variable idata, and using System V semaphore to cordinate concurrent processes. Define a key_t type variable shm_key to storage the IPC key. Using memset(), shmat() to put idata into the shared memory.
Define 3 functions sem_set(), sem_p() and sem_v() to control the semaphore.
Include time.h to get the current time, and use fork() function to create child process. Justify the PID of current processing the identify which process it is and run different code.
Using sleep() to control the after time, and use asctime(), localtime() and time() functions to get and print current time.
(After tested, the code commted during line 24 to 28 is needed in Linux, but not in macOS.)
/* This is the solution to Q2.
*/
#include <time.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/sem.h>
#define FILENAME "/dev/null"
// System V semaphore relative variable
int sem_set(int sem_id);
int sem_p(int sem_id);
int sem_v(int sem_id);
// // !!! The code below should be commted to run in macOS,
// // but it is needed to run in Linux.
// union semun{
// int val;
// struct semid_ds *buf;
// unsigned short *arry;
// };
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int t1, t2, t3, t4, t5, t6;
pid_t child1, child2, grandchild;
t1 = atoi(argv[2]); // get time data from arguments
t2 = atoi(argv[3]);
t3 = atoi(argv[4]);
t4 = atoi(argv[5]);
t5 = atoi(argv[6]);
t6 = atoi(argv[7]);
// shared memory
key_t shm_key = ftok(FILENAME, 0); // get the IPC key
if(shm_key == -1){
perror("ftok");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
int shm_size = getpagesize(); // set shared memory size
int shm_id = shmget(shm_key, shm_size, 0644 | IPC_CREAT);
if(shm_id == -1){
perror("shmget");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
int *idata = (int *)shmat(shm_id, NULL, 0); // put idata into shared memory
if(idata == (int *)-1){
perror("shmat");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
memset(idata, 0, shm_size);
key_t sem_key = shm_key; // set semaphore key
int sem_id = semget(sem_key, 1, 0644 | IPC_CREAT); // set semaphore ID
if(sem_id == -1){
perror("semget");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if(sem_set(sem_id) == -1){
perror("sem_set");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
*idata = atoi(argv[1]); // get initial idata from argument
printf("PID\trole\t\tidata\ttime\n");
// parent process
