This repository contains infrastructure code to set up KubeFlow on AWS EKS (Elastic Kubernetes Service). It requires several dependencies:
- an appropriate
awscliprofile configured using the public/private access keys - a Databricks account provisioned, along with an active API key that must be generated via the Databricks UI.
Databricks requires a special VPC set up for its clusters to run inside.
Terraform is used to provision many of the underlying infrastructure, including the
- core OperatorFlow VPC
- bastion host EC2 instance
- route tables and subnet CIDR blocks
- Databricks subnet
- IAM (Identity Access Management) roles for Databricks to provision Apache Spark EC2 instances
- S3 buckets to store Databricks metadata
- Make sure you are in the
infrastructure/folder. - Run
terraform initto initialize Terraform locally. - Run
terraform planto fetch remote state from AWS and compare against the local Terraform state. - Run
terraform applyto apply the changes and create the necessary infrastructure.
- Make sure that the instance you are running
eksctlon has been properly configured viaawscli. If it has not, runaws configure. - Run
eksctl create cluster --node-type="m5.xlarge" --nodes-min=1 --nodes-max=3 --region=us-east-1 --zones=us-east-1a,us-east-1bto provision the EKS cluster in the us-east-1 region. Note that
you should make sure to properly define the regions and availability zones, since not all availability zones of each region are capable
of supporting a large enough instance type as required by KubeFlow and Istio.
3. Wait a few minutes for the provisioning to finish, and then grab the cluster name.
During the provisioning process, your terminal output will look like this:
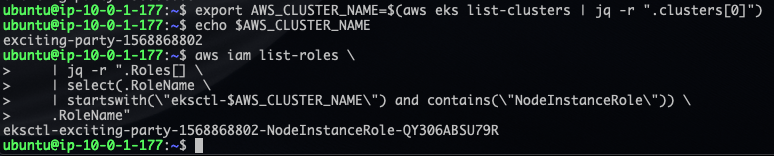
- Run the following command to save the cluster name as an environment variable:
export AWS_CLUSTER_NAME=$(aws eks list-clusters | jq -r ".clusters[]")- Find the appropriate node instance role by using
export AWS_NODE_INSTANCE_ROLE=$(aws iam list-roles \
| jq -r ".Roles[] \
| select(.RoleName \
| startswith(\"eksctl-$AWS_CLUSTER_NAME\") and contains(\"NodeInstanceRole\")) \
.RoleName")This will allow you to later edit the KubeFlow configuration files:
In order to provision KubeFlow, you'll need to first make sure that you download the correct kfctl golang binary:
- From the KubeFlow installation documentation:
# Add kfctl to PATH, to make the kfctl binary easier to use.
tar -xvf kfctl_<release tag>_<platform>.tar.gz
export PATH=$PATH:"<path to kfctl>"- Then download the configuration YAML file:
# Download config file
export CONFIG="/tmp/kfctl_aws.yaml"
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubeflow/kubeflow/v0.6.2/bootstrap/config/kfctl_aws.yaml -O ${CONFIG}- Save the
KFAPPenvironment variable as your cluster name:
export KFAPP=${AWS_CLUSTER_NAME}
echo $KFAPP- Change the role in the
kfctl_aws.yamlconfiguration to the node instance role:
sed -i "s/eksctl-kubeflow-aws-nodegroup-ng-a2-NodeInstanceRole-xxxxxxx/$AWS_NODE_INSTANCE_ROLE/" /tmp/kfctl_aws.yaml
sed -i "s/us-west-2/us-east-1/" /tmp/kfctl_aws.yamlNote: Because of a recent merge into the KubeFlow repo, you'll need to also replace the manifest with the master manifest branch:
sed -i 's/manifests\/archive\/v[0-1]\.[0-9]-branch\.tar\.gz/manifests\/archive\/master\.tar\.gz/' /tmp/kfctl_aws.yaml- Then, initialize the cluster configurations and enter the cluster directory:
kfctl init ${KFAPP} --config=${CONFIG} -V
cd ${KFAPP}- Now, you can use the template in
app.yamlto generate the other manifest YAML files for your Istio deployment and Kubeflow objects:
kfctl generate all -VThis will generate all the Kustomize configuration files that are needed. 7. Prior to actually applying all the changes and implementing your service mesh, you need to set up automatic sidecard injection with Istio:
kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=enabledThis will allow every new pod that is created to have two containers - the target application image to be run, as well as an Istio Envoy sidecar. 8. You can apply the changes to the Kubernetes controller via
kfctl apply all -VOperatorFlow's infrastructure is provisioned via a bastion host that is set up in its own separate VPC
(virtual private cloud). The files in the infrastructure folder provide the Terraform resources necessary for provisioning the
networking and EC2 instance that the bastion host uses. The bastion host EC2 instance uses a default AWS AMI (machine image) that already
contains necessary configurations and packages (awscli, boto3, etc.).
An auto-generated API Gateway Javascript SDK is available inside the api_gateway folder. This SDK can be used within any frontend Javascript
client to quickly make calls to the API Gateway and fetch resources from Databricks.