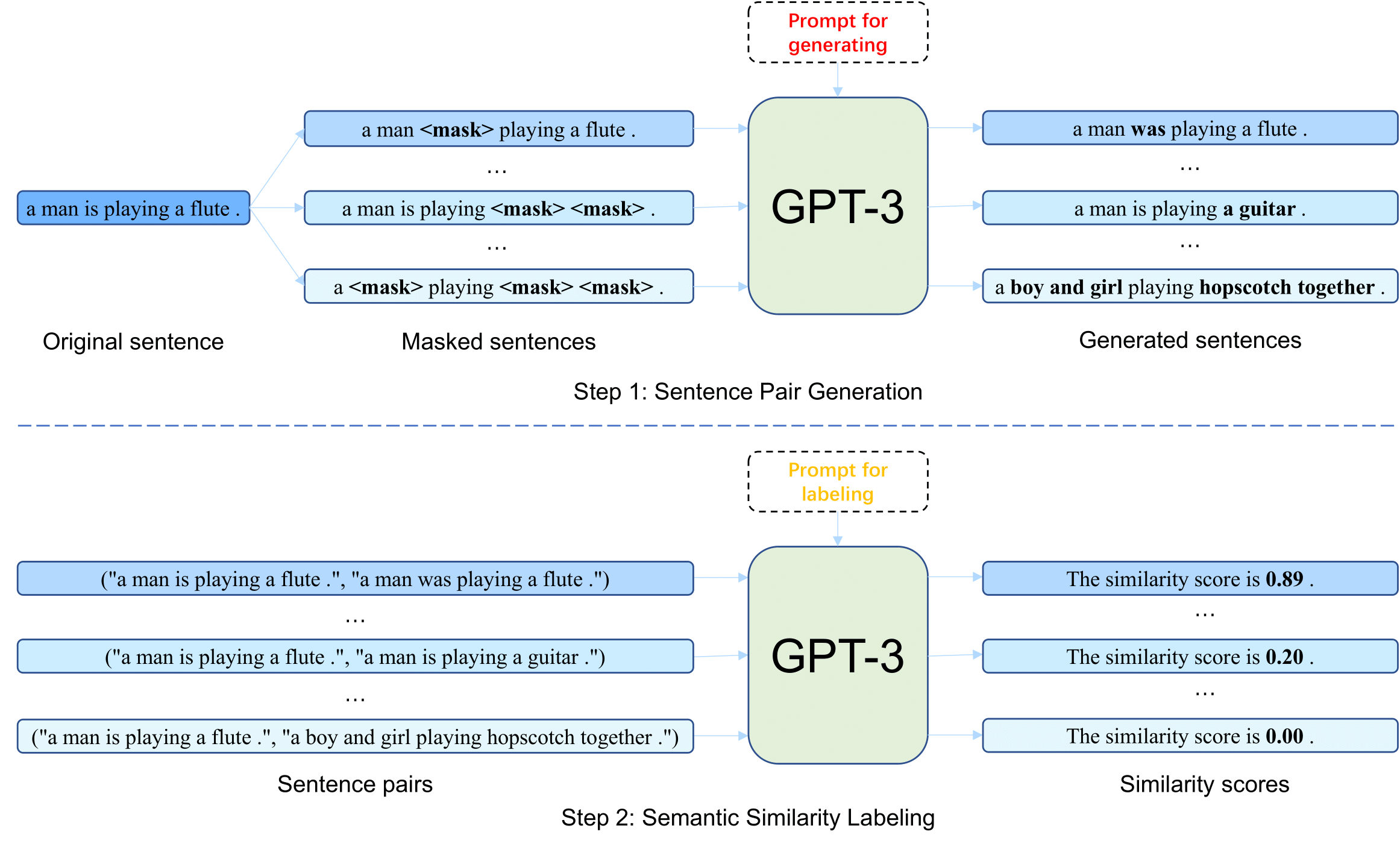
This repository contains the code, data and model checkpoints for our paper Improving Contrastive Learning of Sentence Embeddings from AI
Feedback (CLAIF).
Accepted to Findings of ACL 2023.
conda create -n claif python=3.8
conda activate claif
pip install -r requirements.txt
You can choose your own data as original sentences to construct datasets for sentence embeddings learning. Here we use a small set of sentences as an example to show the whole data generation process.
We use text-davinci-003 as the default engine.
python data_generation.py --generation_stage stage-1 --output_dir sentence_pairs --input_file demo_sentences.csv --input_file_type stsb --batch_size 2 --openai_api_key <your_openai_api_key>After step1, you will get sentence pairs in 'sentence_pairs/generated-dataset.jsonl' with a jsonl format.
We use text-davinci-003 as default.
python data_generation.py --generation_stage stage-2\
--output_dir sentence_pairs_with_labels\
--input_file ./sentence_pairs/generated-dataset.jsonl\
--input_file_type jsonl\
--batch_size 5\
--openai_api_key <your_openai_api_key>After step2, you will get sentence pairs with similarity scores and explainations from AI feedback in 'sentence_pairs_with_labels/generated-dataset.jsonl' with a jsonl format.
We refer to the post-processing pipeline in dino: https://github.com/timoschick/dino/blob/main/scripts/sts/postprocess_dataset.py
python postprocess_dataset.py --input_file ./sentence_pairs_with_labels/generated-dataset.jsonl\
--output_file demo_sentence_pairs_post.jsonl
After post processing, you will get the final data 'demo_sentence_pairs_post.jsonl', which can be used for sentence embeddings learning.
