A rooted phone can make performance data collection much easier. Just use Magisk and follow the instructions online. ; )
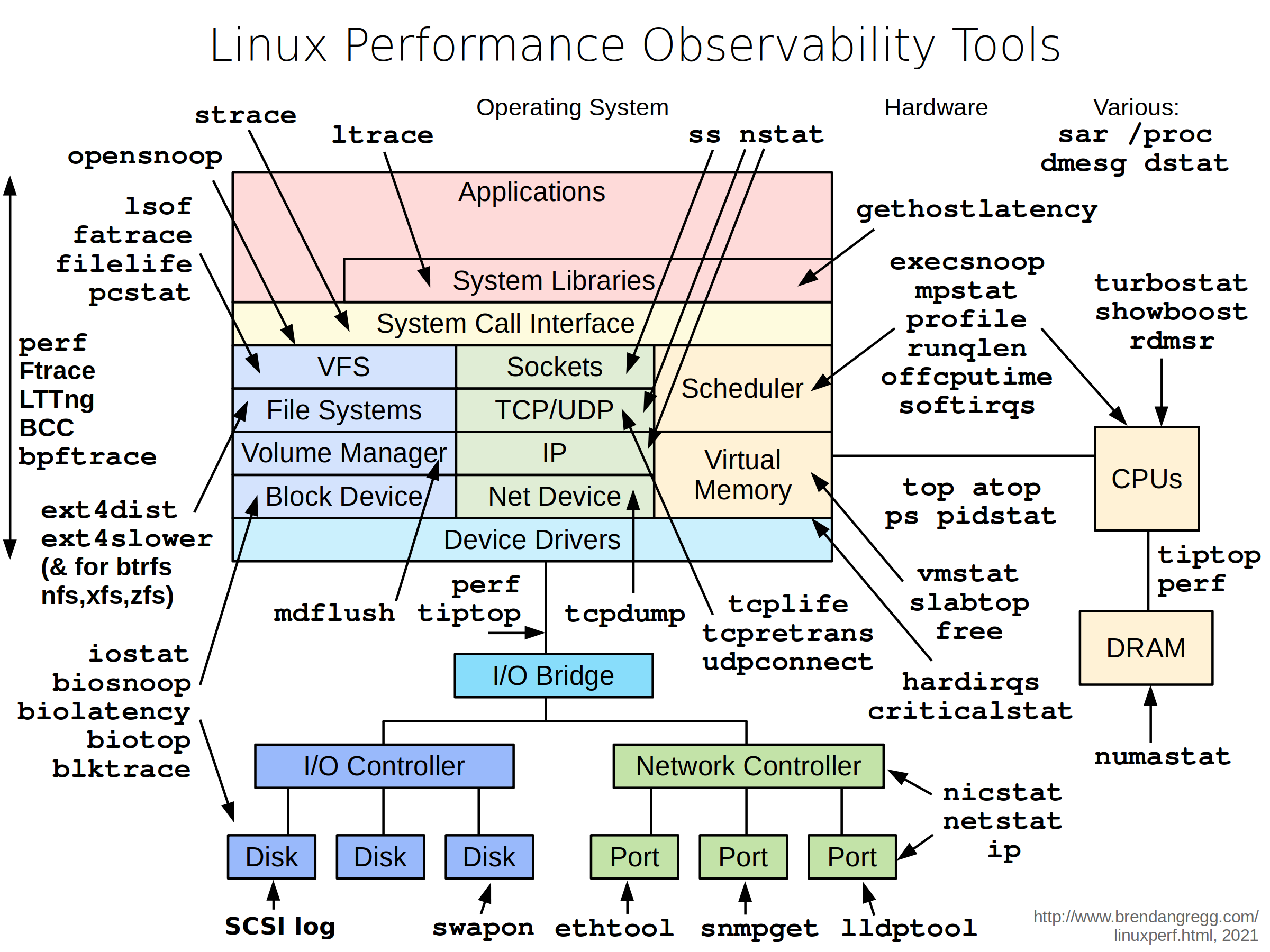
Android OS is based on Linux kernel, so we can use the Linux Performance Tools to gather your App`s performance data. This image is a quick reference from here.
We can use Android Studio Memory Profiler to detect memory leak. If you're more familiar with Eclipse MAT, you can capture
a heap dump with am dumpheap or Debug.dumpHprofData("path")and open it with MAT.
We can use hprof-conv tool located in the android_sdk/platform-tools/ directory to convert the HPROF file from Android format to the Java SE HPROF format.
To exclude non-app heap, e can also use -z param :
hprof-conf [-z] infile outfile
-z: exclude non-app heaps, such as Zygote
or, use OQL :
select * from instanceof java.lang.Object s where s.@objectAddress > [adress].
Some operations will cause memory leak, such as forgetting release Bitmap, temporary byte array, file cache, Activity that contains handler etc.
If the heap usage keeps increase while the App running, there is a big chance that memory leak happens. In this situation LeakCanary is a proper choice for memory leak detection.
If GC frequency is high when executing the test, this usually caused by allocating and then releasing big amount of temporary variations or arrays. Heap Viewer/ Allocation Tracker would help in those situations.
Clean code
Make sure the project has no useless Log, debug plugins and codes that testers write for testing. These codes and Logs may affect memory usage and cause more GC.
Scenarios
Suppose there`s a new feature added to your App, you should get memory usage data before-during-after running the new feature. Compare the data set to find possible memory leak.
Suppose you would like to see the whole memory usage of your App, and detect possible memory leak. You can open your App and do nothing, just let it be there and observe the memory usage. Run the main features of your App, such as play some videos or download some files, multiple times. Switch Activities, multiple times. Switch between foreground and background, multiple times. After several operations, observe the memory usage.