time_t rawtime; // time relatived variable
struct tm * timeinfo;
time(&rawtime); // get the current time
timeinfo = localtime(&rawtime);
printf("%4d\tparent\t\t\t%s\n", getpid(), asctime(timeinfo)); // print process created infomation
fflush(stdout);
sleep(t1);
child1 = fork(); // creat first child process
if (child1 < 0) {
perror("fork first child");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if (child1 == 0)
{
//first child process
time(&rawtime);
timeinfo = localtime(&rawtime);
printf("%4d\tfirst child\t\t%s\n", getpid(), asctime(timeinfo));
fflush(stdout);
sleep(t3);
if(sem_p(sem_id) == -1){ // semaphore wait
perror("sem_p(first child)");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
*idata += 1;
time(&rawtime);
timeinfo = localtime(&rawtime);
printf("%4d\tfirst child\t%d\t%s\n", getpid(), *idata, asctime(timeinfo)); // print procee terminated information
if(sem_v(sem_id) == -1){ // semaphore signal
perror("sem_v(first child)");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if(shmdt(idata) == -1){ // disconnect shared memory
perror("shmdtv(first child)");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
fflush(stdout);
exit(0); // terminate first child
}
else
{
sleep(t2);
child2 = fork(); //create second child
if (child1 < 0){
perror("fork second child");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if (child2 == 0)
{
// second child process
time(&rawtime);
timeinfo = localtime(&rawtime);
printf("%4d\tsecond child\t\t%s\n", getpid(), asctime(timeinfo)); // print process created infomation
fflush(stdout);
sleep(t5);
grandchild = fork(); // grandchild proces
if (child1 < 0){
perror("fork grandchild");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if (grandchild == 0)
{
time(&rawtime);
timeinfo = localtime(&rawtime);
printf("%4d\tgrandchild\t\t%s\n", getpid(), asctime(timeinfo)); // print procee terminated information
fflush(stdout);
sleep(t6);
if(sem_p(sem_id) == -1){ // semaphore wait
perror("sem_p(grandchild)");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
*idata += 1;
time(&rawtime);
timeinfo = localtime(&rawtime);
printf("%4d\tgrandchild\t%d\t%s\n", getpid(), *idata, asctime(timeinfo));
if(sem_v(sem_id) == -1){ // semaphore signal
perror("sem_v(grandchild)");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if(shmdt(idata) == -1){ // disconnect shared memory
