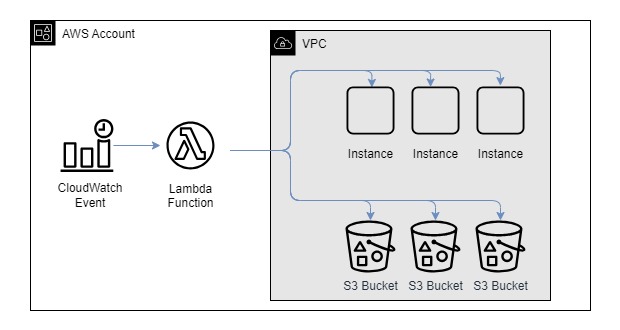
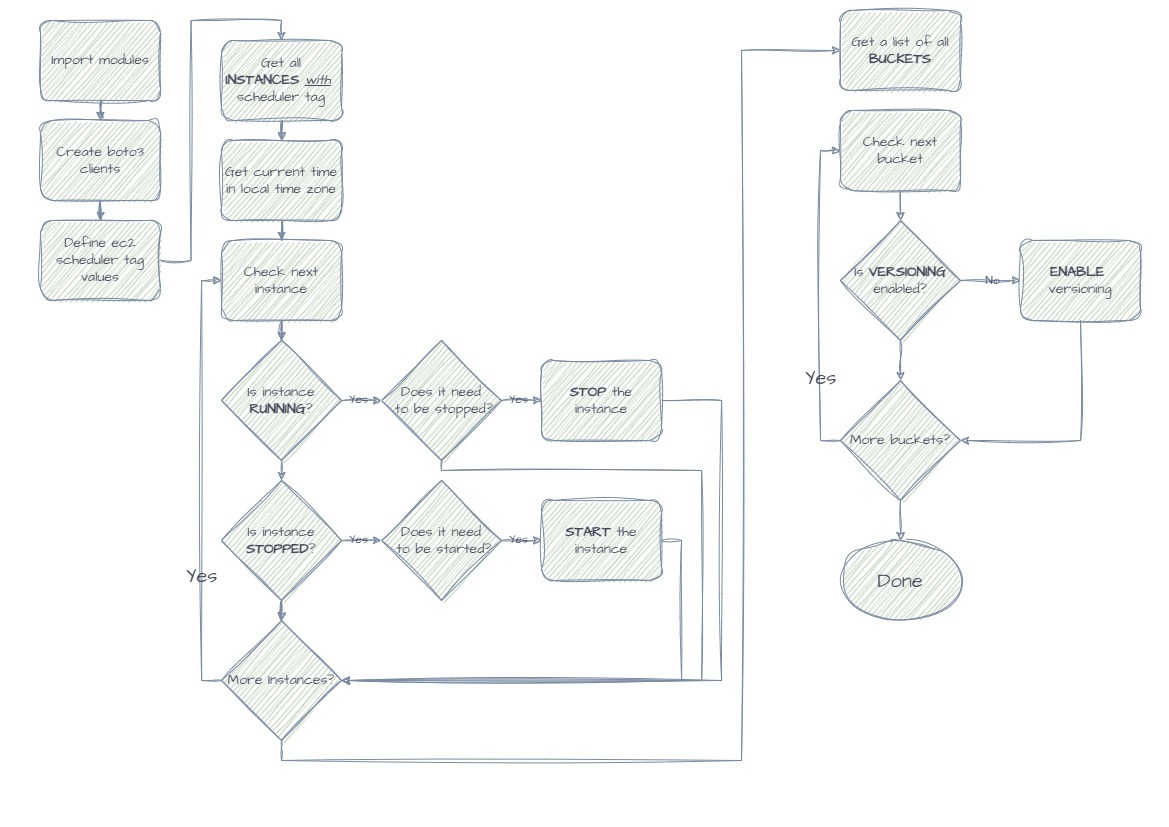
Purpose of this hands-on training is to provide additional exposure to Boto3 and Lambda to develop an EC2 Scheduler and S3 compliance validator. The scheduler will stop instances after hours and restart them at the beggining of the day. The S3 compliance validator will ensure that all S3 buckets in the account have versioning enabled, to remain compliant with the company's storage policies. These are practical problems that are faced in organizations today.
At the end of the this hands-on training, students will be able to:
-
Create a Lambda function and necessary roles and policies.
-
Be able to use the boto3 SDK, specifically with the 'EC2' resource.
-
Parse json output from AWS using boto3.
-
Write a python script from scratch.
