工程简介
这是一个对Halo 的学习项目
数据缓存模块
缓存类设计
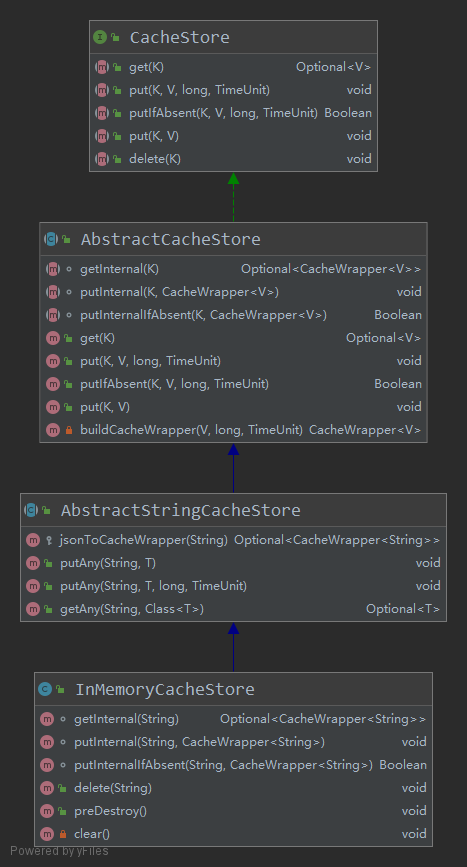
Halo项目中数据缓存有三种实现,可以在配置文件中自定义使用哪种,分别是Inmemory本地内存、redis数据库、level-db数据库。作者对CacheStore类的设计非常值得学习。这是相关的类图:
-
CacheStore:顶层接口是CacheStore,定义了5个基础的数据操作方法。
-
AbstractCacheStore:抽象类AbstractCacheStore实现CacheStore接口并定义了put/getInternal方法实现对CacheWrapper对象的数据操作。
CacheWrapper对象封装了具体数据以及数据的创建时间、过期时间:
class CacheWrapper<V> implements Serializable { /** * Cache data */ private V data; /** * Expired time. */ private Date expireAt; /** * Create time. */ private Date createAt; }
-
AbstractStringCacheStore:抽象类AbstractStringCacheStore继承自AbstractCacheStore类定义了put/getAny方法实现了将任意类型数据与String数据进行转换后再操作的功能。
public <T> void putAny(String key, T value) { try { put(key, JsonUtils.objectToJson(value)); } catch (JsonProcessingException e) { throw new ServiceException("Failed to convert " + value + " to json", e); } } public <T> void putAny(@NonNull String key, @NonNull T value, long timeout, @NonNull TimeUnit timeUnit) { try { put(key, JsonUtils.objectToJson(value), timeout, timeUnit); } catch (JsonProcessingException e) { throw new ServiceException("Failed to convert " + value + " to json", e); } } public <T> Optional<T> getAny(String key, Class<T> type) { Assert.notNull(type, "Type must not be null"); return get(key).map(value -> { try { return JsonUtils.jsonToObject(value, type); } catch (IOException e) { log.error("Failed to convert json to type: " + type.getName(), e); return null; } }); }
-
InMemoryCacheStore/RedisCacheStore等实现类只需重写实现put/getInternal方法以及delete方法即可。
配置中定义缓存实现类
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public AbstractStringCacheStore stringCacheStore() {
AbstractStringCacheStore stringCacheStore;
switch (haloProperties.getCache()) {
case "level":
stringCacheStore = new LevelCacheStore(this.haloProperties);
break;
case "redis":
stringCacheStore = new RedisCacheStore(this.haloProperties);
break;
case "memory":
default:
//memory or default
stringCacheStore = new InMemoryCacheStore();
break;
}
log.info("Halo cache store load impl : [{}]", stringCacheStore.getClass());
return stringCacheStore;
}登录模块(安全模块)
使用ThreadLocal存储用户信息
由于传统的将用户信息存放在Session中有许多缺点,例如需要从HttpServletRequest中获取session再获取信息十分繁琐,业务层等代码中获取用户信息还需Controller层从session中获取后以方法参数的方式传递过来等。放弃使用Session,当前登录的用户信息存储在自定义的ThreadLocal本地线程局部变量中,ThreadLocal中存储的用户信息的生命周期范围是每次请求,在每次请求前的AdminAuthenticationFilter验证过滤器中创建,每次请求结束后销毁。
public class SecurityContextHolder {
private static final ThreadLocal<SecurityContext> CONTEXT_HOLDER = new ThreadLocal<>();
@NonNull
public static SecurityContext getContext() {
...
