See the Audit Report
SafeGuard governance accountability tool built around the Gnosis Safe multisig. It's a multisig system that allows governance to retain veto power over Gnosis Safe contracts, and allows governance to reclaim funds entrusted to multsig holders without requiring multisig signatories approval.
Example use cases include giving final veto power on the execution of multisig transactions to token holders, and the ability to reclaim funds from a multisig where the signatories are unable or unwilling to sign a refund transaction.
On chain governance is slow and cumbersome, requiring coordination of many individual voters as well as substantial gas expenses. This can make it unsuitable for managing day to day operations or expenses.
Protocols can help scale their governance capacities and increase agility by delegating authority to smaller decision making bodies such as multi sigs. But this presents a tradeoff between reducing friction and maintaining security, as governance has no way to claw back funds or authority from a multisig without the cooperation of the multisig signers.
Current multi sigs are a one-way delegation of power. Multi-sigs are secure but lack oversight, transparency and accountability. This lack of accountability limits protocols ability to delegate authority to subcommittees, bottlenecks protocol growth and limits the effectiveness of governance.
Create a modular open source framework built around Gnosis MultiSig, OpenZeppelin Timelocks, Nomic Labs HardHat, and Compound Governor alpha that supports optimistic multi-sig governance.
The proposed solution would work alongside existing governance structures, require no modifications to existing smart contracts, and be entirely optional. The solution would work for any governance ecosystem where the underlying token is an ERC20 and uses a checkpointing system similar to Uniswap and Compound.
As a governance, I want to entrust a budget to a multisig with the confidence that governance has the ability to reclaim funds without requiring the approval of the multisig signers.
As a governance, I want some quorum of governance token holders to have ultimate authority to delay or cancel transactions approved by multisig signers.
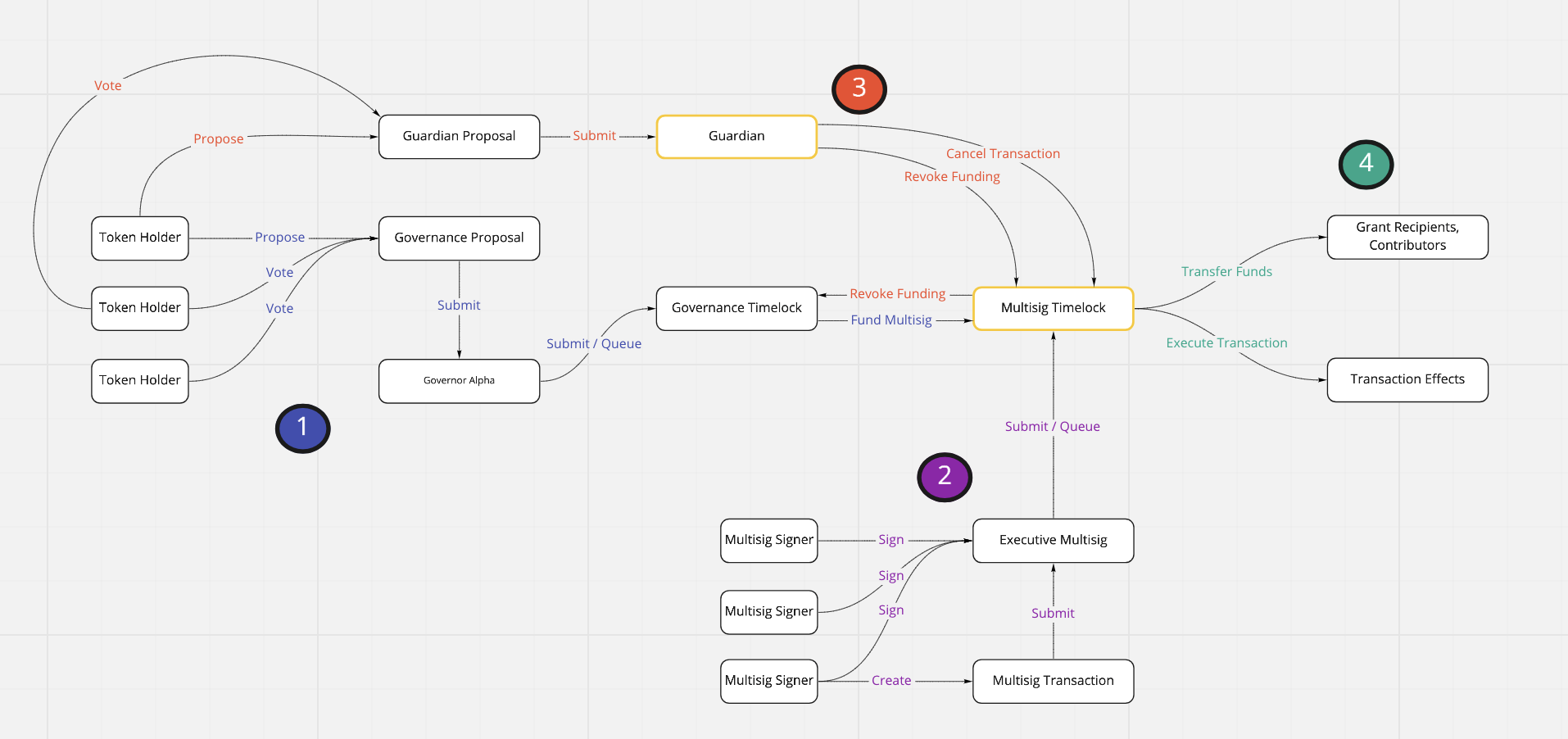
The figure below shows how the proposed mechanism works and interacts with existing governance systems. New components are highlighted in yellow, while process flow is shown via the numbered elements.
Guardian: A modified version of the Governor Alpha contract Main governance timelock has ability to change guardian parameters including voting period, quorum, and proposal threshold
Multisig timelock: A modified version of the Compound timelock contract Admin powers to cancel transactions are split from admin power to queue or execute transactions
Token holders submit and approve a regular Governor Alpha proposal to transfer funds or authority to an external entity/multisig.
Multisig signers generate and sign a transaction, and queue the transaction into the multisig timelock.
If the main governance token holders believes that the multisig took improper actions, the token holders can cancel pending transactions or sweep funds and permissions from the multisig timelock back to the governance timelock. They do this by submitting and passing a proposal through the guardian contract.
If no action is taken to stop the queued transaction, it can be executed by the multisig after the timelock period elapses.
Before running any command, make sure to install dependencies:
$ yarn installCompile the smart contracts with Hardhat:
$ yarn compileCompile the smart contracts and generate TypeChain artifacts:
$ yarn typechainLint the Solidity code:
$ yarn lint:solLint the TypeScript code:
$ yarn lint:tsRun the Mocha tests:
$ yarn testGenerate the code coverage report:
$ yarn coverageSee the gas usage per unit test and average gas per method call:
$ REPORT_GAS=true yarn testDelete the smart contract artifacts, the coverage reports and the Hardhat cache:
$ yarn clean