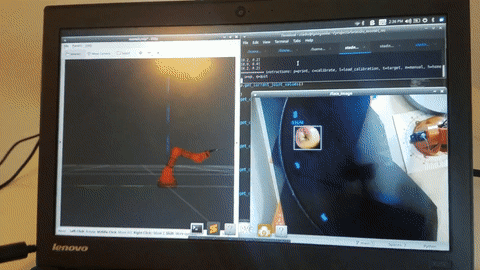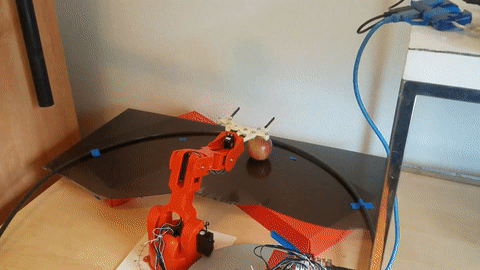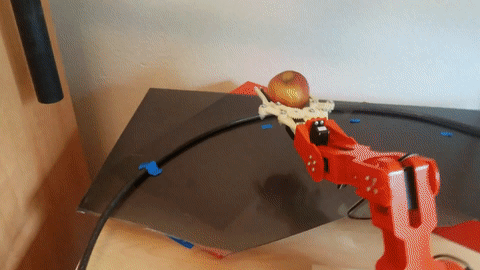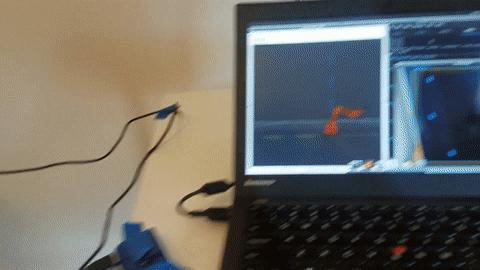
This is a demo project to use an overhead camera and an Arduino Braccio to pick up objects using ROS MoveIt and OpenCV's dnn with YOLOv3 weights. See it in action.
ROS is quite surprisingly awkward to set up, but follow along here and it should get you close to set up. You will probably also have to add more packages as you go through using something like sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-PACKAGE.
First you need an assembled and working Arduino Braccio arm.
You'll also need to install ROS for Arduino following the instructions here as well as adding the specific library in libraries/BraccioLibRos following the instructions here.
Then you can use the Arduino IDE to upload the braccio_ros/braccio_ros.ino file to the Arduino running the Braccio arm.
Clone this repo into the src folder of a catkin workspace.
git clone git@github.com:lots-of-things/ros_braccio_opencv_obj_detect_grab.git braccio_opencv_ws/src/ros_braccio_opencv_obj_detect_grab
Run catkin_make in the root of the workspace.
cd braccio_opencv_ws
catkin_make
Finally you'll need to download the yolov3 weights into the models/ folder.
cd braccio_opencv_ws/src/ros_braccio_opencv_obj_detect_grab/models/
wget https://pjreddie.com/media/files/yolov3.weights
Launch the RViz model visualizer and the OpenCV object detection algorithm.
cd braccio_opencv_ws
source devel/setup.bash
roslaunch ros_braccio_opencv_obj_detect_grab demo.launch start_detection:=true
The above command doesn't connect to the . If you want to actually drive the Braccio arm make sure it is connected by USB and add connect_braccio:=true like so:
roslaunch ros_braccio_opencv_obj_detect_grab demo.launch start_detection:=true connect_braccio:=true
Finally, in a separate terminal run the script to begin the interactive program.
cd braccio_opencv_ws
source devel/setup.bash
rosrun ros_braccio_opencv_obj_detect_grab braccio_xy_bb_target.py
There are a number of options available through the command line interface. Prior to calibration (see next step) only 4 commands will work:
u: go to straight up position
h: go to home position (middle to one side)
p: print current pose
q: quit script
Before you start objects you need to calibrate a mapping from location in the image to motor angle positions in the Braccio. When you are ready to start, run c for calibrate. First, you will be prompted to click on the center base of the robot in the image. Then you will be asked to click in the center of the gripper as the robot arm moves around the field of view.
After you have calibrated, you can press l on subsequent startups to load the calibration from file. However, if you move the camera or the arm, you'll need to recalibrate.
Finally, place your object in the field of view. If the object is detected a box will appear around it with a label. By default it is set up to detect only apples, but this can be changed by passing tracked_object:=other_thing as part of the demo.launch launch command above. Available objects as part of yolov3 can be found in models/yolov3.txt. Additional objects will require training a yolov3 model yourself.
After an object has been detected you can press t to target an object and pick it up. If the object is out of the range that the robot can reach it will fail. If it is too close to pick up, it will try to push it backwards into the reachable window. After it has moved the object you can press t again to reattempt targetting at the new location.
And now you have a robot that can pick stuff up.
I used my old phone as a webcam using droidcam. You can follow the linux setup instructions here.
However, droidcam uses an encoding that doesn't play nicely with the ROS usb_cam package directly. I worked around this by using ffmpeg and v4l2loopback to do the format conversion on the fly like so.
First install ffmepg and v4l2loopback if you don't have them already.
sudo apt install ffmpeg
sudo apt install v4l2loopback-dkms
Now forward from your input device (/dev/video1) to a new device (/dev/video2) using yuyv422 format.
sudo modprobe v4l2loopback
ffmpeg -f v4l2 -i /dev/video1 -c:v rawvideo -pix_fmt yuyv422 -f v4l2 /dev/video2
Finally, you can pass the new video device name as a parameter to demo.launch.
ros_braccio_opencv_obj_detect_grab demo.launch video_device:=/dev/video2