-
Part 1 - Review design and pseudocode for Lambda function
-
Part 2 - Create test instances
-
Part 3 - Setup your AWS credentials file
-
Part 4 - Implement and test the Lambda function
-
Part 5 - Deploy the Lambda function
-
Part 6 - Create a Lambda role
-
Part 7 - Create a CloudWatch scheduled event
-
Part 8 - Test your function
-
Part 9 - Create test buckets
-
Part 10 - Modify to check for S3 buckets with versioning disabled
-
Part 11 - Test you code via Visual Studio Code
-
Part 12 - Deploy your code via the Lambda console
-
Part 13 - Update the Lambda role
-
Part 14 - Delete your resources!
-
Review the proposed architecture.
-
Review the application flow diagram.
-
Review the file
pseudocode.py.
Note: Notice the process being used here. Creating a design is important before going hands-to-keyboard for any project. In this case the design consists of a design diagram and pseudocode.
-
Open the Amazon EC2 console at "https://console.aws.amazon.com/ec2/".
-
Choose Instances on the left-hand menu.
-
Click on 'Launch Instances'.
- Number of instances : 3
- Name : <yourname>-scheduled-server
- Click 'Add additional tags' beside 'Name'
- Add these tags:
- SchedulerStartTime : 8
- SchedulerStopTime : 18
- Amazon Machine Image (AMI) : Amazon Linux 2023 AMI (hvm|ena|ebs|x86_64)
- Instance Type : t2.micro
- Key pair name : choose your key pair
- Network: : no changes required
- Click on 'Launch Instances' again.
- Number of instances : 2
- Name : <yourname>-no-schedule-server
- Amazon Machine Image (AMI) : Amazon Linux 2023 AMI (hvm|ena|ebs|x86_64)
- Instance Type : t2.micro
- Key pair name : choose your key pair
- Network: : no changes required
-
Python will use your credentials file behind the scenes every time you make a AWS API call via boto3.
-
AWS access keys:
- ensure you have valid keys from AWS IAM for your IAM user.
- if you do not:
- open the AWS IAM console,
- click
Userson the left menu, - click on your IAM user name,
- click on the
Security credentialstab, - under
Access keys, click onCreate access key, - for use case, select
Local code, - check the box indicating you understand the recommendation and click
Next, - add a
Description, - click on
Create access key, - Store your access key and secret access key somewhere SAFE,
- You will not be able to see your secret access key again after you navigate away from this page.
-
From a terminal:
- type
aws configure, - enter your access key,
- enter your secret access key,
- for region enter
us-east-1, - for output enter
json.
- type
-
Create a file called
awscode.py. This will be your Lambda script. -
Import the necessary modules and functions that you will need:
- boto3
- json
- datetime from the module datetime
- pytz
-
Implement a
lambda_handlerthat returns without doing anything.- What is a
lambda_handler? - Why do we pass the
eventandcontextparameters to it? - Make sure you comment the function; why do we add these comments?
- What is a
-
Implement the lines of code that will allow the
lambda_handlerto be called from the IDE for testing purposes.- Before deploying the Lambda function, it can be tested and debugged in your IDE; testing and debugging in Lambda directly is not advised.
-
Take a few moments to review the boto3 ec2 reference page with a focus on the
describe_instancesfunction. (https://boto3.amazonaws.com/v1/documentation/api/latest/reference/services/ec2.html)- Which parameters are required?
- What
data structureis returned as part of the response? - How would you know if there were 0 instances returned based on your criteria?
- How would you know exactly how many instances are returned from the function?
- How would you access the
instance idfrom that data structure? - How would you access the
instance statefrom that data structure? - How would you access the
tagsfrom that data structure?
-
Add the lines of code in the
lambda_handlerto implement the following pseudocode:- Get a list of instances with the required tags
- If there are no instances, print a message and exit
- Get the current hour
- Iterate over the list of instances
- At this time, only print the instance id, we will return to this step
- Print a message that processing is complete
- Question:
- What would happen if we don't use the timezone to get the current hour?
-
Test the code you have written so far:
- Run it in debug mode and
step overeach line - Note the variables shown in the window on the left side of the screen (VS Code)
- How many instances did you create? how many are returned in the function? why?
- Why are we running this function now? why not write all of the code first?
- Which IAM entity is used to make the boto3 function / API call to AWS?