perror("shmdt(grandchild)");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
fflush(stdout);
exit(0); // terminate grandchild
}
else{
// second child process
sleep(t4);
if(sem_p(sem_id) == -1){ // semaphore wait
perror("sem_p(second child)");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
*idata += 1;
time(&rawtime);
timeinfo = localtime(&rawtime);
printf("%4d\tsecond child\t%d\t%s\n", getpid(), *idata, asctime(timeinfo));// print procee terminated information
if(sem_v(sem_id) == -1){ // semaphore signal
perror("sem_v(second child)");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if(shmdt(idata) == -1){ // disconnect shared memory
perror("shmdt(second child)");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
fflush(stdout);
exit(0); // termiate second child
}
}
else
{
// parent process
if(sem_p(sem_id) == -1){ // semaphore wait
perror("sem_p(parent)");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
*idata += 1;
time(&rawtime);
timeinfo = localtime(&rawtime);
printf("%4d\tparent\t\t%d\t%s\n", getpid(), *idata, asctime(timeinfo)); // print procee terminated information
if(sem_v(sem_id) == -1){ // semaphore signal
perror("sem_v(parent)");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if(shmdt(idata) == -1){ // disconnect shared memory
perror("shmdt(parent)");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
fflush(stdout);
return 0; // terminate parent process
}
}
return 0;
}
int sem_set(int sem_id){ // set the semaphore
union semun sem_u;
sem_u.val = 1;
if(semctl(sem_id, 0, SETVAL, sem_u) == -1){
return -1;
}else{
return 0;
}
}
int sem_p(int sem_id){ // semaphore wait
struct sembuf sem_b[1];
sem_b[0].sem_num = 0;
sem_b[0].sem_op = -1;
sem_b[0].sem_flg = SEM_UNDO;
if(semop(sem_id, sem_b, 1) == -1){
return -1;
}else{
return 0;
}
}
int sem_v(int sem_id){ // semaphore signal
struct sembuf sem_b[1];
sem_b[0].sem_num = 0;
sem_b[0].sem_op = 1;
sem_b[0].sem_flg = SEM_UNDO;
if(semop(sem_id, sem_b, 1) == -1){
return -1;
}else{
return 0;
}
}
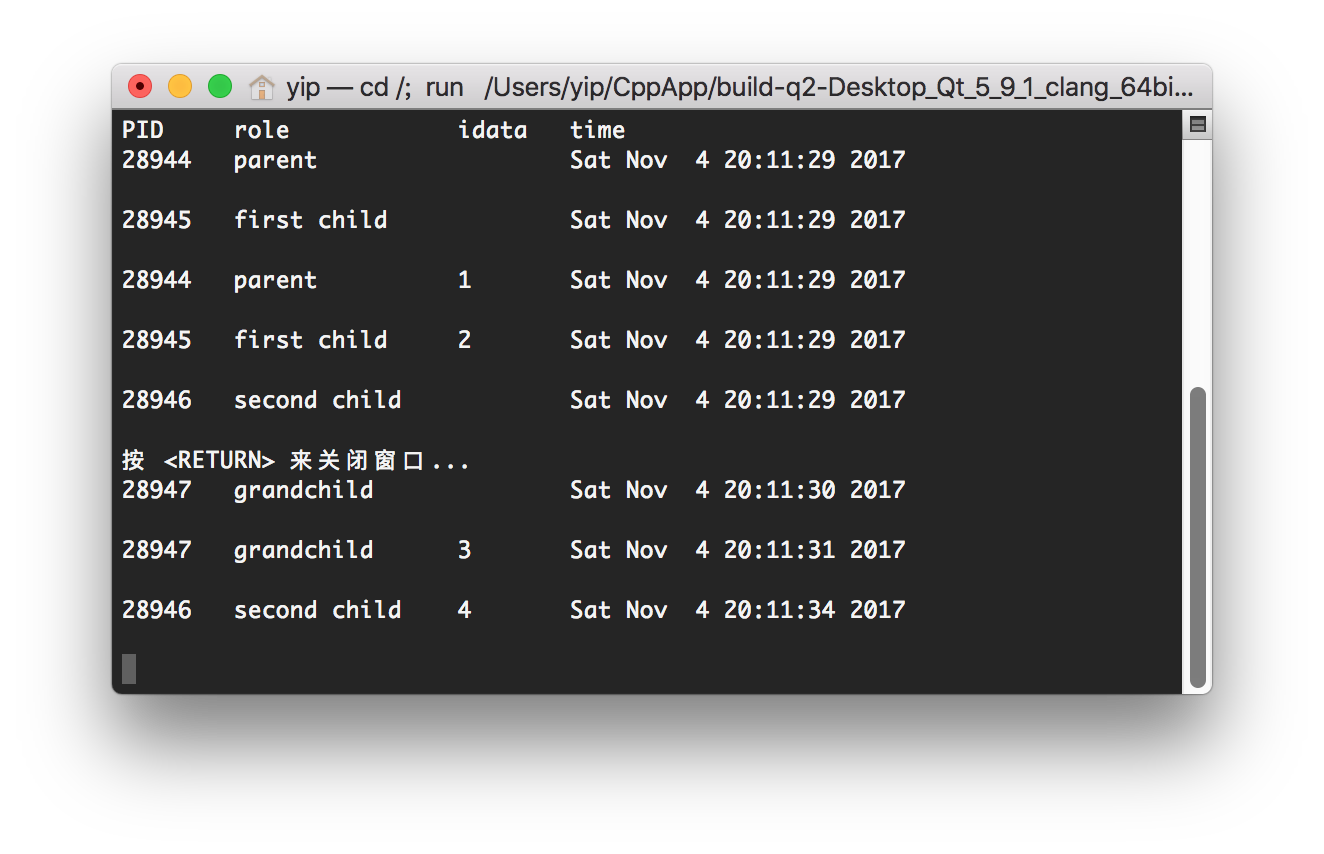
- The parent outlives then the child. Let
$idata = 0, t_1=0, t_2=0,t_3=0,t_4=4,t_5=1,t_6=1$ .
The running result is below.
We can see the process 28947 is the child of 28946, so the parent outlives than the child. idata can be count correctlly.
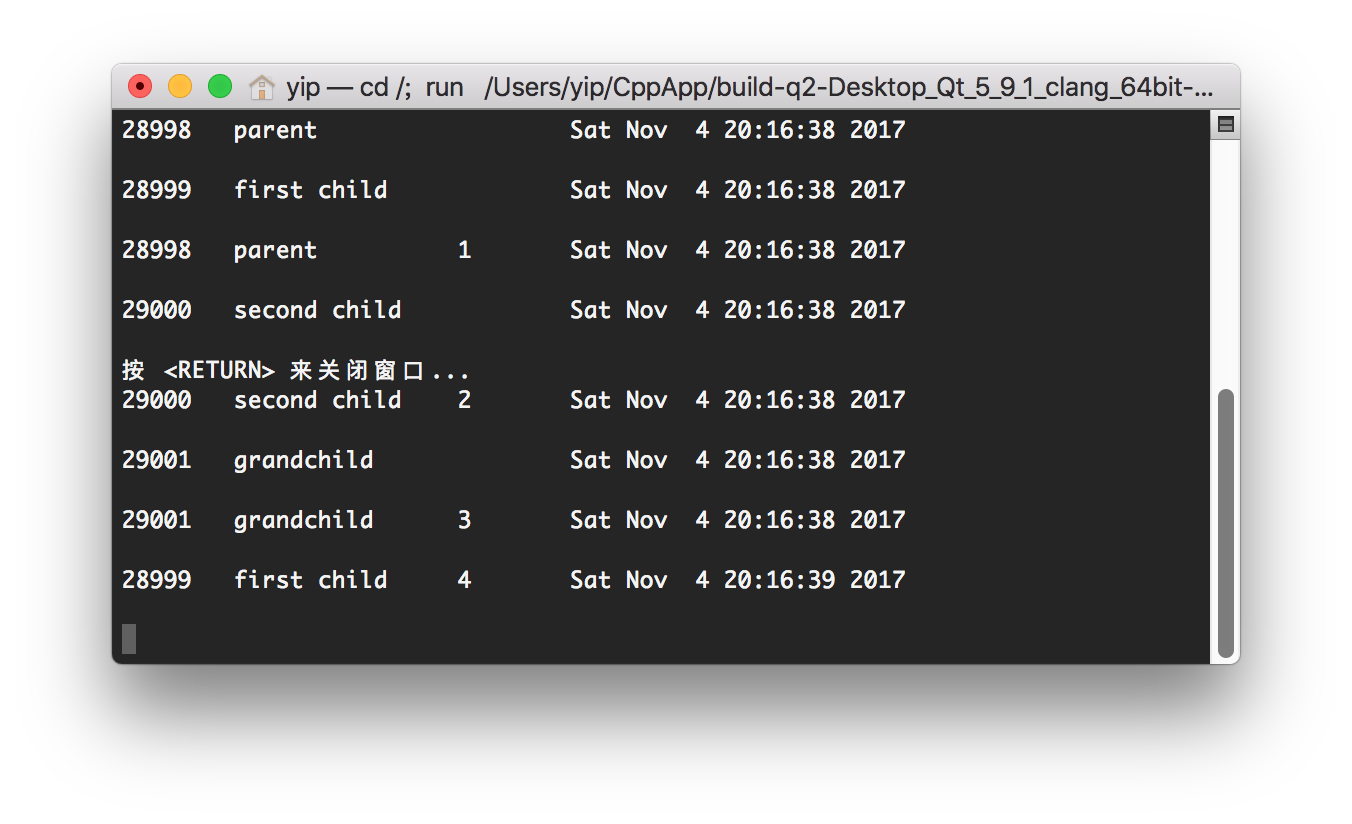
- the (orphaned) child outlives the parent.
