This is a fork of the original IoTSim repository. The goal of our project was to extent the IoTSimEdge simulator to include irradiance data from the BSRN database and create a simple simulation of a device powered by a solar panel. This was part of a 2020/2021 winter semester IoT course at the Faculty of Computer Science, Electronics and Telecommunications of AGH University of Science and Technology, Kraków.
Clone the repository with git clone --recursive https://github.com/wsrtka/IoTSim-Edge.
Add the cloudsim library from lib directory to te project.
To run the example execute the main method from SolarExample class located in src/main/java/org/edge/examples.
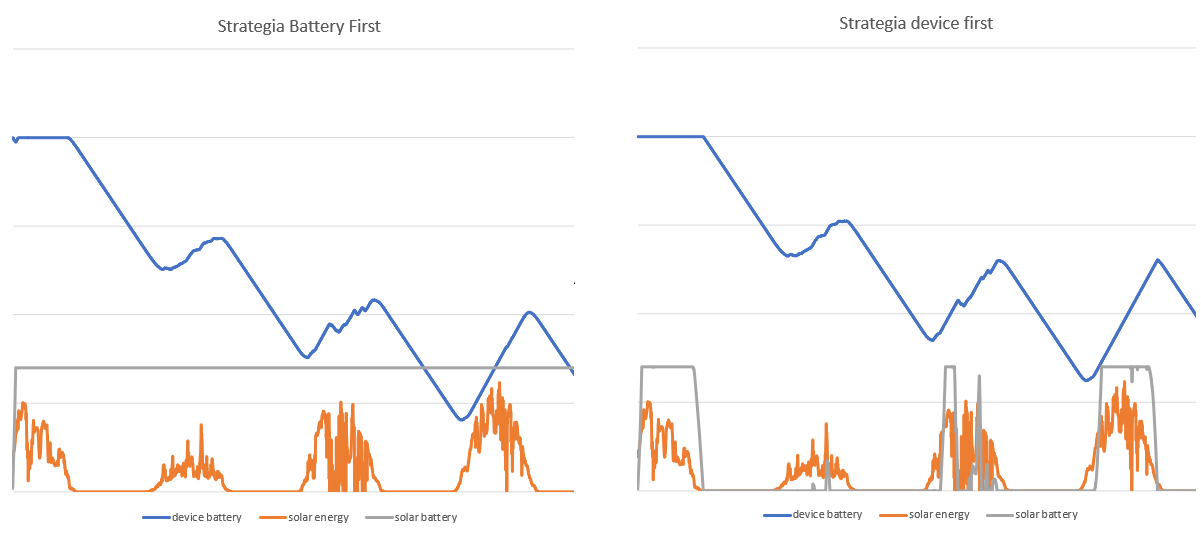
The following graphs show the energy stored both in th device battery and the solar panel battery with regards to the energy produced by the solar panel. The simulation is based on the example descirbed above. The length of the simulation is 4 days and, for better readability, the graph is not to scale.\
As we can see, in the case of the BatteryFirst strategy, the battery was charged to it's maximum capacity in the beginning of the simulation and never dropped afterwards. In case of the DevicesFirst strategy, the battery was only sometimes at it's full capacity, as the energy produced by the solar panel was diverted to the IoT deivce. In fact, the battery was mostly without any charge. However, the device's battery was better supplied and probably would have lasted longer before fully loosing all it's charge.
This poses an interesting question whever the first strategy is better because of it's longer solar panel battery lifespan. This small fork can answer many important questions based around supplying a group of IoT devices with energy - how many panels to use? Is higher solar panel efficiency better than a bigger solar panel area?
Class representing a photovoltaic panel. It has all atributes needed to simulate a real life solar panel: efficiency and area. In addition, the panel stores a list of connected devices, which it supplies with energy, a battery, to which surplus energy is redirected, an energy transfer speed, a supply strategy, described below and a logger for simulation purposes.
Available methods:
setPowerDistributionStrategy - sets the panel's power supply energy.
connect - adds a device to the list of supplied devices.
disconnect - removes a device from the list of supplied devices
supplyEnergy - calculates the panel's energy output and directs it to it's connected devices, according to the supply strategy.
getCurrentPowerOutput - calculates the panel's energy output based on the solar irradiance, the temperature of the panel, it's efficiency and the angle between the solar panel and the solar rays. The formula used is based on the paper Optimal Bidding Strategy for Microgrids Considering Renewable Energy and Building Thermal Dynamics by Duong Tung Nguyen and Long Bao Le, 2014. Angle correction is based on [this website](https://www.ftexploring.com/solar-energy/sun-angle-and-insolation3.htm\).
getCurrentBatteryCapacity - returns the current battery capacity (how much more energy the battery is able to store).
The class responsible for the BSRN data reading from a .tab file. It has the following method:
getData - reads the data file and searchees for a row that corresponds with the given time and date. Returns data about solar irradiance at that time.
A common interface for strategies of distributing the power produced by a solar pannel between its built-in battery and connected devices.
I includes one method, distributePower, which is tasked with completing all charging operations and returns nothing.
And abstract class describing a power distribution strategy using verbose console outputs.
Available methods:
distributePower - abstract method, which will implement strategy-specific power distribution logic.
distributePowerToDevices - evenly distributes power between a given list of devices. You can select if charging should use solar energy and the solar panel's battery, or just solar energy. Prevents overcharging and recursively redistributes excess power between all connected devices.
chargeSolarBattery, chargeDeviceFromSun, chargeDeviceFromBattery - charges a single device or battery and outputs the charge amount as well as current battery capacity.
announceLeftoverPower - outputs the leftover power that was not used while charging.
Power distribution strategy that prioritizes charging the solar battery. It will not use solar battery to power devices. Devices are only charged when battery is full or charging at the maximum speed.
Power distribution strategy that prioritizes charging the device batteries. It will use battery power to charge device batteries if they are not charging at maximum speed. It will only charge the solar battery if each device is either fully charged or charging at the maximum rate.
Nonstatic logger class enabling reading and writing files.
The class contains a simulation of an IoT device powered by a solar panel.\