}
/**
* set context.
*/
public static void setContext(@Nullable SecurityContext context) {
CONTEXT_HOLDER.set(context);
}
/**
* remove context.
*/
public static void clearContext() {
CONTEXT_HOLDER.remove();
}
}使用自定义Token
在用户登录成功后,使用UUID生成一个AccessToken和RefreshToken,与过期信息一并存储在CacheStore中。给用户返回一个AccessToken和一个RefreshToken以及过期时间,以后用户在访问需验证的接口时,在Header或请求参数中带上AccessToken,在过滤器中解析请求中的AccessToken,然后使用AccessToken从CacheStore中获取用户信息并存储到ThreadLocal中。这样,在后续可以直接从ThreadLocal中获取用户信息。
@Data
public class AuthToken {
/**
* access_token
*/
@JsonProperty("access_token")
private String accessToken;
/**
* refresh_token
*/
@JsonProperty("refresh_token")
private String refreshToken;
/**
* Expired in. (seconds)
*/
@JsonProperty("expired_in")
private int expiredIn;
}登陆成功时构建token并存储到CacheStore中
private AuthToken buildAuthToken(@NonNull User user) {
Assert.notNull(user, "User must not be null");
AuthToken authToken = new AuthToken();
authToken.setAccessToken(UUIDUtils.randomUUIDWithoutDash());
authToken.setRefreshToken(UUIDUtils.randomUUIDWithoutDash());
authToken.setExpiredIn(ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRED_SECONDS);
// Cache those tokens with userId as key
cacheStore.putAny(SecurityUtils.buildTokenAccessKeyWithUser(user), authToken.getAccessToken(), ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRED_SECONDS, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
cacheStore.putAny(SecurityUtils.buildRefreshTokenAccessKeyWithUser(user), authToken.getRefreshToken(), REFRESH_TOKEN_EXPIRED_DAYS, TimeUnit.DAYS);
// Cache those tokens with userId as value
cacheStore.putAny(SecurityUtils.buildAccessTokenKey(authToken.getAccessToken()), user.getId(), ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRED_SECONDS, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
cacheStore.putAny(SecurityUtils.buildRefreshTokenKey(authToken.getRefreshToken()), user.getId(), REFRESH_TOKEN_EXPIRED_DAYS, TimeUnit.DAYS);
return authToken;
}过滤器中将用户信息存到ThreadLocal
public class AdminAuthenticationFilter extends AbstractAuthenticationFilter {
@Override
protected void doAuthenticate(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException {
// Get token from request
String token = getTokenFromRequest(request);
if (StringUtils.isBlank(token)) {
throw new AuthenticationException("未登录,请登录后访问");
}
// Get user id from cache
Optional<Integer> optionalUserId = cacheStore.getAny(SecurityUtils.buildAccessTokenKey(token), Integer.class);
if (!optionalUserId.isPresent()) {
throw new AuthenticationException("Token 已过期或不存在").setErrorData(token);
}
// Get the user
User user = userService.getById(optionalUserId.get());
// Build user detail
UserDetail userDetail = new UserDetail(user);
// Set security
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(new SecurityContextImpl(new AuthenticationImpl(userDetail)));
// Do filter
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
}
}public abstract class AbstractAuthenticationFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException {
try {
// Do authenticate 调用上面的方法
doAuthenticate(request, response, filterChain);
} catch (AbstractBaseException e) {
getFailureHandler().onFailure(request, response, e);
} finally {
//请求完成。清理ThreadLocal中的用户信息,防止内存泄漏
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
}
}
}全局异常处理
-
自定义抽象类AbstractHaloException继承自RuntimeException
public abstract class AbstractHaloException extends RuntimeException { private Object errorData; public AbstractHaloException(String message) { super(message); } public AbstractHaloException(String message, Throwable cause) { super(message, cause); } /** * Http status code */ @NonNull public abstract HttpStatus getStatus(); @Nullable public Object getErrorData() { return errorData; } @NonNull public AbstractHaloException setErrorData(@Nullable Object errorData) { this.errorData = errorData; return this; } }
-
自定义异常NotFoundException继承AbstractHaloException类
public class NotFoundException extends AbstractHaloException { public NotFoundException(String message) { super(message); } public NotFoundException(String message, Throwable cause) { super(message, cause); } @Override public HttpStatus getStatus() { return HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND; } }
-
在代码中catch到异常后throw
-
使用@RestControllerAdvice注解定义一个全局异常处理类,捕获到异常后,获取异常信息并返回
