This style guide is different from others you may see, because the focus is centered on readability for print and the web. We created this style guide to keep the code in our books, tutorials, and starter kits nice and consistent — even though we have many different authors working on the books.
Our overarching goals are conciseness, readability, and simplicity.
Writing Objective-C? Check out our Objective-C Style Guide too.
- Whitespace
- Correctness
- Naming
- Default Initializers
- Code Organization
- Spacing
- Comments
- Classes and Structures
- Function Declarations
- Closure Expressions
- Types
- Functions vs Methods
- Memory Management
- Access Control
- Control Flow
- Golden Path
- Semicolons
- Parentheses
- Operator Overloading And Custom Operators
- Error Handling
- Copyright Statement
- Smiley Face
- Credits
- 4 spaces for tab.
- End files with a newline.
- Make liberal use of vertical whitespace to divide code into logical chunks.
- Don’t leave trailing whitespace.
- Not even leading indentation on blank lines.
Operators consist of punctuation characters, which can make them difficult to read when immediately followed by the punctuation for a type or value parameter list. Adding whitespace separates the two more clearly.
Preferred:
func <| (lhs: Int, rhs: Int) -> Int
func <|< <A>(lhs: A, rhs: A) -> ANot Preferred:
func <|(lhs: Int, rhs: Int) -> Int
func <|<<A>(lhs: A, rhs: A) -> AConsider warnings to be errors. This rule informs many stylistic decisions such as not to use the ++ or -- operators, C-style for loops, or strings as selectors.
Use descriptive names with camel case for classes, methods, variables, etc. Type names (classes, structures, enumerations and protocols) should be capitalized, while method names and variables should start with a lower case letter.
Preferred:
private let maximumWidgetCount = 100
class WidgetContainer {
var widgetButton: UIButton
let widgetHeightPercentage = 0.85
}Not Preferred:
let MAX_WIDGET_COUNT = 100
class app_widgetContainer {
var wBut: UIButton
let wHeightPct = 0.85
}Abbreviations and acronyms should generally be avoided. Following the Apple Design Guidelines, abbreviations and initialisms that appear in all uppercase should be uniformly uppercase or lowercase. Examples:
Preferred
let urlString: URLString
let userID: UserIDNot Preferred
let uRLString: UrlString
let userId: UserIdFor functions and init methods, prefer named parameters for all arguments unless the context is very clear. Include external parameter names if it makes function calls more readable.
func dateFromString(dateString: String) -> NSDate
func convertPointAt(column column: Int, row: Int) -> CGPoint
func timedAction(afterDelay delay: NSTimeInterval, perform action: SKAction) -> SKAction!
// would be called like this:
dateFromString("2014-03-14")
convertPointAt(column: 42, row: 13)
timedAction(afterDelay: 1.0, perform: someOtherAction)For methods, follow the standard Apple convention of referring to the first parameter in the method name:
class Counter {
func combineWith(otherCounter: Counter, options: Dictionary?) { ... }
func incrementBy(amount: Int) { ... }
}Following Apple's API Design Guidelines, protocols names that describe what something is should be a noun. Examples: Collection, WidgetFactory. Protocols names that describe an ability should end in -ing, -able, or -ible. Examples: Equatable, Resizing.
Following Apple's API Design Guidelines for Swift 3, use lowerCamelCase for enumeration values.
enum Shape {
case rectangle
case square
case rightTriangle
case equilateralTriangle
}When referring to functions in prose (tutorials, books, comments) include the required parameter names from the caller's perspective or _ for unnamed parameters. Examples:
Call
convertPointAt(column:row:)from your owninitimplementation.If you call
dateFromString(_:)make sure that you provide a string with the format "yyyy-MM-dd".If you call
timedAction(afterDelay:perform:)fromviewDidLoad()remember to provide an adjusted delay value and an action to perform.You shouldn't call the data source method
tableView(_:cellForRowAtIndexPath:)directly.
This is the same as the #selector syntax. When in doubt, look at how Xcode lists the method in the jump bar – our style here matches that.
Swift types are automatically namespaced by the module that contains them and you should not add a class prefix such as RW. If two names from different modules collide you can disambiguate by prefixing the type name with the module name. However, only specify the module name when there is possibility for confusion which should be rare.
import SomeModule
let myClass = MyModule.UsefulClass()Prefixes are still necessary on extension methods of classes not in the current module.
Note: Unlike Obj-C, the Swift compiler will complain about duplicate method names.
Preferred:
extension UIColor {
static func use_primaryColor() -> UIColor {
return UIColor(
red: 100.0 / 255.0,
green: 100.0 / 255.0,
blue: 100.0 / 255.0,
alpha: 1.0
)
}
}Selectors are Obj-C methods that act as handlers for many Cocoa and Cocoa Touch APIs. Prior to Swift 2.2, they were specified using type unsafe strings. This now causes a compiler warning. The "Fix it" button replaces these strings with the fully qualified type safe selector. Often, however, you can use context to shorten the expression. This is the preferred style.