$idata = 0, t_1=0, t_2=0,t_3=1,t_4=0,t_5=0,t_6=0$ .The running result is below.
We can see the process 28998 as the parent, is the first process terminated in all 4 processes. And the opphaned child processes still can run normally and output the correct idata.
So, we can conclude that the parent need not to wait for its child to terminate.
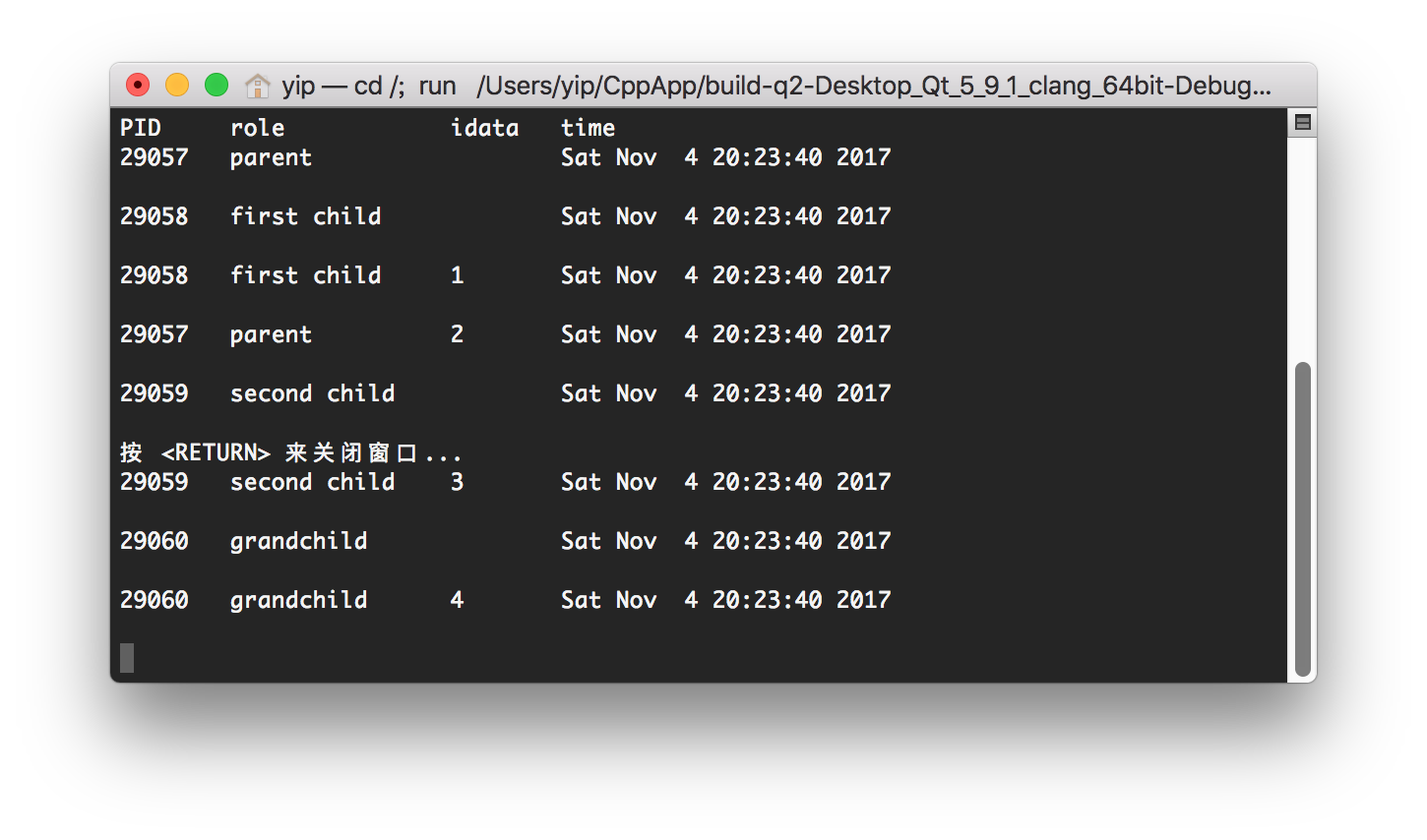
- Let
$idata = 0, t_1=0, t_2=0,t_3=0,t_4=0,t_5=0,t_6=0$ .