@RestControllerAdvice(value = {"run.halo.app.controller.admin.api", "run.halo.app.controller.content.api"}) @Slf4j public class ControllerExceptionHandler { @ExceptionHandler(AbstractHaloException.class) public ResponseEntity<BaseResponse<?>> handleHaloException(AbstractHaloException e) { BaseResponse<Object> baseResponse = handleBaseException(e); baseResponse.setStatus(e.getStatus().value()); baseResponse.setData(e.getErrorData()); return new ResponseEntity<>(baseResponse, e.getStatus()); } @ExceptionHandler(Exception.class) @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR) public BaseResponse<?> handleGlobalException(Exception e) { BaseResponse<?> baseResponse = handleBaseException(e); HttpStatus status = HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR; baseResponse.setStatus(status.value()); baseResponse.setMessage(status.getReasonPhrase()); return baseResponse; } private <T> BaseResponse<T> handleBaseException(Throwable t) { Assert.notNull(t, "Throwable must not be null"); BaseResponse<T> baseResponse = new BaseResponse<>(); baseResponse.setMessage(t.getMessage()); if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.error("Captured an exception:", t); baseResponse.setDevMessage(ExceptionUtils.getStackTrace(t)); } else { log.error("Captured an exception: [{}]", t.getMessage()); } return baseResponse; } }
AOP记录接口日志
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class ControllerLogAop {
@Pointcut("execution(* *..*.*.controller..*.*(..))")
private void controller() {
}
@Around("controller()")
public Object controllerLog(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
//被织入advice的类名
String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName();
//方法名
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
//方法参数
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
HttpServletRequest request = ServletUtils.getCurrentRequest().orElseThrow(() -> new BadRequestExpection("无法获取当前httpServletRequest"));
//记录请求日志
printRequestLog(request, className, methodName, args);
TimeInterval timer = DateUtil.timer();
Object returnObj = joinPoint.proceed();
long cost = timer.interval();
//记录响应日志
printResponseLog(className, methodName, args, returnObj, cost);
return returnObj;
}
}观察者模式-发布订阅模式
系统中观察者模式的运用之一是:用户登录成功、失败、注销时,异步记录到日志表中,这一过程使用的SpringBoot提供的事件监听机制。观察者模式的定义:在对象之间定义一个一对多的依赖,当一个对象状态改变的时候,所有依赖的对象都会自动收到通知。
观察者模式和发布订阅模式是有一些区别,主要有以下几点:
- 观察者模式:观察者订阅主题,主题也维护观察者的记录,而后者:发布者和订阅者不需要彼此了解,而是在消息队列或代理的帮助下通信,实现松耦合。
- 观察者模式主要以同步方式实现,即某个事件发生时,由Subject调用所有监听器的对应方法,发布订阅模式则主要使用消息队列异步实现。
实现SpringBoot事件监听机制
-
定义注册事件
继承ApplicationEvent类
public class LogEvent extends ApplicationEvent { @Getter private final transient LogParam logParam; public LogEvent(Object source, LogParam logParam) { super(source); ... this.logParam = logParam; } public LogEvent(Object source, String logKey, LogType type, String content) { this(source, new LogParam(logKey, type, content)); } }
-
定义监听器
有两种方式:
-
使用@EventListener注解
@Component public class LogEventListener { private final LogService logService; public LogEventListener(LogService logService) { this.logService = logService; } @EventListener @Async public void onApplicationEvent(LogEvent event) { // Convert to log Log logToCreate = event.getLogParam().convertTo(); // Create log logService.create(logToCreate); } }
-
实现EventListen接口
@Component public class LogEventListener implements ApplicationListener<LogEvent> { private final LogService logService; public LogEventListener(LogService logService) { this.logService = logService; } @Override @Async public void onApplicationEvent(LogEvent event) { // Convert to log Log logToCreate = event.getLogParam().convertTo(); // Create log logService.create(logToCreate); } }
-
-
事件发布者发布事件
需发布事件的类中注入事件发布者
@Service @Slf4j public class UserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<UserMapper, User> implements UserService { private final ApplicationEventPublisher eventPublisher; public UserServiceImpl(ApplicationEventPublisher eventPublisher) { this.eventPublisher = eventPublisher; } @Override public AuthToken loginCheck(@NonNull final LoginParam loginParam) { 登录成功逻辑... // Log it then login successful eventPublisher.publishEvent(new LogEvent(this, user.getUsername(), LogType.LOGGED_IN, user.getNickname())); //Generate accessToken return buildAuthToken(user); }