Preferred:
let sel = #selector(viewDidLoad)Not Preferred:
let sel = #selector(ViewController.viewDidLoad)Generic type parameters should be descriptive, upper camel case names. When a type name doesn't have a meaningful relationship or role, use a traditional single uppercase letter such as T, U, or V.
Preferred:
struct Stack<Element> { ... }
func writeTo<Target: OutputStream>(inout target: Target)
func max<T: Comparable>(x: T, _ y: T) -> TNot Preferred:
struct Stack<T> { ... }
func writeTo<target: OutputStream>(inout t: target)
func max<Thing: Comparable>(x: Thing, _ y: Thing) -> ThingUse US English spelling to match Apple's API.
Preferred:
let color = "red"Not Preferred:
let colour = "red"Name the members of your tuples when creating or decomposing tuples.
Preferred:
let foo = (something: "cats", somethingElse: 909_099)
let (something, somethingElse) = fooUse default initializers where possible.
Swift provides a default initializer for any structure or class that provides default values for all of its properties and does not provide at least one initializer itself. The default initializer simply creates a new instance with all of its properties set to their default values.
This example defines a class called ShoppingListItem, which encapsulates the name, quantity, and purchase state of an item in a shopping list:
Preferred:
class ShoppingListItem {
var name: String?
var quantity = 1
var purchased = false
}
var item = ShoppingListItem()Use extensions to organize your code into logical blocks of functionality. Each extension should be set off with a // MARK: - comment to keep things well-organized.
In particular, when adding protocol conformance to a model, prefer adding a separate extension for the protocol methods. This keeps the related methods grouped together with the protocol and can simplify instructions to add a protocol to a class with its associated methods.
Preferred:
class MyViewcontroller: UIViewController {
// class stuff here
}
// MARK: - UITableViewDataSource
extension MyViewcontroller: UITableViewDataSource {
// table view data source methods
}
// MARK: - UIScrollViewDelegate
extension MyViewcontroller: UIScrollViewDelegate {
// scroll view delegate methods
}Not Preferred:
class MyViewcontroller: UIViewController, UITableViewDataSource, UIScrollViewDelegate {
// all methods
}Since the compiler does not allow you to re-declare protocol conformance in a derived class, it is not always required to replicate the extension groups of the base class. This is especially true if the derived class is a terminal class and a small number of methods are being overriden. When to preserve the extension groups is left to the discretion of the author.
For UIKit view controllers, consider grouping lifecyle, custom accessors, and IBAction in separate class extensions.
- Delegate protocols should be limited to classes only by adding class to the protocol's inheritance list (as discussed in Class-Only Protocols).
- If your protocol should have optional methods, it must be declared with the @objc attribute.
- Protocol definitions should be declared near the class that uses the delegate, not the class that implements the delegate methods.
- If more than one class uses the same protocol, it should be declared in its own file.
- Delegate variables should be weak optional vars to avoid retain cycles.
Preferred:
//SomeTableCell.swift
protocol SomeTableCellDelegate: class {
func cellButtonWasTapped(cell: SomeTableCell)
}
class SomeTableCell: UITableViewCell {
weak var delegate: SomeTableCellDelegate?
// ...
}//SomeTableViewController.swift
class SomeTableViewController: UITableViewController {
// ...
}
// MARK: - SomeTableCellDelegate
extension SomeTableViewController: SomeTableCellDelegate {
func cellButtonWasTapped(cell: SomeTableCell) {
// Implementation of cellbuttonwasTapped method
}
}For array and dictionary literals, unless the literal is very short, it should be split into multiple lines, with the opening symbols on their own line, each item or key-value pair on its own line, and the closing symbol on its own line. The last item or key-value pair should have a trailing comma to facilitate future insertion/editing. Xcode will handle alignment sanely.
Preferred:
let anArray = [
object1,
object2,
object3,
]
let aDictionary = [
"key1": value1,
"key2": value2,
]Not Preferred:
let anArray = [
object1,
object2,
object3 //no trailing comma
]
let aDictionary = ["key1": value1, "key2": value2] //how can you even read that?!Unused (dead) code, including Xcode template code and placeholder comments should be removed. An exception is when your tutorial or book instructs the user to use the commented code.
Aspirational methods not directly associated with the tutorial whose implementation simply calls the super class should also be removed. This includes any empty/unused UIApplicationDelegate methods.
Not Preferred:
override func didReceiveMemoryWarning() {
super.didReceiveMemoryWarning()
// Dispose of any resources that can be recreated.
}
override func numberOfSectionsInTableView(tableView: UITableView) -> Int {
// #warning Incomplete implementation, return the number of sections
return 1
}
override func tableView(tableView: UITableView, numberOfRowsInSection section: Int) -> Int {
// #warning Incomplete implementation, return the number of rows
return Database.contacts.count
}Preferred:
override func tableView(tableView: UITableView, numberOfRowsInSection section: Int) -> Int {
return Database.contacts.count
}Keep imports minimal. For example, don't import UIKit when importing Foundation will suffice.
