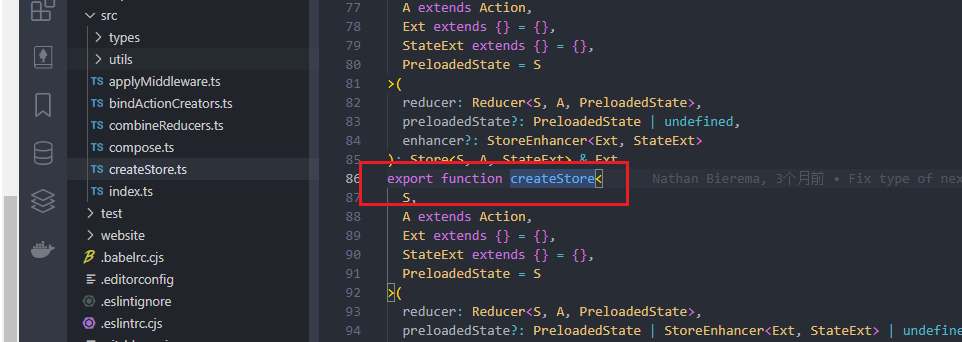
写之前先思考下,为什么在某个页面dispatch更改数据后,其他页面getState拿到的就是最新的数据?这是什么机制?
import { createStore } from 'redux'
import reducer from './reducer'
const store = createStore(reducer)
export default store上面是最简单引用redux的例子,我们用这个例子解析
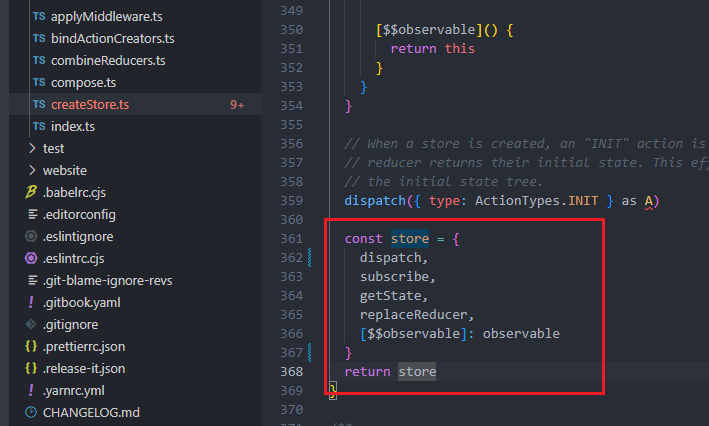
上面两张图,我们可以知道,createStore返回的对象有dispatch,subscribe,getState等属性方法,这些方法在其他页面引用了 store 后就能使用 store.dispatch,store.subscribe,store.getState
接着继续看createStore的内部做了哪些处理
export function createStore(
reducer,
preloadedState,
enhancer
) {
// reducer 不是函数直接报错
if (typeof reducer !== 'function') {
throw new Error(
`Expected the root reducer to be a function. Instead, received: '${kindOf(
reducer
)}'`
)
}
let currentReducer = reducer // reducer 赋值 给内部变量 currentReducer
let currentState = preloadedState // preloadedState 赋值 给内部变量 currentState
let currentListeners = [] // currentListeners 存储执行了 subScribe 方法的订阅器
let nextListeners = currentListeners
let listenerIdCounter = 0 // 订阅数
let isDispatching = false
}
// 定义了很多方法 dispatch subscribe getState等等
/*
...
*/
// 执行 dispatch 方法,给每个reducer都返回一个初始值
dispatch({ type: ActionTypes.INIT })
const store = {
dispatch,
subscribe,
getState,
replaceReducer,
[$$observable]: observable
}
return store createStore 内部进行了一些逻辑判断,定义很多方法,执行了dispatch({type:ActionTypes.INIT})给每个reducer一个初始值,最后返回一个对象。
返回最新的state值
function getState() {
if (isDispatching) {
throw new Error(
'You may not call store.getState() while the reducer is executing. ' +
'The reducer has already received the state as an argument. ' +
'Pass it down from the top reducer instead of reading it from the store.'
