This repository contains the network architecture and pretrained feature models from "Scale-Adaptive Neural Dense Features". Additionally, we provide a simple script to load these models and run inference on a sample Kitti image.
Please cite the following paper if you find SAND useful in your research:
@inproceedings{spencer2019,
title={Scale-Adaptive Neural Dense Features: Learning via Hierarchical Context Aggregation},
author={Spencer, Jaime and Bowden, Richard and Hadfield, Simon},
booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition},
year={2019}
}
How do computers and intelligent agents view the world around them? Feature extraction and representation constitutes one the basic building blocks towards answering this question. Traditionally, this has been done with carefully engineered hand-crafted techniques such as HOG, SIFT or ORB. However, there is no "one size fits all" approach that satisfies all requirements.
In recent years, the rising popularity of deep learning has resulted in a myriad of end-to-end solutions to many computer vision problems. These approaches, while successful, tend to lack scalability and can't easily exploit information learned by other systems.
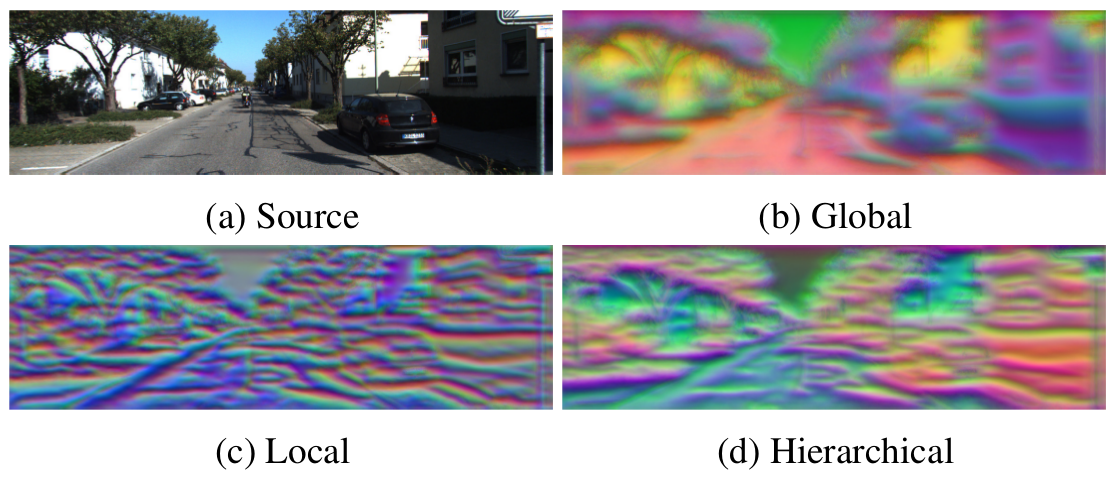
Instead, we propose SAND features, a dedicated deep learning solution to feature extraction capable of providing hierarchical context information. This is achieved by employing sparse relative labels indicating relationships of similarity/dissimilarity between image locations. The nature of these labels results in an almost infinite set of dissimilar examples to choose from. We demonstrate how the selection of negative examples during training can be used to modify the feature space and vary it's properties.
To demonstrate the generality of this approach, we apply the proposed features to a multitude of tasks, each requiring different properties. This includes disparity estimation, semantic segmentation, self-localisation and SLAM. In all cases, we show how incorporating SAND features results in better or comparable results to the baseline, whilst requiring little to no additional training.
- Python >= 3.6
- PyTorch >= 0.4
- Imageio (from image reading)
- Matplotlib (for visualization)
- Sklearn (for PCA reduction)
Breakdown for "main.py":
# Create and load model
model = Sand.from_ckpt(ckpt_file, n_dims=10).to(device) # n_dims is optional sanity check
To visualize the features produced by the network:
features_torch = model(img)
features = ops.fmap2img(features_torch)
plt.imshow(features)
plt.show()
All models have been trained on a subset of the Kitti odometry sequence 00. We provide Global, Local and hierarchical (GL) models for features of dimensionality 3, 10 & 32. Models should be placed in "path/to/repo/ckpts/" and can be loaded using torch.load() or directly with Sand.from_ckpt
You can contact me at jaime.spencer@surrey.ac.uk