-
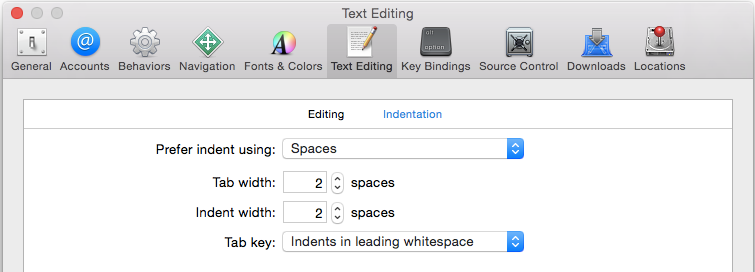
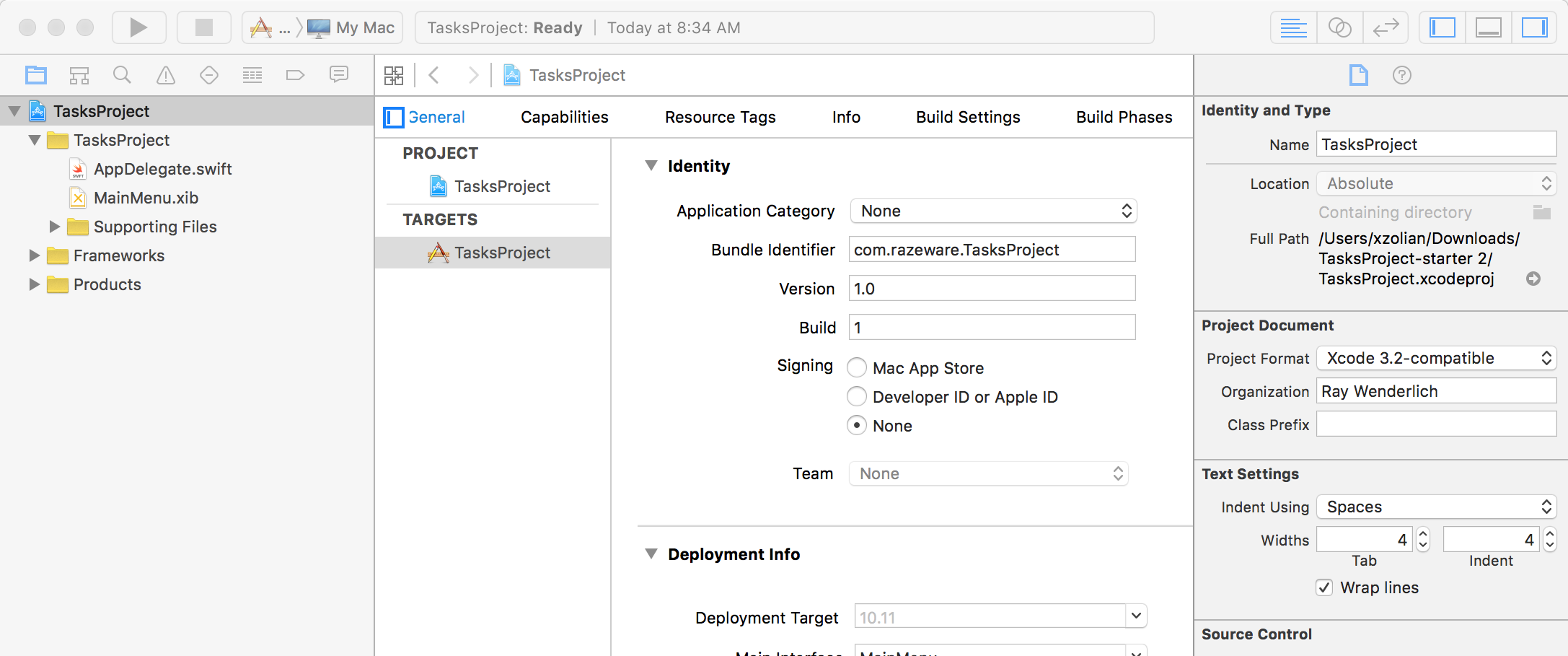
Indent using 2 spaces rather than tabs to conserve space and help prevent line wrapping. Be sure to set this preference in Xcode and in the Project settings as shown below:
-
Method braces and other braces (
if/else/switch/whileetc.) always open on the same line as the statement but close on a new line. -
Tip: You can re-indent by selecting some code (or ⌘A to select all) and then Control-I (or Editor\Structure\Re-Indent in the menu). Some of the Xcode template code will have 4-space tabs hard coded, so this is a good way to fix that.
Preferred:
if user.isHappy {
// Do something
} else {
// Do something else
}Not Preferred:
if user.isHappy
{
// Do something
}
else {
// Do something else
}-
There should be exactly one blank line between methods to aid in visual clarity and organization. Whitespace within methods should separate functionality, but having too many sections in a method often means you should refactor into several methods.
-
Colons always have no space on the left and one space on the right. Exceptions are the ternary operator
? :and empty dictionary[:].