)
}
return currentState
}监听订阅
function subscribe(listener: () => void) {
// 参数必须是一个函数,否则直接报错
if (typeof listener !== 'function') {
throw new Error(
`Expected the listener to be a function. Instead, received: '${kindOf(
listener
)}'`
)
}
let isSubscribed = true
ensureCanMutateNextListeners()
const listenerId = listenerIdCounter++ // 当前订阅编号数
nextListeners.set(listenerId, listener) // 把监听函数push到相应的监听容器中
// 返回一个取消监听的函数,store.subscribe()() 取消监听
return function unsubscribe() {
if (!isSubscribed) {
return
}
if (isDispatching) {
throw new Error(
'You may not unsubscribe from a store listener while the reducer is executing. ' +
'See https://redux.js.org/api/store#subscribelistener for more details.'
)
}
isSubscribed = false
ensureCanMutateNextListeners()
nextListeners.delete(listenerId)
currentListeners = null
}
}- 修改state的值
- 执行订阅器中的监听
function dispatch(action: A) {
if (!isPlainObject(action)) {
throw new Error(
`Actions must be plain objects. Instead, the actual type was: '${kindOf(
action
)}'. You may need to add middleware to your store setup to handle dispatching other values, such as 'redux-thunk' to handle dispatching functions. See https://redux.js.org/tutorials/fundamentals/part-4-store#middleware and https://redux.js.org/tutorials/fundamentals/part-6-async-logic#using-the-redux-thunk-middleware for examples.`
)
}
// action 没有type 直接报错
if (typeof action.type === 'undefined') {
throw new Error(
'Actions may not have an undefined "type" property. You may have misspelled an action type string constant.'
)
}
// action 的 type 不是字符串也直接报错
if (typeof action.type !== 'string') {
throw new Error(
`Action "type" property must be a string. Instead, the actual type was: '${kindOf(
action.type
)}'. Value was: '${action.type}' (stringified)`
)
}
if (isDispatching) {
throw new Error('Reducers may not dispatch actions.')
}
// 直接执行currentReducer(currentState, action),就是 reducer(currentState, action)
try {
isDispatching = true
currentState = currentReducer(currentState, action)
} finally {
isDispatching = false
}
// 纯函数执行完后会修改state的值,接着把订阅器中的监听依次执行
const listeners = (currentListeners = nextListeners)
listeners.forEach(listener => {
listener()
})
// 最后返回action
return action
}上面就是同步条件下所用到的Redux,但往往异步才是难点,接下来介绍中间件
中间件的作用就是让dispatch的参数不只是对象,也可以是一个函数,下面以redux-thunk举例
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux'
import { thunk } from 'redux-thunk'
import reducer from './reducer'
const store = createStore(reducer, applyMiddleware(thunk))