Here wo provide our generated data, which are used in our experiments: https://huggingface.co/datasets/fnlp/CLAIF-data
CLAIF: claif_data.jsonl
CLAIF_scaled: claif_scaled_data.jsonl
NLI_data_with_similarity_scores: nli_data_with_similarity_scores.csv
cd generated_data
bash download_claif_data.sh
cd SentEval/data/downstream/
bash download_dataset.sh
python run_training.py \
--input_file ./generated_data/claif_data.jsonl \
--output_dir result_model \
--model_name roberta-base \
--num_epochs 3 \
--lr 2e-5 \
--using_stsb_devFor the training of CLHAIF, you should use the same environment as the SimCSE, since the version variants of transformers and pytorch may cause some bugs.
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3 bash run_clhaif_simcse.sh
Before evaluation the saved checkpoint, you need to convert it to the huggingface format (the same step as SimCSE):
python simcse_to_huggingface.py --path {PATH_TO_CHECKPOINT_FOLDER}
After that, you can evaluate it by our evaluation code.
Our released models are listed as following. You can import these models by using Sentence Transformers or using HuggingFace's Transformers.
| Model | Avg. STS |
|---|---|
| fnlp/claif-bert-base | 79.63 |
| fnlp/claif-roberta-base | 79.90 |
| fnlp/claif-scaled-bert-base | 82.37 |
| fnlp/claif-scaled-roberta-base | 81.88 |
| fnlp/clhaif-simcse-bert-base | 82.08 |
| fnlp/clhaif-simcse-roberta-base | 82.85 |
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
sentences = ["This is an example sentence", "Each sentence is converted"]
model = SentenceTransformer('fnlp/claif-scaled-bert-base')
embeddings = model.encode(sentences)
print(embeddings)from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModel
import torch
#Mean Pooling - Take attention mask into account for correct averaging
def mean_pooling(model_output, attention_mask):
token_embeddings = model_output[0] #First element of model_output contains all token embeddings
input_mask_expanded = attention_mask.unsqueeze(-1).expand(token_embeddings.size()).float()
return torch.sum(token_embeddings * input_mask_expanded, 1) / torch.clamp(input_mask_expanded.sum(1), min=1e-9)
# Sentences we want sentence embeddings for
sentences = ['This is an example sentence', 'Each sentence is converted']
# Load model from HuggingFace Hub
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained('fnlp/claif-scaled-bert-base')
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained('fnlp/claif-scaled-bert-base')
# Tokenize sentences
encoded_input = tokenizer(sentences, padding=True, truncation=True, return_tensors='pt')
# Compute token embeddings
with torch.no_grad():
model_output = model(**encoded_input)
# Perform pooling. In this case, mean pooling.
sentence_embeddings = mean_pooling(model_output, encoded_input['attention_mask'])
print("Sentence embeddings:")
print(sentence_embeddings)You can run the evaluation script for claif like:
python evaluation_sts.py --model_name_or_path 'fnlp/claif-roberta-base'\
--mode test\
--task_set stswhich is expected to output the results in a tubular format:
------ test ------
+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+--------------+-----------------+-------+
| STS12 | STS13 | STS14 | STS15 | STS16 | STSBenchmark | SICKRelatedness | Avg. |
+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+--------------+-----------------+-------+
| 68.33 | 82.26 | 77.00 | 85.18 | 83.43 | 85.05 | 78.02 | 79.90 |
+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+--------------+-----------------+-------+
You can run the evaluation script for clhaif-bert-base like:
python evaluation_clhaif.py \
--model_name_or_path fnlp/clhaif-simcse-bert-base \
--pooler cls \
--task_set sts \
--mode testwhich is expected to output the results in a tubular format:
------ test ------
+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+--------------+-----------------+-------+
| STS12 | STS13 | STS14 | STS15 | STS16 | STSBenchmark | SICKRelatedness | Avg. |
+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+--------------+-----------------+-------+
| 74.86 | 85.09 | 81.24 | 85.96 | 81.33 | 84.69 | 81.36 | 82.08 |
+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+--------------+-----------------+-------+
You can run the evaluation script for clhaif-roberta-base like:
python evaluation_clhaif.py \
--model_name_or_path fnlp/clhaif-simcse-roberta-base \
--pooler avg \
--task_set sts \
--mode testwhich is expected to output the results in a tubular format:
------ test ------
+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+--------------+-----------------+-------+
| STS12 | STS13 | STS14 | STS15 | STS16 | STSBenchmark | SICKRelatedness | Avg. |
+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+--------------+-----------------+-------+
| 76.23 | 85.46 | 81.48 | 86.47 | 83.40 | 85.93 | 80.95 | 82.85 |
+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+--------------+-----------------+-------+
Our implementation is built on the source code from dino and SimCSE. Thanks for their work.
@inproceedings{DBLP:conf/acl/ChengYSLQ23,
author = {Qinyuan Cheng and
Xiaogui Yang and
Tianxiang Sun and
Linyang Li and
Xipeng Qiu},
title = {Improving Contrastive Learning of Sentence Embeddings from {AI} Feedback},
booktitle = {Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: {ACL} 2023,
Toronto, Canada, July 9-14, 2023},
pages = {11122--11138},
publisher = {Association for Computational Linguistics},
year = {2023},
}