Preferred:
class TestDatabase: Database {
var data: [String: CGFloat] = ["A": 1.2, "B": 3.2]
}Not Preferred:
class TestDatabase : Database {
var data :[String:CGFloat] = ["A" : 1.2, "B":3.2]
}When they are needed, use comments to explain why a particular piece of code does something. Comments must be kept up-to-date or deleted.
Avoid block comments inline with code, as the code should be as self-documenting as possible. Exception: This does not apply to those comments used to generate documentation.
Remember, structs have value semantics. Use structs for things that do not have an identity. An array that contains [a, b, c] is really the same as another array that contains [a, b, c] and they are completely interchangeable. It doesn't matter whether you use the first array or the second, because they represent the exact same thing. That's why arrays are structs.
Classes have reference semantics. Use classes for things that do have an identity or a specific life cycle. You would model a person as a class because two person objects are two different things. Just because two people have the same name and birthdate, doesn't mean they are the same person. But the person's birthdate would be a struct because a date of 3 March 1950 is the same as any other date object for 3 March 1950. The date itself doesn't have an identity.
Sometimes, things should be structs but need to conform to AnyObject or are historically modeled as classes already (NSDate, NSSet). Try to follow these guidelines as closely as possible.
Here's an example of a well-styled class definition:
class Circle: Shape {
var x: Int, y: Int
var radius: Double
var diameter: Double {
get {
return radius * 2
}
set {
radius = newValue / 2
}
}
init(x: Int, y: Int, radius: Double) {
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.radius = radius
}
convenience init(x: Int, y: Int, diameter: Double) {
self.init(x: x, y: y, radius: diameter / 2)
}
func describe() -> String {
return "I am a circle at \(centerString()) with an area of \(computeArea())"
}
override func computeArea() -> Double {
return M_PI * radius * radius
}
private func centerString() -> String {
return "(\(x),\(y))"
}
}The example above demonstrates the following style guidelines:
- Specify types for properties, variables, constants, argument declarations and other statements with a space after the colon but not before, e.g.
x: Int, andCircle: Shape. - Define multiple variables and structures on a single line if they share a common purpose / context.
- Indent getter and setter definitions and property observers.
- Don't add modifiers such as
internalwhen they're already the default. Similarly, don't repeat the access modifier when overriding a method.
For conciseness, avoid using self since Swift does not require it to access an object's properties or invoke its methods.
Use self when required to differentiate between property names and arguments in initializers, and when referencing properties in closure expressions (as required by the compiler):
class BoardLocation {
let row: Int, column: Int
init(row: Int, column: Int) {
self.row = row
self.column = column
let closure = {
print(self.row)
}
}
}For conciseness, if a computed property is read-only, omit the get clause. The get clause is required only when a set clause is provided.
Preferred:
var diameter: Double {
return radius * 2
}Not Preferred:
var diameter: Double {
get {
return radius * 2
}
}Mark classes final when inheritance is not intended. Example:
// Turn any generic type into a reference type using this Box class.
final class Box<T> {
let value: T
init(_ value: T) {
self.value = value
}
}Keep short function declarations on one line including the opening brace:
func reticulateSplines(spline: [Double]) -> Bool {
// reticulate code goes here
}For functions with long signatures, add line breaks at appropriate points and add an extra indent on subsequent lines:
func reticulateSplines(spline: [Double], adjustmentFactor: Double,
translateConstant: Int, comment: String) -> Bool {
// reticulate code goes here
}Use trailing closure syntax only if there's a single closure expression parameter at the end of the argument list. Give the closure parameters descriptive names.
Preferred:
UIView.animateWithDuration(1.0) {
self.myView.alpha = 0
}
UIView.animateWithDuration(1.0,
animations: {
self.myView.alpha = 0
},
completion: { finished in
self.myView.removeFromSuperview()
}
)Not Preferred:
UIView.animateWithDuration(1.0, animations: {
self.myView.alpha = 0
})
UIView.animateWithDuration(1.0,
animations: {
self.myView.alpha = 0
}) { f in
self.myView.removeFromSuperview()
}Only use shorthand argument syntax for simple one-line closure implementations
Preferred:
let doubled = [2, 3, 4].map { $0 * 2 } // [4, 6, 8]For all other cases, explicitly define the argument(s)
Preferred:
let names = ["George Washington", "Martha Washington", "Abe Lincoln"]
let emails = names.map { fullname in
let dottedName = fullname.stringByReplacingOccurrencesOfString(" ", withString: ".")
return dottedName.lowercaseString + "@whitehouse.gov"
}For single-expression closures where the context is clear, use implicit returns:
attendeeList.sort { a, b in
a > b
}Chained methods using trailing closures should be clear and easy to read in context. Decisions on spacing, line breaks, and when to use named versus anonymous arguments is left to the discretion of the author. Examples:
let value = numbers.map { $0 * 2 }.filter { $0 % 3 == 0 }.indexOf(90)
let value = numbers
.map {$0 * 2}
.filter {$0 > 50}
.map {$0 + 10}Xcode will try to be helpful when autocompleting closures for you by giving you the full type signature of the closure (input type(s) and return type). Simplify that information so that it's easier to read.