export default store
// 具体使用
useEffect(() => {
store.dispatch(getHotRecommendAction(8))
},[])
const getHotRecommendAction = (limit) => {
return dispatch => {
getHotRecommends(limit).then(res => {
dispatch(changeHotRecommendAction(res))
})
}
}上面的代码有几个不同点,applyMiddleware(thunk),getHotRecommendAction返回的是一个函数等等,接下来一步一步解析
function createThunkMiddleware(extraArgument) {
const middleware = ({ dispatch, getState }) =>
next =>
action => {
if (typeof action === 'function') {
return action(dispatch, getState, extraArgument)
}
return next(action)
}
return middleware
}
export const thunk = createThunkMiddleware()thunk 就是一个 函数,参数为一个对象,属性是dispatch、getState。下面回到 redux 中去
applyMiddleware(thunk) 返回是一个函数,函数形参是 createStore
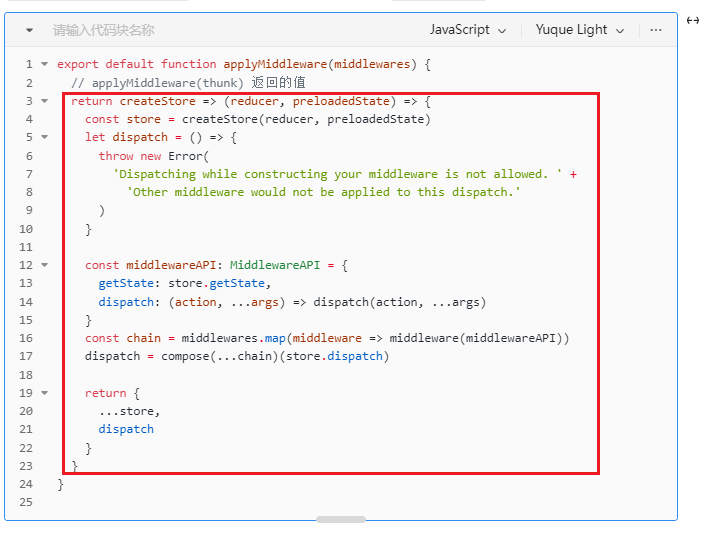
export default function applyMiddleware(middlewares) {
// applyMiddleware(thunk) 返回的值
return createStore => (reducer, preloadedState) => {
const store = createStore(reducer, preloadedState)
let dispatch = () => {
throw new Error(
'Dispatching while constructing your middleware is not allowed. ' +
'Other middleware would not be applied to this dispatch.'
)
}
const middlewareAPI: MiddlewareAPI = {
getState: store.getState,
dispatch: (action, ...args) => dispatch(action, ...args)
}
const chain = middlewares.map(middleware => middleware(middlewareAPI))
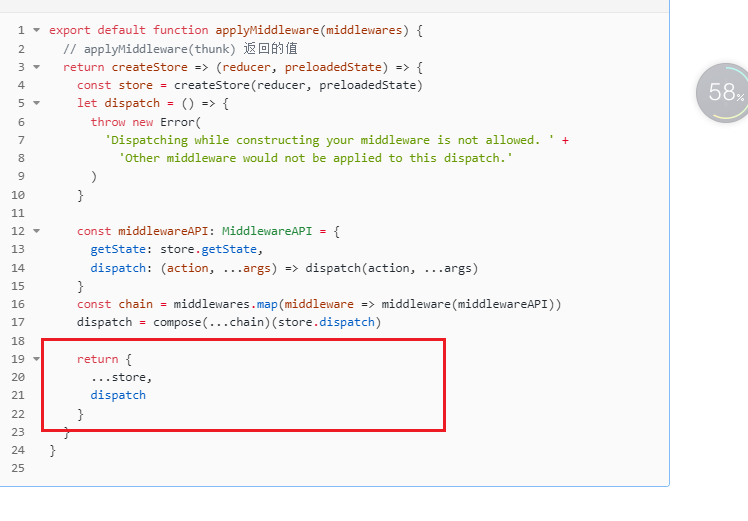
dispatch = compose(...chain)(store.dispatch)
return {
...store,
dispatch
}
}
}执行完 applyMiddleware(thunk) 、接着继续执行createStore(reducer,applyMiddleware(thunk)),重新看createStore的内部逻辑,比之前多了一个参数
// 前面讲过的逻辑省略,直接给结果
export function createStore(
reducer,
preloadedState,
enhancer
){
// preloadedState 就是 applyMiddleware(thunk) 是一个函数
if (typeof preloadedState === 'function' && typeof enhancer === 'undefined') {
// 两者互换
enhancer = preloadedState
preloadedState = undefined
}
if (typeof enhancer !== 'undefined') {
if (typeof enhancer !== 'function') {
throw new Error(
`Expected the enhancer to be a function. Instead, received: '${kindOf(
enhancer
)}'`
)
}
// 执行 enhancer
// 其实也就是执行 applyMiddleware(thunk)(createStore)(reducer,undefined)
// 并把上述结果返回赋值给了 store
return enhancer(createStore)(
reducer,
preloadedState
)
}
}本篇文章最难的点就是看懂applyMiddleware的返回结果,接下来一步一步解析
(reducer, preloadedState) => {
const store = createStore(reducer, preloadedState)
let dispatch = () => {
throw new Error(
'Dispatching while constructing your middleware is not allowed. ' +
'Other middleware would not be applied to this dispatch.'