- Run it in debug mode and
-
Implement the
process_instance()function:- Implement this function which takes an
instanceandcurrent_houras input and realizes the psedocode below:- If instance is running and stop_time is now, stop it
- If instance is stopped and start_time is now, start it
- In all other cases, leave the instance as is
- The function should return a message indicating the acion that was taken
- Implement this function which takes an
-
In the
lambda_handler, replace theprintstatement with a call to theprocess_instance()function. -
Add a
try-exceptblock in the lambda_handler.- Ehy would this be needed?
-
Test and debug the entire script.
-
Open the Lambda console in AWS.
-
Click on
Create Function. -
Details:
- Choose
Author from scratch - Function name: -ec2-s3-checker
- Runtime: Python 3.11 (or later)
- Architecture: leave as is
- Execution role: leave as is
- Advanced settings: leave as is
- Choose
-
Change default timeout for Lambda function.
- Why is this necessary?
- What is the longest time a Lambda function can run?
- From the function details window:
- Click the
Configurationtab. - Click
General configuration. - Click
Edit. - Change timeout to
1 min 0 sec.
- Click the
-
Go back to
Function overviewand deploy the code:- Click on the
Codetab. - In the
lambda_functiontab, delete the existing code. - Paste your code in the same tab.
- Click
Deploy. - Create a test configuration with the default JSON configuration.
- Test the function.
- Questions:
- What permissions does your lambda role have?
- What more permissions does it need?
- What would have happened without the try-except block?
- How did the print messages help?
- How long did it take for the function to execute?
- What would have happened if the timeout wasn't extended?
- Click on the
-
On the
Function overviewpage, clickConfiguration. -
Click on
Permissions. -
Click on the role name (note this was created automatically when the Lambda function was created).
-
On the
Permissionstab of the IAM role, notice which permissions the Lambda role already has- Why is this needed?
-
Click on
Add permissions|Inline policy. -
Click on
EC2and add the following permissions:EC2:StartInstancesEC2:StopInstancesEC2:DescribeInstances
-
Click
Next. -
Type
<yourname>-ec2-s3-checker-policyfor the policy name. -
Click
Create policy. -
Go back and test your function.
-
Open the CloudWatch console.
-
Click on
Rules(this takes you to EventBridge). -
Click the
Create rulebutton. -
Enter the following details:
- Name:
<yourname>-ec2-s3-check - Description:
Scheduled rule to check ec2 instances and s3 buckets - Event bus: leave as
default - Enable: leave
enabled - Rule type: select
Schedule
- Name:
-
Click
Continue to create rule. -
Enter the cron schedule as: cron(* * * * ? *):
- this schedules the job to run every minute
- Note that practically you would not run this every MINUTE, but every HOUR most likely; we are running every minute just for testing purposes
-
Click
Next. -
Under Select target(s), choose
AWS Serviceand selectLambda function. -
Select your lambda function.
-
Click
NextandNextagain, thenCreate rule.
-
Check the CloudWatch logs and see that your function is running.
-
Modify the tags on your EC2 instances and see that they stop and start as they should.
-
Open the Amazon EC2 console at "https://console.aws.amazon.com/s3/"
-
Choose
Create bucket:- Enter a name such as "-testbucket-disabled-001".
- Leave the remaining defaults, including versioning being "DISABLED".
- Repeat this 3 times (change the 001 to 002, then 003).
-
Choose
Create bucket- Enter a name such as "-testbucket-enabled-001".
- Change the versioning setting to be "ENABLED".
- Repeat this 2 times (change 001 to 002).
-
Create a function
process_buckets()which, first, gets a list of buckets. -
Next iterate over the list and send them to a
process_bucket()function to check if versioning is enabled- If not, enable versioning.
-
Ensure the new code works via Visual Studio Code.
-
Go back and change the buckets named "-disabled" to "suspend" bucket versioning (note you cannot disable it now).
-
Ensure the new code works via Visual Studio Code.
-
Go back and change the buckets named "-disabled" to "suspend" bucket versioning (note you cannot disable it now)
-
Run your code. What happens?
-
On the
Function overviewpage, clickConfiguration. -
Click on
Permissions. -
Click on the role name.
-
On the
Permissionstab, click the+sign on the inline policy you created earlier. -
Choose
Edit. -
Click
+ Add more permissions. -
Under
Select a service, click onS3and add the following permissions:S3:ListAllMyBucketsS3:GetBucketVersioningS3:PutBucketVersioning
-
Click
Next. -
Click
Save changes. -
Go back and test your function.
-
Delete the CloudWatch (EventBridge) rule.
-
Delete the lambda function.
-
Delete the lambda role.
-
Delete the log group in CloudWatch logs.
-
Terminate the 5 test instances.
-
Delete the 5 test buckets.