Remove return types of Void and parentheses around single input parameters. This is especialy relevant if the closure takes no input and returns no output.
Preferred:
UIView.animateWithDuration(0.5) {
//no need to specify type information for a no input, no output closure
}
//note the formatting of this example is further changed from the suggestion for better readability
UIView.animateWithDuration(0.5,
animations: {
...
},
completion: { complete in
//the return type is inferred to be `Void` and `complete` does not need parens
}
)Not Preferred:
UIView.animateWithDuration(0.5) { () -> Void in
...
}
UIView.animateWithDuration(0.5, animations: { () -> Void in
...
}) { (complete) -> Void in
...
}Always use Swift's native types when available. Swift offers bridging to Objective-C so you can still use the full set of methods as needed.
Preferred:
let width = 120.0 // Double
let widthString = (width as NSNumber).stringValue // StringNot Preferred:
let width: NSNumber = 120.0 // NSNumber
let widthString: NSString = width.stringValue // NSStringIn Sprite Kit code, use CGFloat if it makes the code more succinct by avoiding too many conversions.
- Define constants for unchanging pieces of data in the code. Some examples are CGFloat constants for cell heights, string constants for cell identifiers, key names (for KVC and dictionaries), or segue identifiers.
- Where possible, keep constants private to the file they are related to.
- File-level constants should be declared with private let.
- File-level constants should be capital camel-cased to indicate that they are named constants instead of properties.
- Prefer declaring constants outside the scope of a class to give them static storage.
- If the constant will be used outside of one file, private should be omitted.
- If the constant will be used outside of the module, it should be declared public (mostly useful for Pods or shared libraries).
- If the constant is declared within a class or struct, it should be declared static to avoid declaring one constant per instance.
Constants are defined using the let keyword, and variables with the var keyword. Always use let instead of var if the value of the variable will not change.
Tip: A good technique is to define everything using let and only change it to var if the compiler complains!
You can define constants on a type rather than an instance of that type using type properties. To declare a type property as a constant simply use static let. Type properties declared in this way are generally preferred over global constants because they are easier to distinguish from instance properties. Example:
Preferred:
enum Math {
static let e = 2.718281828459045235360287
static let pi = 3.141592653589793238462643
}
radius * Math.pi * 2 // circumferenceNote: The advantage of using a case-less enumeration is that it can't accidentally be instantiated and works as a pure namespace.
//SomeTableCell.swift
//not declared private since it is used in another file
let SomeTableCellIdentifier = "SomeTableCell"
class SomeTableCell: UITableViewCell {
...
}//ATableViewController.swift
//declared private since it isn't used outside this file
private let RowHeight: CGFloat = 150.0
class ATableViewController: UITableViewController {
...
private func configureTableView() {
tableView.rowHeight = RowHeight
}
func tableView(tableView: UITableView, cellForRowAtIndexPath indexPath: NSIndexPath) -> UITableViewCell {
return tableView.dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier(SomeTableCellIdentifier, forIndexPath: indexPath)
}
}Not Preferred:
let e = 2.718281828459045235360287 // pollutes global namespace
let pi = 3.141592653589793238462643
radius * pi * 2 // is pi instance data or a global constant?Where appropriate, constants can also be grouped using an enum with a rawValue type that is relevant to the type you need to work with. An enum with a rawValue of type String will implicitly assign its rawValue from the name of the case if nothing is already explicitly defined for the rawValue. This can be useful when all the names of the cases match with the value of the constant. Be aware that if you use an enum for constants, you need to explicitly use rawValue every time you need to access the value of the constant:
Preferred:
enum HTTPMethods: String {
case GET
case PUT
case POST
case PATCH
case DELETE
// Explicitly defined rawValue
case OptionsMethod = "OPTIONS"
// ...
}
print(HTTPMethods.OptionsMethod.rawValue) // "OPTIONS"
print(HTTPMethods.POST.rawValue) // "POST"
guard let url = NSURL(string: "http://www.example.com") else {
return
}
let mutableURLRequest = NSMutableURLRequest(URL: url)
mutableURLRequest.HTTPMethod = HTTPMethods.POST.rawValue
print(mutableURLRequest.HTTPMethod) // "POST"Static methods and type properties work similarly to global functions and global variables and should be used sparingly. They are useful when functionality is scoped to a particular type or when Objective-C interoperability is required.
Declare variables and function return types as optional with ? where a nil value is acceptable.
Use implicitly unwrapped types declared with ! only for instance variables that you know will be initialized later before use, such as subviews that will be set up in viewDidLoad.
Preferred:
guard let url = NSURL(string: "http://www.example.com/") else {
return
}
UIApplication.sharedApplication().openURL(url)Not Preferred:
// NSURL init(string:) is a failable initializer and will crash at runtime with a force unwrap if initialization fails!
let url = NSURL(string: "http://www.example.com/")!