)
}
const middlewareAPI: MiddlewareAPI = {
getState: store.getState,
dispatch: (action, ...args) => dispatch(action, ...args)
}
const chain = middlewares.map(middleware => middleware(middlewareAPI))
dispatch = compose(...chain)(store.dispatch)
return {
...store,
dispatch
}
}(reducer, preloadedState) => {
// 获取同步条件下的store
const store = createStore(reducer, preloadedState)
// 定义dispatch变量
let dispatch = () => {
throw new Error(
'Dispatching while constructing your middleware is not allowed. ' +
'Other middleware would not be applied to this dispatch.'
)
}
// 定义中间件具有的api,getState和dispatch
const middlewareAPI = {
getState: store.getState,
dispatch: (action, ...args) => dispatch(action, ...args)
}
// 获取thunk执行后的结果,并把它存入chain数组中
const chain = middlewares.map(middleware => middleware(middlewareAPI))
// dispatch是引用值,被修改后,中间件的dispatch也会被修改
dispatch = compose(...chain)(store.dispatch)
// 将被修改的dispatch返回出去
return {
...store,
dispatch
}
}返回结果是双层函数,取名为dobuleFun函数
const middleware = ({ dispatch, getState }) =>
next =>
action => {
if (typeof action === 'function') {
return action(dispatch, getState, extraArgument)
}
return next(action)
}
middleware(
{
getState: store.getState,
dispatch: (action, ...args) => dispatch(action, ...args)
}
)
const dobuleFun = (next) =>
action => {
if (typeof action === 'function') {
return action(dispatch, getState, extraArgument)
}
return next(action)
}如果参数长都只有1的话就是直接返回该函数,即dobuleFun函数
export default function compose(funcs) {
if (funcs.length === 0) {
// infer the argument type so it is usable in inference down the line
return <T>(arg: T) => arg
}
if (funcs.length === 1) {
return funcs[0]
}
return funcs.reduce(
(a, b) =>
(...args: any) =>
a(b(...args))
)
}最后的返回结果,我们取名为finallyFun,并赋值给了dispatch,该函数内部进行了判断传入的action是否是函数
- 是函数,先执行该函数,并把dispatch当作参数传进去
- 不是就执行dispatch(action)操作
const dobuleFun = (next) =>
action => {
if (typeof action === 'function') {
return action(dispatch, getState, extraArgument)
}
return next(action)
}(store.dispatch)
const finallyFun = action => {
if (typeof action === 'function') {
// 这个dispatch 是来自于 middlewareAPI.dispatch,也就是当前这个finallyFun函数
// 因为这个函数赋值给了dispatch dispatch = compose(...chain)(store.dispatch)
return action(dispatch, getState, extraArgument)
}
return next(action)
}// 具体使用
useEffect(() => {
store.dispatch(getHotRecommendAction(8))
},[])
const getHotRecommendAction = (limit) => {
return dispatch => {
getHotRecommends(limit).then(res => {
dispatch(changeHotRecommendAction(res))
})
}
}
// 1.解析
store.dispatch(getHotRecommendAction(8))
// 2.相当于
const finallyFun = action => {
if (typeof action === 'function') {
// 这个dispatch 是来自于 middlewareAPI.dispatch,也就是当前这个finallyFun函数
// 因为这个函数赋值给了dispatch dispatch = compose(...chain)(store.dispatch)
return action(dispatch, getState, extraArgument)
}
return next(action)
}((dispatch) => {
getHotRecommends(limit).then(res => {
dispatch(changeHotRecommendAction(res))
})
})
// 3.结果就是
(dispatch) => {
getHotRecommends(limit).then(res => {
dispatch(changeHotRecommendAction(res))
})
}()
// 上面就是为什么thunk能执行异步操作的所有逻辑 dispatch 就是 middlewareAPI中的 API
// redux-thunk 就是利用了闭包,给store返回了一个加强的dispatch,所以dispatch可以
// 传入函数当作参数