The running result is below.
This situation is that the child run fastest, due to it do not need any sleeping, the first child still terminate before the parent, which means he child terminates before its parent has had a chance to wait.
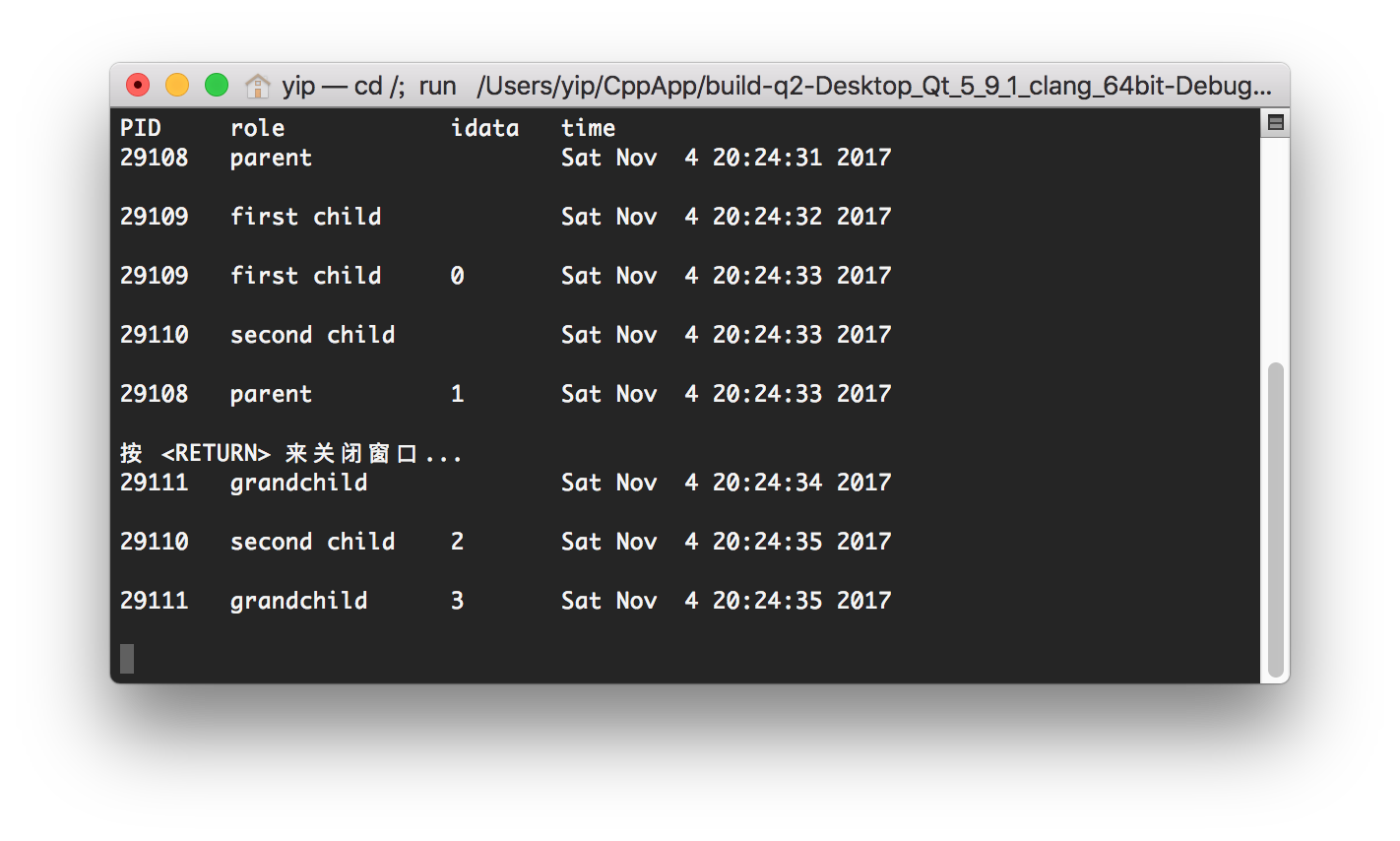
- Let
$idata = -1, t_1=1, t_2=1,t_3=1,t_4=1,t_5=1,t_6=1$ .
The running result is below.