UIApplication.sharedApplication().openURL(url)When accessing an optional value, use optional chaining if the value is only accessed once or if there are many optionals in the chain:
self.textContainer?.textLabel?.setNeedsDisplay()Use optional binding when it's more convenient to unwrap once and perform multiple operations:
if let textContainer = self.textContainer {
// do many things with textContainer
}When naming optional variables and properties, avoid naming them like optionalString or maybeView since their optional-ness is already in the type declaration.
For optional binding, shadow the original name when appropriate rather than using names like unwrappedView or actualLabel.
Preferred:
var subview: UIView?
var volume: Double?
// later on...
if let subview = subview, volume = volume {
// do something with unwrapped subview and volume
}Not Preferred:
var optionalSubview: UIView?
var volume: Double?
if let unwrappedSubview = optionalSubview {
if let realVolume = volume {
// do something with unwrappedSubview and realVolume
}
}Preferred:
guard let detailViewController = segue.destinationViewController as? DetailViewController else {
return
}
detailViewController.person = personNot Preferred:
// segue.destinationViewController is declared to be of type UIViewController, so forcing a downcast to type
// DetailViewController here will crash if the type is not DetailViewController at runtime!
let detailViewController = segue.destinationViewController as! DetailViewController
detailViewController.person = personUse the native Swift struct initializers rather than the legacy CGGeometry constructors.
Preferred:
let bounds = CGRect(x: 40, y: 20, width: 120, height: 80)
let centerPoint = CGPoint(x: 96, y: 42)Not Preferred:
let bounds = CGRectMake(40, 20, 120, 80)
let centerPoint = CGPointMake(96, 42)Prefer the struct-scope constants CGRect.infinite, CGRect.null, etc. over global constants CGRectInfinite, CGRectNull, etc. For existing variables, you can use the shorter .zero.
Consider using lazy initialization for finer grain control over object lifetime. This is especially true for UIViewController that loads views lazily. You can either use a closure that is immediately called { }() or call a private factory method. Example:
lazy var locationManager: CLLocationManager = self.makeLocationManager()
private func makeLocationManager() -> CLLocationManager {
let manager = CLLocationManager()
manager.desiredAccuracy = kCLLocationAccuracyBest
manager.delegate = self
manager.requestAlwaysAuthorization()
return manager
}Notes:
[unowned self]is not required here. A retain cycle is not created.- Location manager has a side-effect for popping up UI to ask the user for permission so fine grain control makes sense here.
Prefer compact code and let the compiler infer the type for constants or variables of single instances. Type inference is also appropriate for small (non-empty) arrays and dictionaries. When required, specify the specific type such as CGFloat or Int16.
Preferred:
let message = "Click the button"
let currentBounds = computeViewBounds()
var names = ["Mic", "Sam", "Christine"]
let maximumWidth: CGFloat = 106.5Not Preferred:
let message: String = "Click the button"
let currentBounds: CGRect = computeViewBounds()
let names = [String]()For empty arrays and dictionaries, use type annotation. (For an array or dictionary assigned to a large, multi-line literal, use type annotation.)
Preferred:
var names: [String] = []
var lookup: [String: Int] = [:]Not Preferred:
var names = [String]()
var lookup = [String: Int]()NOTE: Following this guideline means picking descriptive names is even more important than before.
Prefer the shortcut versions of type declarations over the full generics syntax.
Preferred:
var deviceModels: [String]
var employees: [Int: String]
var faxNumber: Int?Not Preferred:
var deviceModels: Array<String>
var employees: Dictionary<Int, String>
var faxNumber: Optional<Int>- Create typealiases to give semantic meaning to commonly used datatypes and closures.
- typealias is equivalent to typedef in C and should be used for making names for types.
Preferred:
typealias IndexRange = Range<Int>
typealias JSONObject = [String: AnyObject]
typealias APICompletion = (jsonResult: [JSONObject]?, error: NSError?) -> Void
typealias BasicBlock = () -> VoidFree functions, which aren't attached to a class or type, should be used sparingly. When possible, prefer to use a method instead of a free function. This aids in readability and discoverability.
Free functions are most appropriate when they aren't associated with any particular type or instance.
Preferred
let sorted = items.mergeSort() // easily discoverable
rocket.launch() // clearly acts on the modelNot Preferred
let sorted = mergeSort(items) // hard to discover
launch(&rocket)Free Function Exceptions
let tuples = zip(a, b) // feels natural as a free function (symmetry)
let value = max(x,y,z) // another free function that feels naturalCode (even non-production, tutorial demo code) should not create reference cycles. Analyze your object graph and prevent strong cycles with weak and unowned references. Alternatively, use value types (struct, enum) to prevent cycles altogether.
Extend object lifetime using the [weak self] and guard let strongSelf = self else { return } idiom. [weak self] is preferred to [unowned self] where it is not immediately obvious that self outlives the closure. Explicitly extending lifetime is preferred to optional unwrapping.