It is better to get the memory usage data several times and take the average, for GC and broadcast may disturb the memory usage data.
Here are some scenarios that may cause memory leak: (a) layouts that contains images; (b) large data transfer through internet; (3) operations that cache data.
Here is a case we went through at work that related to Dalvik VM memory fragmentation. Developers added some code, memory usage displayed by Android Studio Profiler almost the same with the older version. But memory usage displayed by Android system increased big. In this case, we have to check the memory use of the App`s process using dumpsys:
dumpsys meminfo <package name| pid>
TOTAL Pss Total(1) is what you see in Android system memory use like this:
Dalvik Heap Alloc(2) is what you see in Android Studio Memory.
In our case, we found App`s process memory use increased due to Dalvik Heap Pss, and Dalvik Heap Free also increased, but why?
Android developers best practices document give us suggestions about how to manage App's memory , also we can go through Dalvik source code(dalvik/vm/alloc) to get better understanding of how memory allocated by DVM. When we get our researches done, here is our guess: the problem may be related to memory fragmentation.
To check on our guess, we run the App and get the hprof file. Use Eclipse MAT, chose all objects list_objects java.* and export to csv. Objects that have the same high bit address(&0xfffff000) share the same page.
So that, we can get all pages that used less than 2KB, and use OQL to import the objects back into MAT. Then, we can have a better look at these objects, and catch those who cause memory fragmentation.
Here is the code that cause memory fragmentation:
private Object res[] = new Object[100];
void foo(){
for(int i=0; i<100; i++){
byte[] tmp = new byte[2000];
res[i] = byte[4];
}
}When foo() method be running, DVM allocates memory for tmp and res by 4KB pages. After foo() method finish running and GC, large objects be recollected but small objects still holding 4KB pages. JVM will do compacting after GC, but the Dalvik VM
version we then tested did not have compacting operation.
We found dex mmap takes a big portion of the PSS Total. We got about 10,000 class in our project and the size of classes.dex is about 10MB. When the App was running, about 1500 class were loaded into memory and dex mmap size was about 4~6MB. It means lots of memory was wasted.
This is because dex is loaded into memory by 4KB pages. Suppose we use class A, dalvik vm loads the 4KB page that contains class A into memory. If class A uses class B, then dalvik vm loads the 4KB page that contains class B. If class A and class B in the same 4KB page, dalvik vm just load one page, that is efficient.
dexdump classes.dex, we found classes in dex file are arranged by alphabet. So we can use proguard to change class names, let classes that are frequently used arranged together.
/proc/pid/maps
/proc/pid/smaps
There are several ways to get traffic statistics:
a./proc/net/xt_qtaguid/stats ( e.g. adb shell cat /proc/net/xt_qtaguid/stats | grep (uid#))
b.TrafficStats.getUidRxBytes (int uid) & TrafficStats.getUidTxBytes(int uid) (some systems may return 0)
how to get a pid: adb shell dumpsys package com.example.appname | grep userId=
c./proc/uid_stat/[uid]/tcp_snd & /proc/uid_stat/[uid]/tcp_rcv (some systsems do not have those files)
Column 6 is rx_bytes, column 8 is tx_bytes, rx_bytes + tx_bytes = traffic statistics
Column 5 is cnt_set with value 0 or 1, represents the foreground and background process with the same uid.
d. tcpdump
tcpdump -p -vv -s 0 -w /sdcard/capture.pcap
1.You can decompile /system/framework-res.apk from Android ROM source code to get res/xml/power_profile.xml. Power_profile.xml contains device's hardware power values that provided by device manufacturers.
Or you can use the methods in com.android.internal.os.PowerProfile class to get this hardware power values.
2.Batterystats tool shows detail usage of energy, before data gathering, it's better running these two commands:
dumpsys batterystats --enable full-wake-history
dumpsys batterystats --reset
3.When device is in sleep mode, the main energy consumption comes from device being wakeup. Use dumpsys alarm and Wakelock Detector helps to analyze who wakeup the device.
4.High CPU usage will certainly end up with high battery usage. We once came across a bug that due to an always running while loop in a thread. To find a certain thread`s CPU consumption,we can use top -H -p pid command or htop -p pid, or we can
check
/proc/pid/task/thread_id/stat file
and get CPU
usage. Another useful tool is dumpsys cpuinfo. Here is a reference about proc.
Use adb shell dumpsys gfxinfo <package name> to test UI performance.
Or use Choreographer.FrameCallback interface to detect if the system updates 60 frames per second. Here is the sample code
Based on our experiences about UI performance issues, we can follow these steps to solve them:
1.Detect UI overdraw problems.Here's some advices for Reduce GPU Overdraw. Tracer for OpenGL ES and Hierarchy Viewer are useful tools.
2.Use Lint to detect code that may affect UI performance.
3.Use System tracing to find out what stalls main thread.
-
One way to measure the App start-up time is recording the whole start-up procedure and count it's time-consuming. You can do this manually or automatically.
-
Systracetool is another choice. Enable theActivity Managertag, analyse the trace and getstartup-time = bindApplication + activityStart. -
You can find more in android Docs. We found disk I/O, network data transfer, operations that is cpu-consuming in UI thread that affect app's start-up time in practice.
Reduce your app size gives us several advices. And here are something we can do more:
-
Use UCDetector to find unnecessary code.
-
Use Simian tool to find duplication in code.
-
Find unused images in older version. Pay attention to
android:visibility="gone"in xml file andview.setVisibility(View.GONE)in java code.