Preferred
resource.request().onComplete { [weak self] response in
guard let strongSelf = self else { return }
let model = strongSelf.updateModel(response)
strongSelf.updateUI(model)
}Not Preferred
// might crash if self is released before response returns
resource.request().onComplete { [unowned self] response in
let model = self.updateModel(response)
self.updateUI(model)
}Not Preferred
// deallocate could happen between updating the model and updating UI
resource.request().onComplete { [weak self] response in
let model = self?.updateModel(response)
self?.updateUI(model)
}Full access control annotation in tutorials can distract from the main topic and is not required. Using private appropriately, however, adds clarity and promotes encapsulation. Use private as the leading property specifier. The only things that should come before access control are the static specifier or attributes such as @IBAction and @IBOutlet.
Preferred:
class TimeMachine {
private dynamic lazy var fluxCapacitor = FluxCapacitor()
}Not Preferred:
class TimeMachine {
lazy dynamic private var fluxCapacitor = FluxCapacitor()
}Prefer the for-in style of for loop over the while-condition-increment style.
Preferred:
for _ in 0..<3 {
print("Hello three times")
}
for (index, person) in attendeeList.enumerate() {
print("\(person) is at position #\(index)")
}
for index in 0.stride(to: items.count, by: 2) {
print(index)
}
for index in (0...3).reverse() {
print(index)
}Not Preferred:
var i = 0
while i < 3 {
print("Hello three times")
i += 1
}
var i = 0
while i < attendeeList.count {
let person = attendeeList[i]
print("\(person) is at position #\(i)")
i += 1
}- break is not needed between case statements (they don't fall through by default)
- Use multiple values on a single case where it is appropriate:
Preferred:
var someCharacter: Character
...
switch someCharacter {
case "a", "e", "i", "o", "u":
print("\(someCharacter) is a vowel")
...
}When pattern matching over an enum case with an associated value, use case .CASENAME(let ...) rather than case let ... syntax for value binding.
Preferred:
enum AnEnum {
case Foo
case Bar(String)
case Baz
}
let anEnumInstanceWithAssociatedValue = AnEnum.Bar("hello")
switch anEnumInstanceWithAssociatedValue {
case .Foo: print("Foo")
// Correct
case .Bar(let barValue): print(barValue) // "hello"
case .Baz: print("Baz")
}Not Preferred:
enum AnEnum {
case Foo
case Bar(String)
case Baz
}
let anEnumInstanceWithAssociatedValue = AnEnum.Bar("hello")
switch anEnumInstanceWithAssociatedValue {
case .Foo: print("Foo")
// Incorrect
case let .Bar(barValue): print(barValue) // "hello"
case .Baz: print("Baz")
}Use map when transforming Arrays (flatMap for Arrays of Optionals or Arrays of Arrays)
Preferred:
let array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
let stringArray = array.map { item in
return "item \(item)"
}
let optionalArray: [Int?] = [1, nil, 3, 4, nil]
let nonOptionalArray = optArray.flatMap { nonNilValue in
return nonNilValue * 2
}
let arrayOfArrays = [array, nonOptionalArray]
let anotherStringArray = arrayOfArrays.flatmap { item in
return "thing \(item)"
}If you are not performing a transform, or if there are side effects do not use map/flatmap, use a for in loop instead. When to use map, flatMap, or for loops in Swift.
If you have an Array of Arrays and want to loop over all contents, consider a for in loop using flatten() instead of nested loops:
let arraysOfNames = [["Moe", "Larry", "Curly"], ["Groucho", "Chico", "Harpo", "Zeppo"]]Preferred:
for name in arraysOfNames.flatten() {
print("\(name) is an old-timey comedian")
}Not Preferred:
for names in arraysOfNames {
for name in names {
print("\(name) is an old-timey comedian")
}
}Avoid the use of forEach except for simple one line closures, similar to makeObjectsPerformSelector: in Objective-C.
When coding with conditionals, the left hand margin of the code should be the "golden" or "happy" path. That is, don't nest if statements. Multiple return statements are OK. The guard statement is built for this.
Preferred:
func computeFFT(context: Context?, inputData: InputData?) throws -> Frequencies {
guard let context = context else { throw FFTError.noContext }
guard let inputData = inputData else { throw FFTError.noInputData }
// use context and input to compute the frequencies
return frequencies
}Not Preferred:
func computeFFT(context: Context?, inputData: InputData?) throws -> Frequencies {
if let context = context {
if let inputData = inputData {
// use context and input to compute the frequencies
return frequencies
}
else {
throw FFTError.noInputData
}
}
else {
throw FFTError.noContext
}
}When using guard, if, or while to unwrap multiple optionals, each constant and/or variable should be broken up onto its own line, and followed by a , except for the last line, which should be followed by else { for guard, or { for if and while.
Preferred:
guard let
constantOne = valueOne,
constantTwo = valueTwo,
constantThree = valueThree else {
return
}
if let
constantOne = valueOne,
constantTwo = valueTwo,
constantThree = valueThree {
// Code
}Not Preferred:
if let constantOne = valueOne,
let constantTwo = valueTwo,
let constantThree = valueThree {
// Code
}
guard let constantOne = valueOne,
constantTwo = valueTwo,
constantThree = valueThree
else {
return
}
if let
constantOne = valueOne,
constantTwo = valueTwo,
constantThree = valueThree
{
// Code
}
guard let constantOne = valueOne, constantTwo = valueTwo, constantThree = valueThree else {
return
}
if let constantOne = valueOne, let constantTwo = valueTwo, let constantThree = valueThree {
// Code
}When unwrapping multiple optionals with a mix of lets and vars, avoid mixing the two. Group them together by making a line-break after guard, if, or while, specify let or var on its own line, and list the constants and variables on their own lines.
Preferred:
guard
let
constantOne = valueOne,
constantTwo = valueTwo,
constantThree = valueThree,
var
variableOne = valueFour,
variableTwo = valueFive,
variableThree = valueSix else {
return
}
if
let
constantOne = valueOne,
constantTwo = valueTwo,
constantThree = valueThree,
var
variableOne = valueFour,
variableTwo = valueFive,
variableThree = valueSix {
// Code
}Not Preferred:
guard let
constantOne = valueOne,
var variableOne = valueTwo,
let constantTwo = valueThree else {
return
}
if let constantOne = valueOne,
var variableOne = valueTwo,
variableTwo = valueThree,
variableThree = valueFour,
let constantTwo = valueFive {
// Code
}Guard statements are required to exit in some way. Generally, this should be simple one line statement such as return, throw, break, continue, and fatalError(). Large code blocks should be avoided. If cleanup code is required for multiple exit points, consider using a defer block to avoid cleanup code duplication.
Swift does not require a semicolon after each statement in your code. They are only required if you wish to combine multiple statements on a single line.
Do not write multiple statements on a single line separated with semicolons.
The only exception to this rule is the for-conditional-increment construct, which requires semicolons. However, alternative for-in constructs should be used where possible.
Preferred:
let swift = "not a scripting language"Not Preferred:
let swift = "not a scripting language";NOTE: Swift is very different to JavaScript, where omitting semicolons is generally considered unsafe
Parentheses around conditionals are not required and should be omitted.
Preferred:
if name == "Hello" {
print("World")
}Not Preferred:
if (name == "Hello") {
print("World")
}The use of operator overloading and custom operators is strongly discouraged as this can hurt readability and potentially create a significant amount of confusion for other developers on a shared project. There are cases that it would be necessary (ex. overloading == to conform to Equatable). When writing a custom operator or overloading an existing one, the operator function should call another explicitly named function that performs that actual work. For more guidance on best practices on this matter, view the guidelines at the bottom of this NSHipster article Guidelines for Swift Operators.
Avoid using the forced-try expression try! as a way to ignore errors from throwing methods as this will crash your app if the error actually gets thrown. Safely handle errors using a do statement along with try and catch. A rare reason to use the forced-try expression is similar to force unwrapping optionals; you actually want the app to crash (ideally during debugging before the app ships) to indicate an implementation error. An example of this would be loading a bundle resource that should always be there unless you forgot to include it or rename it.
Preferred:
do {
let json = try NSJSONSerialization.JSONObjectWithData(data, options: .AllowFragments)
print(json)
} catch {
print(error)
}Not Preferred:
// This will crash at runtime if there is an error parsing the JSON data!
let json = try! NSJSONSerialization.JSONObjectWithData(data, options: .AllowFragments)
print(json)The following copyright statement should be included at the top of every source file:
/**
* Copyright (c) 2016 Razeware LLC
*
* Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
* of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
* in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
* to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
* copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
* furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
*
* The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
* all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
*
* THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
* IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
* AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
* LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
* OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN
* THE SOFTWARE.
*/
Smiley faces are a very prominent style feature of the raywenderlich.com site! It is very important to have the correct smile signifying the immense amount of happiness and excitement for the coding topic. The closing square bracket ] is used because it represents the largest smile able to be captured using ASCII art. A closing parenthesis ) creates a half-hearted smile, and thus is not preferred.
Preferred:
:]
Not Preferred:
:)
Ray Fix currently maintains this style guide. It is a collaborative effort from the most stylish raywenderlich.com team members and its community:
- Jawwad Ahmad
- Soheil Moayedi Azarpour
- Scott Berrevoets
- Eric Cerney
- Sam Davies
- Evan Dekhayser
- Jean-Pierre Distler
- Colin Eberhardt
- Ray Fix
- Joshua Greene
- Greg Heo
- Matthijs Hollemans
- Erik Kerber
- Christopher LaPollo
- Ben Morrow
- Andy Pereira
- Ryan Nystrom
- Andy Obusek
- Cesare Rocchi
- Ellen Shapiro
- Marin Todorov
- Chris Wagner
- Ray Wenderlich
- Jack Wu
Hat tip to Nicholas Waynik and the Objective-C Style Guide team!
We also draw inspiration from Apple’s reference material on Swift: